Lab exam 1 Bio 115
1/109
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
What color would be produced in a negative reaction for a reducing sugar test when using Benedict's reagent?
A blue color
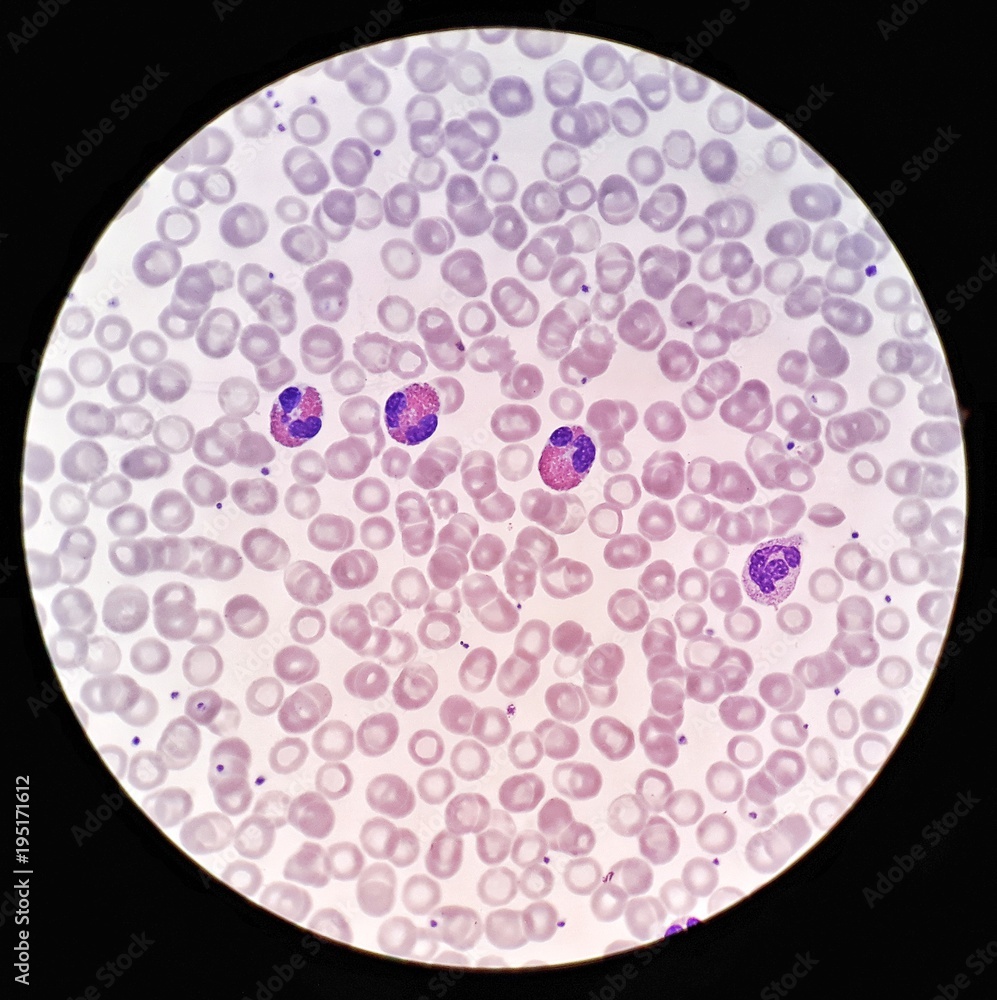
What is this?
human red blood cells

What is it and what mag
Stentor 40x
What are the weight changes in hypotonic bags?
weight increase
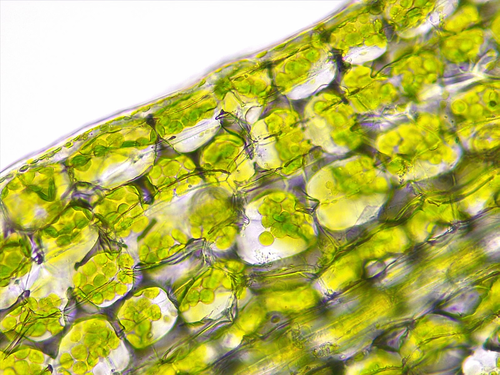
Is it Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic. What mag is being used.
hyper tonic-40X
What is the color of DPIP when it is reduced
clear
How does phenolpthalein turn pink?
It turns pink in basic solutions.
substrate for enzymes lab
starch
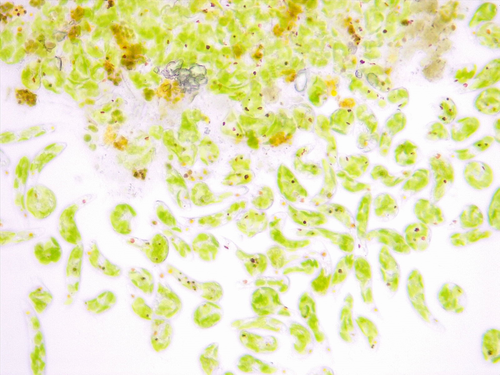
What is it? What mag.
Euglena10x
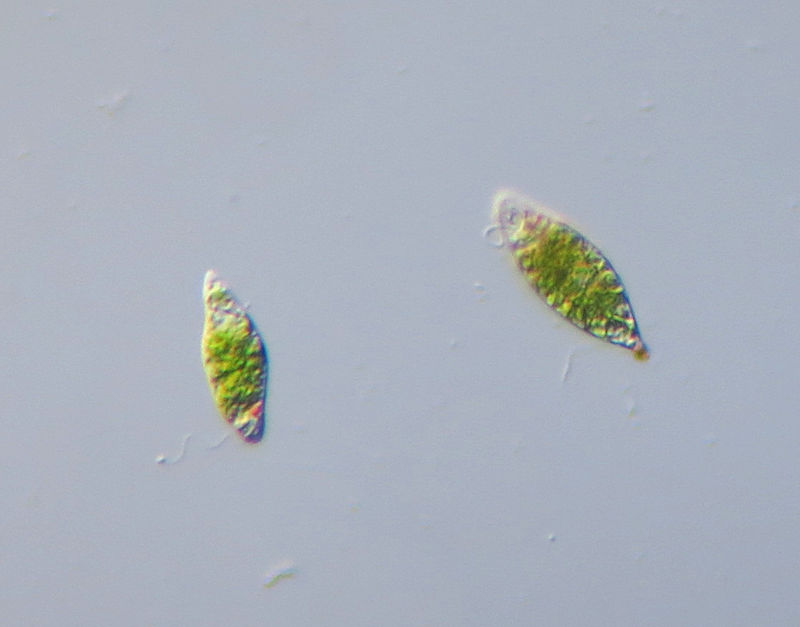
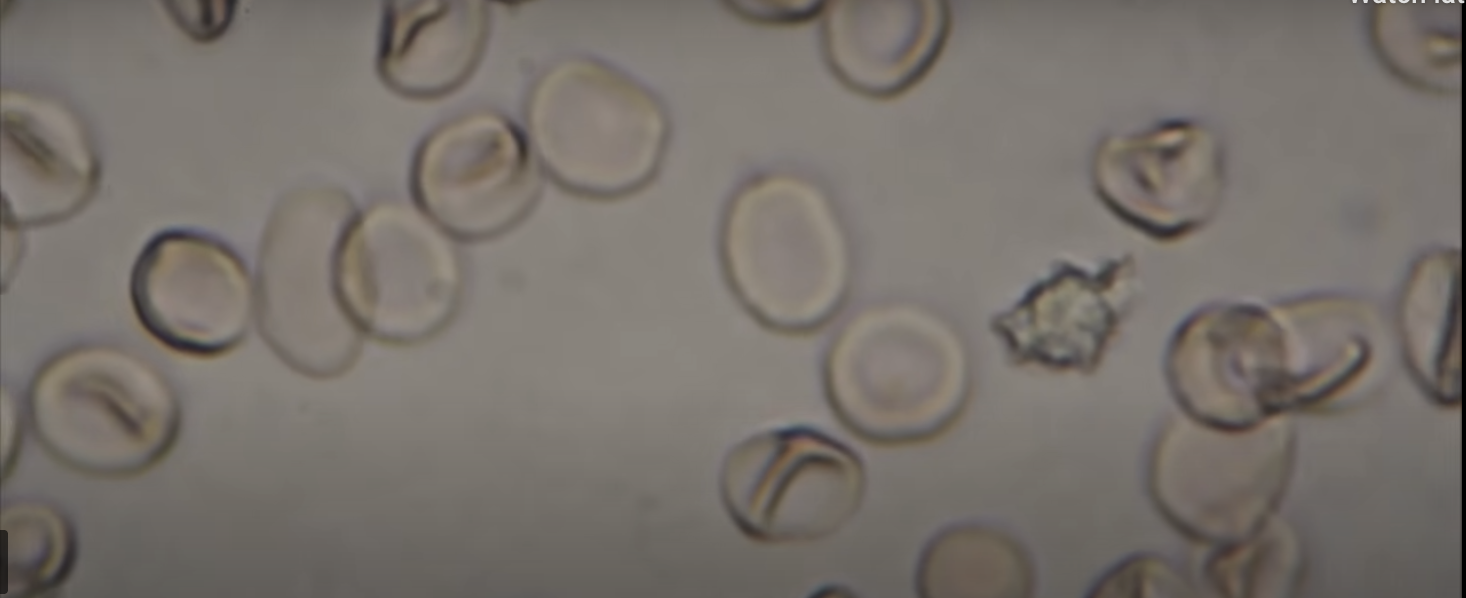
Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic.What kind of cells
Hypertonic blood cells
What can be used to make a hypotonic solution for red blood cells
distilled water
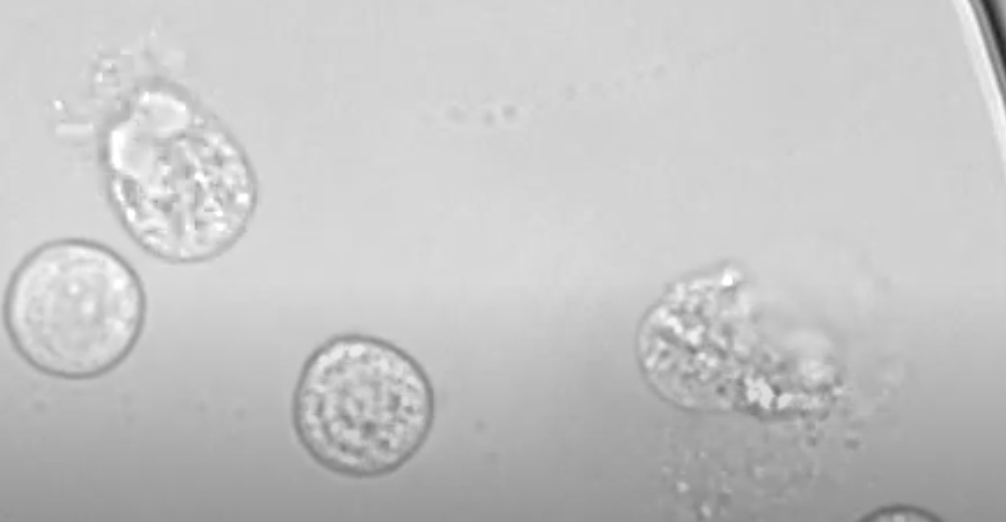
Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic
Hypotonic
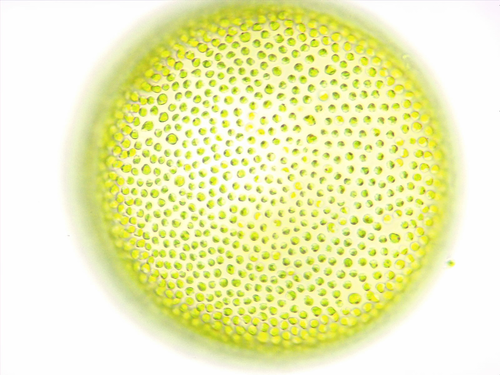
What kind of cell, and what mag?
protist cell volvox 40x
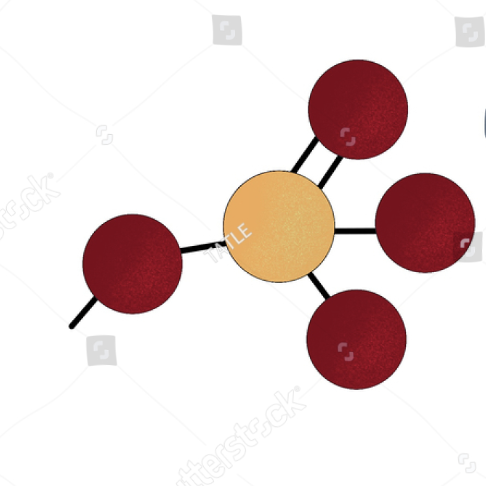
PO4
phosphate group

What mag?What kind of cell?
