Digestion and Industry
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Digestion
A process that breaks down large insoluble molecules into smaller useful soluble molecules via enzymes, chemicals and mechanical action
Large insoluble molecules
Such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids, need to be broken down during digestion into dissolvable products that can be absorbed by the body
Small soluble molecules
Products of digestion such as glucose, amino acids, glycerol and fatty acids, these molecules are small enough to be absorbed by the body for specific uses
Absorption
Small soluble molecules can be absorbed in the small intestine following digestion, they diffuse into the blood and are then transported around the body for specific purposes
Carbohydrates
Provide energy for chemical reactions and can break down into sugars
Proteins
The building blocks of cells and tissues that can break down into amino acids
Lipids
An energy store of fats and oils that can break down into glycerol and fatty acids
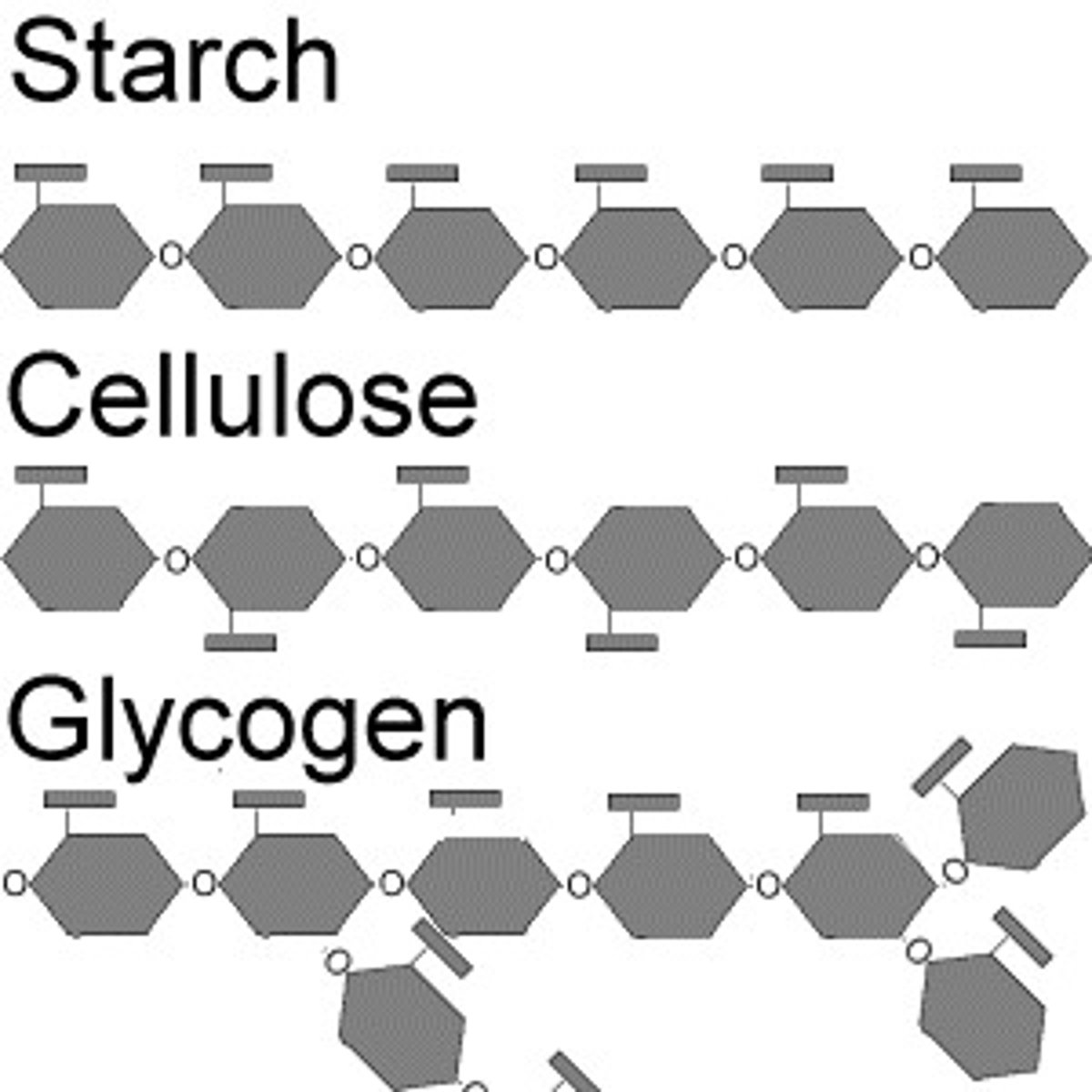
Conversion of glucose to complex carbohydrates
