GEPC PRELIM
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Communication
is the process by which messages are transferred from a source to a receiver. (Roger & Shoe Maker)
Roger & Shoe Maker
Communication is the process by which messages are transferred from a source to a receiver. (_________________)
Communication
originated from the Latin word communis, which means 'common', suggesting that there must be a common understanding of the message between the source and the receive
Communis
Communication originated from the Latin word ____________, which means 'common', suggesting that there must be a common understanding of the message between the source and the receive
Common
Communication originated from the Latin word communis, which means '____________', suggesting that there must be a common understanding of the message between the source and the receive
People communicate to satisfy the needs for belonging,
People communicate to keep in touch with and connect with others
People communicate to socialize.
Humans can socialize because of their ability to communicate.
People communicate to get things done
People communicate with specific purposes in mind.
Why do we communicate?
Verbal Communication
Non-Verbal Communication
2 Types of Communication
Verbal Communication
is communicating using words. This includes sounds, words. language, and speaking.
Verbal Communication
It is also done through writing.
Non-verbal Communication
is the process of conveying meaning through non-word messages.
Non-Verbal Communication
A good example of _____________________ is sign language, which can be used by anyone at any time.
Sign Language
A good example of non-verbal communication is ____________ which can be used by anyone at any time.
Sender
Message
Channel
Receiver
Encode
Decode
Feedback
7 Elements of the Communication Process
Sender
The person who delivers the message.
Message
The information that is communicated
Channel
The way that communications are sent.
Receiver
The one that receives the message
Encode
the process of converting thoughts into communication.
Decode
the process of turning communication into thoughts
Feedback
the response or reaction of the receiver to the sender.
Communication ethics
refers to the principles and values that guide our communication behavior.
honesty
respect
fairness
responsibility
Some key principles of communication ethics include ___________, ___________, ____________, and ________________.
Linear Model
Interactive Model
Transactional Model
3 COMMUNICATION MODELS:
Linear Model
is a one-way process where the sender sends a message to the receiver without expecting feedback.
Interactive Model
a two-way process where the sender and receiver exchange messages and provide feedback.
Transactional model
The process in which people are both senders and receivers of messages at the same time.
Aristotles Model
Lasswells Model
Shannon Weaver Model
Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model
4 TYPES OF LINEAR COMMUNICATION MODEL:
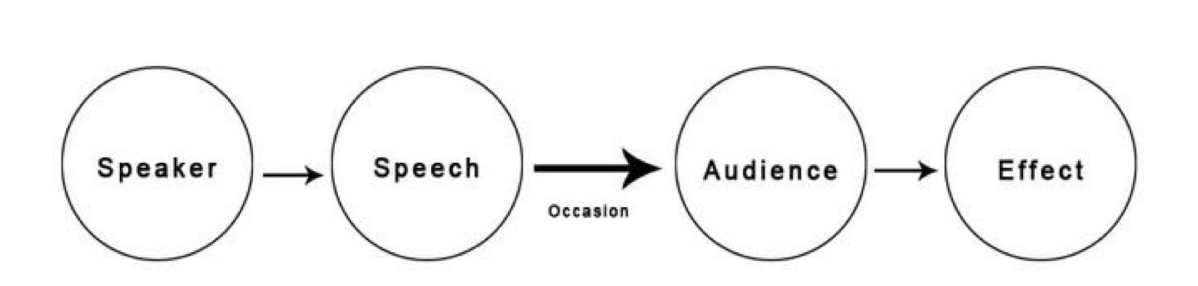
Aristotles Model
a linear model that puts a greater emphasis on public speaking instead of interpersonal communication that other models do
Aristotles Model
Straightforward & Speaker-centered
Ethos
is about establishing credibility and trust with your audience.
Pathos
is about appealing to the emotions of your audience.
Logos
is about using logic and reason to persuade your audience.
