LA final (life is not good)
1/113
Earn XP
Description and Tags
not cumulative!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
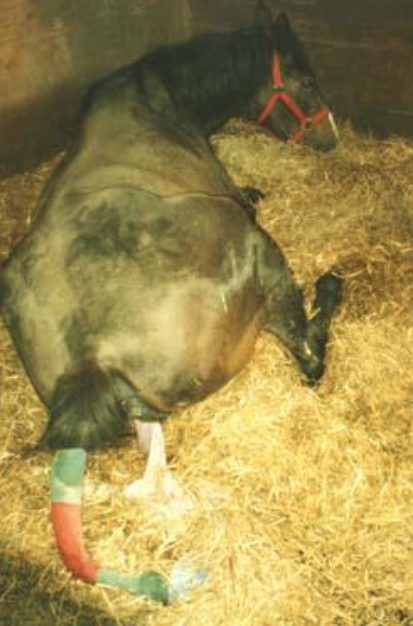
what are causes of LA recumbency
-neurologic disease
-neuromuscular disease
-musculoskeletal disease
-metabolic disease
what are the viral neurologic diseases in equine
-west nile virus
-equine herpesvirus (EHV-1)
-encephalitis viruses (EEE/WEE/VEE)
^dont ask cause idk wtf
what are the core vaccines in horses
rabies, tetanus, EEE/WEE, WNV
what is a neurologic disease for all species
rabies
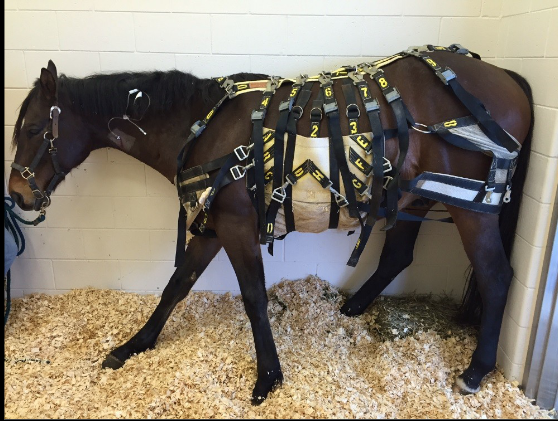
they be wearing this for what
EHV-1
parasitic neurologic disease for equine
equine protozoal myeloencephalopathy (EPM)
parasitic neurologic disease in camelids
parelaphostrongylus tenuis (meningeal worm)
true or false: horses are most sensitive to tetanus
true
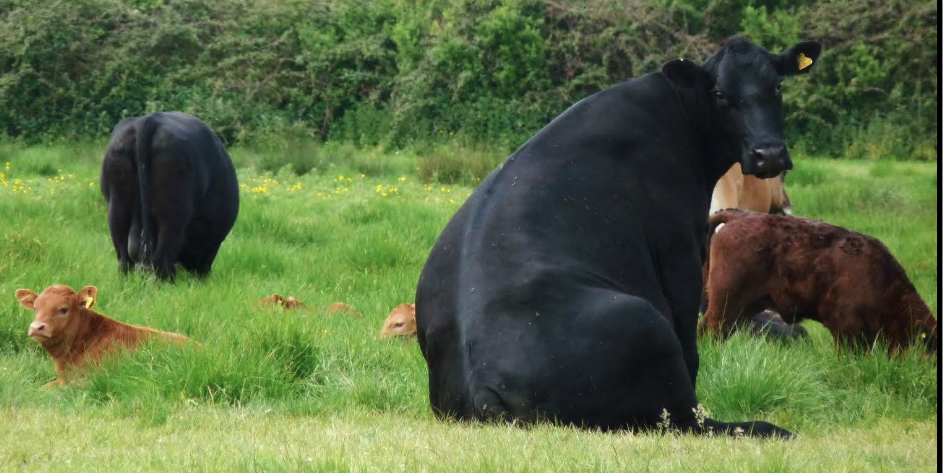

a trauma related neurologic disease
calving paralysis
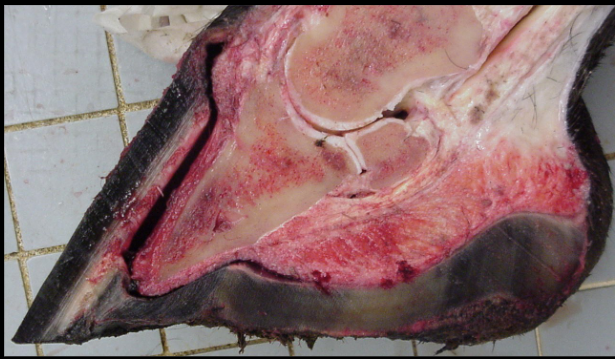
musculoskeletal disease in equine
-laminitis
-P3 (coffin bone) rotation
list some of the musculoskeletal diseases
-laminitis
-severe arthritis
-myositis
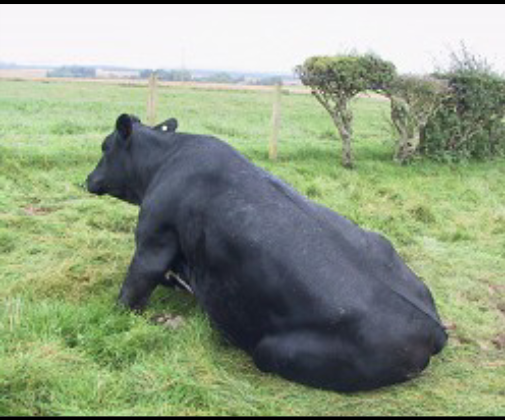

type of metabolic disease
milk fever (hypocalcemia)
list the types of metabolic disease
-milk fever (hypocalcemia)
-heat stress
-pregnancy toxemia
-copper deficiency - goat kid
-severe anemia (weakness), all species
managing LA recumbency includes
-moving the patient
-bedding
-slings
-float tank
-nutrition/fluids
different types of bedding
-deep bedding (straw, shavings, sand)
-waterbed
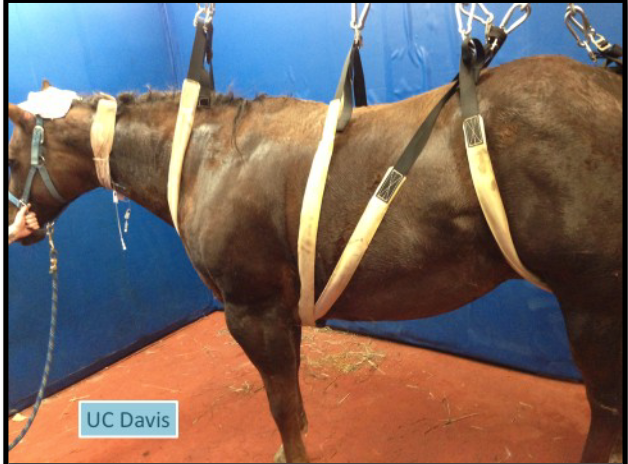
what type of sling is this
UC Davis Lift
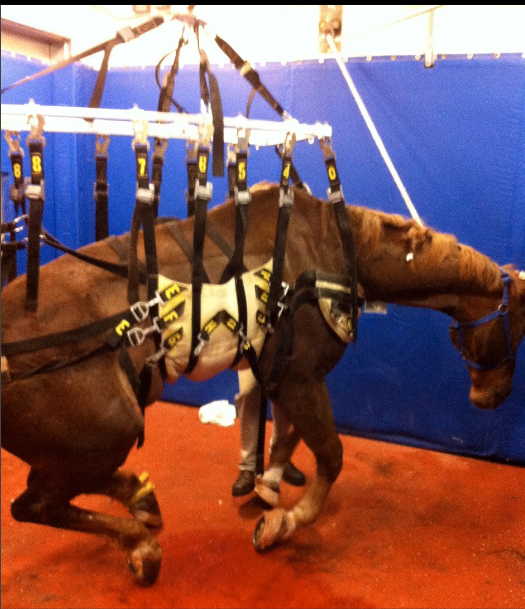

what type of sling is this
Anderson Sling
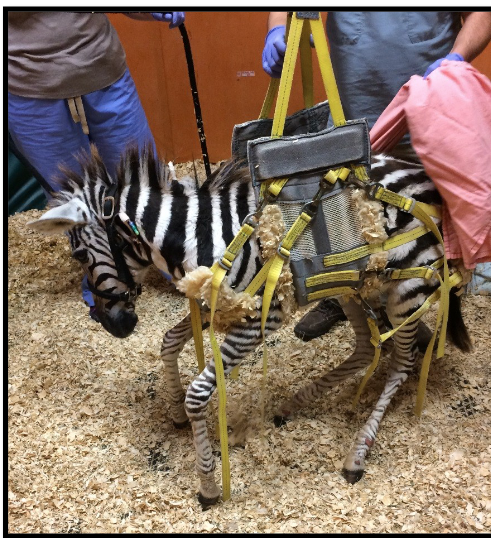

what type of sling is this
Modified sling
complications of recumbency
-decubital ulcers (bed sores)
-muscle damage
-pneumonia
-corneal ulcers
