Lecture 4: Female Reproductive System and Hormones
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
Uterus
Myometrium and endometrium structure of the female reproductive system.
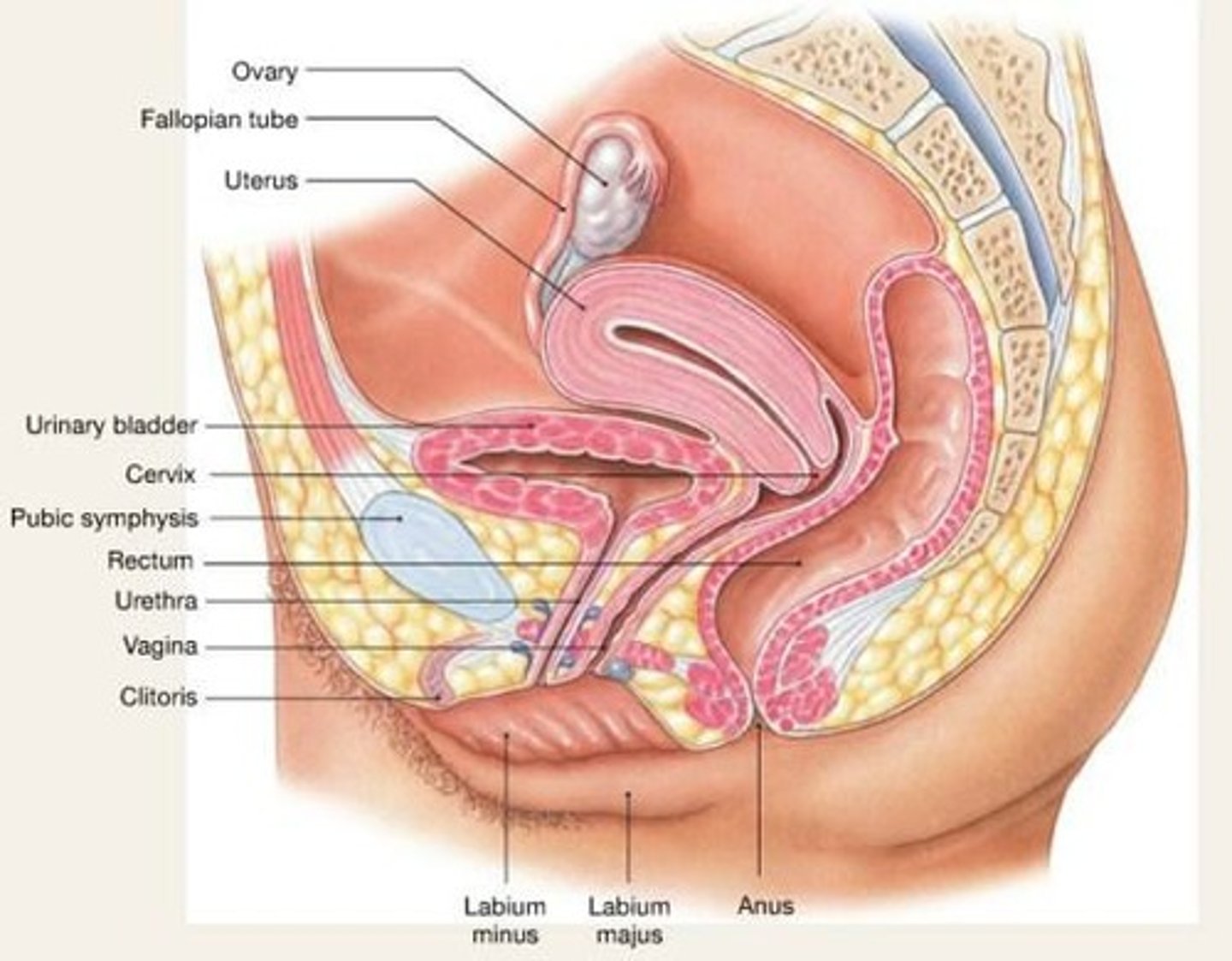
Ovary
Organ where oogenesis and ovulation occur.
Oocyte
The female gamete or egg.
Vagina
The muscular tube leading from the external genitals to the cervix of the uterus.
Cervix
The lower part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
Clitoris
A small sensitive organ located at the top of the vulva.
Oviduct (Fallopian tube)
The tube through which an egg passes from an ovary to the uterus.
Follicle
A fluid-filled sac in the ovary that contains an immature egg.
Corpus luteum
A hormone-secreting structure that develops in an ovary after an ovum has been discharged.