hypotonic 40x- Plant cell
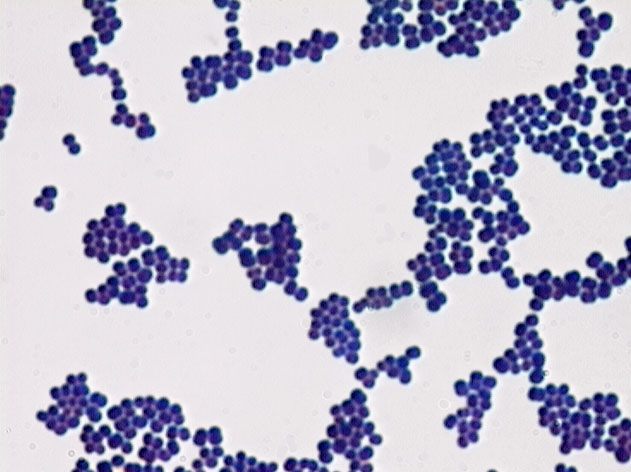
What kind of bacteria is it?
coccus (cocci)A spherical-shaped bacterium.
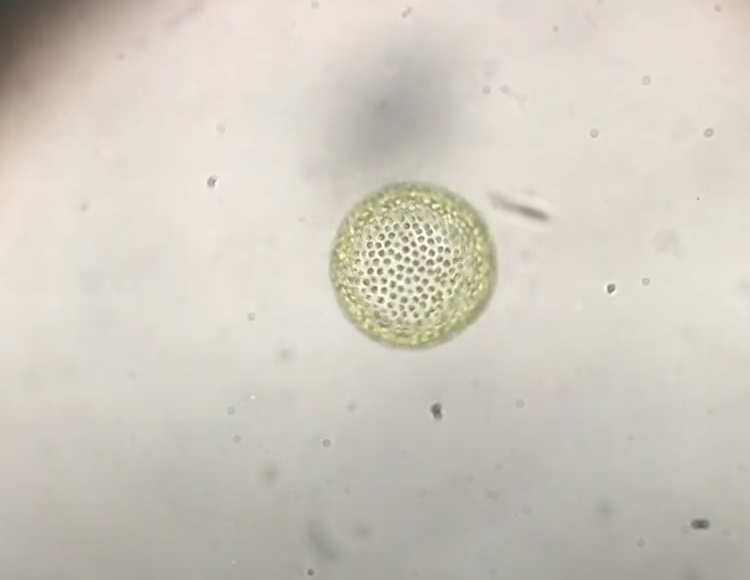
What is it? What magnefication?
volvox 10x
Which part of the homogenate has the mitochondria?
The mitochondrial fraction, which is isolated during the centrifugation process of cell homogenates.
what ingredients will we use to conduct the fermentation reaction ?
sugars, yeast, and water.
What does a positive reaction for starch look like, when tested with iodine
blueish black
What would present a negative reaction for starch, when testing with iodine
a yellow or brown color
A positive control for testing for reducing sugars is typically
a solution containing glucose.
What is used as a negative control in the Biuret test
Water
In a homogenate after centrifugation, the pellet is located
at the bottom of the centrifuge tube.
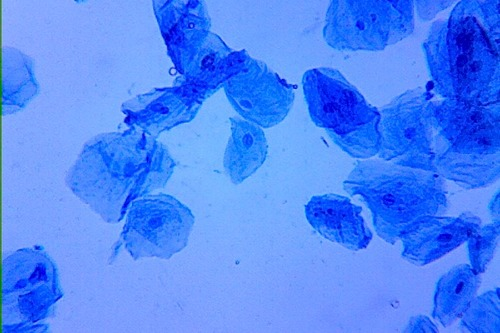
What type of cells are these?
human cheek cells
What is the weight change in an isotonic bag?
There is no weight change, as the concentration of solutes is equal inside and outside the bag.
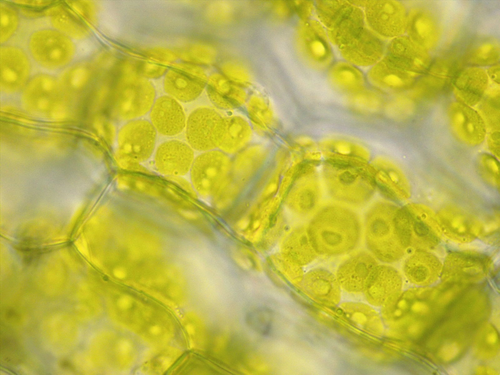
Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic? What magnification? What type of cell?
Hypotonic. 100x. Plant cells.