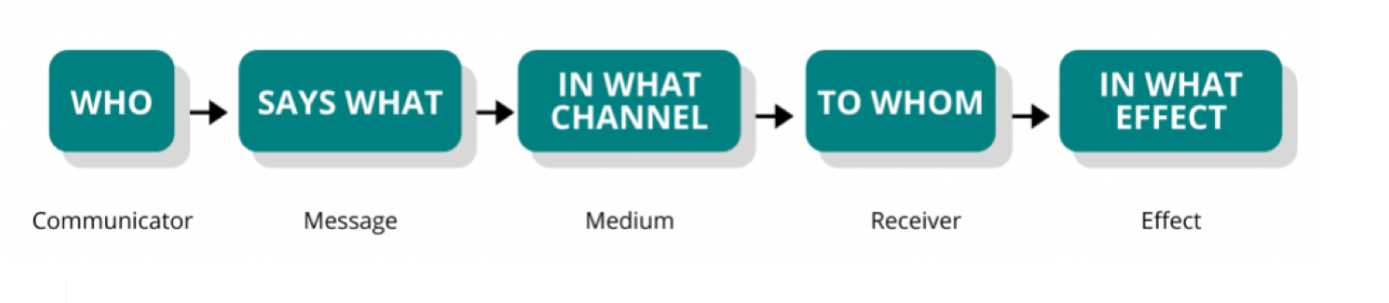
Lasswell's Model
this model of communication attempts to understand a communication event by asking five important questions.
Who? (Communicator)
Says What? (Message)
In what Channel? (Medium)
To whom? (Receiver)
In what Effect? (Effect)
5 Important Questions In Lasswells Model:
Effect
is the result the message leads to.
Knowledge, Attitude, Behavior
The so-called triangle of success '__________,_____________,and ______________' is often used to describe the desired effect
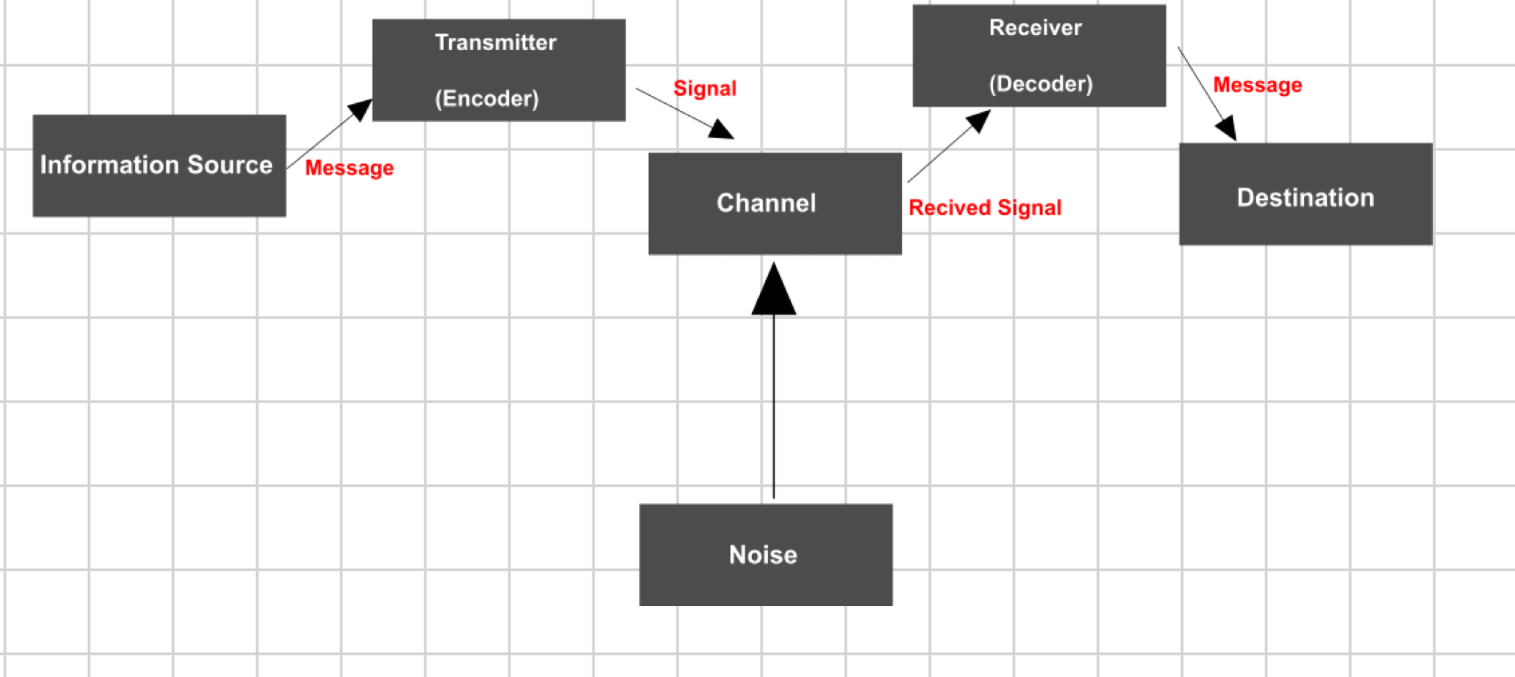
Shannon-Weaver Model
the first model to acknowledge the existence of noise in communication that occurs during the process of encoding, sending and decoding and could disrupt or alter a message.
