CNS Exam 3
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Broca's area lies where?
Inferior frontal gyrus (area of the primary motor cortex)
The primary visual cortex lies along where?
The calcarine fissure of the occipital lobe
Anterior cerebral hemisphere circulation is supplied by what arteries?
Bilateral internal carotid arteries
ICA arises from what arteries?
Aorta and brachiocephalic arteries
MCA supplies what parts of the brain?
Lateral surface of frontal, parietal and posterior lobes
Anterior choroidal artery arises from what artery?
ICA
Recurrent artery of Heubner arises from what artery?
ACA
Thalamoperforator arteries arise from what artery?
PCA and basilar
MCA superior division supplies what?
Lateral frontal lobe a little of parietal too
MCA inferior division supplies what?
Lateral temporal lobe
PCA supplies what?
Inferior and medial temporal lobes and medial occipital cortex
Anterior choroidal artery supplies what?
Lateral ventricles***, basal ganglia, internal capsule and thalamus
PCA deep branches supply what?
Thalamus and internal capsule
Ischemic events are more common in which artery?
MCA because of its large territory
Infarcts in the MCA occur in what 3 regions?
Superior division, inferior division, and deep territory
Proximal MCA occlusions affecting all 3 regions is called a what?
MCA stem infarct
What deficits would a patient exhibit if they have an MCA infarct?
-Aphasia
-Hemineglect (R MCA)
-Hemianopsia
-Contralateral face and arm, or face, arm and leg sensorimotor loss
-Gaze preference toward the side of the lesion (tegmentum of the midbrain)
Transcortical motor aphasia
nonfluent, good comprehension, good repetition, may have difficulty spontaneously answering questions
Transcortical sensory aphasia
Fluent, repetition of words/phrases good; may repeat questions rather than answering them
Non dominant strokes can produce what?
Contralateral neglect
ACA stroke may result in what?
Impaired judgement, apraxia, abulia, incontinence
Definition of apraxia
Being unable to make voluntary movements or gestures even though you have the physical ability and understanding to do so
PCA stroke can cause what?
Contralateral homonymous hemianopsia, alexia without agraphia, contralateral sensorimotor loss (when thalamus and posterior limb of the internal capsule are involved)
Alexia without agraphia definition
reading problem without writing problem
Damage to the left visual cortex (dominant hemisphere) that includes splenium of corpus callosum causes what?
Alexia without agraphia*********
Alexia without agraphia patients can still write because of what?
Left and right motor vortices are intact, so writing is preserved
Watershed infarcts are what?
Ischemic lesions along the border zones between 2 major arteries (ex; ACA-MCA or MCA-PCA)*****
ACA-MCA watershed infarcts are caused by what?
Occlusion of the ICA
ACA-MCA watershed infarcts can produce what impairment?
Proximal arm, trunk, and leg weakness****
Memory issues/loss**
With an ACA-MCA watershed infarct, if the lesion is in the dominant hemisphere we can observe what?
Transcortical aphasia
MCA-PCA watershed infarct can cause what disturbance?
Visual process disturbances
Balance issues
Memory issues/loss
Bitemporal hemianopsia can be caused by what?
Neoplasm, tumors
Grasp deficits are a caused by what side stroke? (Mention artery too)
L ACA
R MCA stroke is more likely to cause what impairment?