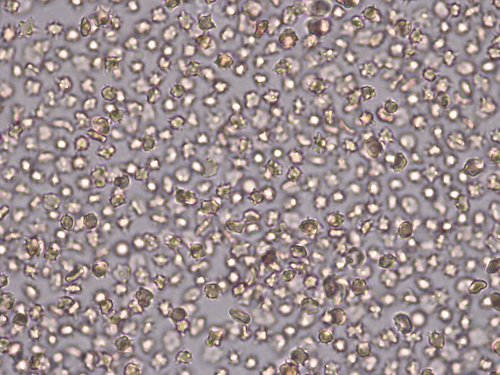
Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic? What type of cell?
Hypertonic. Blood cells.
How do you get your amylase to start hydrolyzing the starch in lab 8?
mix the amylase enzyme with a starch solution under optimal conditions, typically at a slightly alkaline pH and a moderate temperature (37°C).
What does the Amylase help with?
It helps to hydrolyze starch into glucose.
What does catalase help to break down?
Hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen.
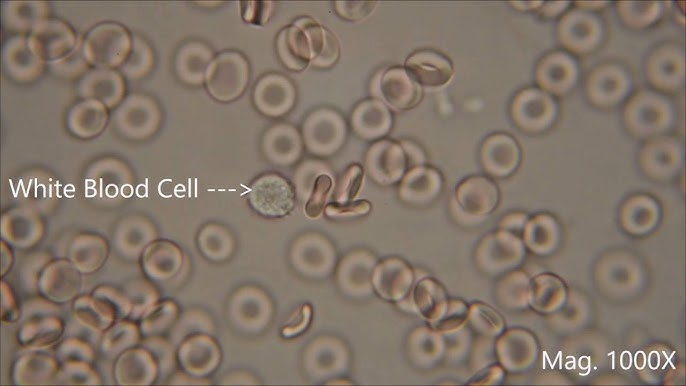
Hypo, Hyper, Isotonic?
Isotonic
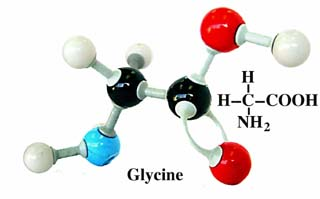
What group is NH2 (glycine) in?
Amino
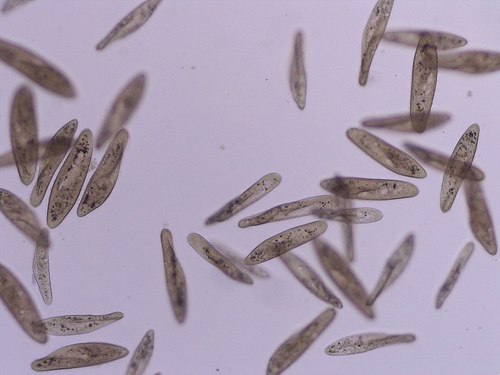
What is it called? What magnification?
Paramecium 10x
What are the reagents used to test for lipids?
Sudan IV
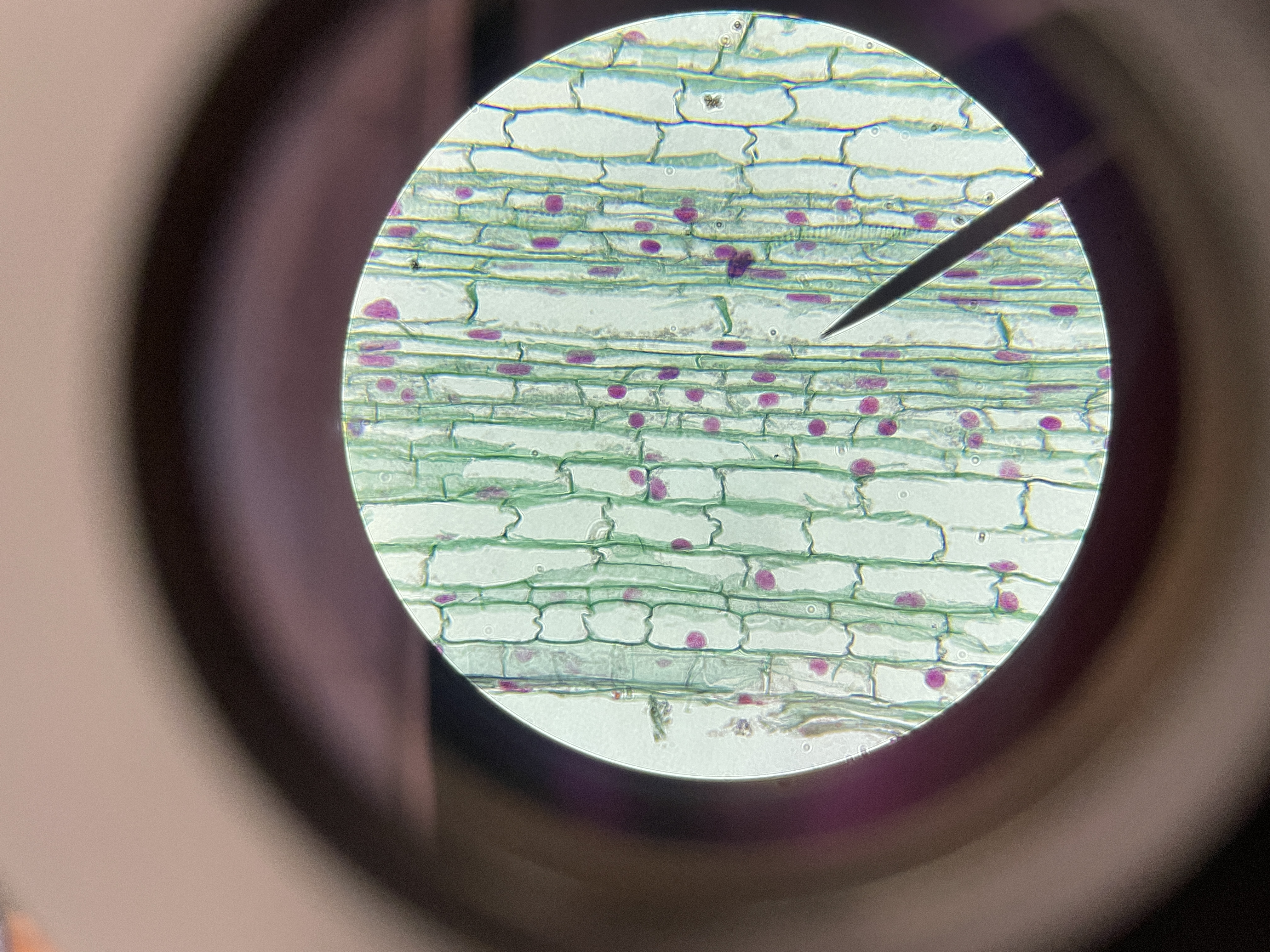
What kind of cells are these?
Onion root tip.
What is the tool used for fermentation?
fermentation tube

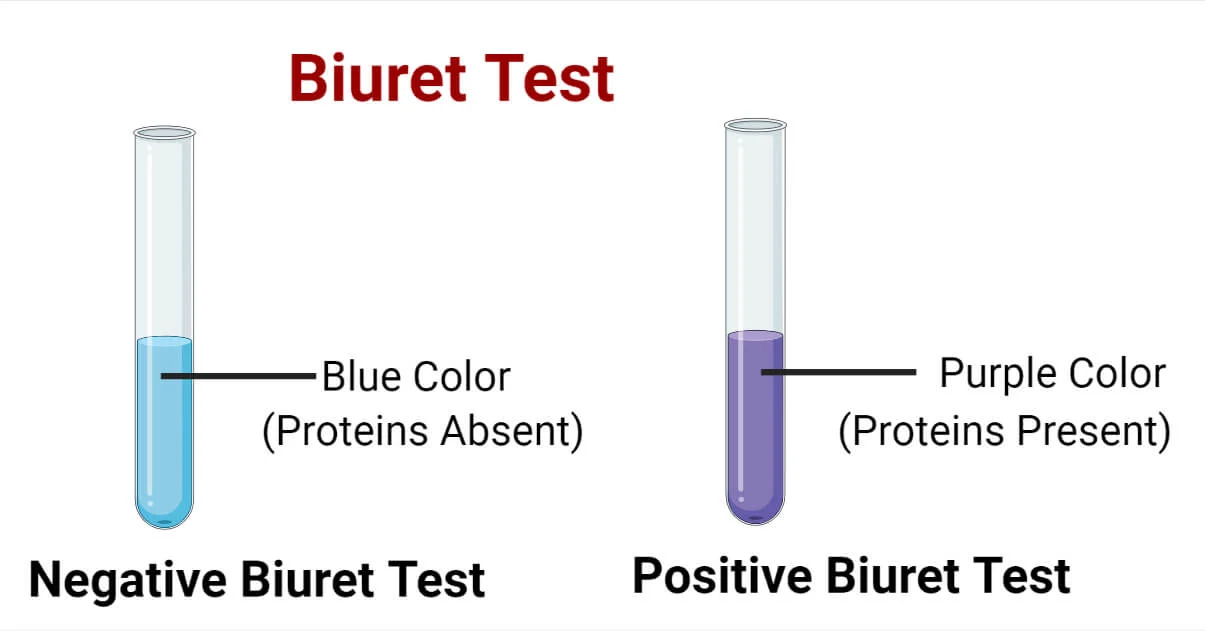
What color would be produced in a negative reaction in a Biuret test? Meaning what?
