Antipsychotics
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
1
New cards
What is the central dopamine hypothesis?
suggests that a dysregulated dopamine system contributes to positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of the disease.
2
New cards
What are the systems and what type of symptoms do they cause?
* Hyperactive **mesolimbic** pathway **→** **positive** symptoms
\
* Hypoactive **mesocortical** pathway **→** **negative** symptoms
\
* **Nigrostriatal** pathway **→** neurological & **motor** symptoms
\
* Hypoactive **mesocortical** pathway **→** **negative** symptoms
\
* **Nigrostriatal** pathway **→** neurological & **motor** symptoms
3
New cards
What is the mesolimbic pathway?
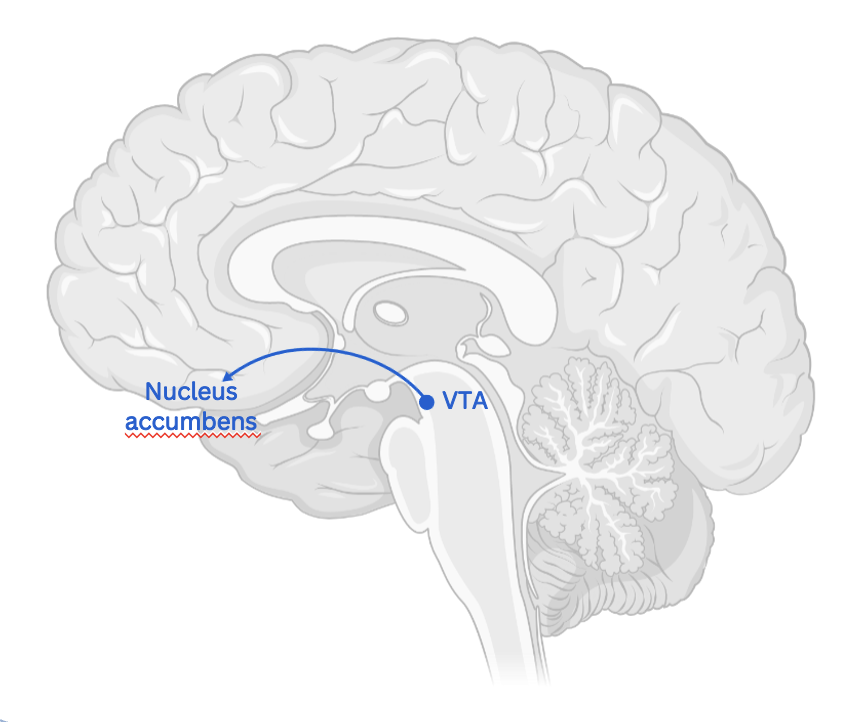
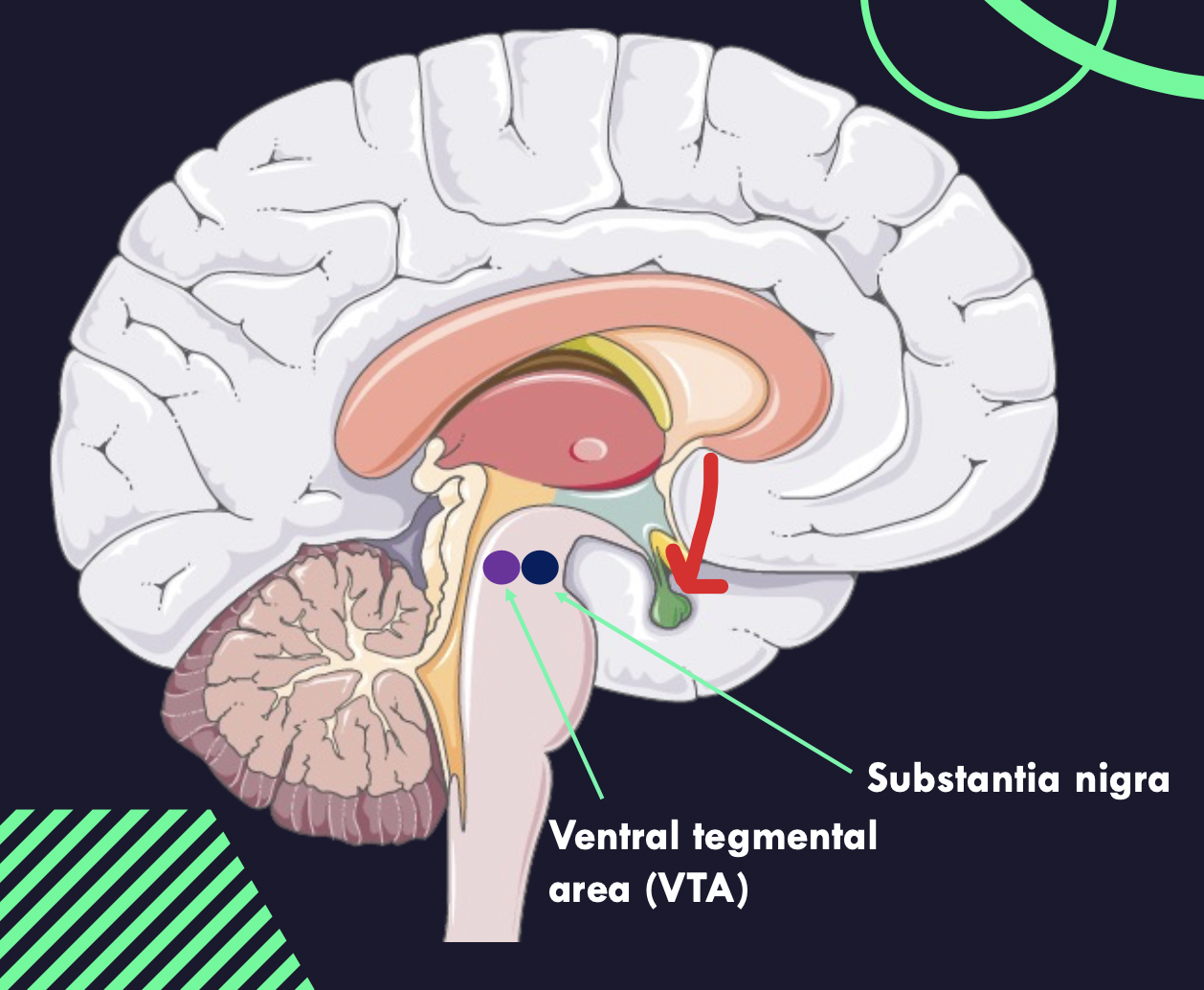
Dopamine is produced in the **Vental Tegmental Area** (VTA).
\
Mesolimbic pathway—**transports** __**dopamine**__ **from the VTA to the** ==**nucleus accumbens and** __**amygdala**__.== The nucleus accumbens is found in the ventral medial portion of the striatum and is believed to play a **role in reward, desire, and motivation**
\
The mesolimbic dopaminergic (ML-DA) system has been recognized for its central role in **motivated behaviors, various types of reward, and, more recently, in cognitive processes**.
\
Too much dopamine in in mesolimbic pathway = positive symptoms
\
Mesolimbic pathway—**transports** __**dopamine**__ **from the VTA to the** ==**nucleus accumbens and** __**amygdala**__.== The nucleus accumbens is found in the ventral medial portion of the striatum and is believed to play a **role in reward, desire, and motivation**
\
The mesolimbic dopaminergic (ML-DA) system has been recognized for its central role in **motivated behaviors, various types of reward, and, more recently, in cognitive processes**.
\
Too much dopamine in in mesolimbic pathway = positive symptoms
4
New cards
What is the mesocortical pathway?