Hemineglect
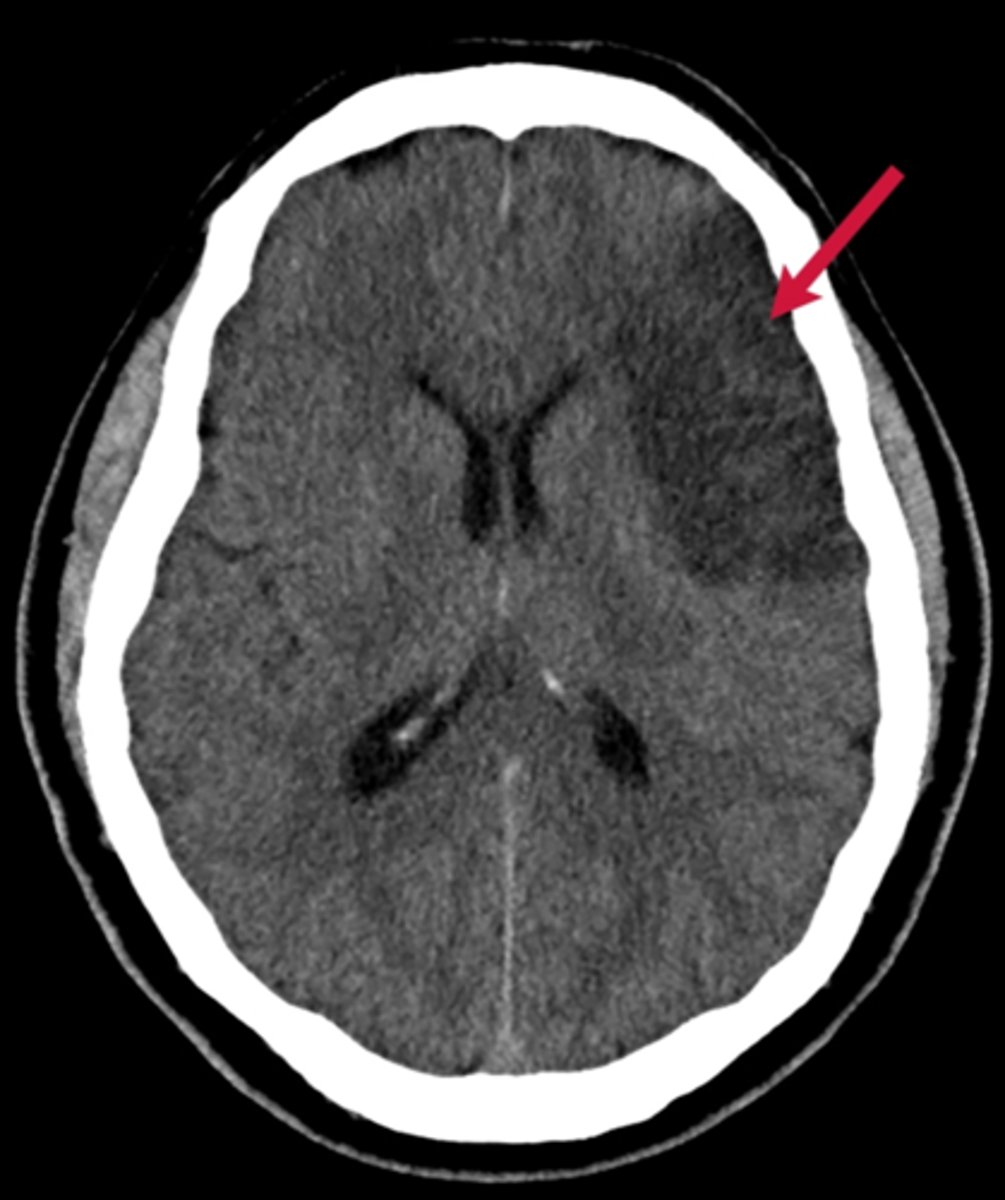
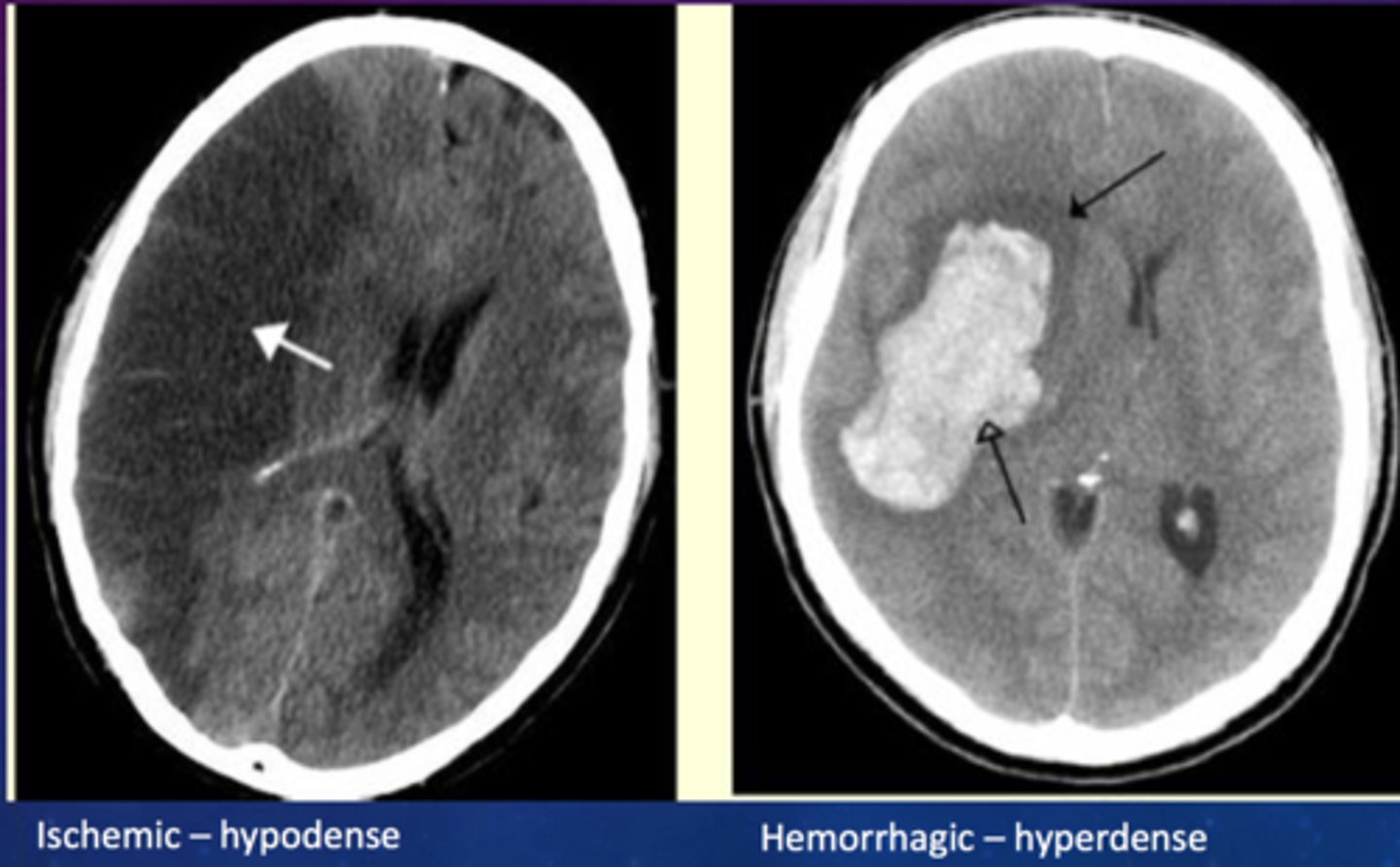
Ischemic stroke image
Hemorrhagic stroke image
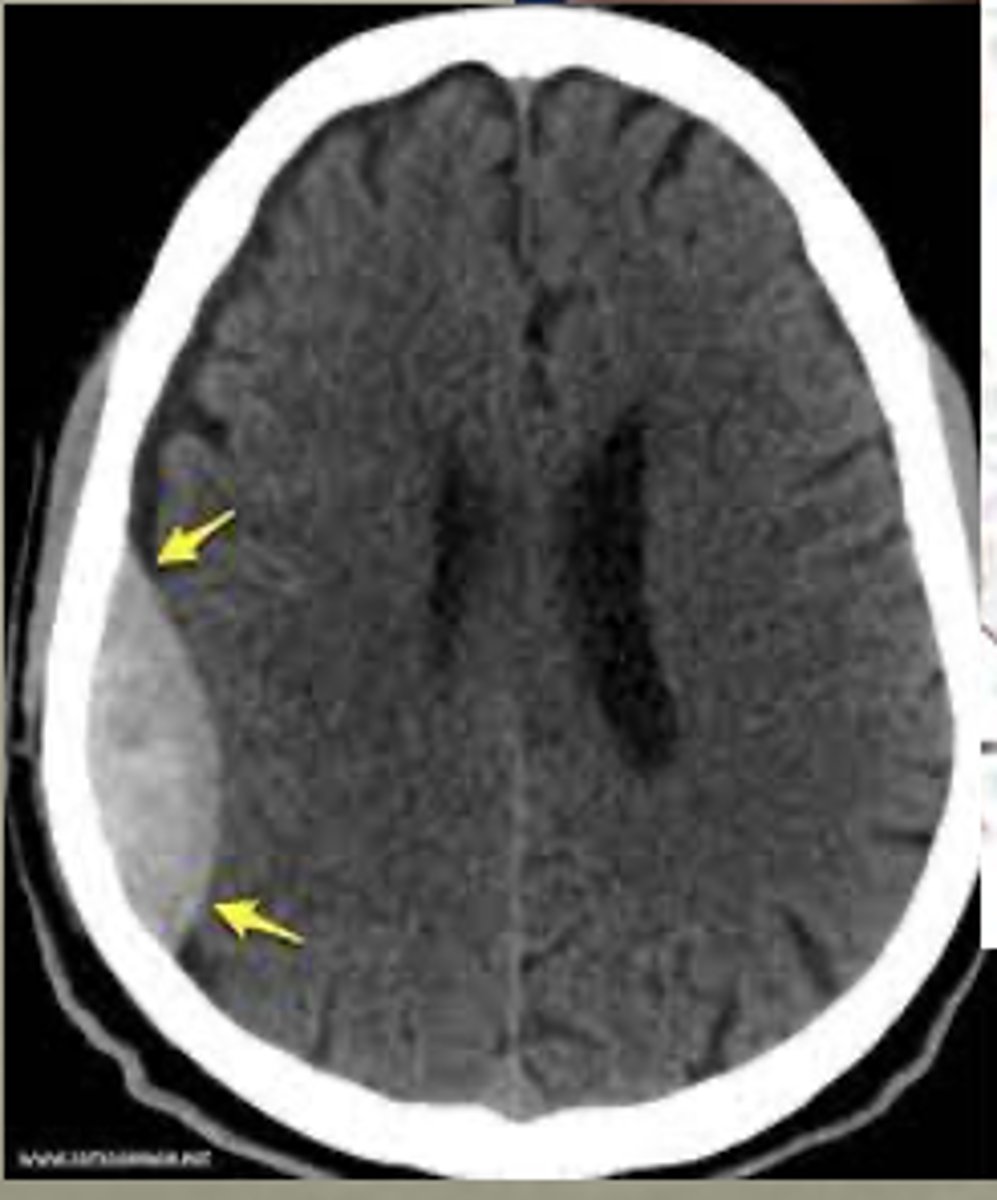
Acute imaging
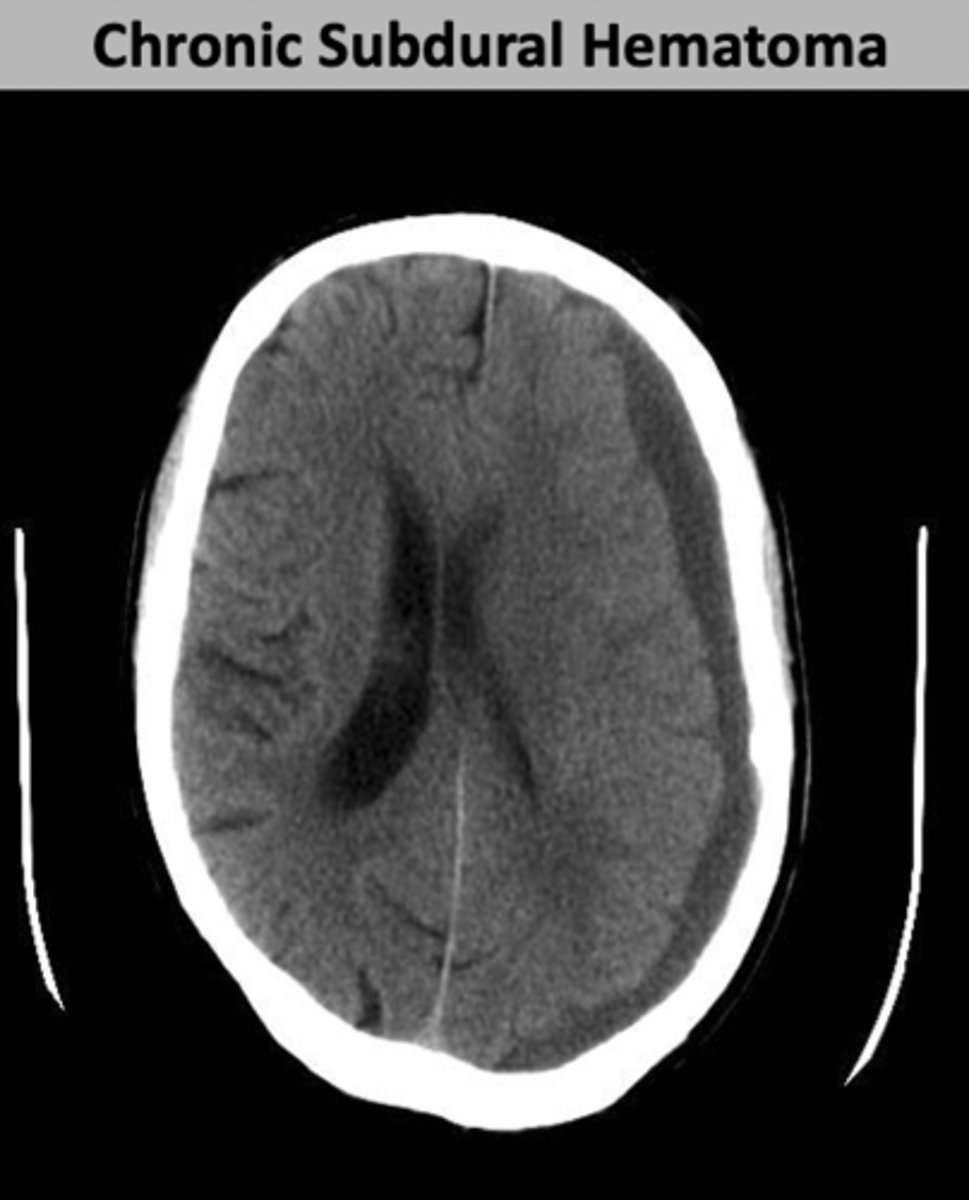
Chronic imaging
A patient with a stroke affecting the inferior division of MCA would present with what type of aphasia?
Wernicke's aphasia
Ischemic stroke definition
Occlusion of a cerebral artery or arteriole (most common 87%)
Hemorrhagic stroke definition
Bleeding in the brain (13%)
Anterior circulation is composed by what arteries?
ACA, ICA, MCA, Acomm
ACA supplies what structures in the brain?
Maxillary bodies, corpus callosum (minus the splenium of it)
PCA supplies what structures in the brain?
Thalamus, splenium of corpus callosum, and bottom of surface/medial aspect of brain
MCA superior branch supply what area and radiations?
