EXAM #1 STUDY SET
1/435
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
436 Terms
4 properties of ACIDS
SOUR
RED
rxn w/ some metals to produce hydrogen gas
rxn w/ bases to form salt & water
4 properties of BASES
BITTER
BLUE
slippery feeling on skin (rxn w/ fats/oils on skin)
rxn w/ acids to form salt & water (neutralization rxn)
dissociates means…
move away from
produce
give off
3 theories that explain acid-base rxns
Arrhenius
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis (not the structure)
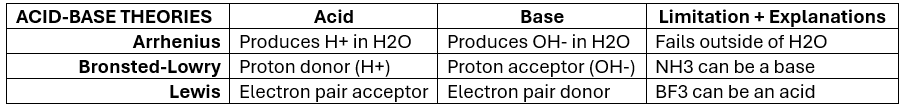
arrhenius acid
molecular compound that produces / gives off a H+ ion when placed in H2O
what is a solvent
substance that dissolves other compounds - causes H+ / OH- ions to fall off from the other compounds (Arrhenius theory)
usually written above the rxn arrow (i.e., when H2O is the solvent, it is written above the rxn arrow(s))
gives acids their properties
hydrogen ions (H+)
gives bases their properties
hydroxide ions (OH-)
Conjugate Acid / Base pairs definition
two species that differ by one proton (H+) — i.e., an acid and its conjugate base or a base and its conjugate acid
Arrhenius base
molecular compound that dissociates / dissolves in H2O (solvent/dissolver) and gives off a hydroxide ion (OH-)
neutralization rxn
rxn between an acid and a base that produces H2O (neutral molecule) and salt (ionic compound)
ionic compound definition
molecular compound made up of oppositely charged atoms — cations and anions — held together by STRONG electrostatic attraction (think: balloon on wall)
cations
positively charged ions
anions
negatively charged ions
hydrogen ion (H+) described
contains 1 e-, 1 proton, and no neutrons
if it gives up its 1 e-, it becomes positively charged — i.e., H+ or hydrogen ion
hydrogen ion becomes PROTON
valence electrons are responsible for what?
covalent bonding between atoms
where are valence electrons found on the periodic table?
in the one’s place on the element’s group number (number at the top of each column; i.e., group 17 has 7 valence electrons, group 2 has 2 valence electrons, etc.)
Are atoms with unpaired electrons more or less reactive with environment?
more reactive — more willing to form covalent bonds because a “buddy” electron creates a full octet on the atom’s outer shell (low-energy)
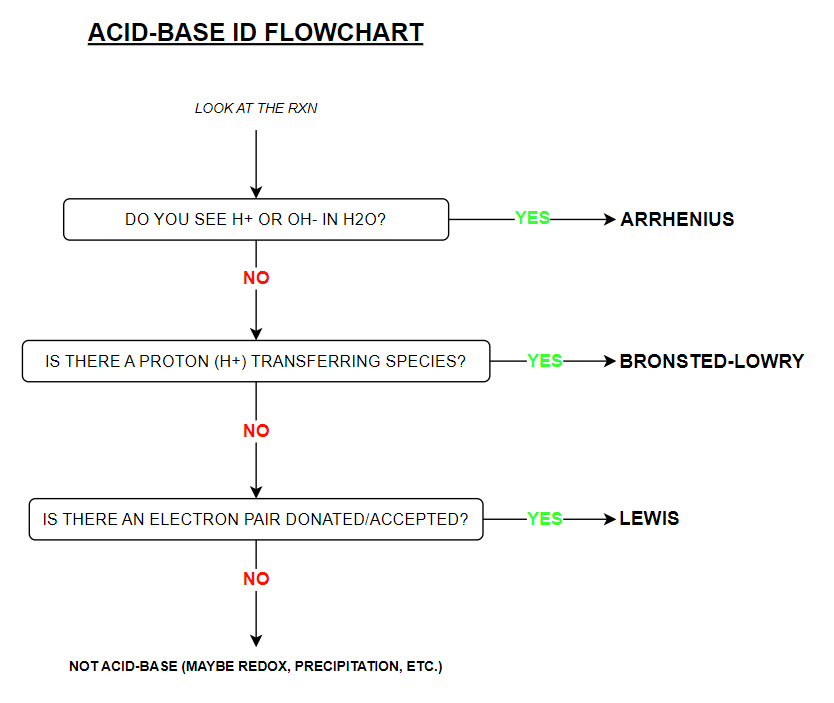
Arrhenius theory describes acid-base chemistry only within the confines of what?
an aqueous solution (H2O)
3 Arrhenius Theory Limitations
H+ cannot exist within H2O solution
Does not explain how ammonia (NH3), contains no OH-, and yet, acts as a BASE.
