Lesson 1 Division of the Nervous System/Neurons
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CSD380
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
Two major structural components of the nervous system
Central & Peripheral
Two major functions of the nervous system
Autonomic & Somatic
The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of what?
Brain (cerebrum, cerebellum, & brain stem), and spinal cord
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) consists of what?
Cranial, spinal, & sensory nerves
Involuntary bodily functions that also help maintain homeostasis
Autonomic
Conscious, voluntary bodily functions that control all skeletal muscles
Somatic
Autonomic can be divided further into…
Sympathetic & Parasympathetic
Active during times of rest.
Return to resting state.
Parasympathetic
Fight or flight response during stressful situations.
Sympathetic
Somatic nervous system can divide further into…
Pyramidal (Direct) & Extrapyramidal System
Largely responsible for the initiation of voluntary motor acts.
Pyramidal System (Direct)
Responsible for the background tone and movement supporting the primary acts.
Extrapyramidal System (Indirect)
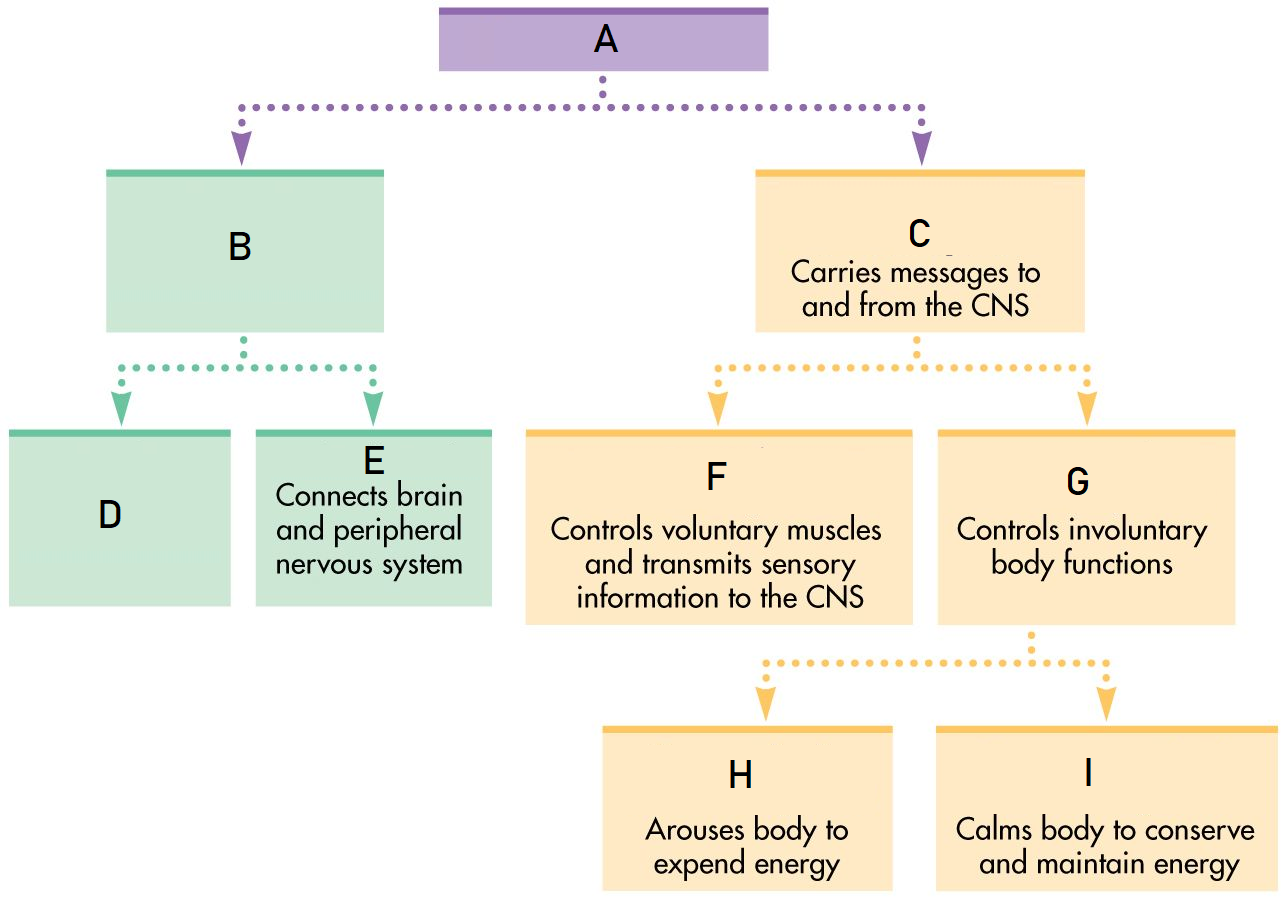
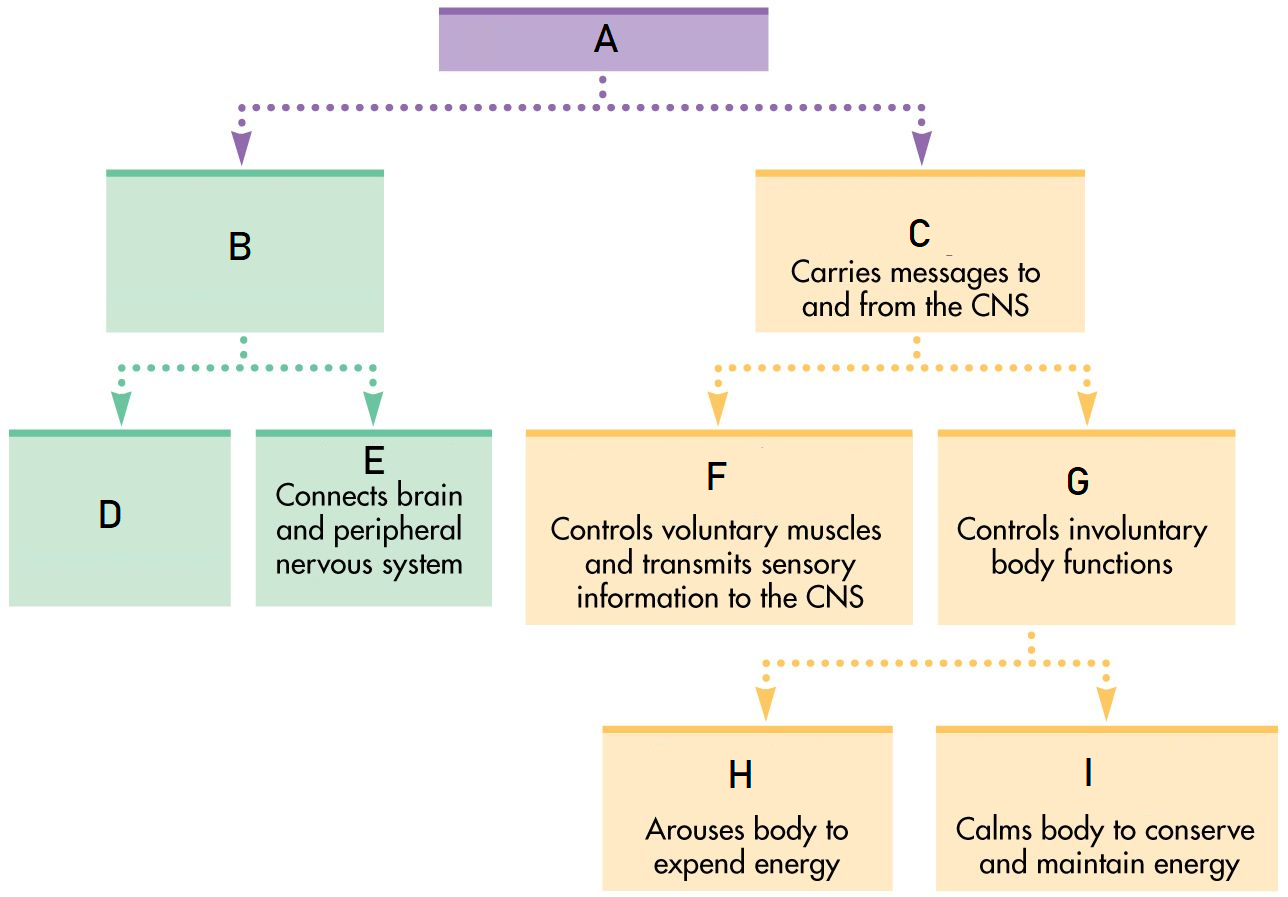
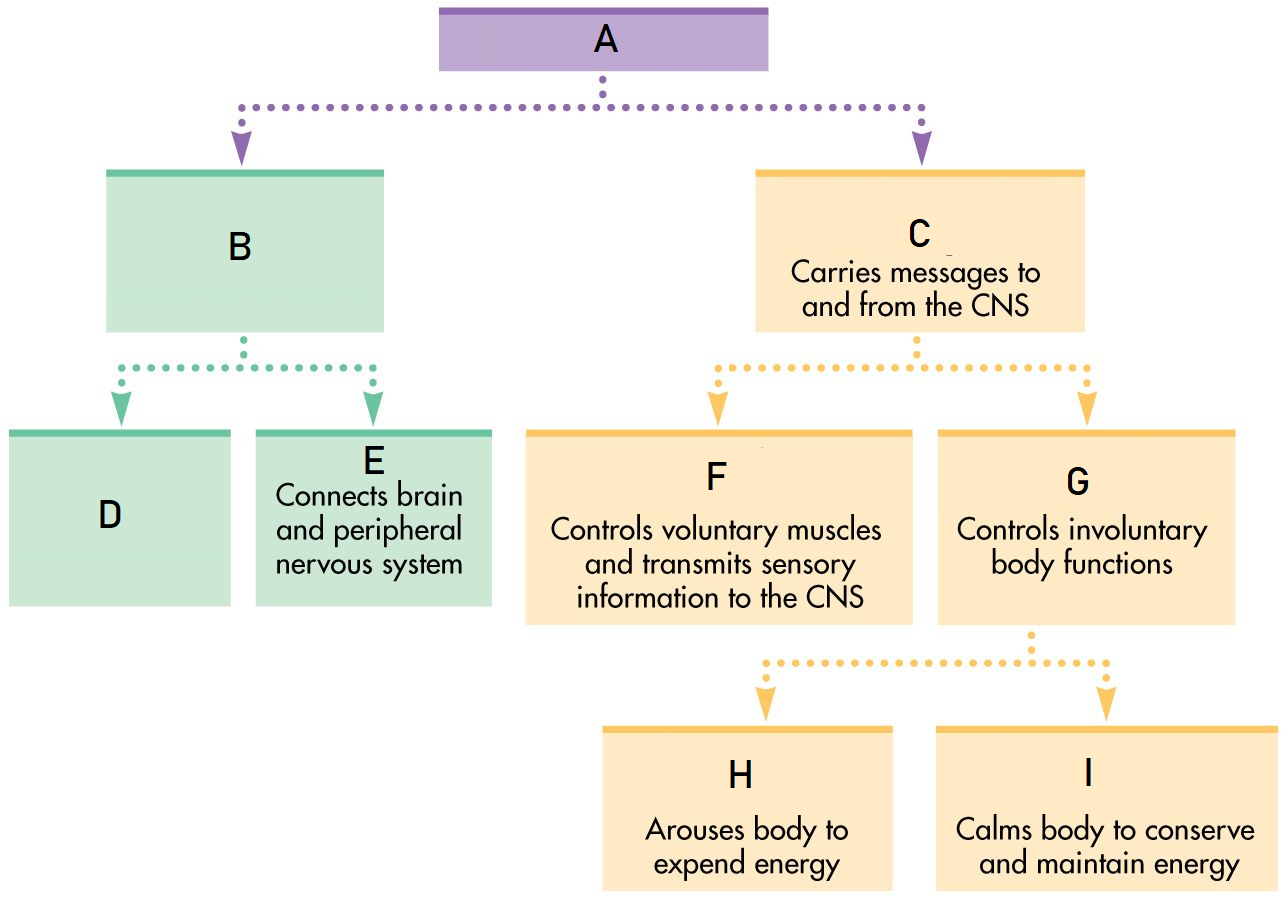
