OLI - 3. Semantics
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:25 PM on 8/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
1
New cards
Truth-Value Assignment
A ***_____*** specifies a unique truth-value (either T or F) for each atomic formula.
2
New cards
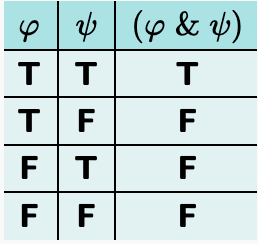
Characteristic Truth-table for Conjunction
3
New cards
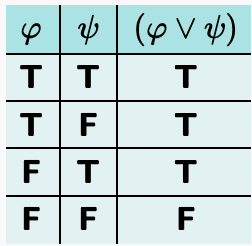
Characteristic Truth-table for Disjunction
4
New cards
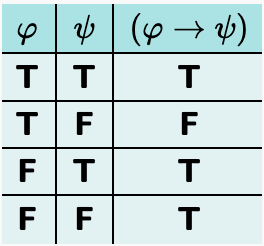
Characteristic Truth-table for the Conditional
5
New cards
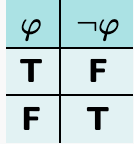
Characteristic Truth-table for Negation
6
New cards
Truth and Falsity Relative to a Truth-Value Assignment
* \n If φ is an atomic formula (sentential letter) of sentential logic, then φ is true on σ∗ just in case σ assigns the value T to φ, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form ¬ψ, then φ is true on σ∗ just in case ψ is false on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ&ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case both ψ and ρ are true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ∨ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case either ψ is true on σ∗ or ρ is true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ→ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case either ψ is false on σ∗ or ρ is true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form ¬ψ, then φ is true on σ∗ just in case ψ is false on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ&ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case both ψ and ρ are true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ∨ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case either ψ is true on σ∗ or ρ is true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
* If φ is a formula of the form (ψ→ρ), then φ is true on σ∗ just in case either ψ is false on σ∗ or ρ is true on σ∗, and false otherwise.
7
New cards
Tautology
A formula is called ***logically true*** or a ***_____*** just in case it is true on every truth-value assignment.
8
New cards
Contradictory Formula
A formula is called a ***_____*** just in case it is false on every truth-value assignment.
9
New cards
Contingent Formula
A formula is called a ***_____*** just in case it is true on some truth-value assignments, and false on others.
10
New cards
Logical Consequence
The conclusion of an argument is a ***_____*** of its premises if and only if any truth-value assignment that makes all the premises true also makes the conclusion true.
11
New cards
Validity
An argument is ***_____*** if and only if its conclusion is a logical consequence of its premises.
12
New cards
Invalidity
An argument is ***_____*** in case it is not valid, that is, if there is some truth-value assignment that makes the premises true, but the conclusion false.
13
New cards
Counterexample
A truth-value assignment that makes the premises of an argument true and its conclusion false is called a ***_____*** to the argument.
14
New cards
Conditional Analogue
The ***_____*** of an argument with premises φ1,...,φn and conclusion χ is the formula ((φ1&(...&φn))→χ).
15
New cards
Truth-Tree Construction Rules
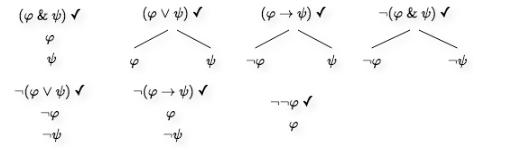
16
New cards
Truth-Tree: Closed Branch
A branch of truth-tree is ***_____*** if and only if it contains both any formula φ and the negation ¬φ of that formula.
17
New cards
Truth-Tree: Open Branch
A branch of truth-tree is ***_____*** if and only if it is not closed.
18
New cards
Truth-Tree: Completed Branch
A branch of truth-tree is _____ if no further decomposition rules can be applied on that branch. All closed branches are completed. An open branch is completed if every formula on the branch is either a literal or already decomposed.
19
New cards
Completed Truth-Tree
A truth-tree is ***_____*** if every branch of the tree is completed.
20
New cards
Procedure for Generating Truth-Trees
1. Start by writing down the formula for which you want to generate a truth-tree.
2. Based on the syntactic form of the expression, apply the appropriate truth-tree rule, putting a check mark next to the formula to indicate that it has been analyzed.
3. For each open branch, determine whether the branch contains both any formula φ and its negation ¬φ. If any branch does contain a formula and its negation, mark the branch closed. If all branches in the tree are closed, you are done. Otherwise, continue to the next step.
4. If the only formulae on open branches that do not have check marks next to them are atomic formulae or negations of atomic formulae, you are done. Otherwise, continue to the next step.
1. Choose an unchecked formula on an open branch in the truth-tree that is not atomic and not the negation of an atomic formula, and apply this procedure to that formula, starting with step 2.
21
New cards
Truth-values
22
New cards
Truth-functional
23
New cards
Function
24
New cards
Truth-tables
25
New cards
Truth-conditions
26
New cards
Characteristic truth-table
27
New cards
Logically true
28
New cards
Logical consequence
29
New cards
Contradictory
30
New cards
Truth-trees