light blue color. This means no change in color, signifying the absence of protein or peptide bonds in the sample.This means there is no change in color, which signifies
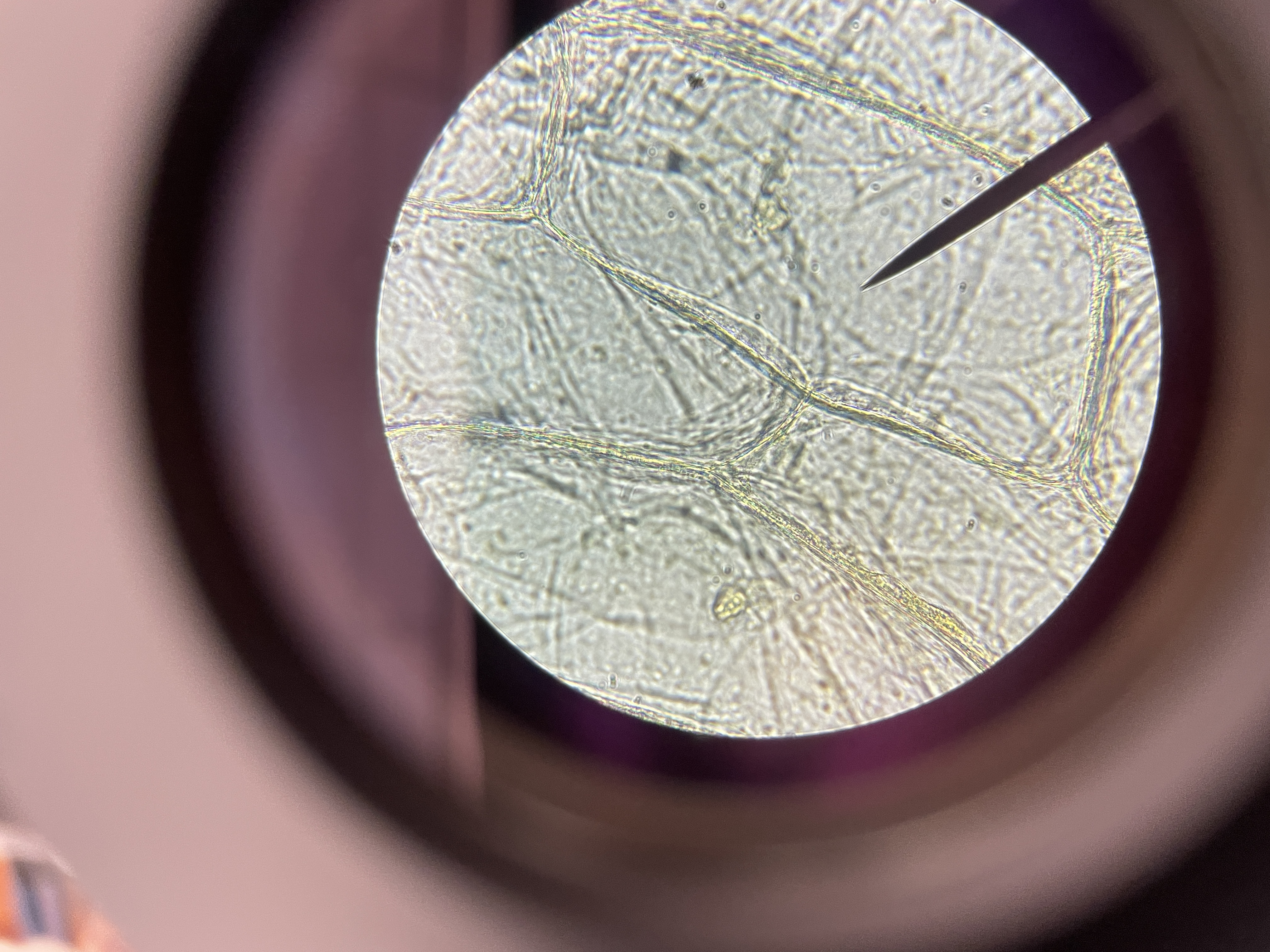
What does this represent?What did we add to it to make it more visable?
Onion cell Wall wet. We added a drop of Iodine.
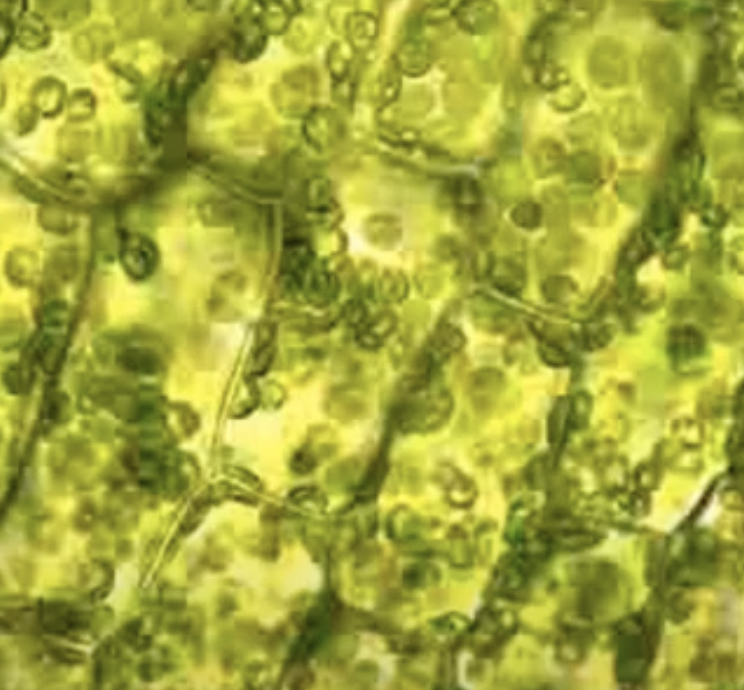
What kind of cell is this from? What magnification? What can we see from it?
Elodea leaf. 40x. Cell wall & chloroplast.
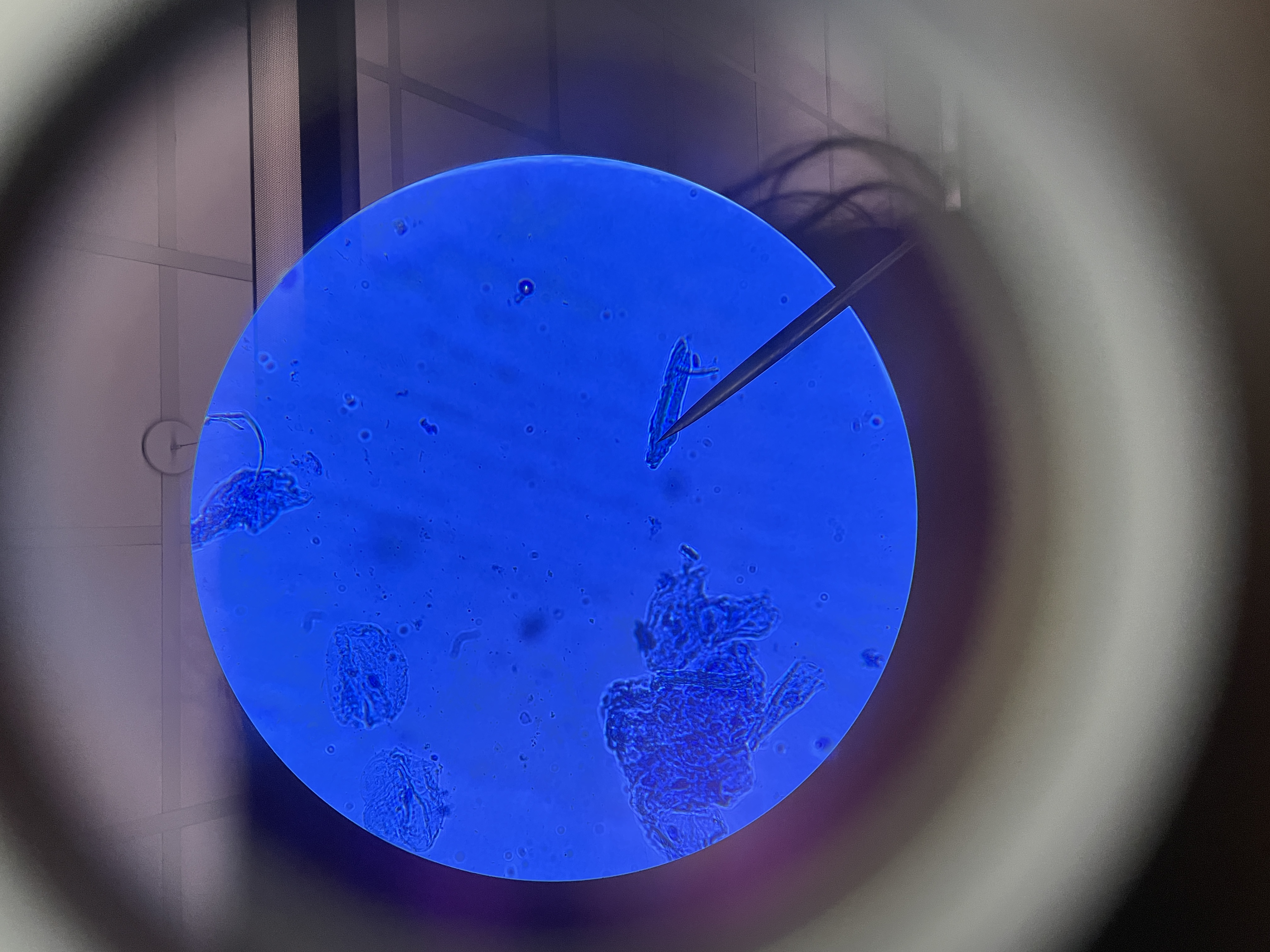
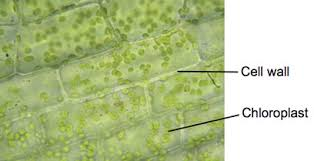

How do cheek cells appear different from plant cells?