Corpus albicans
The scar tissue that replaces the corpus luteum if pregnancy does not occur.
Zona pellucida
The thick transparent membrane surrounding a mammalian ovum before implantation.
Corona radiata
A layer of cells that surround the oocyte and provide nutrients.
Myometrium
The smooth muscle layer of the uterus responsible for contractions.
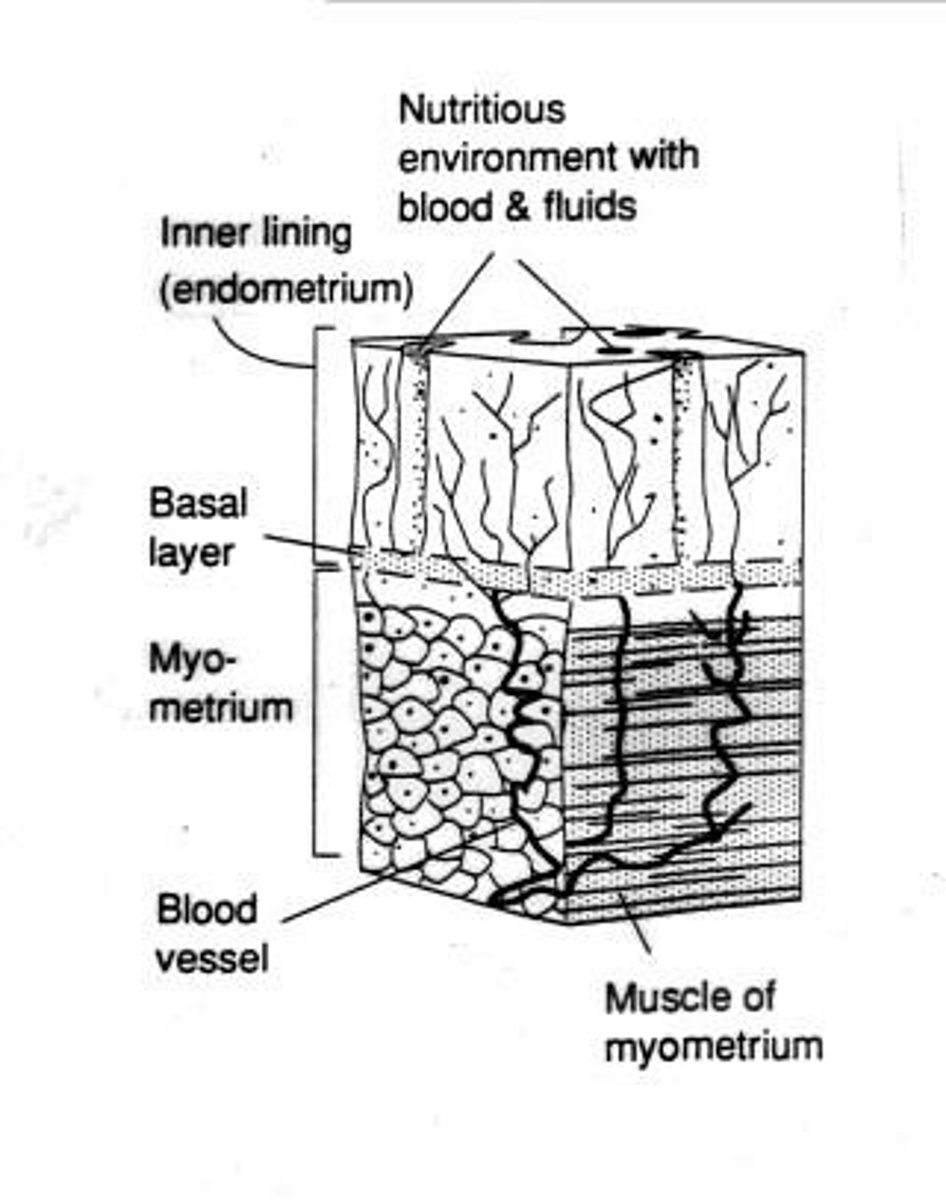
Endometrium
The inner lining of the uterus that provides a nutritious environment for implantation.
GnRH
produced in the brain that stimulates the release of FSH and LH.
FSH
produced in the brain that stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles.
LH
produced in the brain that triggers ovulation.
Estrogen
Hormone produced in the ovaries that regulates the menstrual cycle and reproductive system.
Progesterone
Hormone produced in the ovaries that prepares the endometrium for a potential pregnancy.
Oogenesis
The process of egg formation in the ovaries.
