AP Psychology: Unit 2 Vocabulary
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocab for Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Selective Attention
Focusing conscious awareness on a particular stimulus
“Flashlight” since our consciousness can only focus on one thing at a time.
filters stimuli depending on each person. what’s important or interesting
Cocktail party effect
An example of selective attention. ability to attend to only one specific sound in a noisy environment.
What happens when we shift our selective attention?
Our brain activity for each activity decreases.
Shift attention → decreased brain activity → more room for error
Driving & texting: the brain struggles to process both tasks effectively, leading to impaired driving performance.
Inattentional blindness
Inability to see or notice another stimuli when our attention is directed somewhere else
inability to see the dancing chicken when we are focusing on the number of jumps from a person wearing a green t-shirt.
proves that humans are very good at focusing attention to certain part of our environment
Change blindness
Inability to notice/see a change in the environment. A type of inattentional blindness
Perceptual Set
mental tendency of perceiving one thing over another
affects what we hear: “stuffy nose” VS “stuff he knows”
affects what we taste: fries in a McDonald bag vs plain white bag
affects what we feel, see, etc.
Where does our perceptual set come from?
Comes from our past experiences, or also known as top-down processing
Schemas
What are the 3 ways that affects how we interpret something? Give an example of each
Context
we will hear “stuffy nose” when someone is holding a tissue box