They lack a distinct cell wall, have a smaller vacuole, and often have an irregular shape. They also don’t have any chloroplasts.
Draw a mitochondrion and label the inner and outer membranes, cristae, matrix, and intermembrane space.
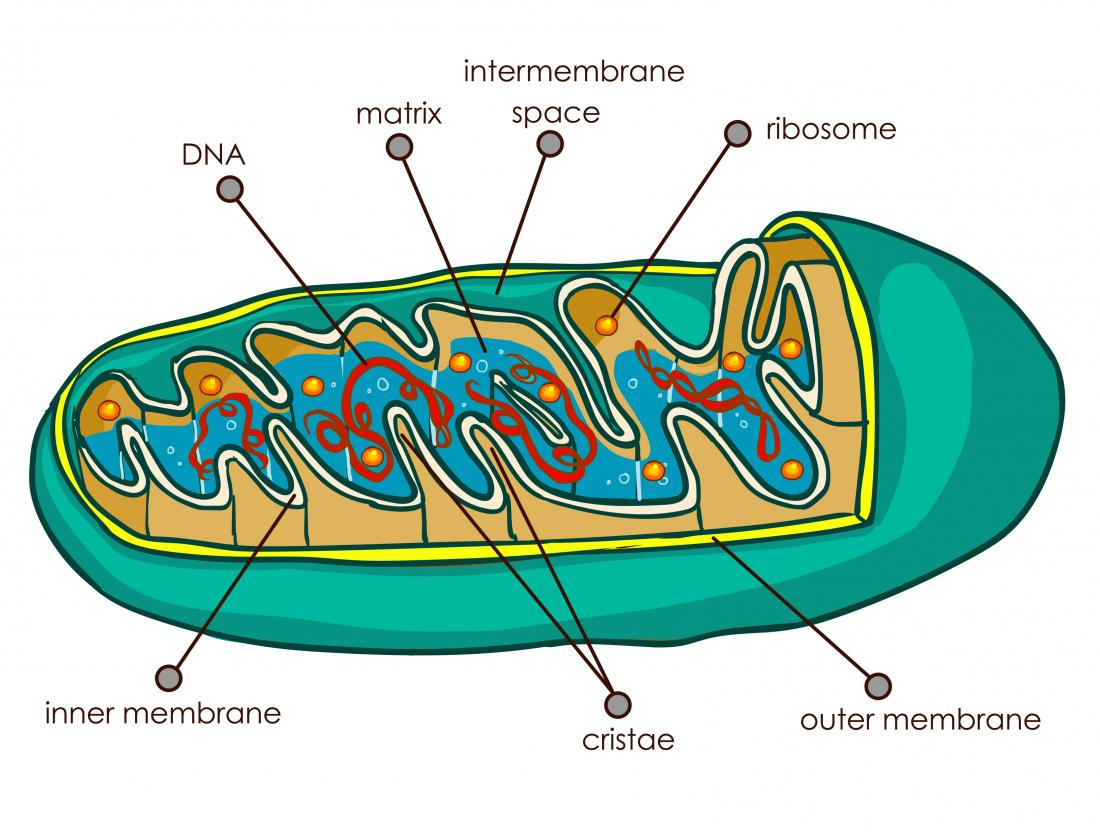
What types of cells contain mitochondria?
Any cell that has a nucleus will contain mitochondria, with the exception of mature red blood cells which lack them completely.
What types of cells do not contain mitochondria?
Bacteria, archaea and red blood cells.
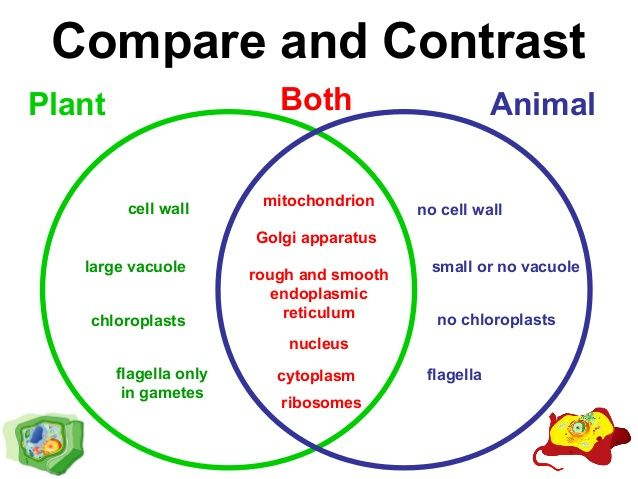
Compare and contrast animal and plant cells using the venn diagram.
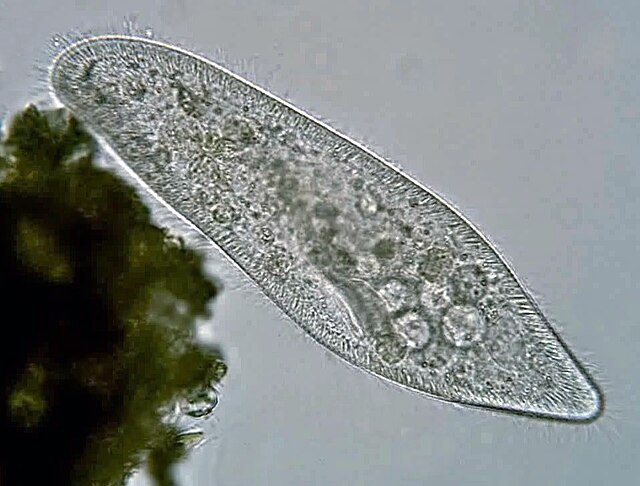
What kind of protists is this?