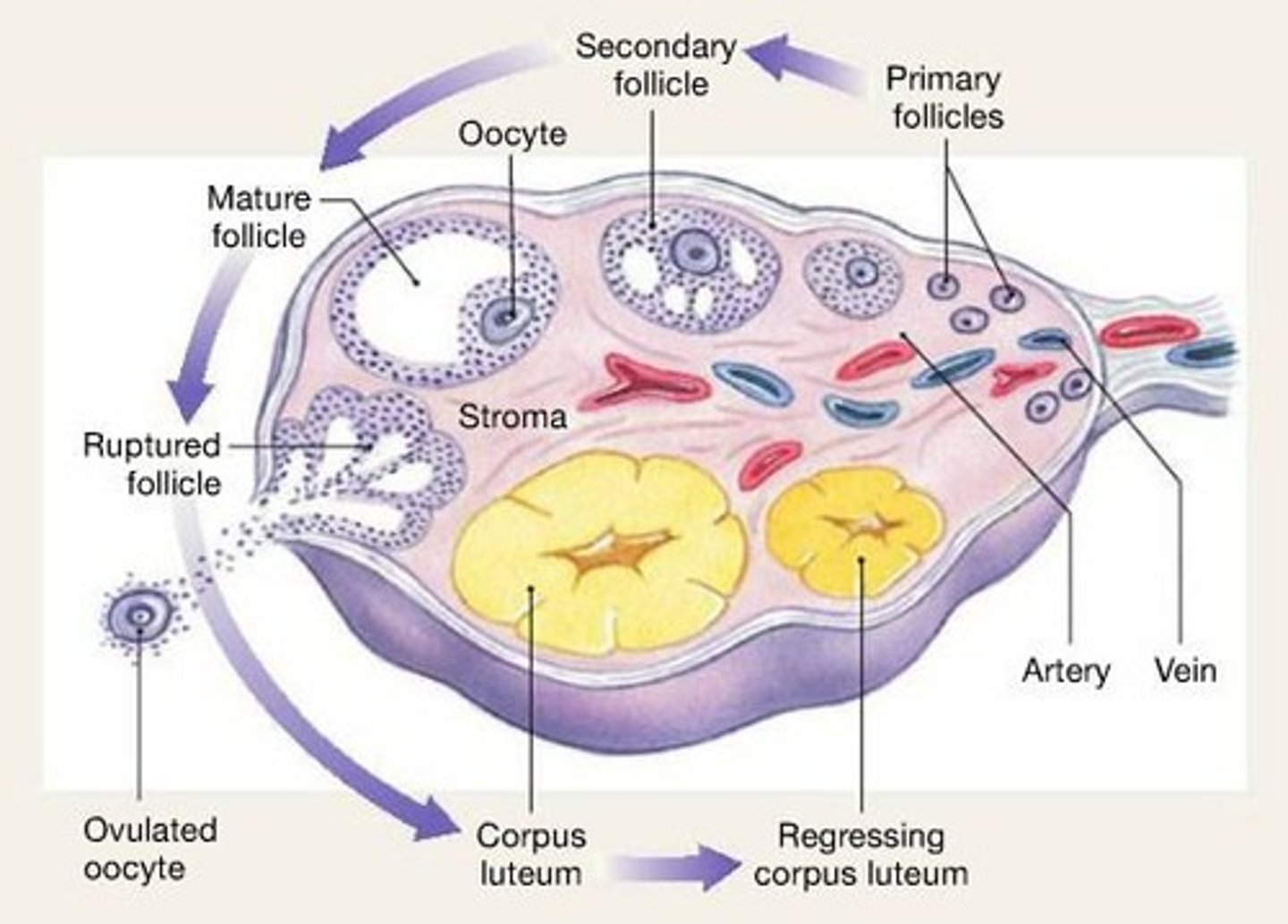
Ovulation
The release of an oocyte from the ovary.
