Lesson Content - Midterms
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is Literature
“Written works, especially those considered of superior or lasting artistic merit. "a great work of literature"
Themes
Ideas that are central to a story,
How do we recognize themes in a story
Consider the context in which the story was written.
Analyze the major characters
What is the conflict.
Have a lookout for repetition.
Examine the major turning points in the story
Plot structure and Freytag’s pyramid
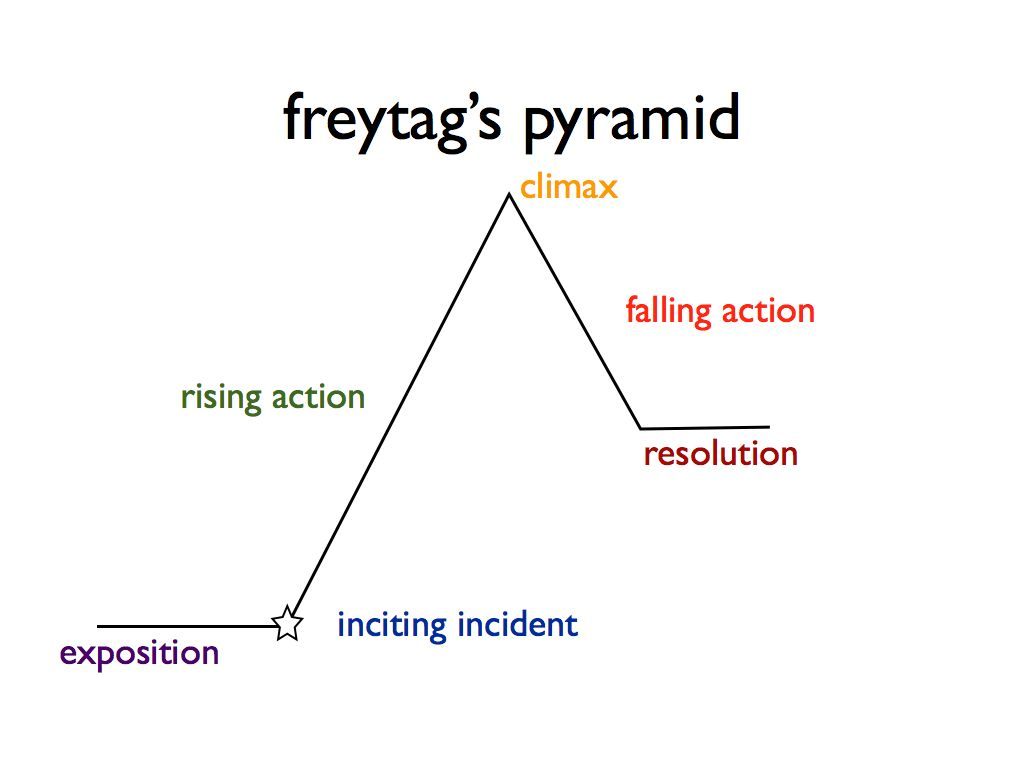
Symbolism
Uses objects, people, places, or actions to represent deeper, often abstract ideas, adding layers of meaning beyond the literal text to explore themes like love, death, or hope
Hermaneutics
The theory and practice of interpretation, focusing on understanding the meaning of texts, symbols, and human actions
Atmosphere
The feeling or emotions a writer instills in their work
The period of The Enlightenment
a transformative 17th and 18th-century European intellectual movement emphasizing reason, individualism, and scientific inquiry to challenge tradition, superstition, and absolute authority (church and state
The head vs the heart
The "head vs. heart" conflict in literature explores the classic struggle between logic/reason (head) and emotion/passion (heart
Romantacism
A movement emphasizing emotion, individualism, nature, and the common person, reacting against Enlightenment reason and Industrialization by valuing subjective experience, imagination, and spiritual connection with the natural worl
Strum und Drang
A late 18th-century German literary and artistic movement emphasizing intense emotion, individualism, and rebellion against societal norms
Modernism
A revolutionary movement marked by a conscious break from traditional forms, experimenting with style and structure to reflect rapid societal changes, industrialization, and the aftermath of World War I, focusing on subjective experience, fragmentation, alienation, and the inner consciousness
“The wasteland”
A highly eloquent account of despair, its powerful vision of urban alienation spoke to a generation of young post-war readers and in doing so, it changed poetry forever.
The dark satanic mills
The grim, polluting factories of Britain's Industrial Revolution
Ad fontes
(Latin for "to the sources") literature refers to the classical texts of Greek and Roman antiquity,