Glucose, a product of digestion, can be converted into new complex carbohydrates such as glycogen
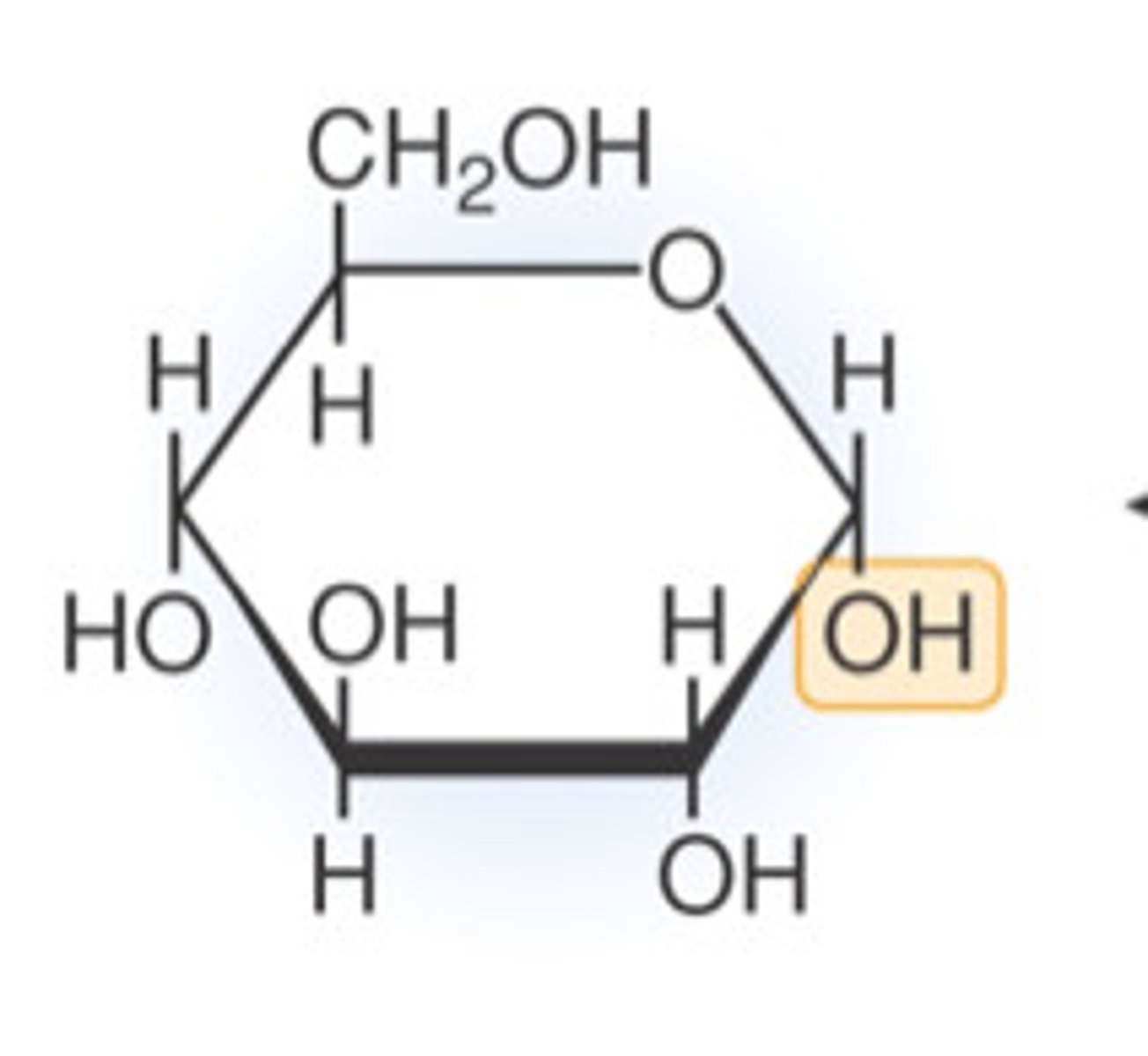
Glucose
A soluble product of digestion, essential for respiration to release energy and is also needed to synthesise new molecules