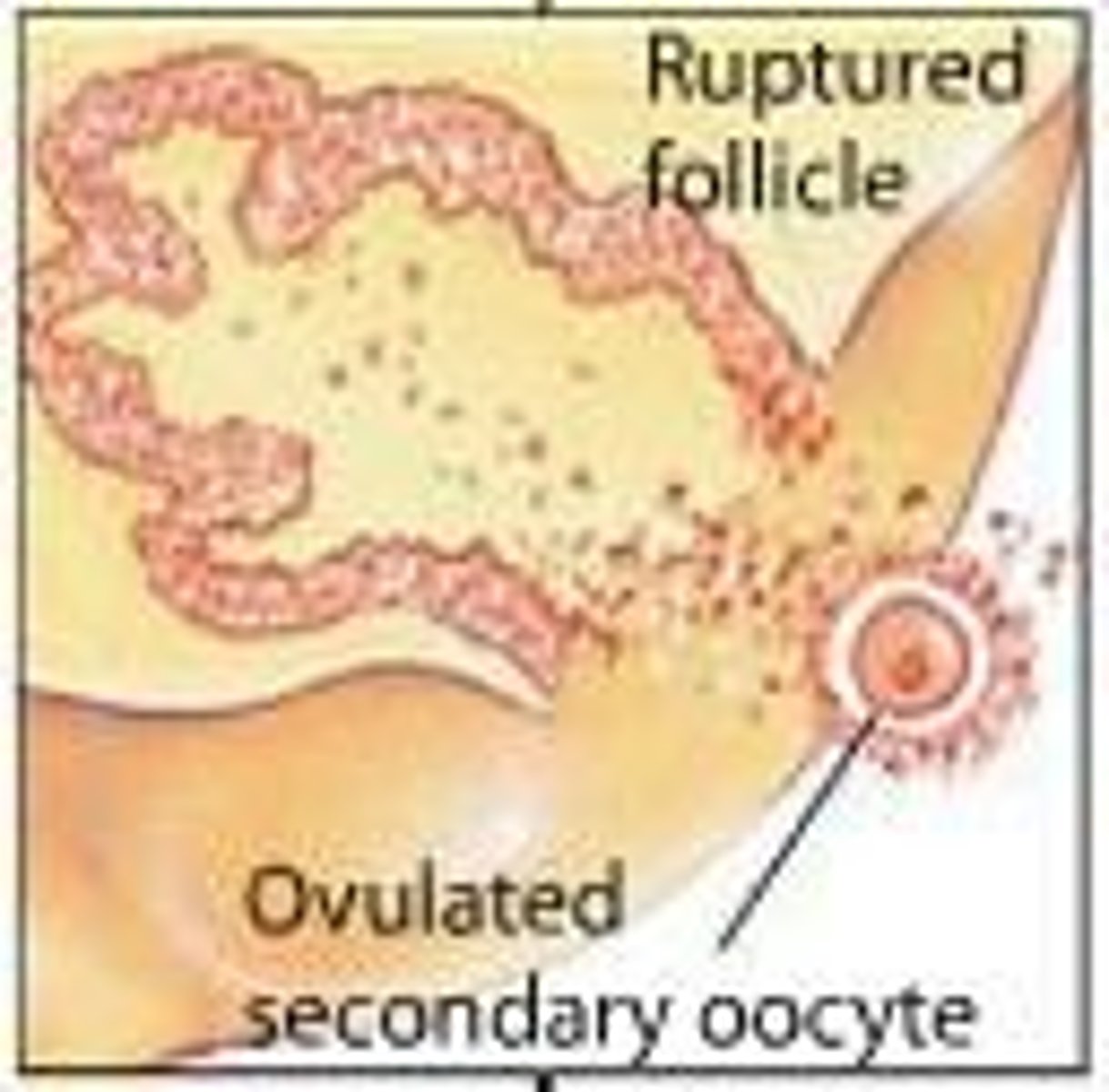
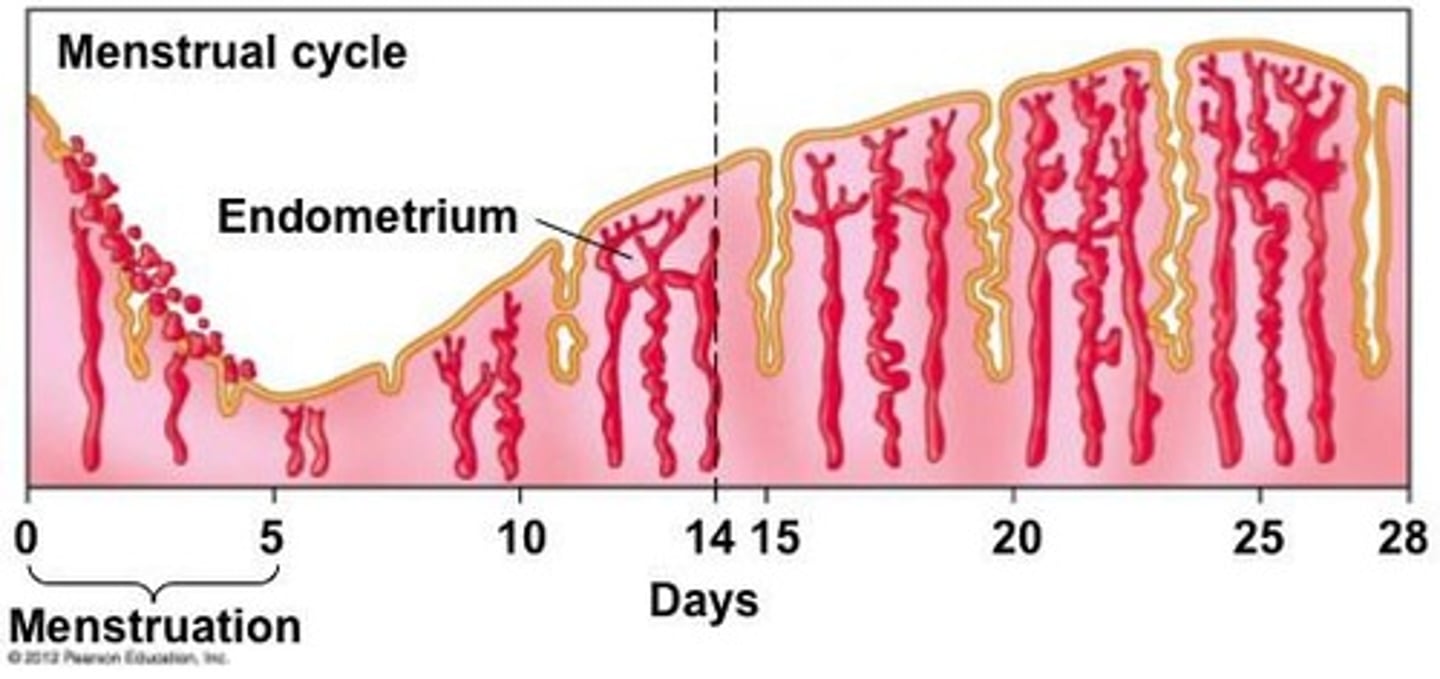
Menstrual cycle
The monthly cycle of changes in