Paramecium
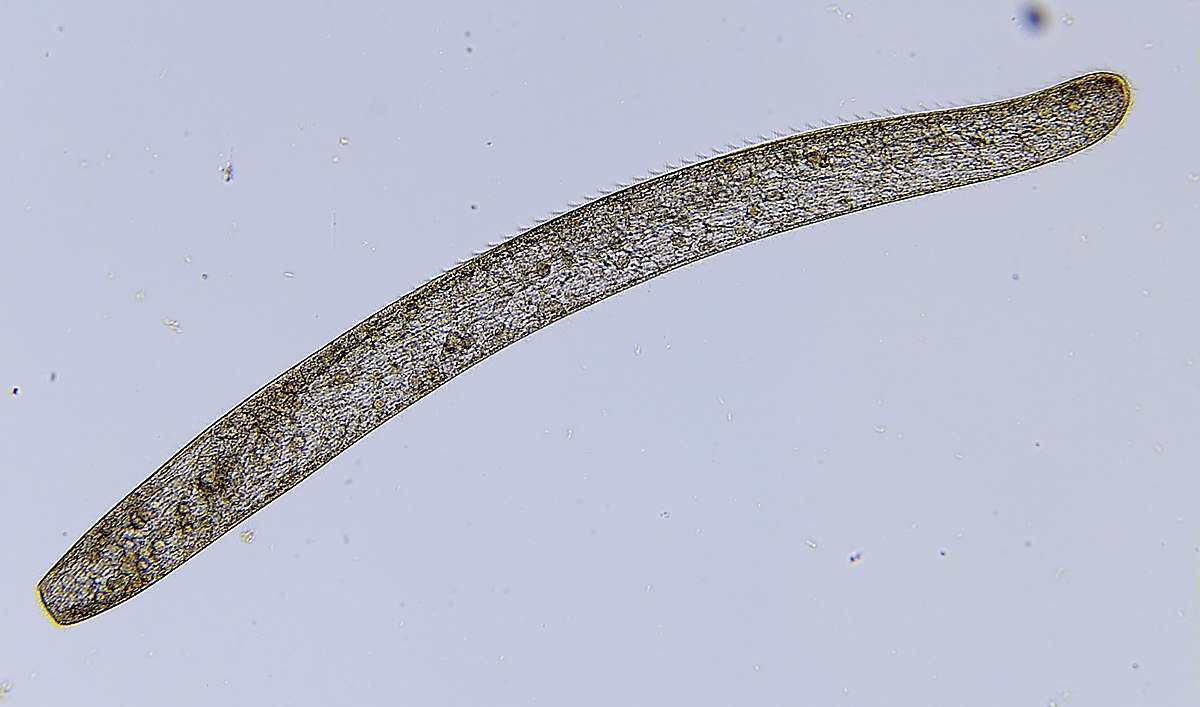
What kind of protists is this?
spirostomum
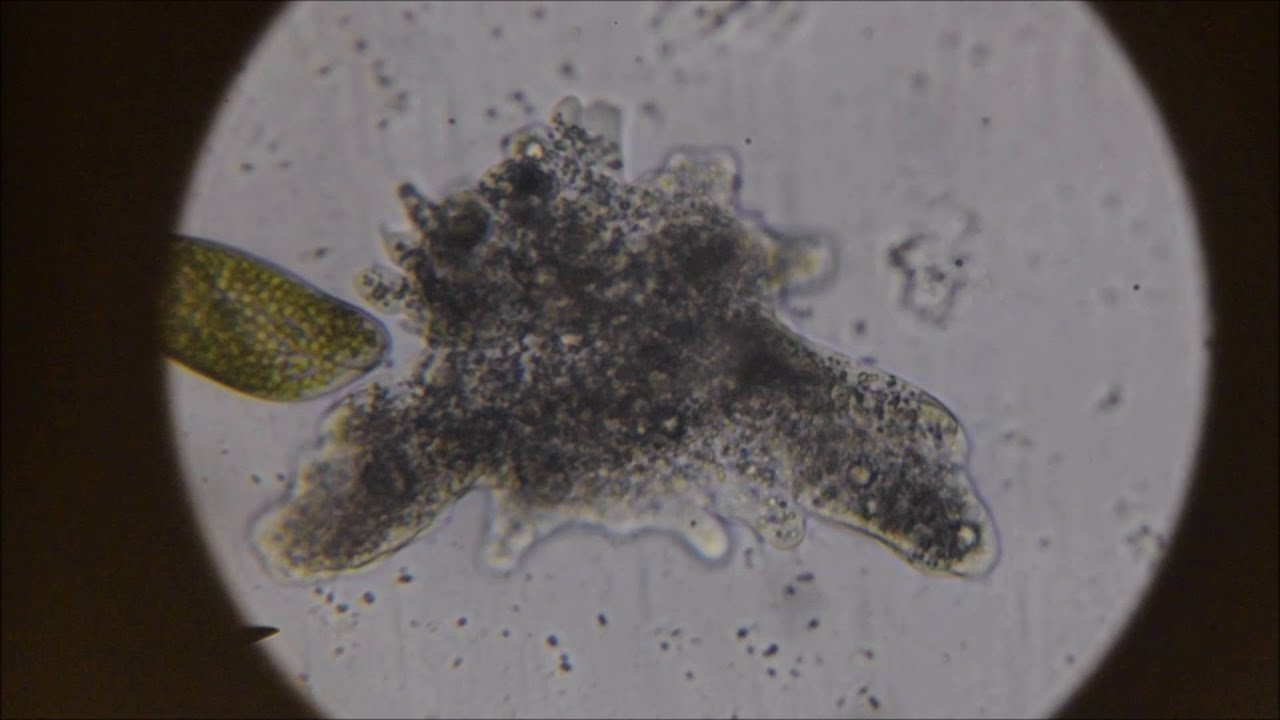
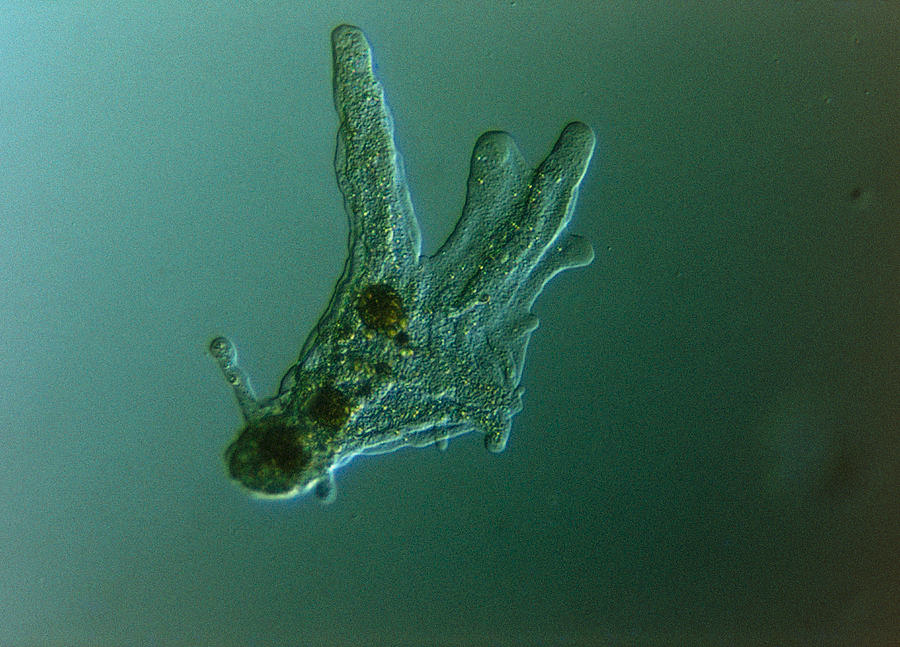
What kind of protists is this?
Amoeba
What is the iodine test used for?
To detect the presence of starch, a complex carbohydrate.
In the Iodine test, what color does it turn to when it reacts with starch?
Blue-black

What can be used as a negative control for the iodine test?
Distilled water
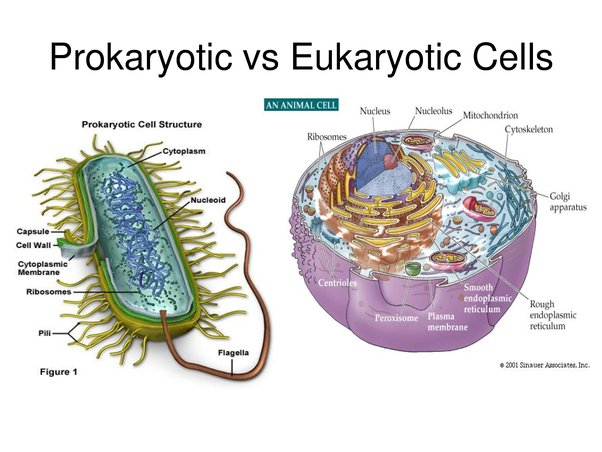
Cells with nuclei and membrane-bound organelles are called…
Eukaryotic cells.

How are glycine and alanine similar amino acids?
They both have an amino group and a carboxyl group.

How are glycine and alanine different amino acids?
difference is that alanine has a side chain consisting of a methyl group (essentially a methane molecule) while glycine has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain, making it the simplest amino acid.

What ingredients did we use to conduct the fermentation reaction?
5ml corn syrup and 1ml Yeast solution.
What were the best temperatures where we saw fermentation occur?
25C & 37C
Why did we not see fermentation occur at 60'C
Because once it reaches this temperature or higher, it kills the bacteria.
If an enzyme's optimal temperature is 20 degrees, then at very low temperatures the enzyme will become
Inactive
amylases are mainly found in ___________.
The digestive system of humans and other mammals
Catalysts speed up chemical reactions and are used up by that reaction
true or false
False
sucrase is the ________ that hydrolyzes the substrate _____________
Enzyme, sucrose
What enzyme hydrolyzes starch?
Amylase
What was the most optimum temperature form bovine catalase?
37’C
What is the most optimum pH for bovine catalase?