-self trauma
-urine/fecal scald
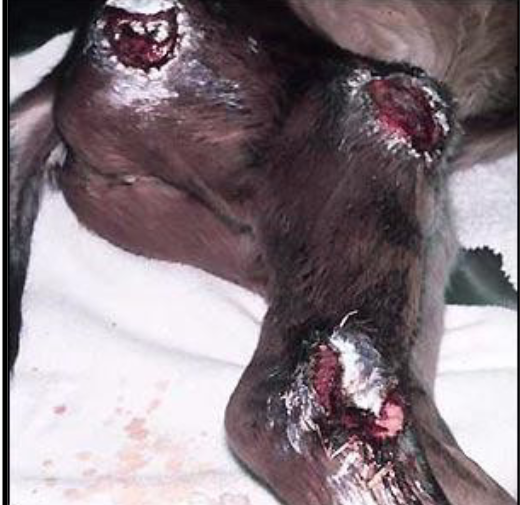
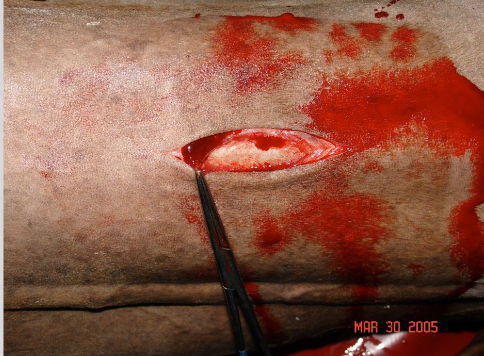
what dis and what are treatments/prevention
decubital ulcers
treatment:
-clean wounds
-silver sulfadiazine (SSD)
prevention:
-deep bedding
-keep skin clean/dry
-rotate patient every 2-4 hrs
what causes muscle damage in recumbent LA
-pressure from weight —> muscle necrosis
-compartment syndrome
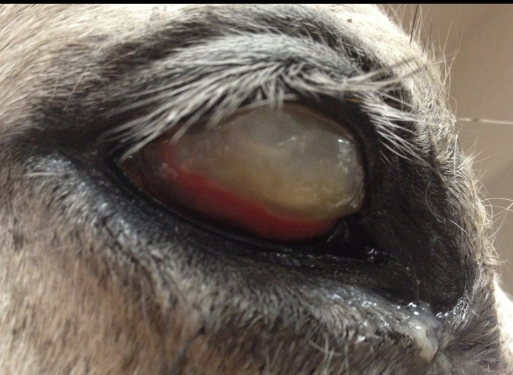
what this
corneal ulcer
inner layer/dressing items for bandaging
-release or non-stick gauze
-gel or “moist” pads in place of gauze
-silver impregnated pads
-foam pads
-wet to dry & wet to moist
release or non-stick gauze: characteristics
-still may adhere
-better for less exudative wounds
gel or “moist” pads in place of gauze: characteristics
-cost effective
-speed healing
silver impregnated pads: characteristics
-Ag - anti-bacterial
-treats and prevents infection
-aid in rapid healing
foam pads: characteristics
-absorbent
-ideal for exudative wounds
-do not disrupt wound bed when removed
what are disadvantages of wet to dry & wet to moist bandage dressing
-no longer considered “standard of care”
-impedes healing
-increased infection rate
-increased inflammation
-expensive
common middle layer bandaging items
-cotton bandage
-brown gauze
cotton bandage characteristics- middle layer
-sheet cotton (redi roll or roll cotton)
-provides padding and stability
-decreases mobility to allow healing
common outer layer bandaging materials
-VetWrap (NOT on skin)
-Elasticon (top and bottom, stick to skin)
cattle bandaging supplies
-non-stick pad over wound on 4×4 gauze
-cling wrap
-vet wrap
-white tape
-duct tape
*difficult to maintain bandage due to “cone-shaped” leg
indications for bandaging
-wounds/lacerations
-under splints/casts
-post-surgery
-support
-protection
types of bandages
foot bandages:
protect sole, heel bulb lacerations
duct tape or boot