the female reproductive system.
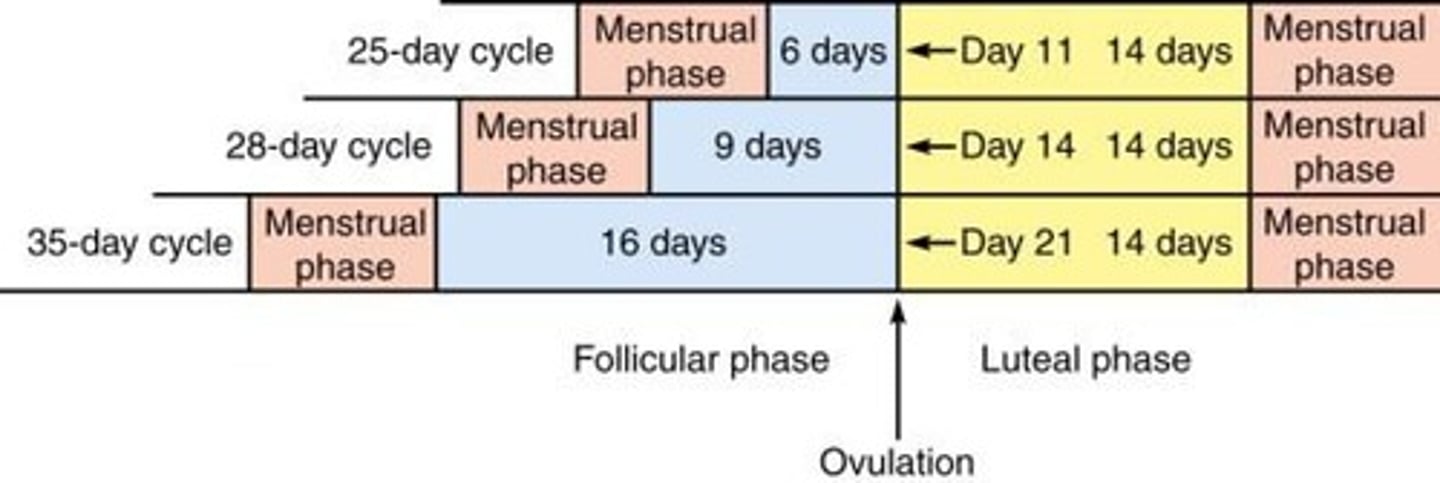
Menstrual cycle length
Variable among women: 21 to 35 days.