A pH 6/8
At 0º C, the chemical reaction between amylase and starch no longer occurs (or is very slow), because the enzyme is
Inactive
At 100°C, the chemical reaction between amylase and starch no longer occurs, because the enzyme is…
Denatured
What are enzymes?
Proteins that catalyze chemical reactions.
What is a substrate?
The molecule that an enzyme acts on.
What is starch?
A polysaccharide produced by plants and used for energy storage.
What is the simplest form of starch?
Amylose.
What is amylase?
An enzyme that digests starch.
What is the name of the reagent to detect proteins
Biuret reagent
A positive reaction for reducing sugar in a Benedicts reagent is indicated by what color?
Reddish- orange brown
A carboxyl group is made of what functional group?
Hydroxyl group (OH) and a carbonyl group (O) attached to a carbon atom
Chemical formula for Carboxyl group?
COOH
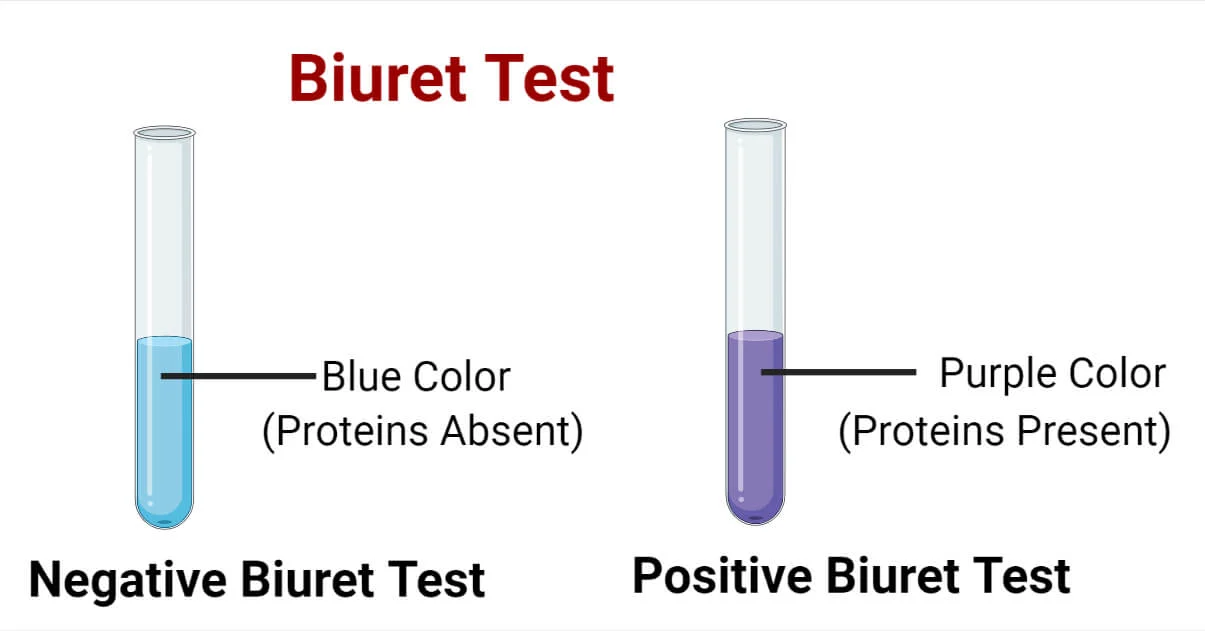
A positive reaction in a Biuret test is indicated by
A purple color
What does a positive reaction in a Biuret test indicate?
The presence of protein due to the interaction between copper ions and peptide bonds within the protein molecule.
Why wouldn’t Sudan IV not dissolve?
Because there is a negative reaction for lipids
What was our control in the fermentation tube lab?
Corn syrup and yeast
What was our Negative in the fermentation tube lab?
Water and corn syrup
Methane
CH4
What does DPIP stand for
2,6-dichlorophenol-indophenol
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
Phosphate group, pentose sugar and nitrogenous base.
what functional group is attached to the 3 carbon
hydroxyl group (-OH)
What functional group is attached to the 5’ carbon
A phosphate group
What nucleotides exist in DNA?
adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T)
What two molecules will make up the backbone of the DNA strand?
deoxyribose sugar and phosphate groups
How can you tell the 5’end of the molecule and the 3’ end of the molecule of DNA?
The 5' end of a DNA molecule is identified by a free phosphate group attached to the 5th carbon of the sugar molecule at the beginning of the strand, while the 3' end has a free hydroxyl group attached to the 3rd carbon of the sugar molecule at the end of the strand
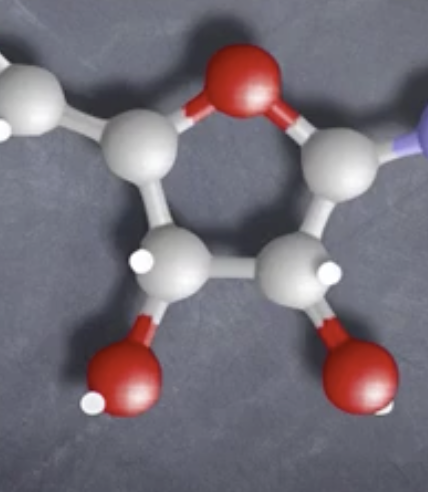
What is this called?-DNA question.
Deoxyribose
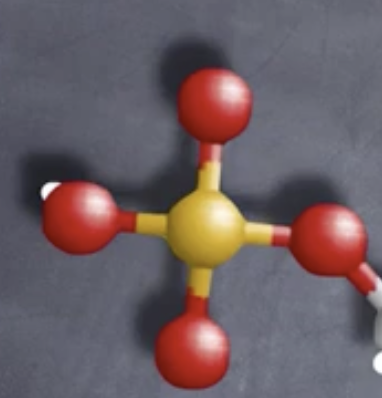
What is this called?-DNA question.
Phosphate
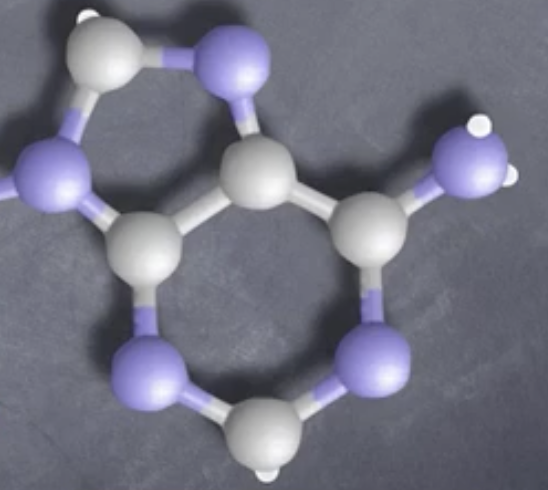
What is this called?-DNA question.
Nitrogenous Base
WHat four nitrogenous bases make up DNA nucleotides?
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Cytosine (C), and Guanine (G).
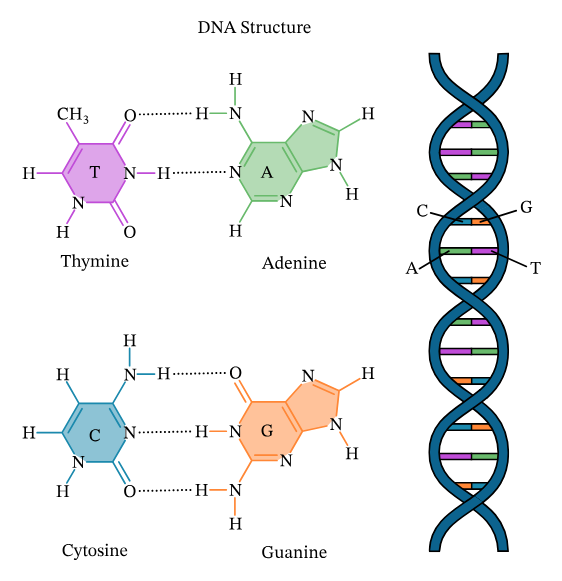
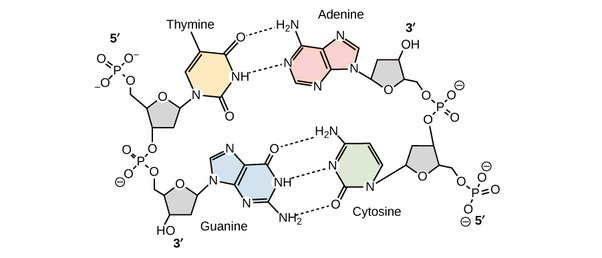
In DNA what bases go together?