Noise
This _________could refer to something like the static on a radio broadcast, but it could even include spelling errors in written communication or the receiver mishearing the message.
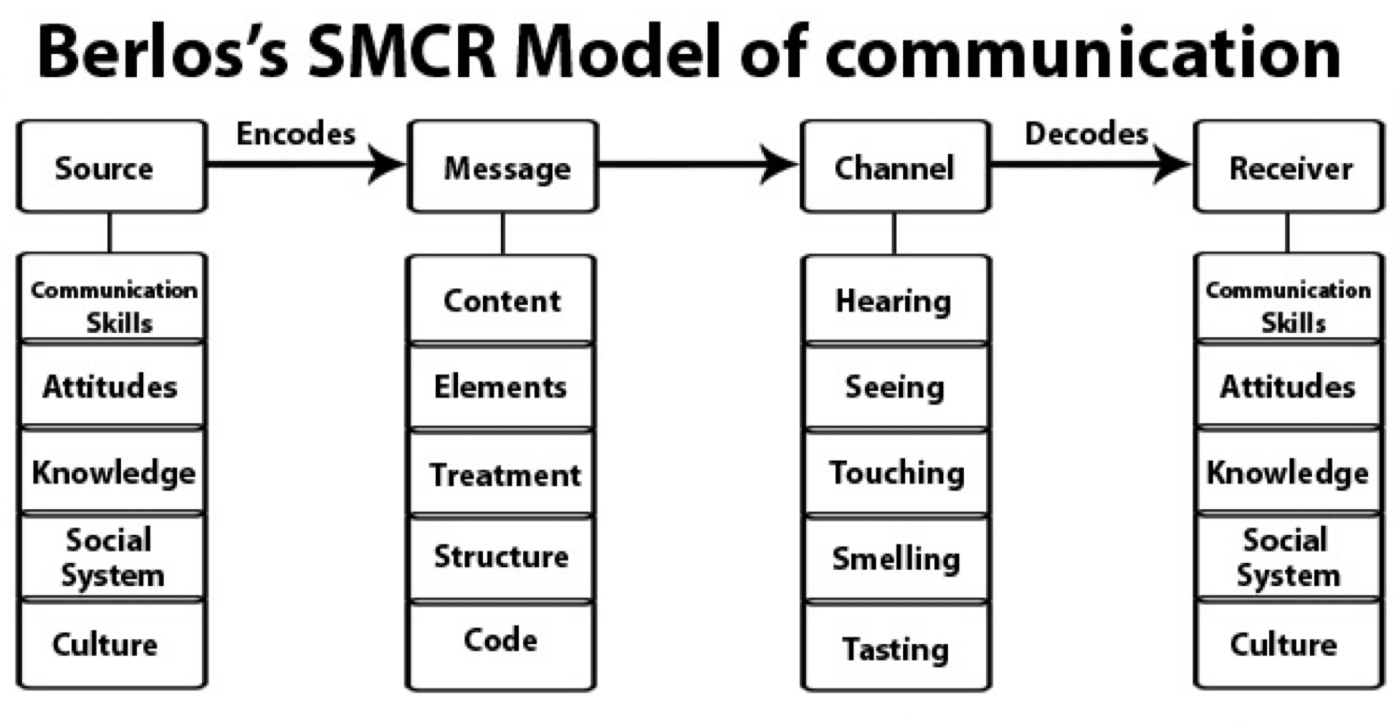
Berlo's S-M-C-R Model
explains communication in four steps: Source, Message, Channel, & Receiver.
Berlo's S-M-C-R Model
This model provides a thorough account of the key elements in every one of the steps that will affect the manner in which the message is communicated.
Source, Message, Channel, Receiver
Berlo's model explains communication in four steps: ________, _________, _________, & _________.
Aristotles Model
Lasswells Model
Shannon Weaver Model
Berlo's S-M-C-R Model
Assertive communication
is about expressing your needs and wants clearly and respectfully.
Aggressive communication
is about expressing your needs and wants at the expense of others.
Passive communication
is about avoiding expressing your needs and wants.
Intrapersonal Communication
Interpersonal Communication
Extended Communication
Organizational Communication
Intercultural Communication
TYPES OF COMMUNICATION ACCORDING TO CONTEXt:
Intrapersonal Communication
The Latin prefix intra- means within or inside.