Menstrual cycle definition
Length defined from start of menstruation to start of menstruation.
Ovulation timing
Occurs almost always 14 days before the start of menstruation.
Menstrual phase duration
Assumed to be 5 days.
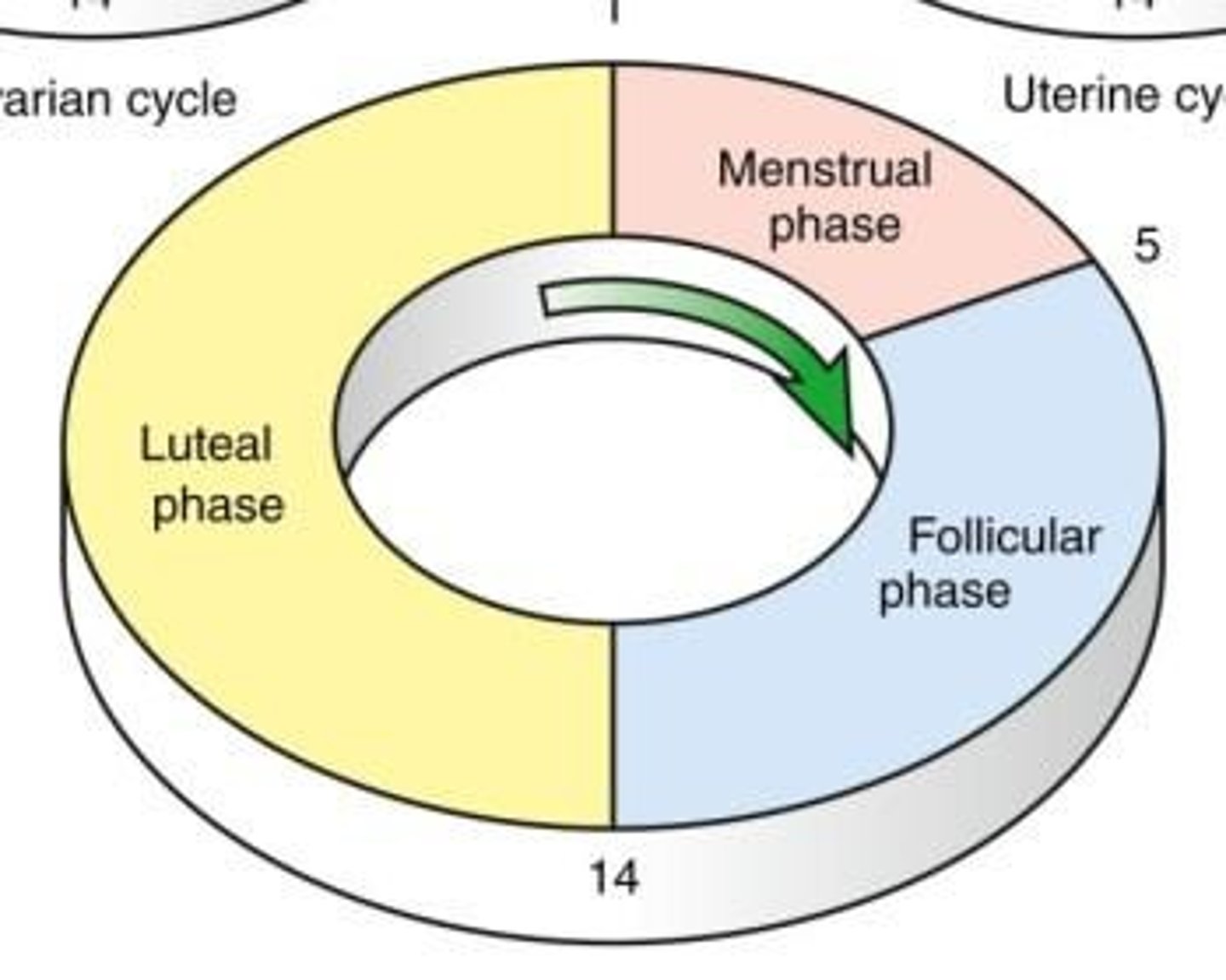
Phases of the menstrual cycle
Includes menstrual phase, follicular phase, and luteal phase.
Hormones produced in the brain
GnRH, FSH, LH.
Hormones produced in ovaries
Estrogen, progesterone.
Positive feedback
A feedback loop that enhances the output of a system.
Negative feedback
A feedback loop that reduces the output of a system.
Ovarian cycle
The cycle that includes the growth of follicles and ovulation.