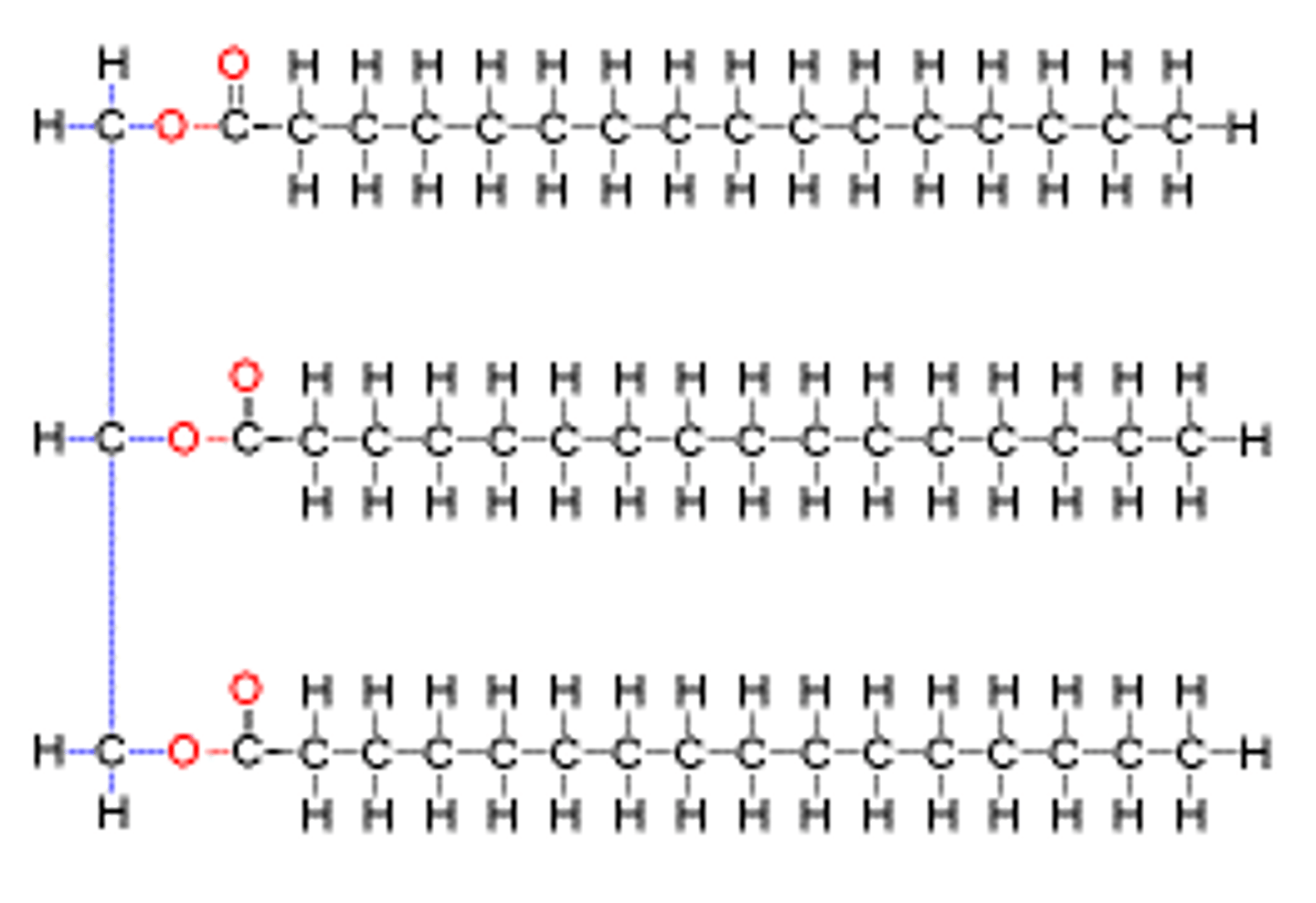
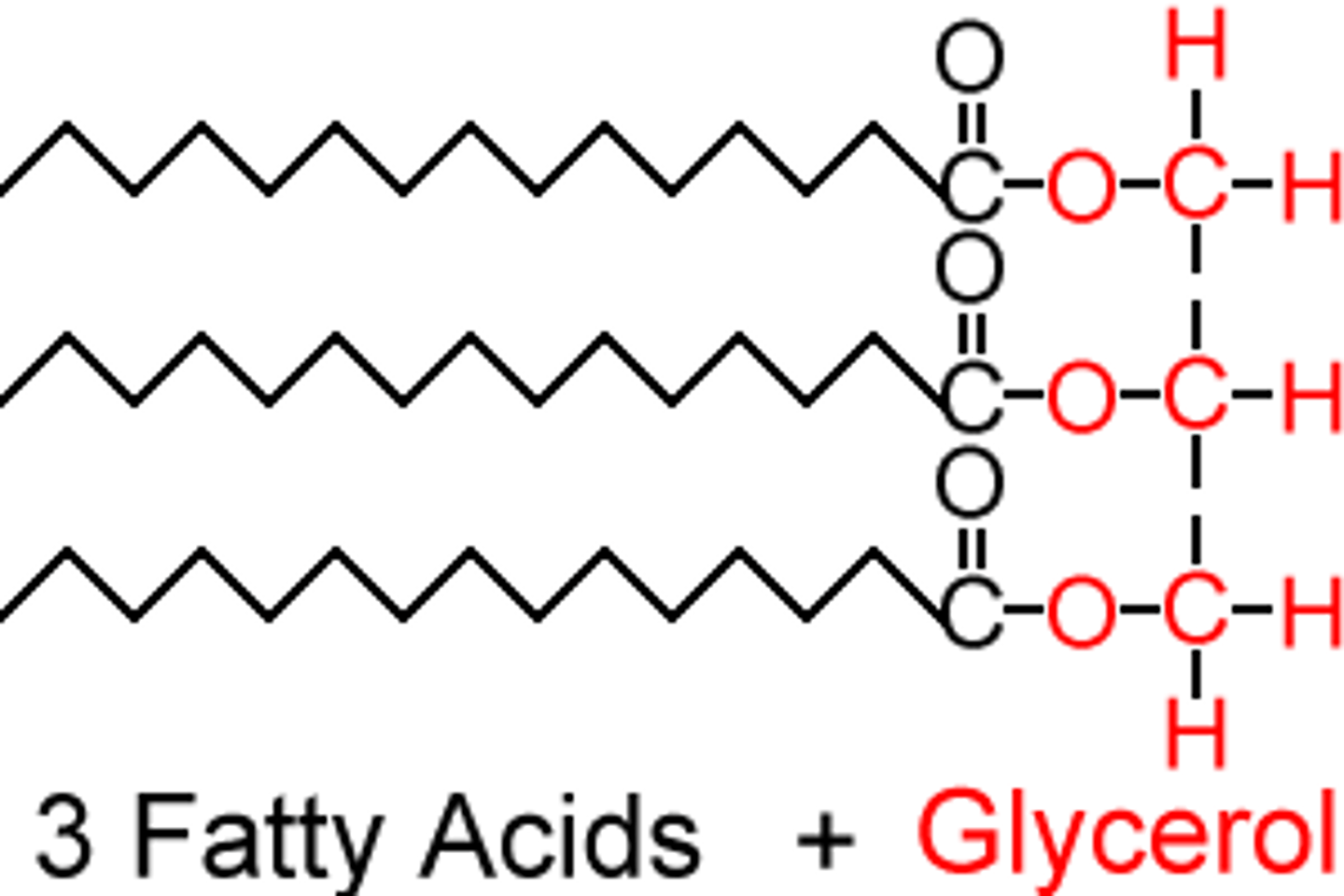
Formation of lipid molecules
Glycerol and fatty acids, products of digestion, join together to form new lipids
Protein synthesis
Amino acids, products of digestion, join together in specific