Motivation
walking distance will feel longer when we are tired
emotion
Our emotion can affect words that we hear: sad → Mourning/morning, die/dye, pain/pane
Module 2.1B
Gestalt
an organized whole of the big picture
our visual sensations are organized into gestalts
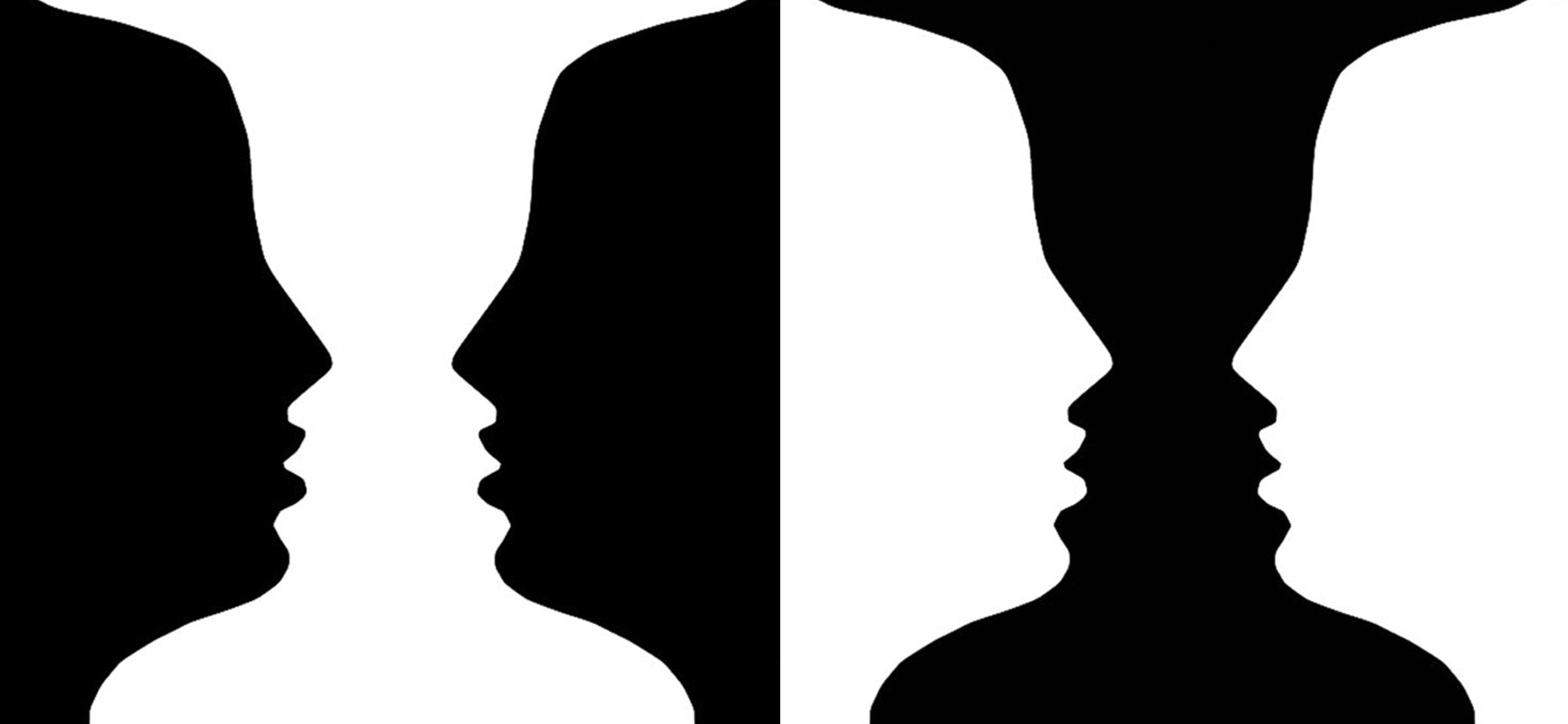
Figure Ground
organization and tendency to view our objections (figure) as standing out from the background (ground)

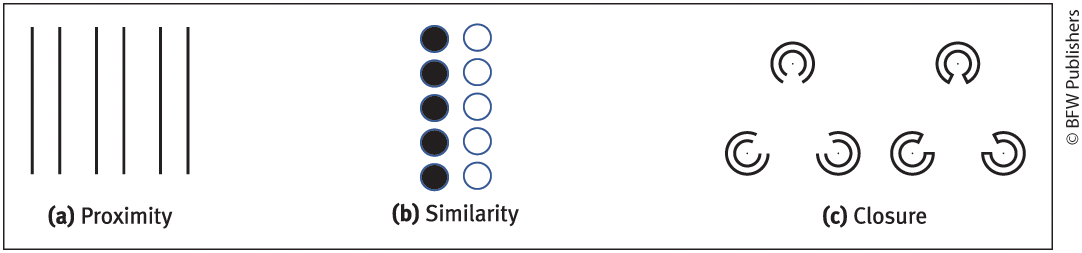
Grouping (what are the different types of groupings?)
tendency to organize stimuli into groups
Proximity
Similarity
Closure
Depth Perception
ability to see in 3d although our retinal images are in 2d. Allows us to judge distance
Visual cliff. What are the findings?
a modeled cliff with a “drop” that is covered by glass panel
visual cliff found that infants are born with an innate depth perception as they refused to go across the cliff
Binocular Cues
Depth cue that is dependent on the use of 2 eyes. Allows us to judge distance of nearby objects
Convergence
A type of binocular cue. A cue to nearby objects when brain combines retinal images.
As object moves closer, our eyes “converge” closer, vice versa.
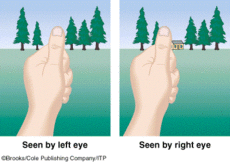
Retinal Disparity
A type of binocular cue. Cue for perceiving depth.
The disparity is the difference of the placement of an object when using the right vs left visual field.
More disparity between 2 images → the closer the object
Monocular Cues
Depth cue that is available to each eye separately. Both eyes are not needed to view the depth.
What does motion perception look like in humans?
Brain computes shrinking objects as getting further away and enlarging objects as approaching us.