Theory only describes acid-base rxns in terms of H2O (aqueous) solutions [NH3 exists as a gas] — when base rxns can occur in other solvents (like methanol)
Bronsted-Lowry Acid
substance that is a proton (H+) donor
Bronsted-Lowry base
substance that is a proton (H+) acceptor
What Arrhenius acid-base theory limitation does Bronsted-Lowry ANSWER?
Explains why NH3 is a base without the existence of hydroxide ions (OH-)
[NH3 will act as a proton acceptor (i.e., B-L base)]
Coordinate bond
when both e- in a covalent bond come from the same atom
-
[example: creation of ammonium (NH4+) — H+ does not have e-]
Lewis acid
substance is an electron pair acceptor
Hint: “Louis complains and does the opposite of Lestat (B-L acid)”
Lewis base
substance is an electron pair donor
Hint: “Louis complains and does the opposite of Lestat (B-L base)”
Acid-Base Identification Flowchart (know the info on here)
Acid-Base Theories — Summary Chart (KNOW)
Hydrochloric (HCl) strength & purpose
strong acid
crucial to proper digestion and defense against pathogens in the digestive system
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) strength & purpose
strong acid
car battery acid
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) strength & purpose
moderate strength acid
component in DNA or ATP
Acetic acid (CH3COOH) strength & purpose
weak acid
component of acetyl-coA (energy metabolism)
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) strength & purpose
strong base
neutralize acids and soap making
Magnesium Hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) strength & purpose
strong base
laxatives and antacids
Acetate (CH3COO-) strength & purpose
weak base
product of acetic acid dissociation, precursor of biomolecules
Ammonia (NH3) strength & purpose
weak base
intermediate in protein degradation
polyprotic acids
refers to acids capable of donated >1 proton (H+) per molecule
-
there are mono- (1 H+), di- (2 H+), tri- (3 H+), tetra- (4 H+), penta- (5 H+), and hexa- (6 H+)
acids can differ based upon the number of ____ they can donate in an aqueous solution
protons (H+ ions)
monoprotic acids
acids that can only donate 1 proton per molecule in an aqueous solution
each monoprotic acid contains ____
1 acidic hydrogen
what is an acidic hydrogen
this is the hydrogen atom in an acid that forms an H+ ion when the acid dissociates (falls apart)
diprotic acids
acids that donate 2 protons per molecule during a 2-staged ionization rxn
why does a diprotic rxn need 2 ionization stages?
after the 1st ionization / dissociation, the resultant negatively charged anion will attract the remaining (not yet dissociated) H+ proton even more strongly — i.e., this 2nd proton (2nd ionization/dissociation) is harder to come off of the anion than the first dissociation
thicker arrow in reaction
means rxn occurs with more “ease”
thinner arrow in reaction
rxn occurs with less “ease” (harder) due to the increased negativity on the molecule you are pulling from
triprotic acids
acids that can donate 3 protons per molecule
why does triprotic acids rxn require 3 ionization stages?
similar reason to diprotic — the 1st stage is the easiest stage, and the third stage is the hardest stage (increasing negativity on main molecule)
T/F: The higher the degree of dissociation, the stronger the acid!
True
1st stage = weak vs. 3rd stage = strong
T/F: All hydrogen atoms in a molecule are acidic.
False
-
Whether a hydrogen atom can be donated as a H+ proton depends upon the nature of the atom or group to which it is bonded.
T/F: H bonded to C cannot be an acidic H!
True
electronegativity definition
ability of atoms to attract and hold electrons within chemical bonds
the higher the electronegativity of an atom, the greater the attraction towards the electrons
Electronegativity determines ____ and ____ of chemical bond!
polarity
type
nonpolar covalent bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
0 — 0.4
polar covalent bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
0.5 — 1.9
ionic bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
2.0 and above
acidic hydrogens are H atoms that are bonded to _____
electronegative elements (such as N, O, F, Cl) in a molecule
conjugate acid-base pairs
occur within acid-base equilibrium rxns
an acid and its conjugate base, as well as its base and conjugate acid, differ only by 1 proton.
HA + B ←→ A- + HB+
[acid + base ←→ conjugate base + conjugate acid]
amphoteric compounds
molecule or ion that can react both as an acid and as a base
-
when HA accepts a proton, it acts as a base!
Zwitterion definition
neutral dipolar ion that has one positively charged group and one negatively charged group — canceling each other out!