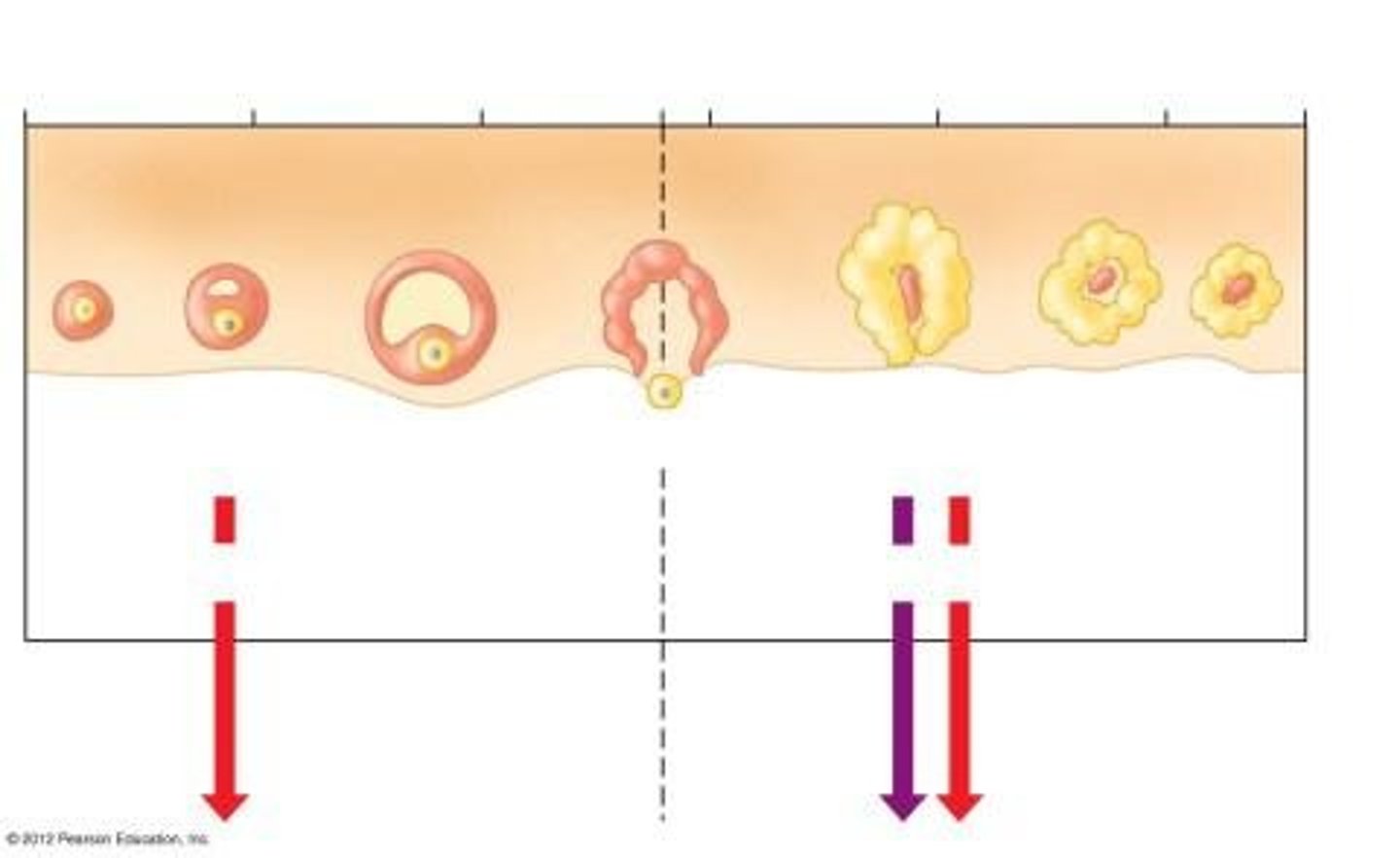
Growth of follicle
Occurs during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
Degenerating corpus luteum
Occurs during the luteal phase.
GnRH (Gonadotropin releasing hormone)
Promotes FSH and LH release.
FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone)
Promotes follicle development.
LH (Luteinizing hormone)
Promotes ovulation and corpus luteum maintenance.
Estrogen (estradiol)
Promotes maturation of female reproductive structures and secondary sexual characteristics.
Progesterone (progestin)
Promotes secretory function of uterus.
Primary follicle
Developing structure in the ovary that produces estrogen.
Hypothalamus
Brain region that controls the release of GnRH.