When large & small object is moving at the same speed, the large object seems to be slower (how a train seems slower than cars)
Stroboscopic Movement
illusion of continuous movement in a rapid series of images that slightly varies
cartoons, flipbooks
explains why we often don’t notice when we blink
Phi Phenomenon
illusion of movement when adjacent lights blink in a succession
autokinetic effect
Illusion of movement of a stationary light in a dark room
Perceptual constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging even from a different distance or angle because of our top-down processing
Color constancy
perceiving familiar objects as having a consistent color, even when the light changes its actual wavelength
Size Constancies
ability to perceive objects as having an unchanging size, even with varying distances
size of a bus doesn’t seem smaller just because it’s further away.
Perceptual Adaptation
ability to adapt to a sensory input (artificially displaced or inverted vision). humans are ability to adapt to dramatic distortions.
new prescription, invert goggles
Cognition
all mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communication
metacognition
cognition about our cognition. “thinking about thinking.
assessing our knowledge, evaluating our performance
students with metacognition tend to do better academically.
concepts
mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people
high chair, dentist chair, massage chair, wheel chair, spinny chair = all chairs
simplifies our thinking
prototype
mental image of the best example of a category.
a crow may better fit into the prototype than an ostrich
assimilate
we use our schemas to interpret new experience
toddler sees a 4-legged animal and learns that it’s a dog. Now every 4-legged animal, they categorize it as a dog (foxes, cats, etc.)
accommodate
adapts or adjusts our schema to incorporate new info
toddler learns that the other 4-legged animals are other animals.
creativity
ability to produce new and valuable info
convergent thinking
narrow available problems to determine the best solution
divergent thinking
ability to expand the # of possible solutions to a problem
What are 5 different ways you can use a brick?
Module 2.2B
Executive Functions
cognitive skills that work together to allow us to problem solve. effectively make decisions
Algorithms
a step-by-step procedure that will guarantee a solution
can be long and be laborious
unscramble SPLOYOCHYG by placing each letter in its possible placement.
would take 907,200 possible sequences to find the right word
Heuristics
a simpler thinking strategy that allows us to make quick judgements efficiently.
faster but more error-prone
unscramble SPLOYOCHYG by grouping letters together (letters that are often seen together)
playing wordle
Insight
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution. No strategy or algorithm is used
confirmation bias
tendency to seek information that supports/affirms our beliefs, ignore those that contradicts
fixation
inability to approach a problem from a new perspective
once we get hung up on one view, becomes difficult to approach it from a new angle
can be an obstacle to problem solving
mental set
tendency to approach a problem in a way that was successful in the past
Find the sequence
O-T-T-F-?-?-? → Five, Six, Seven → After recognizing, makes it easier to solve #2.
J-F-M-A-?-?-?
Intuition
an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling/thought
we often use our intuition when making every day decisions
Representativeness Heuristics
judging the likelihood of something based on how well we think it categorizes into a prototype. How well it seems to represent or match the prototype.
Short, slim, likes to read poetry → Ivy League English professor OR truck driver?
people think Ivy league professor but they dismiss the fact that there is >400 Ivy league English professors compared to 3.5 billion truck drivers
Availability Heuristics
judging the likelihood of events based on the availability in our memory
how often something (a memory) pops into our thoughts depends on the vividness of the memory
Celebrity’s child get’s autism after getting vaccinated → this caused people to believe that there is a link between vaccination and autism
Using vivid/graphic imagery on cigarette packaging to prevent people from buying it
Overconfidence
tendency to be more confident than correct. overestimates the accuracy of our beliefs and judgements
can lead to planning fallacy: overestimates our future leisure time
students overestimate how much work they can get done in a certain time period, but in reality, it takes almost double the time
can lead to sunk-cost fallacy: sticking to the original plan because time was already invested into that plan. however, trying a new approach could actually save time
Belief Perseverance
persistence of one’s belief even after the basis/foundation of that belief was discredited.
Framing
the way an issue is presented. can affect decisions and judgements
Nudge
framing choices to encourage people to make beneficial decisions
appealing names of healthy snacks: “Herb n’ Honey Balsamic Glazed Turnips
Faming can nudge us to make certain attitudes and decisions