When H2O reacts with a stronger acid, it acts a ____.
base
when H2O reacts w/ a stronger base, it acts as an ____.
acid
HSO4- acts as a ___ by accepting a proton from H3O+ to form H2SO4-
base
HSO4- acts as an ____ by donating a proton to hydroxide ion to form SO42-
acid
In acidic solution, amino acids accepts a proton and acts as a ___.
base
In basic solution, amino acid act as an ___ by releasing a proton.
acid
![<p>Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?</p><p>NH<sub>2</sub> & COOH groups?</p><p>Condition [H<sup>+</sup>]: basic or acidic or neutral?</p><p>Charge: +, -, or no charge?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/89053539-44ce-4c6b-bf93-f033c3e49327.png)
Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?
NH2 & COOH groups?
Condition [H+]: basic or acidic or neutral?
Charge: +, -, or no charge?
cation
protonated amino group
acidic (high)
positive
![<p>Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?</p><p>NH<sub>2</sub> & COOH groups?</p><p>Condition [H<sup>+</sup>]: basic or acidic or neutral?</p><p>Charge: +, -, or no charge?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/03fe389f-c61d-43d0-bede-33bee4b087b1.png)
Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?
NH2 & COOH groups?
Condition [H+]: basic or acidic or neutral?
Charge: +, -, or no charge?
zwitterion
protonated amino group & deprotonated carboxyl group
neutral
no net charge
![<p>Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?</p><p>NH<sub>2</sub> & COOH groups?</p><p>Condition [H<sup>+</sup>]: basic or acidic or neutral?</p><p>Charge: +, -, or no charge?</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1e2a8931-3e58-428f-96aa-02aff47a3678.png)
Form: anion or cation or zwitterion?
NH2 & COOH groups?
Condition [H+]: basic or acidic or neutral?
Charge: +, -, or no charge?
anion
deprotonated carboxyl group
basic (low)
negative
Strength of an acid refers to its relative ability to ____.
donate a proton
A strong acid will have a ____.
weak conjugate base
A weak acid will ____ only slightly in water.
ionize
A weak acid will have a ___.
strong conjugate base
If the forward rxn is favored, then there will be ___ conjugate base & conjugate acid at equilibrium.
more
If the reverse rxn is favored, then there will be ___ acid & base at equilibrium.
more
In every acid-base proton transfer rxn, the position of the equilibrium favors the transfer of the proton from the ___ acid to the ___ acid, or from a ___ base to a ___ base.
stronger to weak (both)
Single Forward Arrow (in rxns)
irreversible rxn
Equal Arrows (in rxns)
neither forward nor reverse rxn is strongly favored - balanced
Longer Forward Arrow (in rxns)
Products are more prominent, and forward rxn is favored
Longer Reverse Arrow (in rxns)
Reactants are more prominent, and the reverse rxn is favored
A rxn is in ____ when the rate of the forward rxn equals the rate of the of the reverse rxn.
chemical equilibrium
[R] = [P] → CONSTANT
The equilibrium constant (K) definition
equal to the multiplication of products divided by the multiplication of reactants
K = ? (equation)
[H3O+][A-] / [HA][H2O]
Acid-Dissociation Constant Equation
Ka = [H3O+][A-] / [HA]
H2O is considered constant
K[H2O] is considered constant and unchanging in acid-base rxns
Ka for a strong acid
large number
equilibrium shifts to the right and favors the formation of H3O+ and A-
Ka for a weak acid
small number
equilibrium shifts to the left and favors the formation of HA
the acid dissociation constant (Ka) is a measure of what?
the strength of an acid in solution
strong acids have ___ Ka values and dissociate ___ in water
high
almost completely (flies apart)
weak acids have ___ Ka values and dissociate ___ in water.
low
only partially
Ionization / dissociation of polyprotic acids occur in ___ and each has its own Ka value.
stages
Ka values of dissociation / ionization of polyprotic acids stages ranked
Ka1 > Ka2 > Ka3 … etc.
each ionization stage becomes more difficult to remove H+ from a molecule as its negative charge increases
pKa = ? (equation)
pKa = -logKa
In Ka, the larger the value, the ___ the acid.
stronger
In pKa, the larger the value, the ___ the acid.
weaker
Arrhenius theory establishes an acid
as a compound that can dissociate in H2O to yield H+ (same thing as H3O+)
What is it specifically that gives the properties of acids? (i.e., what determines the level of acidity in H2O-based solutions)
[H+]
What does it mean that H2O is amphoteric?
one H2O molecule can react with another H2O molecule to form OH- anion (base) and H3O+ cation (acid)
H2O is never by itself, there are 3 species that exist - there is no “pure water”.
[OH-] = [H3O+] = ?
1 × 10-7 M (constant)
Ion-product constant for water (Kw)
Kw = [OH-][H3O+]
1 × 10-14 M2
T/F: The Kw equation cannot be applied to any and all aqueous solutions?
False; it can.
pH defined and equation
Potential or power of hydrogen
used to specify the acidity of an aqueous solution
pH = -log[H+]