A&T, C&G
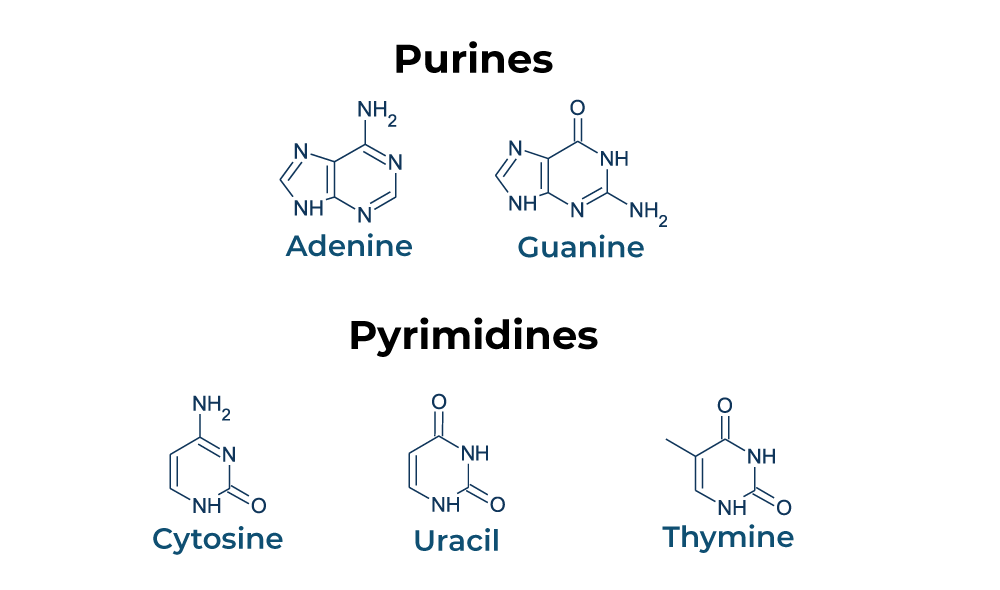
what bases are pyrimidines
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil
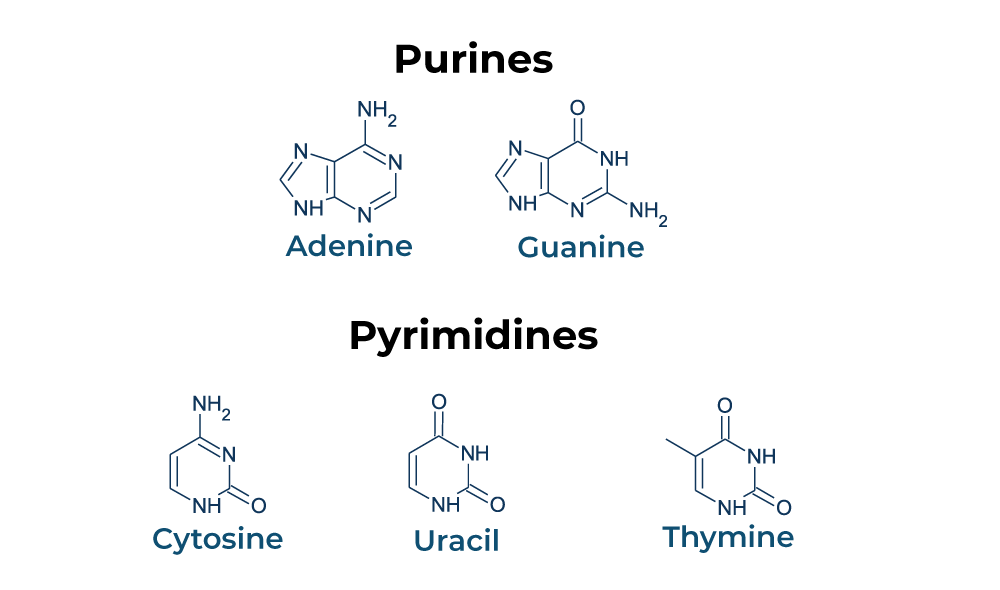
What bases are purines?
adenine (A) and guanine (G)
How was the structure of the bases useful in determining the structure of the double helix
It dictated how the two strands of DNA could pair up and twist around each other.
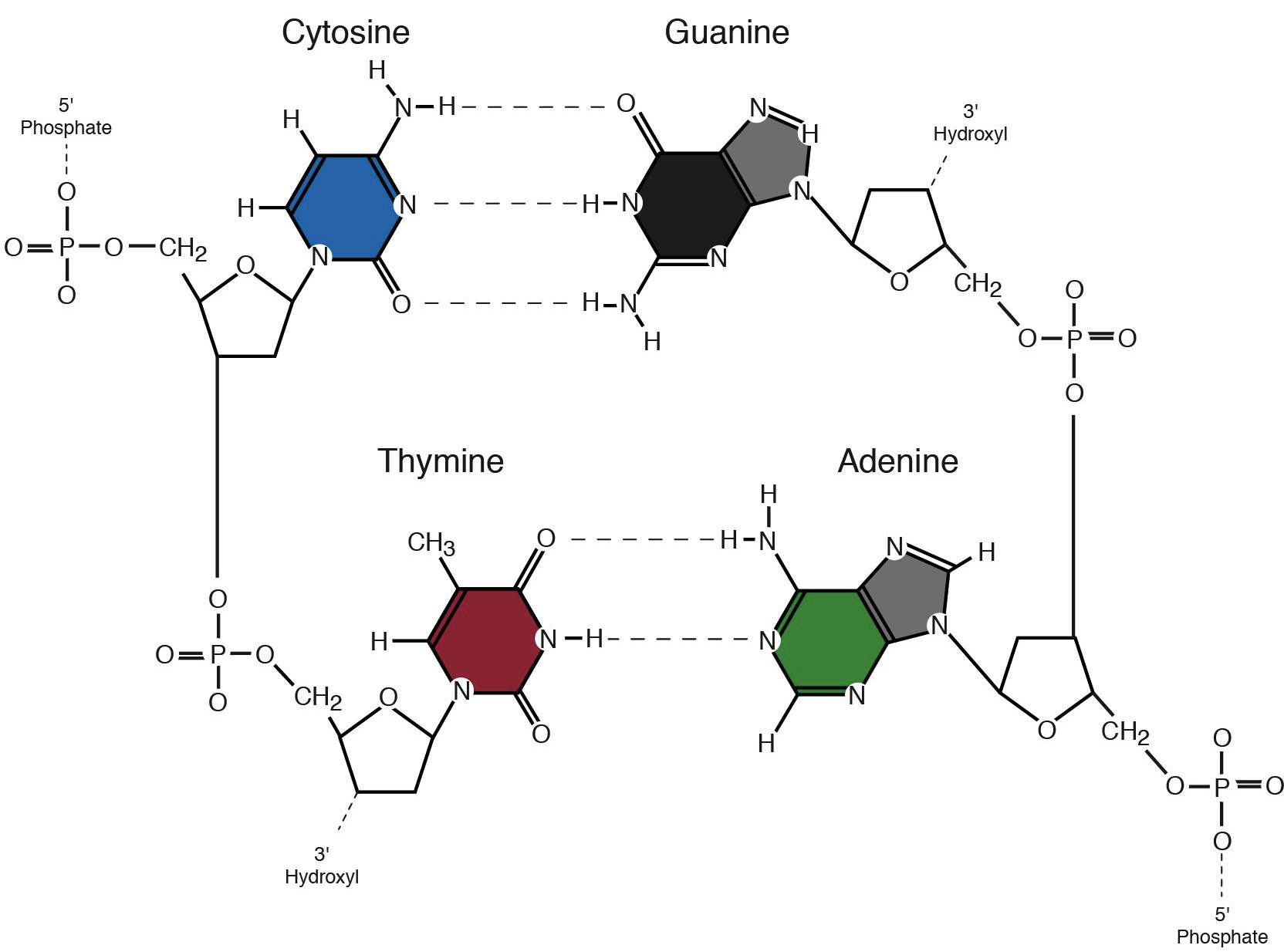
How many hydrogen bonds hold an A-T pair together?
2
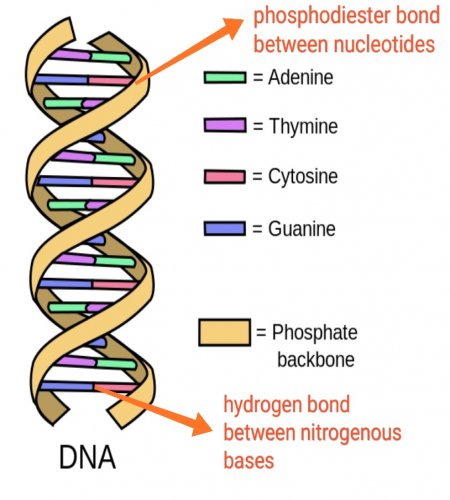
How many hydrogen bonds hold a C-G pair together
3
What is the function of phenolphtalein?
It is a pH indicator
What are the three fundamental domain of life?
Archaea, Eukarya, and Bacteria