arrangements to form new proteins for growth and repair
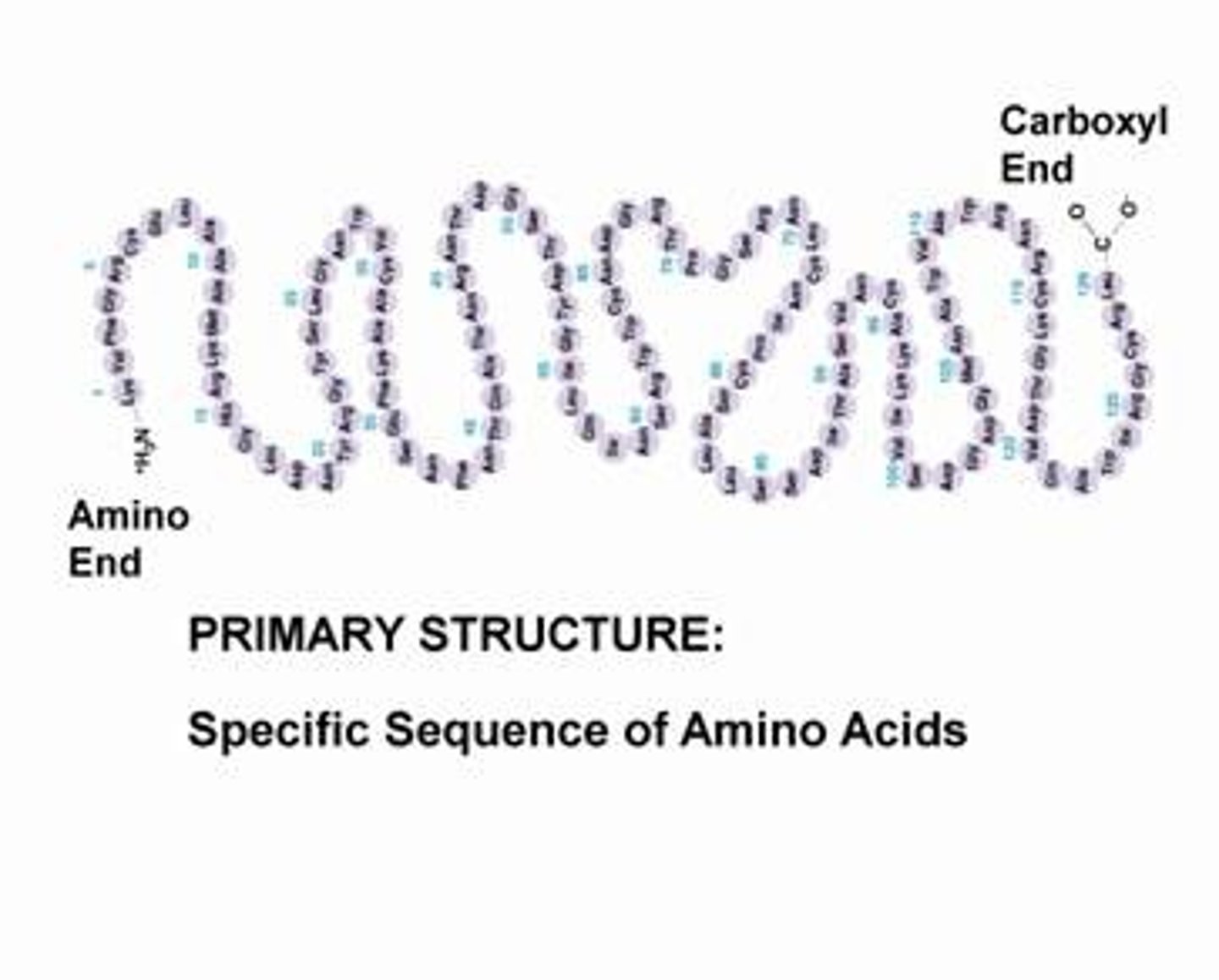
Enzymes
Biological catalysts which speed up reactions without being used up, essential for the digestion of large insoluble molecules
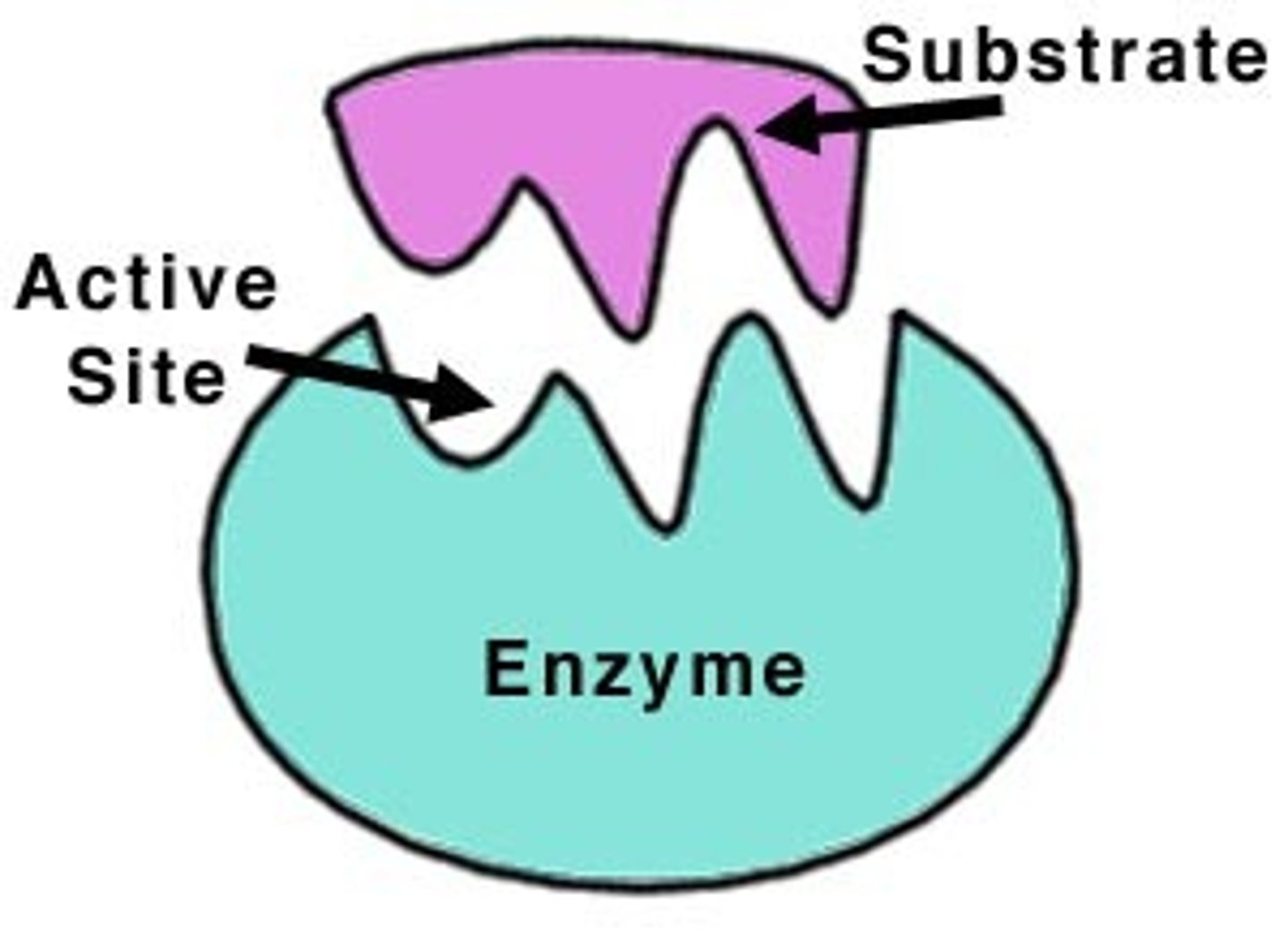