Anterior pituitary
Gland that releases FSH and LH in response to GnRH.
LH surge
Triggers ovulation and corpus luteum formation.
Secretory phase
Phase in the menstrual cycle where the endometrium prepares for potential implantation.luteal
Negative feedback loops
Mechanisms that inhibit hormone release to maintain homeostasis.
Positive feedback loops
Mechanisms that enhance hormone release to promote physiological changes.
Menstruation
Triggered by low levels of estrogen.
hCG
Human chorionic gonadotropin secreted by a fertilized egg that maintains the corpus luteum.
Home pregnancy test kits
Detects the presence of hCG in urine, can give a result 15 days after fertilization.
Pre-ovulatory phase
Phase before ovulation characterized by follicle growth and estrogen secretion.
Post-ovulatory phase
Phase after ovulation characterized by corpus luteum activity.
Menstruation begins
Occurs when estrogen and progesterone levels decrease.
FSH levels rise
Occurs when negative feedback stops due to decreased estrogen and progesterone.
Uterine lining
Does not shed if estrogen and progesterone levels remain high.
New follicle growth
Does not start if estrogen and progesterone levels remain high.
Male reproductive system
The system responsible for the production and delivery of sperm.
Sperm
The male gamete involved in reproduction.
Semen
The fluid containing sperm and other secretions from male reproductive glands.
Gamete
A reproductive cell that contains half the genetic material of an organism.
Penis
The external male reproductive organ used for sexual intercourse and urination.
Acrosome
A cap-like structure on the head of a sperm cell that contains enzymes to help penetrate the egg.
Sperm head
The part of the sperm that contains the nucleus and genetic material.
Nucleus
The part of the sperm cell that contains the genetic information.
Middle piece
The part of the sperm that contains mitochondria to provide energy for movement.
Tail (flagellum)
The whip-like structure that propels the sperm forward.
Seminiferous tubule
The site in the testes where sperm production occurs.
Spermatogonia
The precursor cells that develop into sperm cells.
Leydig cell (interstitial cell)
Cells in the testes that produce testosterone.
Sertoli cell (nurse cell)
Cells that support and nourish developing sperm cells. in testis
Scrotum
The pouch of skin that contains the testes and regulates their temperature.
Testis
The male reproductive organ that produces sperm and hormones.
Epididymis
The structure where sperm mature and are stored.
Vas deferens
The duct that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
Seminal vesicle
Glands that produce a fluid that nourishes sperm and forms part of semen.
Prostate gland
A gland that produces fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
Cowper's gland
Glands that produce a pre-ejaculatory fluid that lubricates the urethra.
Ejaculatory duct
The duct through which sperm is expelled during ejaculation.
Urethra
The tube that carries urine and semen out of the body.
Testosterone
The primary male sex hormone responsible for the development of male reproductive tissues.
Sertoli cells
These cells are lipoid in character; they can be colourless or can be stained yellowish, and they have light vesicular nuclei.
Sperm cell parts
Nucleus, tail, middle piece, mitochondrion, head, acrosome (penetrator)
Semen composition
Semen contains 10% sperm; the rest is made up of fluids from various glands.
Seminal vesicles
Contribute nutrients and enzymes to semen.
Pathway of sperm
Sperm travels through the epididymis, seminal vesicles, Cowper's gland, prostate gland.
Hormone
A chemical signal that regulates body activities.
Anabolic steroid
Synthetic substances that mimic testosterone to increase strength and muscle mass.
Benefits of steroids
Increased strength and faster recovery.
Side effects of steroids
Acne, rage and hostility, heart damage and disease, decreased sperm count, testicular atrophy.
Insulin
Hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels.
Epinephrine
Hormone released in response to stress that increases heart rate and blood pressure.
Gland
An organ that produces and releases substances that perform specific functions in the body.
Leydig cell
Cell that produces testosterone in the testes.
Androgen
A group of hormones that includes testosterone and is involved in male traits and reproductive activity.
Pituitary gland
Gland that releases hormones affecting growth and reproduction.
Feedback loops
Mechanisms that regulate hormone levels and effects in the body.
Leydig cells
Cells that produce testosterone in response to LH.
Anabolic steroids
Synthetic substances that mimic testosterone; can lead to testicular atrophy and reduced sperm counts.
Trenbolone acetate
An anabolic steroid that is 3x stronger than testosterone.
Testicular atrophy
Shrinkage of testicles due to lack of LH and FSH production.
Seminiferous tubules
Structures in the testes where sperm production occurs.