distal limb bandages:
extend from coronary band or fetlock to just below carpus
full limb bandages:
robert jones (FATTTT bandage)
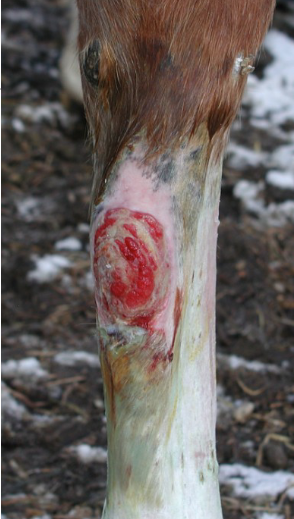
wut happened
bandage sore
steps for fracture stabilization and wound management
assess the patient
stabilize the patient
control hemorrhage
treat hypovolemia
provide pain relief
initiate wound management
goals:
prevent additional damage
immobilize joint ABOVE and BELOW fracture
external coaptations for fracture stabilization
-bandage
-splint
-bandage cast
-cast
-bling
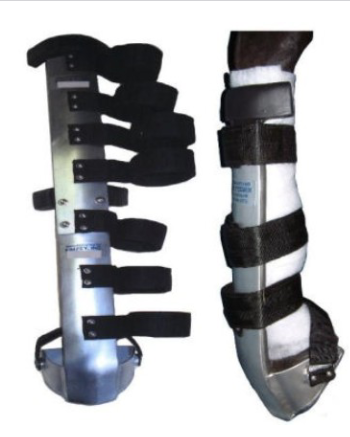
whats this
Kimsey leg saver splint
transportation with fractures
preferred:
-load hind limb fractures forward
-load front limb fractures backward
indications of LA fluid therapy
-dehydration
-shock
-replace losses
-diuresis
-administer other products and treatments
what is dehydration
-loss of total body water
-occurs over time
-cells shrink
what are the 3 body water compartments and their percentages
-total body water = 60% of patient’s body weight
-intracellular fluid ~ 67% (2/3) of TBW
-extracellular fluid ~ 33% (1/3) of TBW
summary of Equine Protozoal Myeloencephalitis
-Transmission: by ingesting material contaminated with opossum urine/ feces that contains the pathogen S. neurona
-Prevention: better biosecurity
-Treatments: drugs, PT, and supportive care
-Clinical Signs: dullness, dysphagia, head tilt/ leaning, facial nerve abnormalities
summary of West Nile Virus
-Transmission: mosquitos
-Prevention: vaccination and mosquito control
-Treatment: supportive care 30% of cases die or are euthanized
-Clinical Signs: fever, muscle fasciculations, personality changes, cranial nerve defects, spinal abnormalities
summary of Eastern and Western Equine Encephalitis
-Transmission: mosquitos
-Prevention: vaccination and mosquito control
-Treatment: supportive care
-Clinical Signs: depression, fever, lethargy, anorexia
summary of tetanus
