Physics y11 cohort test
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Describe what a wave is
A wave is a movement of energy
Describe the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves and give examples of each.
The direction of transverse waves is perpendicular to the movement (displacement) of the source (water waves, Mexican waves, seismic waves). The direction of longitudinal waves is parallel to the movement (displacement) of the source (sound waves, Ultrasound waves)
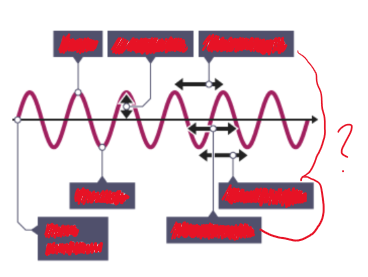
Define the amplitude of a wave and apply this knowledge to diagrams and questions
the maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its rest position
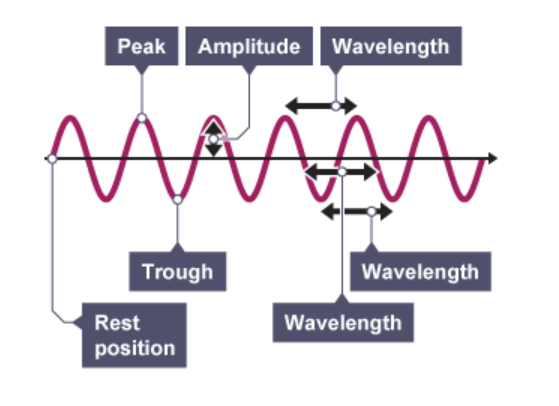
Define the wavelength of a wave and apply this knowledge to diagrams and questions
distance covered by a full cycle of the wave, usually measured from peak to peak, or trough to trough
Define the frequency of a wave and apply this knowledge to diagrams and questions
the number of waves passing a point each second
Define the time period of a wave and apply this knowledge to diagrams and questions
the time it takes to complete one cycle
Describe what can happen to a wave when it crosses a boundary between two different materials.
it will change speed which will cause the direction of the wave's motion to change and the wave will appear to bend which is called refraction.
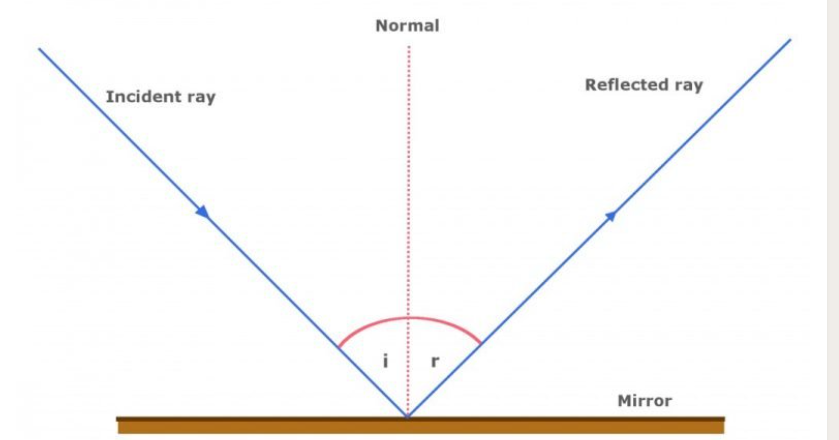
Apply the Law of Reflection and draw ray diagrams to demonstrate this.
The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence
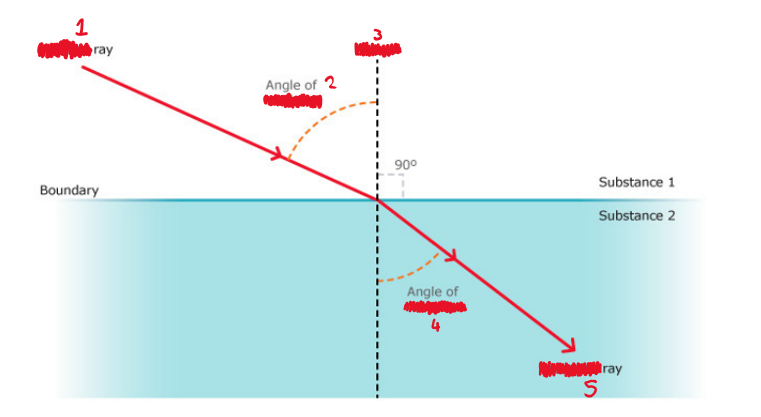
Use the wave front model to explain the refraction of light and water waves
incident
incidence
Normal
refraction
refracted
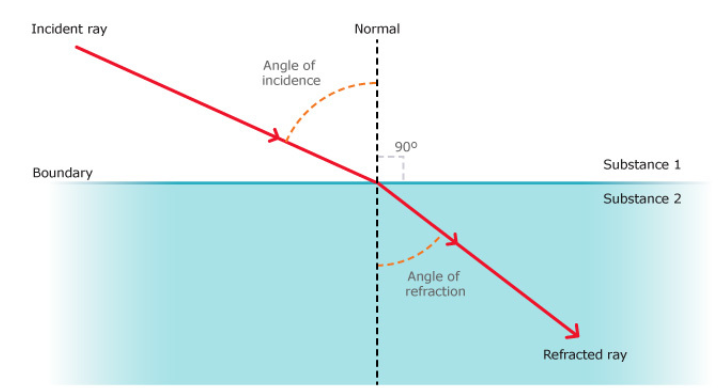
State what sound waves are.