Intrapersonal Communication
means talking to oneself. Some label it as inner dialogue, inner monologue, or self- or inner talk.
Within, Inside
The Latin prefix intra- means ________ or ________.
Inner Dialogue, Inner Monologue, Self-or Inner Talk
Some label Intrapersonal Communication as _______________, ______________, or __________________.
Intrapersonal Communication
Psychologists use other names for it, such as self-statement or self-verbalization.
Self-Statement, Self-Verbalization
Psychologists use other names for Intrapersonal Communication such as __________________ or _____________________.
Interpersonal Communication
As opposed to intra, the Latin prefix inter- means between, among, and together.
Interpersonal Communication
An interactive exchange takes place in ___________________________ takes place.
Between, Among, Together
As opposed to intra, the Latin prefix inter- means ___________, ____________, and _____________.
Extended communication
involves the use of electronic media
Extended Communication
may be expanded to include tele, audio, or phone conferencing; video conferencing; Skype calls; and other technological means.
Organizational Communication
With this type, the focus is on the role that communication plays in organizational contexts.
Organizational Communication
With this type, the focus is on the role of those who work for the company.
Formal Structure
Informal Structure
two types of organizational structure:
Formal Structure
allows communication to take place via designated channels of message flow between positions in the organization.
downward communication
upward communication
horizontal communication
crosswise communication.
Four Approaches of Formal Structure:
Downward Communication
flows from upper to lower positions, that is, from the president to a manager or supervisor or from a manager to an ordinary staff member.
Downward Communication
The communication flow is top-down or from a superior to a subordinate.
Upward Communication
is bottom-up, where subordinates communicate to their superiors/bosses.
Horizontal Communication
has a lateral approach because it takes place among people from the same level but from different departments.
Crosswise Communication/ Cross-Functional Approach
is diagonal in nature because employees from different units or departments that work at various levels communicate with each other
Informal Communication
comes from unofficial channels of message flow.
Informal Communication
Likewise known as "grapevine," messages from the different levels of the organization are conveyed.
Informal Communication
This happens because of the dissatisfaction of some employees.
Grapevine
Likewise known as "______________," messages from the different levels of the organization are conveyed.
Organizational Culture
Each organization has its own culture. This is referred to as
"______________________."
Organization
Based on its history and development, an ___________ develops its own core values, vision and mission statements, goals, and objectives.
Organizational Culture
is of utmost significance as it will dictate the kind of behavior that employees should have.
Peter Drucker
“Company cultures are like country cultures. Never try to change one. Try, instead,
to work with what you've got”
To Inform
To Evoke
To Entertain
To Argue
To Persuade
Purposes of Communication:
Evoke
To __________ means to produce a reaction, emotion, or memory in someone or something.
Emotional Response
Memory Recall
Creative Response
To evoke can be used in various contexts, such as:
To entertain
It means to engage, amuse, or pleasantly divert someone’s attention.
To Argue
It means to present reasons or evidence to support a claim, opinion, or point of view, often in a debate or discussion.
Presenting Evidence
Logical Reasoning
Counterarguments
Arguing can involve:
To persuade
To clarify
To challenge
To learn
The purpose of arguing can be:
Clear and concise language
Respectful tone
Evidence-based reasoning
Effective Arguing Involves:
Clear and Concise Language
using language that is easy to understand.
Respectful Tone
maintaining a respectful and open-minded tone.
Evidence-Based Reasoning
using evidence and logical reasoning to support one's argument.
To persuade
is to influence someone's thoughts, feelings, or actions by presenting a compelling argument, appeal, or reason.
Sales and Marketing
Public Speaking
Negotiation
Debate
Persuasion is a powerful tool in various contexts, Including:
Credibility
Emotional Appeal
Logical Reasoning
Storytelling
Key Elements Of Persuasion Include:
Understanding the Audience
Clear and Concise Communication
Building Rapport
Effective persuasion requires:
Manuscript Speech
is a type of speech delivery where the speaker reads from a fully written script.
Scripted
The speech is written out in full, and the speaker reads from the script.
Verbatim
The speaker sticks to the script, without deviating from the written text.
Control
The speaker has complete ____________ over the words and message
Precision
Accuracy
Complex Information
Advantages of Manuscript Speech:
Lack of Spontaneity
Limited Audience Engagement
Difficulty with Audience Feedback
Disadvantages of Manuscript Speech:
Formal Occasions
Technical or Complex Information
When to use manuscript speech: