Neuron/neurotransmitter
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Info from Module 9-Biological Psychology and Neurotransmission & Module 10- The Nervous and Endocrine Systems
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Neuron
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
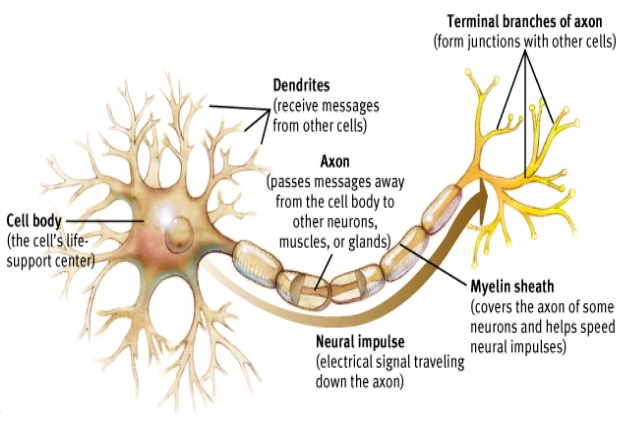
Key parts of a neuron
-Cell body: contains the nucleus. It is the cell’s life support center
-dendrites: a neuron’s bushy, branching extensions that receive and integrate messages, conducting impulses toward the cell body
-axons: neuron extensions that pass messages through its branches to other neurons or to muscles or glands
-myelin sheath: fatty tissue layer that encases some axons to enable greater transmission speed
-terminal branches of axon
Glial cells
cells in the nervous system that support, nourish, & protect neurons
they also play a role in learning, thinking, & memory
Synapse, synaptic gap/cleft
The___is the junction b/t the axon tip of the sending neuron & the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at the junction is the___or___.
this is what happens in the synaptic gap
The sending neuron reabsorbs the excess neurotransmitter molecules
Action potential
a neural impulse; a brief charge that travels down an axon.
Threshold
the lvl of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
refractory period
a brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired
substantial action potentials can’t occur again until the axon returns to its resting state
all-or-nothing response
a neuron’s reaction of either firing a full strength response or not firing
agonist molecules
increase neurotransmitters actions
some can increase production
antagonist molecules
inhibits or blocks a neurotransmitters’ action by blocking production
reuptake
a neurotransmitter’s reabsorption by the sending neuron
Sensory (afferent) neurons
neurons that carry incoming info from the body’s tissues & sensory receptors to the brain & spinal chord
Interneurons
neurons w/in the brain & spinal chord
they communicate internally & process info b/t the sensory inputs & motor outputs
Motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing info from the brain & spinal cord to the muscles & glands
Acetylcholine (ACh)
-neurotransmitter that enables muscle action, learning, and memory
-under supply linked to Alzheimer’s disease, a progressive disease
Dopamine
-neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion
-excess linked to schizophrenia
-under supply linked to the tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson’s disease
Serotonin
-neurotransmitter that affects mood, hunger and appetite, sleep, arousal and also sexual desire & temperature regulation
-under supply linked to depression and also OCD & anger
-Prozac and some other antidepressant drugs help raise levels
Norepinephrine
-helps control alertness and arousal
-Stress & fear will stimulate this neurotransmitter
-prevalent in sympathetic nervous system (increases heart rate & blood pressure; often released w/ adrenaline)
-under supply can depress mood
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
-a major inhibitory neurotransmitter
-calms the brain
-natural tranquilizer
-under supply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia/sleepless nights, & anxiety
Glutamate
-a major excitatory neurotransmitter (stimulates the brain); involved in memory
-most common neurotransmitter
-Plays a role in long-term potentiation (LTP); pattern of neural firing that strengthens synaptic connections
-oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
Endorphins
-involved in pain control (natural opiate)
-many of our most addictive drugs deal w/ this neurotransmitter