-Transmission: toxic bacteria clostridium tetani in open wounds
-Prevention: vaccination, wound management, biosecurity
-Treatment: antitoxin injection, controlling muscle spasms, general supportive care 50% mortality
-Clinical Signs: muscle stiffness, difficulty moving/ eating, protruding third eyelid, seizures, muscle spasms
rabies symptoms in horses
-fever
-colic
-lameness
lyme symptoms in horses
lameness, joint swelling, muscle stiffness, lethargy, poor performance
summary of botulism in horses
-Transmission: exposure to Clostridium botulinum (found in round bales)
-Prevention: vaccination and biosecurity
-Treatment: antitoxin injection, IV antibiotics, supportive care
-Clinical Signs: progressive muscle weakness, dysphagia, muscle tremors, lethargy, respiratory difficulties
what is hypovolemia
-loss of blood volume; loss of intracellular fluid (plasma volume)
-decreased perfusion of organs —> shock
clinical signs of dehydration
-prolonged skin tent
-sunken eyes
-dry corneas
-tacky MM
-dark urine
mild dehydration symptoms: 5-7%
1-3 second skin tent
moist or slightly tacky MM
<2 sec CRT
HR: 40-60 bpm
decreased urine output
moderate dehydration symptoms: 8-10%
3-5 sec skin tent
tacky MM
2-3 CRT
61-80 bpm
decreased arterial BP, slight to moderate sunken eyes, decreased glisten of cornea
severe dehydration symptoms: 10-12%
5+ sec skin tent
dry MM
>4 sec CRT
80+ bpm
reduced jug fill, barely palpable pulses, obvious sunken eyes, no corneal glistening
clinical signs of hypovolemia
-decreased mentation
-tachycardia
-weak pulse pressure
-cool extremities
-pale MM
routes of fluid administration
-PO
-IV
-SQ
-IP
-IO
what are fluid additives
-Potassium
-Calcium
-Sodium bicarbonate
-Dextrose
-DMSO
-CRI: lidocaine, ketamine, butorphanol, insulin
what 3 things must you account for when developing a fluid plan
replace deficit
provide maintenance
account for OGL
maintenance fluid requirements for neonate, juvenile, and adult