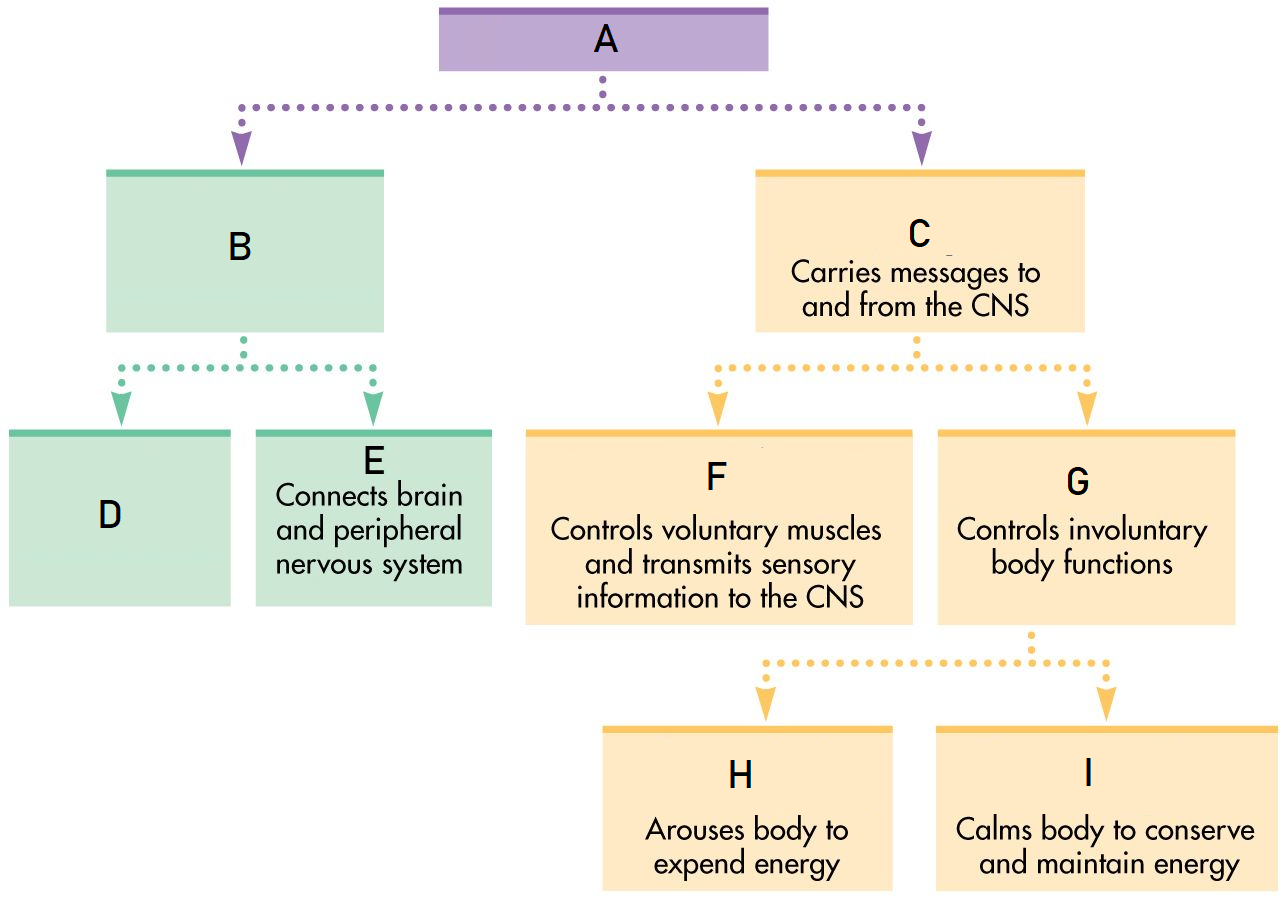
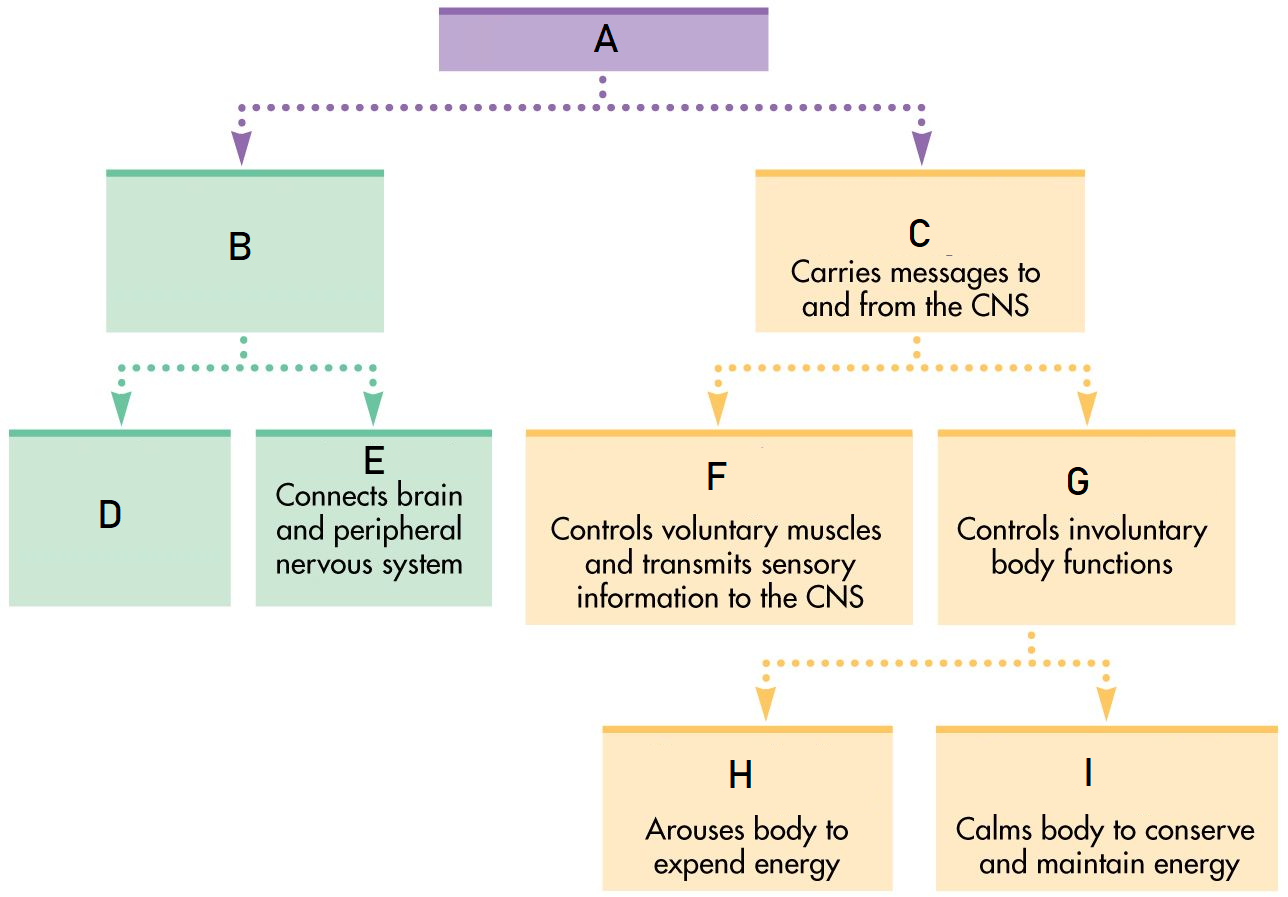
A
Nervous System
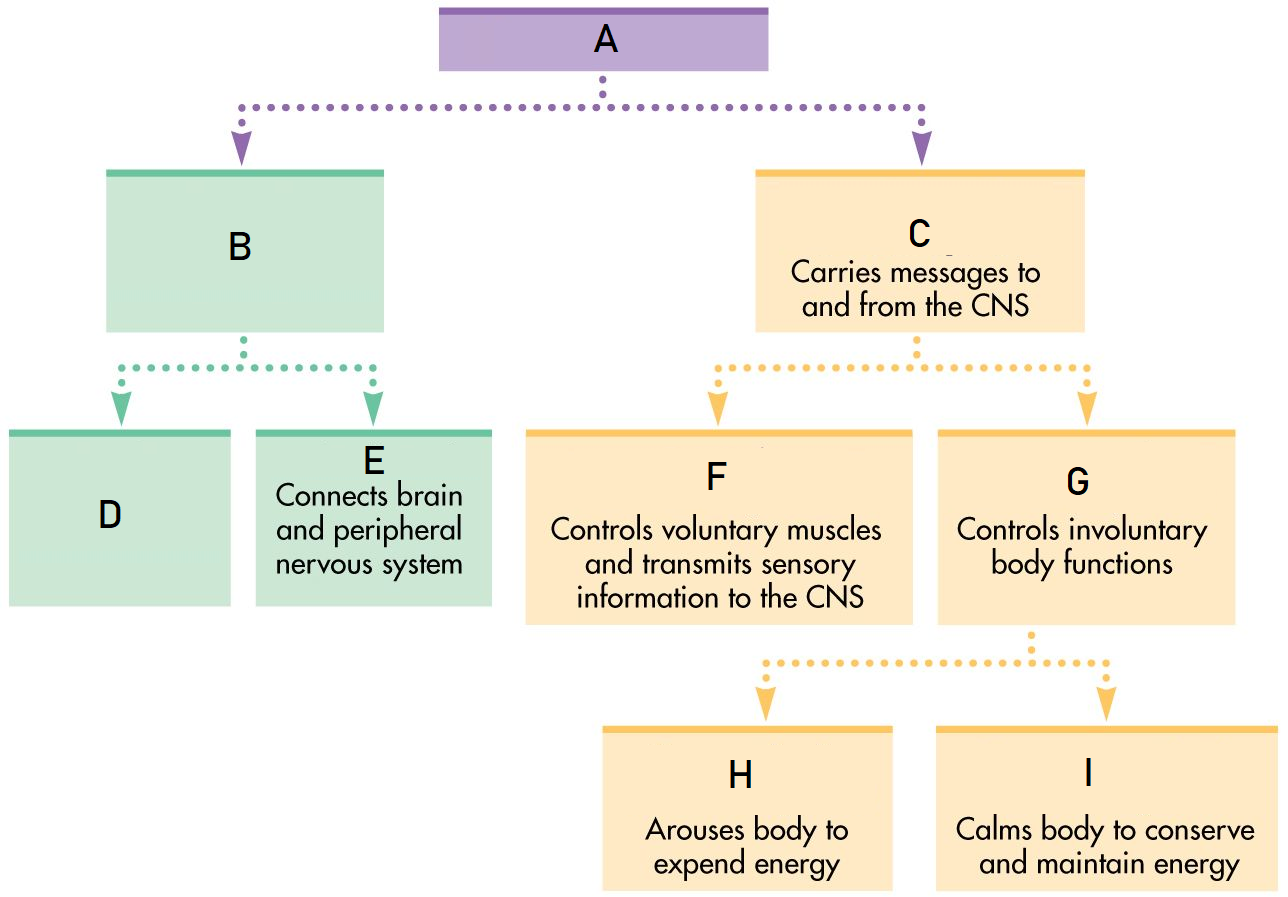
B
Central Nervous System
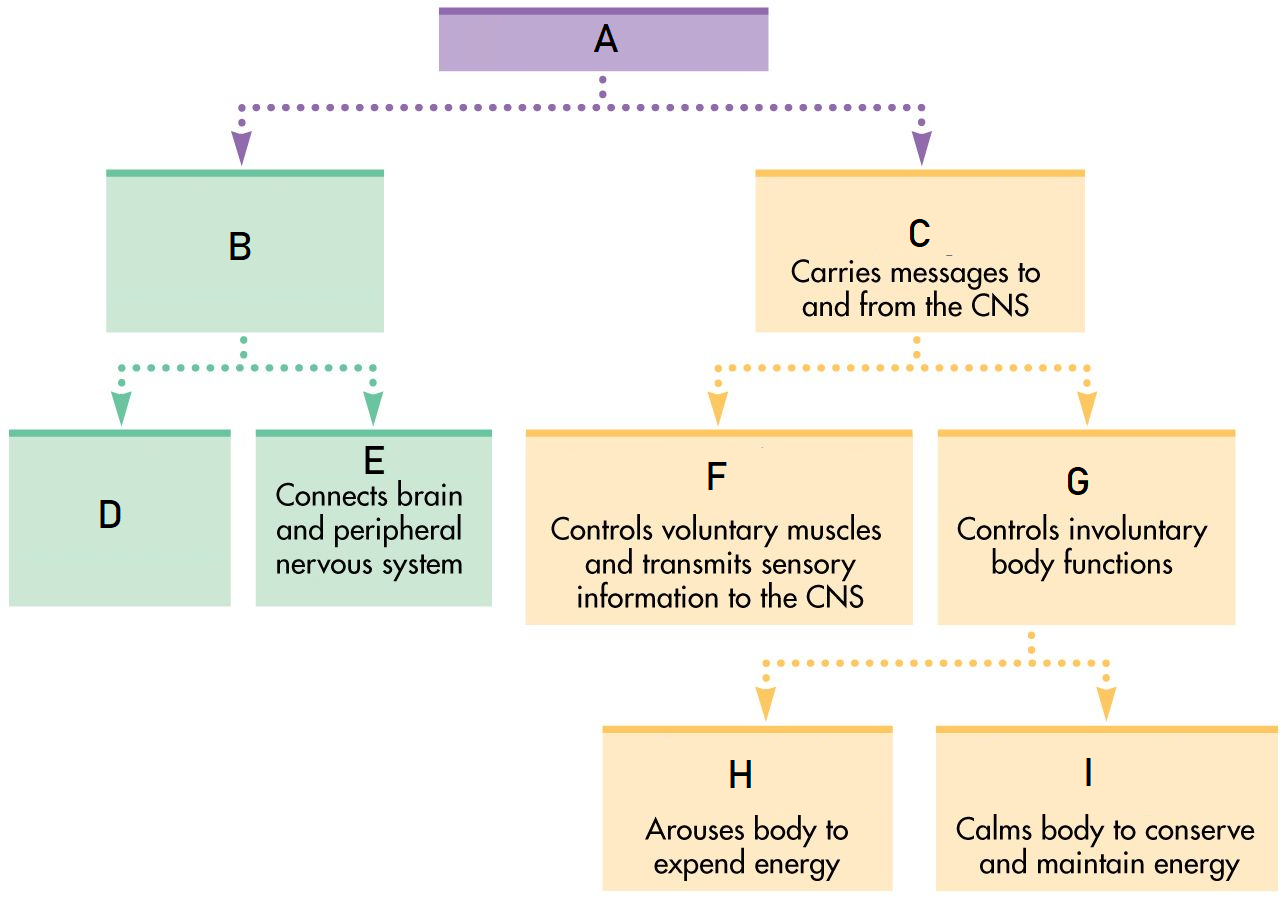
C
Peripheral Nervous System
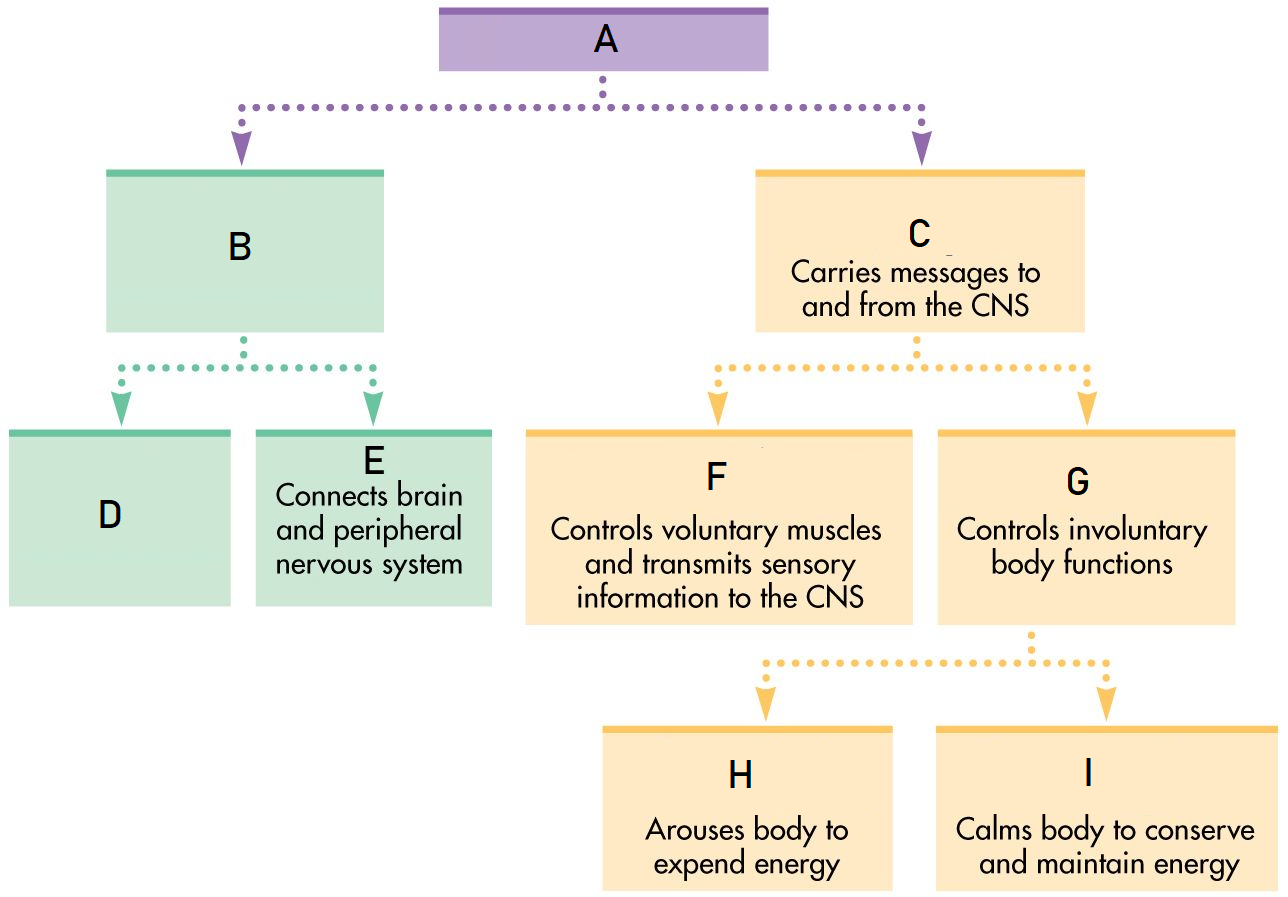
D
Brain
E
Spinal Cord
F
Somatic Nervous System
G
Autonomic Nervous System
H
Sympathetic Nervous System
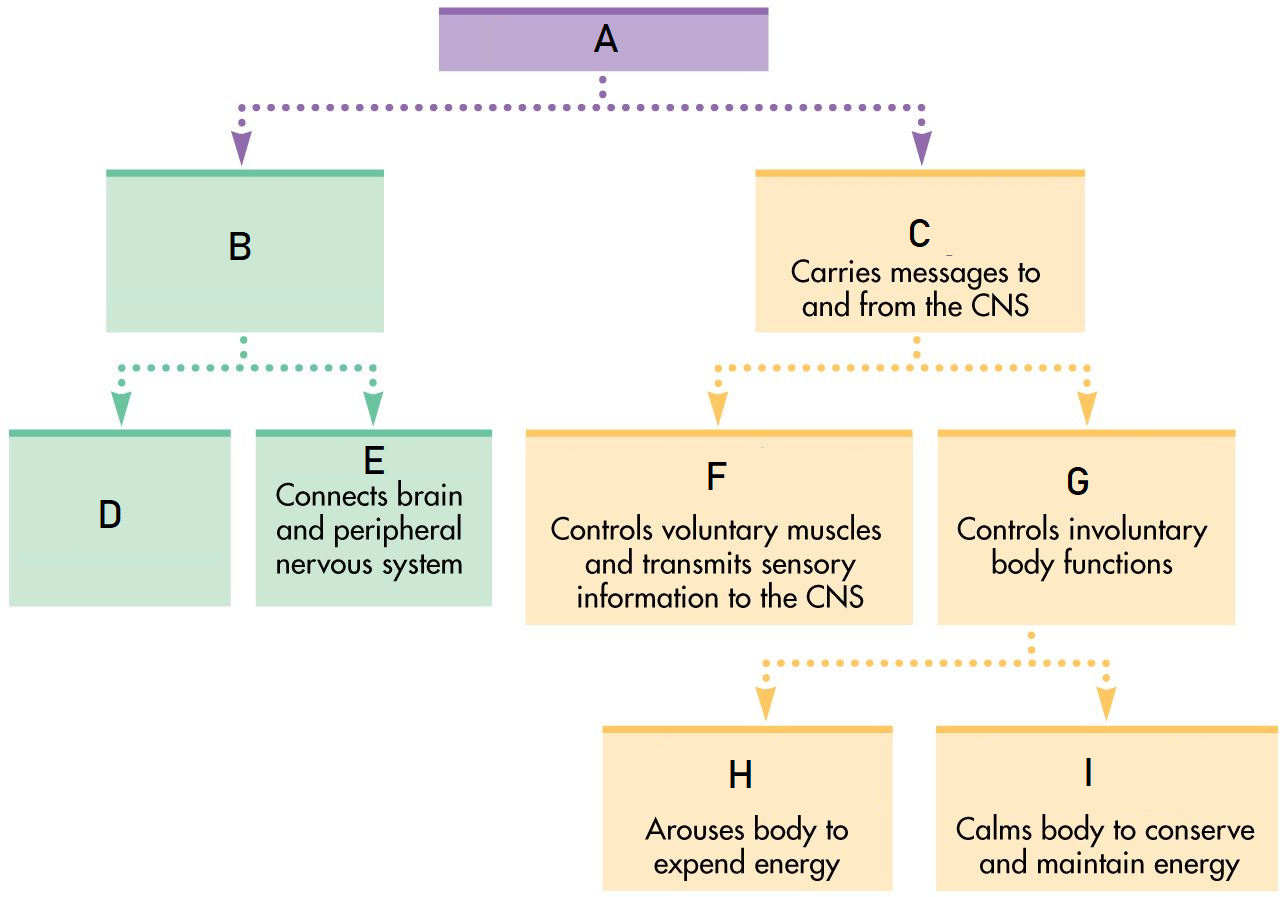
I
Parasympathetic Nervous System