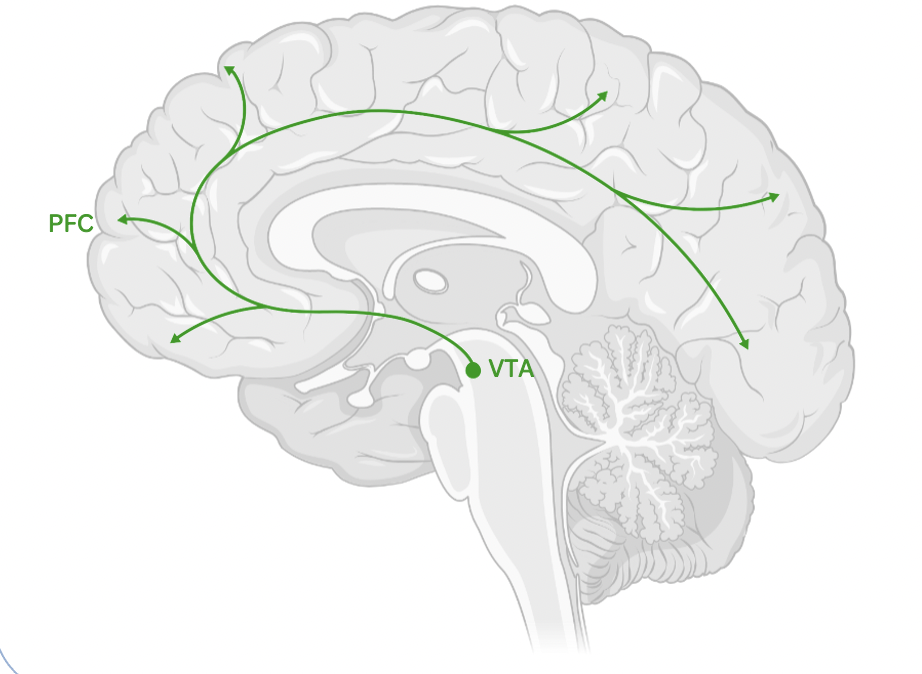
**The mesocortical pathway transmits dopamine from the VTA to the prefrontal cortex**.
\
VTA links to the **Prefrontal Cortex** (PFC).
This **changes how you prioritise and** ***plan*****.**
\
one of the main dopamine pathways of the brain, the mesocortical pathway **runs from the ventral tegmental area to the cerebral cortex**. **It forms extensive connections** with the **frontal lobes**, and is thought to be important to a wide range of functions, such as **motivation, emotion,** and **executive functions**.
\
\
Drugs (e.g. cocaine) cause overstimulation and reliance on **mesolimbic** pathway
They act on VTA (which links to nucleus accumbens and PFC)
\
Too little dopamine in mesocortical pathway = negative pathway
\
VTA links to the **Prefrontal Cortex** (PFC).
This **changes how you prioritise and** ***plan*****.**
\
one of the main dopamine pathways of the brain, the mesocortical pathway **runs from the ventral tegmental area to the cerebral cortex**. **It forms extensive connections** with the **frontal lobes**, and is thought to be important to a wide range of functions, such as **motivation, emotion,** and **executive functions**.
\
\
Drugs (e.g. cocaine) cause overstimulation and reliance on **mesolimbic** pathway
They act on VTA (which links to nucleus accumbens and PFC)
\
Too little dopamine in mesocortical pathway = negative pathway
5
New cards
What is the nigrostriatal pathway?
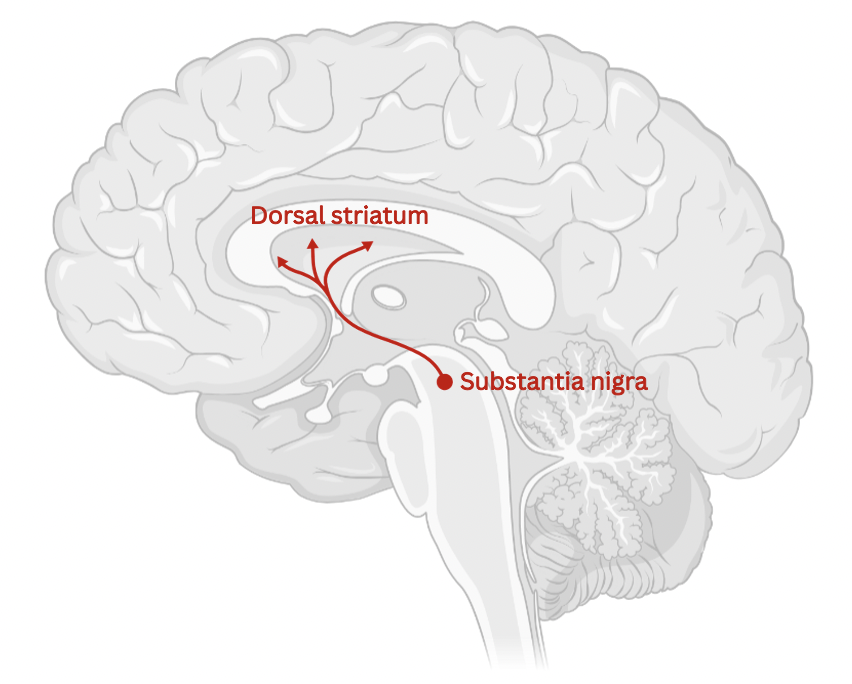
Most dopamine producing neurons are found in the VTA and **Substantia Nigra**
\
The Substantia Nigra forms the **Nigrostriatal Pathway** which is black due to (neuro)melanin (byproduct of dopamine synthesis)
\
Nigrostriatal pathway links substantia nigra to the **basal ganglia** with the **caudate** and **putamen**
\
The dorsal striatum **consists of the caudate nucleus and the putamen**. A white matter, nerve tract (the internal capsule) in the dorsal striatum separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen.
\
The main function of the nigrostriatal pathway is to **influence voluntary movement** through **basal ganglia motor loops**.
\
The Substantia Nigra forms the **Nigrostriatal Pathway** which is black due to (neuro)melanin (byproduct of dopamine synthesis)
\
Nigrostriatal pathway links substantia nigra to the **basal ganglia** with the **caudate** and **putamen**
\
The dorsal striatum **consists of the caudate nucleus and the putamen**. A white matter, nerve tract (the internal capsule) in the dorsal striatum separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen.
\
The main function of the nigrostriatal pathway is to **influence voluntary movement** through **basal ganglia motor loops**.
6
New cards
What illnesses are in nigrostriatal pathway?
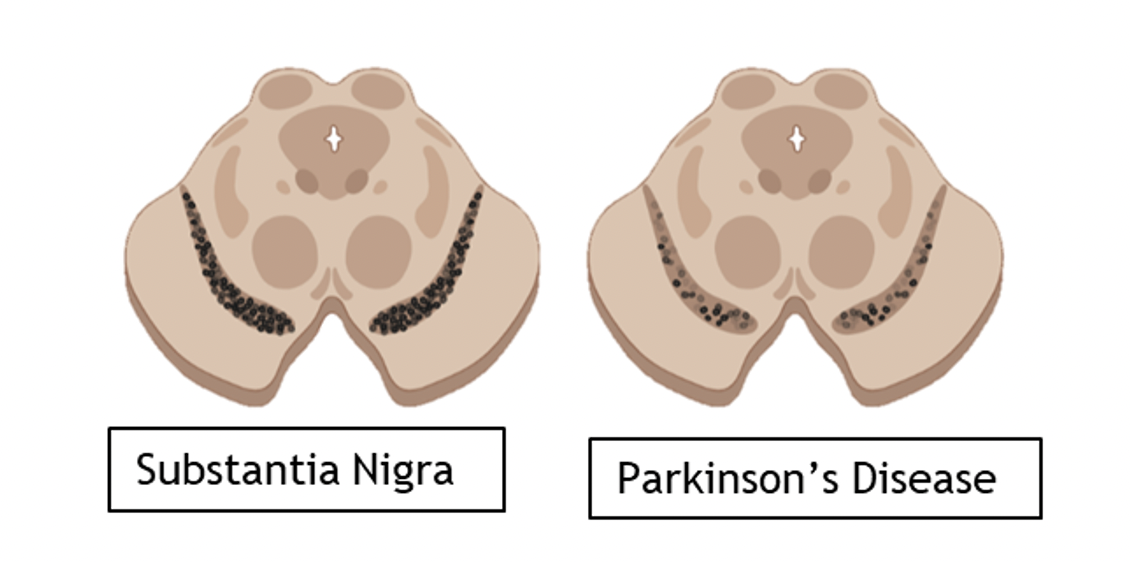
In Parkinson’s the **Substantia Nigra degenerates**
**Lewy Bodys** form – abnormal aggregations of protein
This leads to the **movement and** ***initiation*** **difficulties** seen in Parkinson’s
Lose **nigrostriatal pathway** → lose upper/higher control of processing movement
**Lewy Bodys** form – abnormal aggregations of protein
This leads to the **movement and** ***initiation*** **difficulties** seen in Parkinson’s
Lose **nigrostriatal pathway** → lose upper/higher control of processing movement
7
New cards
What is the **TUBEROINFUNDIBULAR pathway?**
**Hypothalamus to pituitary gland**
* **Increased levels of dopamine will cause decreased levels of prolactin**
* **Increased prolactin: amenorrhoea (increased prolactin decreases FSH), galactorrhoea**
* **ADR: hyperprolactinemia (as antipsychotics reduce levels of dopamine, it increases levels of prolactin causing lactation)**
* **Increased levels of dopamine will cause decreased levels of prolactin**
* **Increased prolactin: amenorrhoea (increased prolactin decreases FSH), galactorrhoea**
* **ADR: hyperprolactinemia (as antipsychotics reduce levels of dopamine, it increases levels of prolactin causing lactation)**
8
New cards
What are examples of 1st generation/ typical?