-neonate (<2 weeks): 100 mL/kg/day
-juvenile: 80 ml/kg/day
-adult: 60 ml/kg/day
how much do you bolus if dehydrated
bolus ½ the deficit in first 1-2 hours
what is the shock dose for equine
give in boluses of 6-20 ml/kg and reassess
what is fluid diuresis
-promoting increased or excessive production of urine
-most commonly used in cases of acute kidney injury or chronic kidney disease
true or false: coiled sets are the best fluid lines for ambulatory animals
true
true or false: you should keep foals with the mares if hooked up to CRI
false
Which gauge catheter is best used for moderate to large volumes of fluid for your hospitalized horse?
14g
How often should you roll a recumbent horse patient to prevent decubital ulcers?
q 2 hours
Your patient is a 1045 lb horse that is estimated to be 8% dehydrated.
a. What is the volume (in Liters) needed for dehydration replacement?
b. What is the volume (in Liters) needed for maintenance requirements (per
day)?
c. What is the total volume for dehydration and maintenance combined for 24
hrs?
d. What is the hourly IV fluid rate (in Liters per hour) ?
a. 38 L
b. 28.5 L
c. 66.5 L
d. 2.8 L/hr
PCV = 9% (normal = 25-35%)
Weight = 750 lbs
Diagnosis: anemia from chronic GI parasitism
He needs a blood transfusion!
Donor (a llama): PCV = 30%
1. What is the total blood volume (in liters) of the camel?
Blood volume (L) = 8% of BW (kg)
2. Use the following equation to calculate how much blood to give the camel
[example uses 25 for normal PCV]
Deficit = blood volume x ([normal PCV – actual PCV]/donor PCV)
Then give 20-40% of the deficit
Body weight 750 lbs/2.2 = 341 kg
1. Blood volume = 341 kg x 0.08 = 27 L
2. Deficit = blood volume x ([normal PCV – actual PCV]/donor PCV)
= 27 L x ([25-9]/30) = 14.4 L
Give 20-40% of deficit
20%: 0.2 x 14.4 = 2.89 L
40%: 0.4 x 14.4 = 5.76 L
Give 3-5.5 L
Initial diagnostics reveal hypoglycemia (Glucose = 24; reference range 80-120
mg/dL)