Broca's area and superior optic radiations
MCA inferior branches supply what area and radiations?
Wernicke's area and inferior optic radiations
If a patient has damage to the R inferior optic radiation what type of visual loss impairment do they present with?
L homonymous superior quadrantanopia*****
Basal ganglia function
Plans movement
Cerebellum function
coordination/ correction of voluntary movements and balance
The internal capsule contains what?
Tracts (DCML, corticospinal, ACST)
What impairment is seen with R optic nerve lesions?****
R monocular anopia or visual loss
What impairment is seen with a lesion at the optic chiasm?****
Bitemporal hemianopsia
What impairment is seen with a lesion to the R optic tract?****
L hemianopsia or L homonymous hemianopsia
What impairment is seen with a lesion to the R superior and inferior optic radiations?****
L homonymous hemianopsia
What impairment is seen with a lesion to the R superior optic radiation?****
L inferior quadrant hemianopsia
Lesion to the primary visual cortex ends up in what?
Complete blindness (if MCA is involved)
Lesion to the primary visual cortex without the involvement of the MCA present how?
Homonymous hemianopsia with monocular sparing (they see a light in the center of their eye)
The primary visual cortex is located where?
Occipital lobe (calcarine fissure- cuneus)
If a patient has superior optic radiations, the specific location of damage is where?****
Calcarine fissure (cuneus)
If a patient has inferior optic radiations, the specific location of damage is where?****
Calcarine fissure (lingula)
Optic tracts, optic chiasm, and optic nerves receive blood supply from where?
Small branches of ACA and MCA
Face and hands areas of the sensorimotor homunculi are on what surface of the cerebral cortex?
Lateral surface
Leg areas of the sensorimotor homunculi are on what surface of the cerebral cortex?
Interhemispheric fissure
Wernicke's area lies where?
superior temporal gyrus (adjacent to the primary auditory cortex)
Why is association cortex important?
For attention to contralateral body and space
The optic radiations carry visual information from the ___ to the ___.
thalamus to the visual cortex
Circle of Willis is composed by what arteries?
ACA
ICA
MCA
PCA
Acomm
Pcomm
Posterior cerebral hemisphere circulation is supplied by what arteries?
Bilateral vertebral arteries
Bilateral vertebral arteries arise from what arteries?
Subclavian arteries
Anterior and posterior brain circulation meet where?
Circle of Willis
ACA supplies what parts of the brain?
Most of the cortex on the anterior medial surface, from the frontal to the anterior parietal lobes including the medial sensorimotor cortex
ACA is part of what circulation?
Anterior circulation
Does MCA bifurcate?
Yes, into superior and inferior division within the sylvian fissure
PCA supplies what parts of the brain?
Inferior and medial temporal lobes and medial occipital cortex
MCA (superior division) supplies what lobes?
Lateral frontal lobe and a little of parietal lobe
MCA (superior division) supplies what structures within the brain?
Superior optic radiations
Broca's area
MCA (inferior division) supplies what lobes?
Lateral temporal lobe and variable portion of the temporal lobe
MCA (inferior division) supplies what structures within the brain?
Inferior optic radiation
Werneck's area
MCA arises from what artery?
ICA
What's the name of the small arteries that arise from MCA?
Lenticulostriate arteries (deep cerebral structures)
What does the lenticulostriate arteries supply?
Large regions of the basal ganglia and internal capsule
Anterior choroidal artery supplies what parts of the basal ganglia and thalamus?
Portions of the globus pallidus, putamen, thalamus, posterior limb of the internal capsule and lateral ventricle
Recurrent artery of Heubner supplies what parts of the basal ganglia and thalamus?
Portions of the head of the caudate***, anterior putamen, globus pallidus and internal capsule
Thalamoperforator arteries supplies what parts of the basal ganglia and thalamus?
Thalamus and a portion of the posterior limb of the internal capsule
MCA deep branches supply what?
Basal ganglia and internal capsule