Chlorpromazine
**Haloperidol**
**Haloperidol**
9
New cards
What is the MOA of typical antipsychotics?
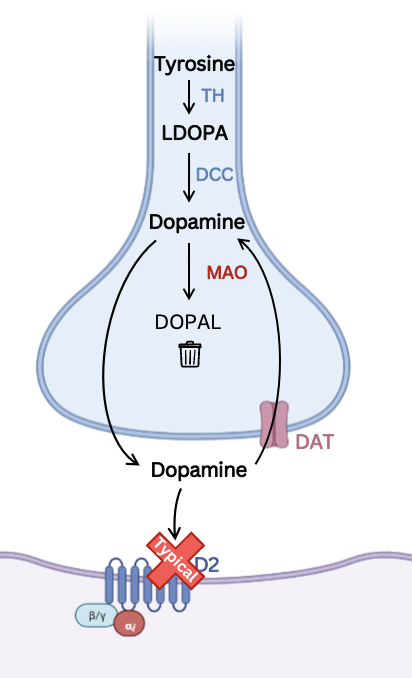
dopamine receptor antagonist
High affinity for **D2 receptors**
\
Improves only +ve symptoms
High affinity for **D2 receptors**
\
Improves only +ve symptoms
10
New cards
What is the ADR of typical antipsychotics?
* Extrapyramidal symptoms and tardive dyskinesia e.g. restlessness, tremor, and stiffness due to the blockage of D2 receptors in nigrostriatal pathway
* Causes **parkinsonism**
* ==prolonged QT==
* hyperprolactinemia
* ==weight gain==
* ==Movement disorders==
* Causes **parkinsonism**
* ==prolonged QT==
* hyperprolactinemia
* ==weight gain==
* ==Movement disorders==
11
New cards
What are examples of 2nd generation/ atypical?
Olanzapine
Colzapine
Quetiapine
Colzapine
Quetiapine
12
New cards
What is the MOA of atypical antipsychotics?
Serotonin/dopamine receptor antagonist
Higher affinity to **5-HT2A** receptors than **D2** receptors
Higher affinity to **5-HT2A** receptors than **D2** receptors
13
New cards
What is the ADR of atypical antipsychotics?
Because they have lower D2 affinity, atypical antipsychotic drugs produce **significantly fewer extrapyramidal symptoms** and having a lower risk of tardive dyskinesia in vulnerable clinical populations at doses that produce comparable control of psychosis.