Problems: dehydration and hypoglycemia
1. What is the fluid deficit?
2. If you decide to add 2.5% dextrose to 1 L of fluids, how many mL of 50%
dextrose would you add? Hint: use C1V1=C 2V2 calculation
1. 4 lbs = 1.8 kg; 1.8 kg x 0.06 = 0.10 L = 100 mL
2. (2.5%) x (1000 mL) = (50%) x V2
2500 mL/50% = 50 mL
* you would add 50 mL of 50% Dextrose to a 1 L bag of fluids
general considerations for post-op care
-PE
-suture removal; 10-14 days
-drugs: label, check and re-check
-paper work
LA anesthetic recovery considerations
padded recovery stall
-good footing
-safe environment
-access to animal*
assisted recovery:
-head and tail ropes
-sling, pool
-foals
-dark, quiet environment
LA anesthetic recovery grading scale
excellent
good
poor
serious complications
anesthesia recovery related death
preparing patient for anesthetic recovery
-remove shoes and/or tape feet
-remove halter
-sedation (xylazine)
-ropes if desired
-good footing
problems encountered in anesthetic recovery
-myositis/neuritis
-trauma during recovery- tongue/face common
-post anesthetic hypoxia- protect airway
-fractures- tibia, femur, cannon bone, hip luxation
-exhaustion- severe colics
true or false: vomiting is a sign of colic
false
What is the most common cause of emergencies in horses
colic
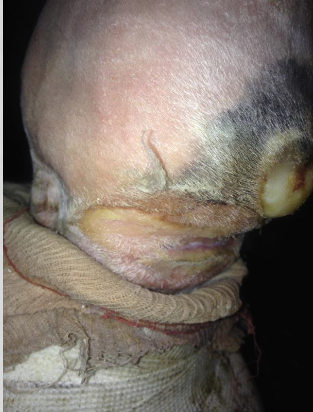
whats this
laceration
caused by bad bandage maintenance
observe cast for:
discharge
swelling above cast
cracks- fetlock, foot
sore development
common in hind legs
what is this
-caesarian section
-trueeeee emergency for live foal
-similar observations to colic surgery
-blood loss
-retained placenta- 50%
what is this
-tracheotomy
-relief/prevention of resp diseases
-performed ventral neck region
-palpate trachea
-standing w/ local ax
what are the elective surgeries
castration/crytorchids
bleeding. swelling
eventration
orthopedic surgery
lameness
incisions
bandages/splints/casts
resp surgery
tie back
laser
laryngotomy
sinusotomy
foal surgery
elective or emergency
true or false: It is best to feed your sick horse in a hay net off the ground to prevent respiratory issues and colic.
true
what is a form of assessing dehydration that is only reliable in foal
sunken eyes
fluid requirements: total volume=
maintenance + deficit + ongoing losses
fluid deficit =
body weight (kg) x % dehydration
true or false: SQ fluids are inadequate for replacing fluid deficits in LA
true
in equine, using the intravenous route of administration allows rapid ?
fluid administration/restore fluid volume
4 phases of fluid therapy
resuscitation, rehydration, maintenance, ongoing losses
fluid of choice for maintenance fluid therapy
crystalloid fluid
How soon will clinical signs for rabies occur?
1 week after bite
What is a parasitic neurologic disease camelids can contract?
meningeal worm
What are some clinical signs of otitis interna?
Ear, eyelid, and face drop, Cranial nerve 7, the facial nerve, is affected by this

whats this
float tank
where can LA get decubital ulcers?
bony prominences, skin folds
What can cause corneal ulcers? (Bedding)
straw
Why are bandages on lower limbs of horses so common?
They are more prone to damage. Low muscle mass and high amount of tendons, ligaments, nerves, and blood vessels. Muscles at the end of the carpus
How often should you monitor a bandage? Why?
Minimally every day. Check for swelling and wounds.
Where are distal limb bandages applied?
From the top of the metacarsus/metatarsus to just below the coronary band.
How many layers are there for a bandage in a leg that has a wound?
5 layers. Layers one and two include a wound dressing and a layer to hold wound dressing. If no wound, not needed.
In a limb bandage that does not have a wound, what are the layers?
1) padding
2) securing layer
3) finishing layer