Sound waves are longitudinal waves that cause particles to vibrate parallel to the direction of wave travel. The vibrations can travel through solids, liquids or gases, and the speed of sound depends on the medium.
Describe how to measure the speed of sound in air, including using an echo.
Two people stand in front of a wall. Measure the distance between the people and the wall one person bangs two bricks together. The other person starts the stop clock when they see the bricks come together and stops it when they hear the echo. Then do S = D/T and multiply D by 2
Required practical: make observations to identify the suitability of apparatus to measure the wavelength of waves in a ripple tank and waves in a solid.
Place a metre ruler at right angles to the waves shown on the card, count how many waves are in a set distance, then divide the length by the number of waves counted to get wavelength
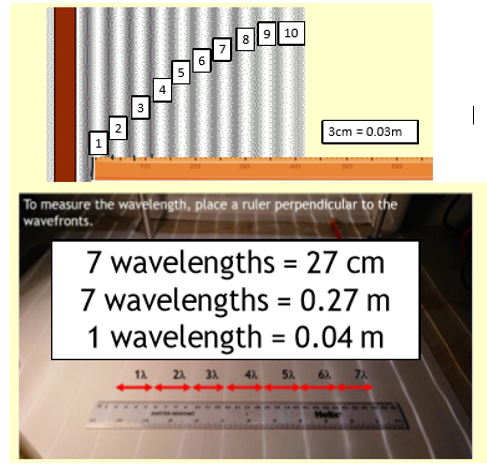
Required practical: make observations to identify the suitability of apparatus to measure the frequency of waves in a ripple tank and waves in a solid.
Count the number of waves passing a point in over a chosen time, then divide the number of waves counted by the time spent counting to get frequency
State the 7 sections of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of increasing frequency and decreasing wavelength.
Raging Martians Invaded Venus Using X-ray Guns
Radio, Micro, infrared, visible, UV, Xray, Gamma
State the similarities and differences between the 7 sections of the electromagnetic spectrum.
All electromagnetic waves transfer energy as radiation from the source of the waves to an absorber, can travel through a vacuum such as in space, travel at the same speed through a vacuum or the air. Their differences are their wavelengths and frequencies.
List 2 uses of radio waves and why they are suitable for their job
Communications and MRI because they do not cause damage to humans, and can be reflected to change their direction which is good for communications.
List 2 uses of micro waves and why they are suitable for their job
cooking food, satellite communications because they pass easily through the atmosphere, so they can pass between stations on Earth and satellites in orbit.
List 2 uses of infrared waves and why they are suitable for their job
Cameras, electrical heating because the internal energy of its bonds increase when they absorb infrared light, which causes heating.
List 2 uses of visible light waves and why they are suitable for their job
Photosynthesis, human vision because it is the light we can see, so is used in photography and illumination.
List 2 uses of UV waves and why they are suitable for their job
Sterilisation, Vitamin D production because they have powerful radiation so it is for reliable disinfection
List 2 uses of x-ray waves and why they are suitable for their job
Security, cancer therapy because its penetrating power allows us to take internal images of the human body or objects.
List 2 uses of gamma waves and why they are suitable for their job
Nuclear medicine, Medical diagnosis because they are transmitted through body tissues with very little absorption which makes them good for internal imaging
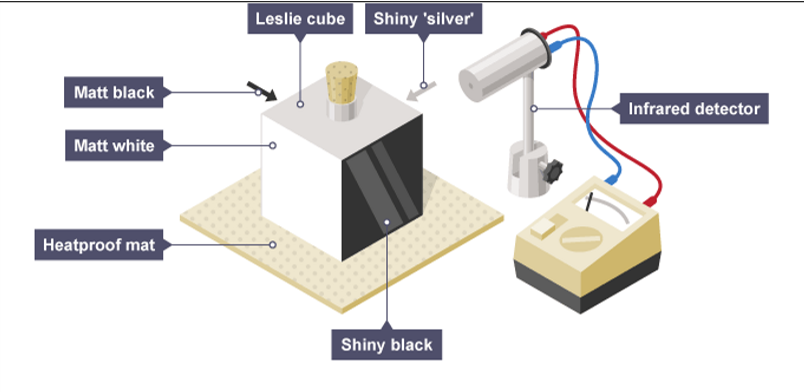
Required practical: investigate how the amount of infrared radiation absorbed or radiated by a surface depends on the nature of that surface.
Darker colours absorb more infrared radiation and emit more radiation. Lighter colours absorb and emit less radiation
Describe how radio waves are produced and detected.
Radio waves can be produced by oscillations in electrical circuits. When radio waves are absorbed by a conductor they create an alternating current.
State that gamma rays are….
released from the nuclei of atoms.
Explain why UV, X-ray and gamma rays are harmful to living cells.
They all produce ionising radiation, a form of radiation that has the potential to harm living tissue/cells and cause cancer.
Equation that relates wave speed, frequency and wavelength and units
wave speed (m/s) = frequency (Hz) x wavelength (m)
Equation that relates speed, distance and time and units
speed (m/s) = distance (m) / time (s)