\
Antipsychotics **block repolarisation of K+ channel** in myocardium
**Prolong QT** interval (QTc)
\
Olanzapine- **weight gain,** metabolic syndrome, **QT prolongation, movement disorders**
Colzapine- **weight gain, QT prolongation, sexual dysfunction**
Quetiapine- **weight gain, QT prolongation, movement disorders**
\
Antipsychotics **block repolarisation of K+ channel** in myocardium
**Prolong QT** interval (QTc)
\
Olanzapine- **weight gain,** metabolic syndrome, **QT prolongation, movement disorders**
Colzapine- **weight gain, QT prolongation, sexual dysfunction**
Quetiapine- **weight gain, QT prolongation, movement disorders**
14
New cards
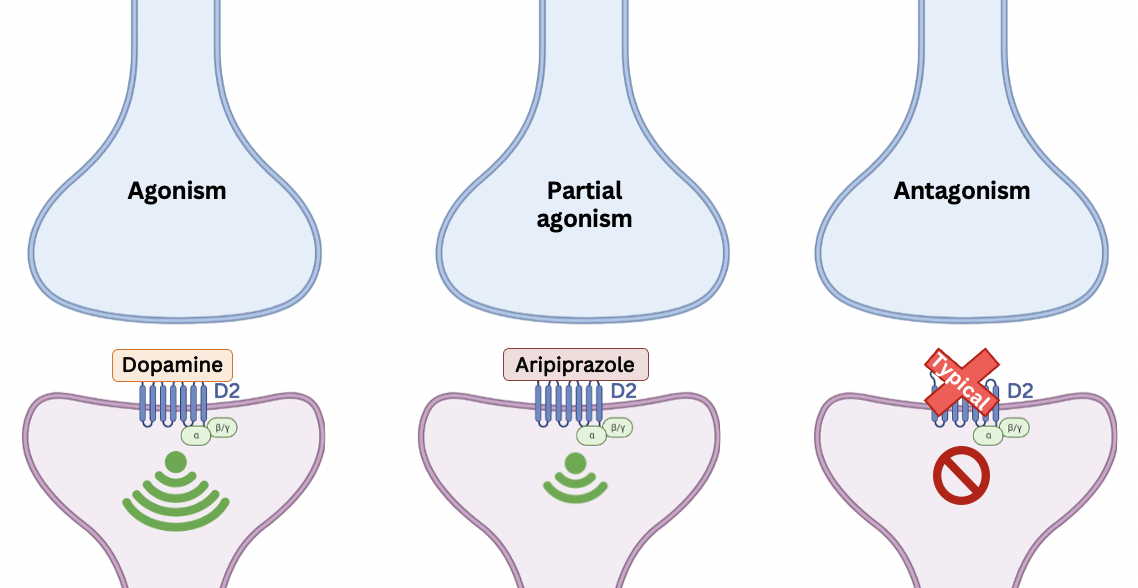
Aripiprazole – Partial Dopamine Agonist
Aripiprazole binds to the D2 receptor with the same affinity as dopamine, but has a **lower intrinsic efficacy**, so the **response** it triggers is **lower than dopamine** but **higher than an antagonist.**
\
Aripiprazole might **decrease activity in the mesolimbic pathway** through partial D2 agonism, which would, in turn, **reduce positive symptoms.**
One postulated mechanism of action of aripiprazole in schizophrenia is the ability of the drug to increase dopaminergic activity from a subnormal level to normal activity in the mesocortical pathway. *Partial D2 agonism might increase dopaminergic activity in the mesocortical pathway therefore reducing negative symptoms*
\
\
•Aripiprazole is a partial agonist at D2 receptors.
•It may act as an antipsychotic by:
•**Lowering** dopaminergic **neurotransmission in the mesolimbic p**athway.
•**Enhancing** dopaminergic activity in the **mesocortical pathway.**
\
Aripiprazole might **decrease activity in the mesolimbic pathway** through partial D2 agonism, which would, in turn, **reduce positive symptoms.**
One postulated mechanism of action of aripiprazole in schizophrenia is the ability of the drug to increase dopaminergic activity from a subnormal level to normal activity in the mesocortical pathway. *Partial D2 agonism might increase dopaminergic activity in the mesocortical pathway therefore reducing negative symptoms*
\
\
•Aripiprazole is a partial agonist at D2 receptors.
•It may act as an antipsychotic by:
•**Lowering** dopaminergic **neurotransmission in the mesolimbic p**athway.
•**Enhancing** dopaminergic activity in the **mesocortical pathway.**
15
New cards
What is an example of an alkali metal?
Lithium carbonate
16
New cards
What is the MOA of lithium?
Supress dopaminergic + glutamatergic synaptic activity (pre + post cells) while also upregulating GABA synapti activity.