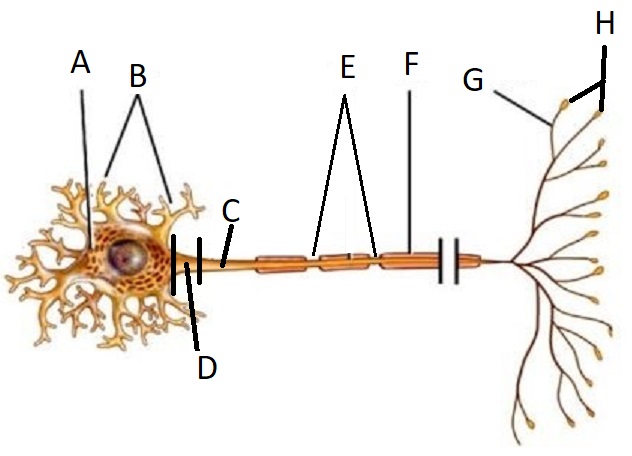
A
Cell Body/Soma
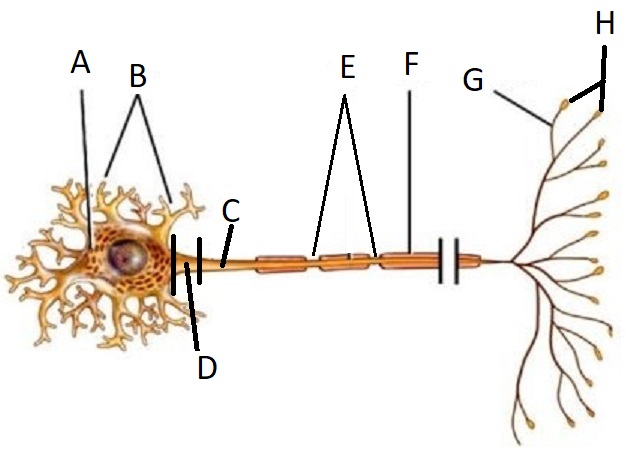
B
Dendrite
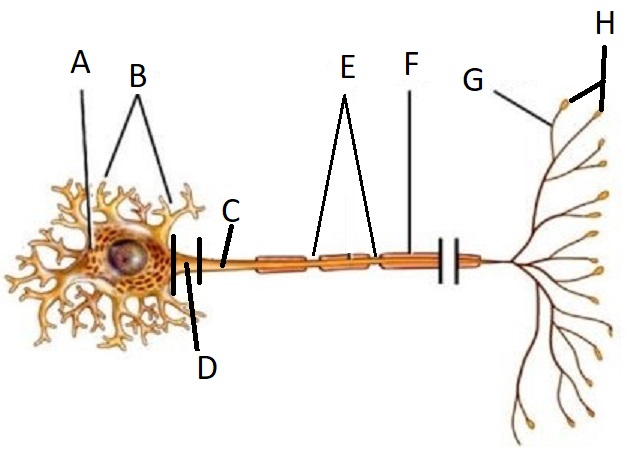
C
Axon
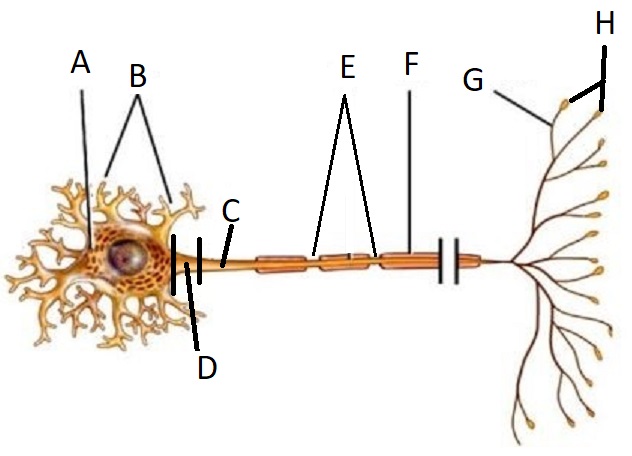
D
Axon Hillock
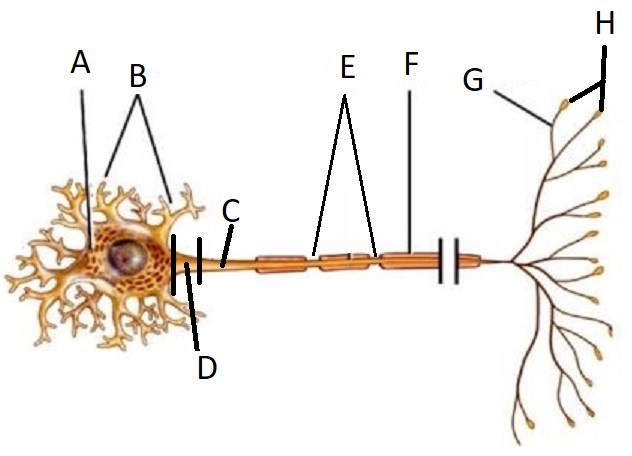
E
Node of Ranvier
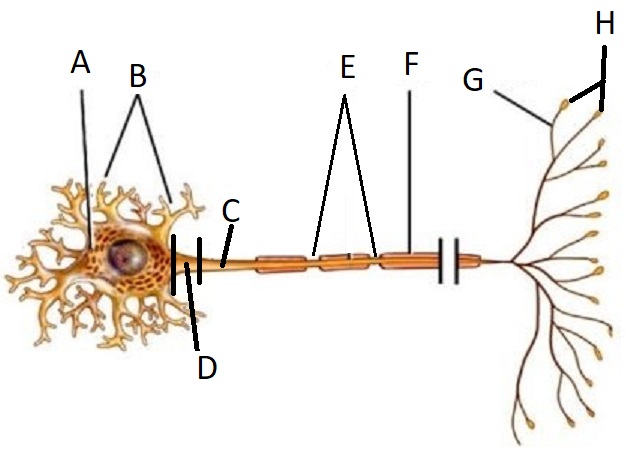
F
Myelin Sheath
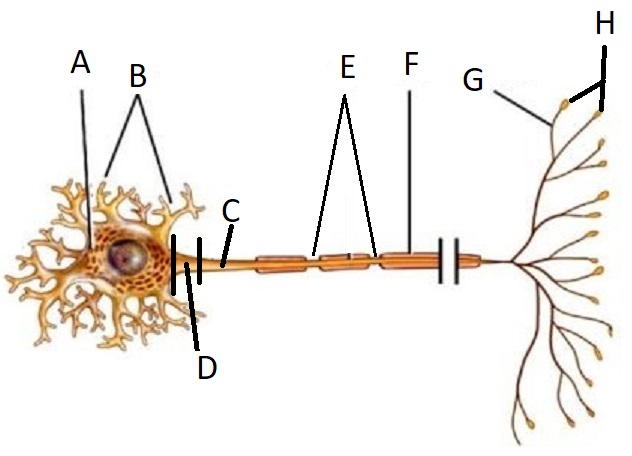
G
Telodendria/ Axon Branches
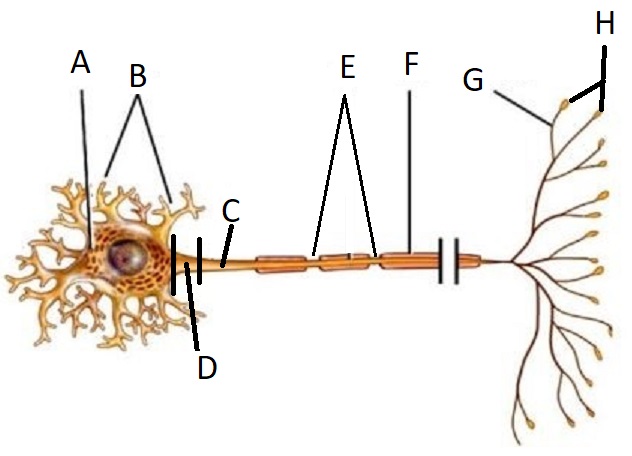
H
Terminal End Buttons
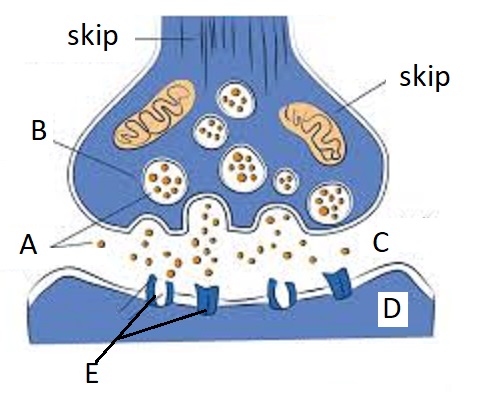
A
Neurotransmitters
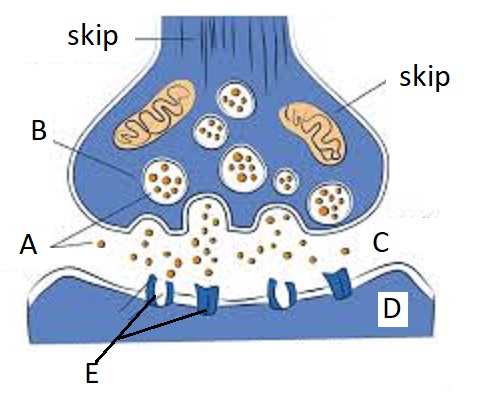
B
Synaptic Vesicles
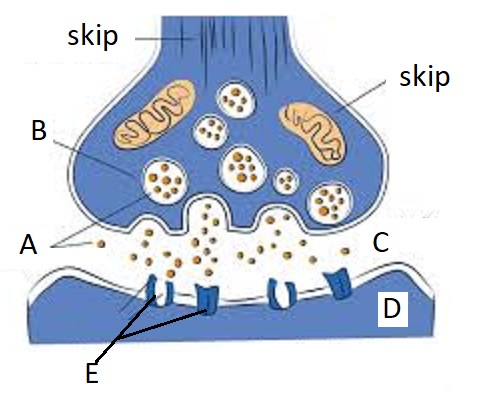
C
Synaptic Cleft
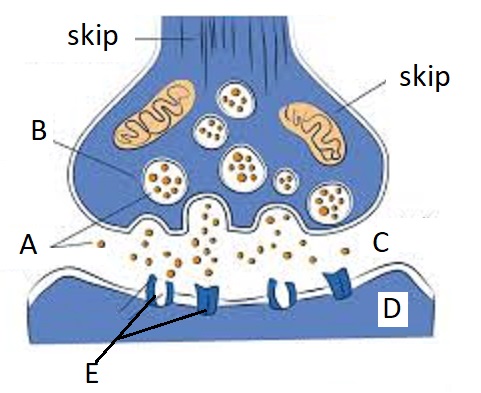
D
Dendrite
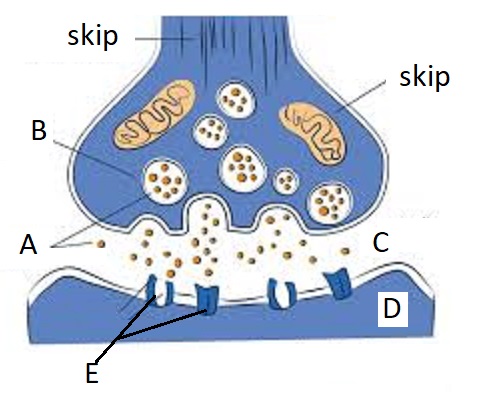
E
Receptor Site

E
Oligodendrocyte
CNS support tissue is…
Glial cells
Name all 4 glial cells
Astrocytes, Oligodendrocytes, microglia, & ependymal cells
What is the function of the astrocytes?
Regulating blood-brain barrier
What is the function of the oligodendrocytes?
Generates myelin
What is the function of the microglia?
Immune support & phagocytosis (destroys foreign substances)
What is the function of the ependymal cell?
Is the wall of the ventricle and supports with cerebrospinal fluid.
What two cells support tissues in the peripheral nervous system?
Schwann & satellite cells
What is the function of the Schwann cells?
Form myelin sheath & guide regrowth of damage axons
What is the function of the satellite cells?
Enclose the cell body & regulate internal environment of cell body.
Chemical compounds responsible for activating next neuron.
Neurotransmitters
Facilitates firing of neuron (respond to stimulation)
Excitation
Inhibits firing of neuron (respond to stimulation)
Inhibition