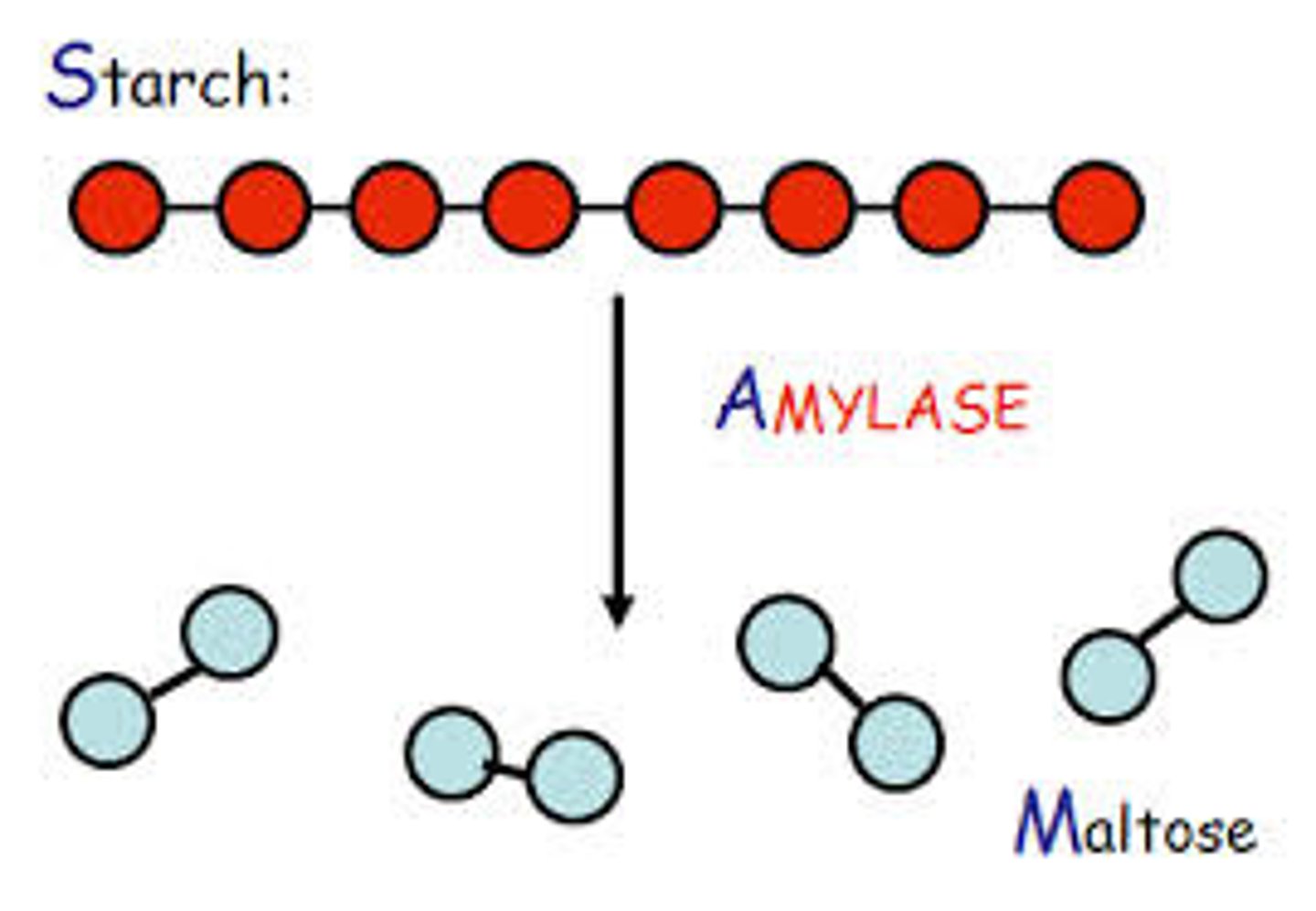
Amylase
A carbohydrase enzyme found in saliva and the small intestine that breaks the chemical bonds in starches
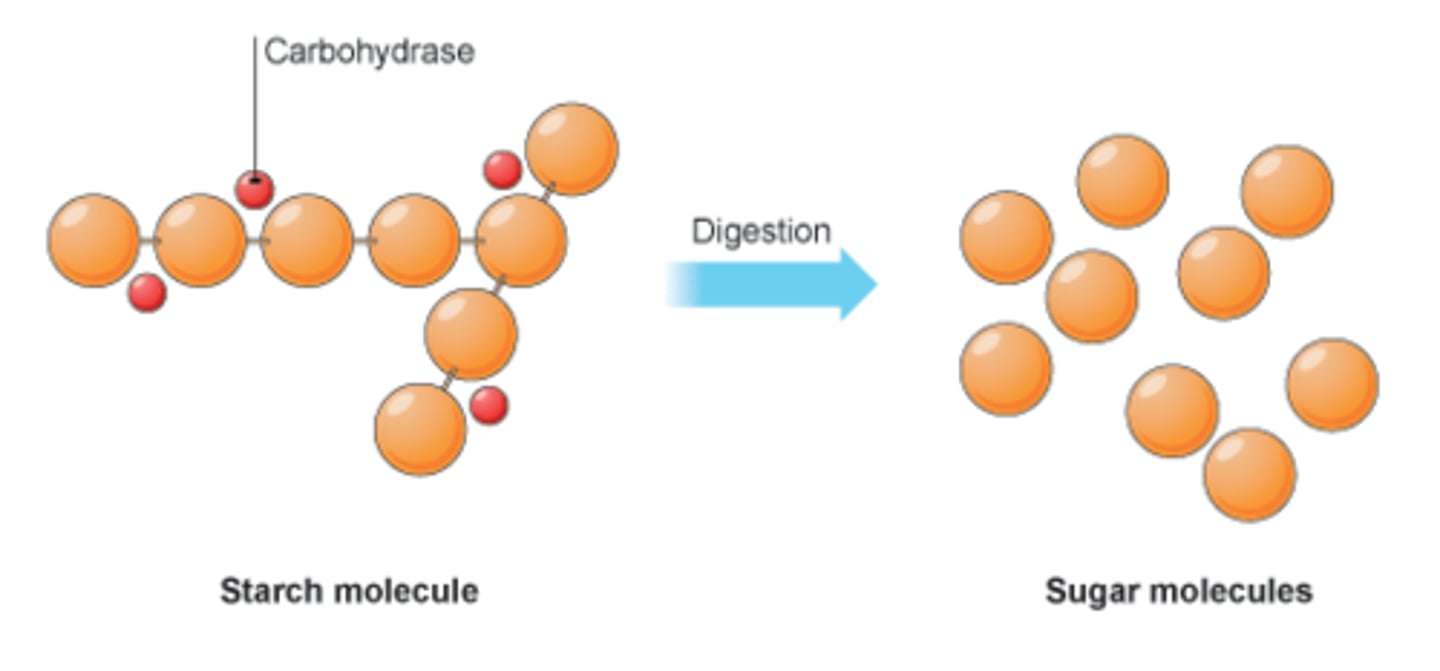
Carbohydrases
Enzymes that speed up the breakdown of carbohydrates into simple sugars
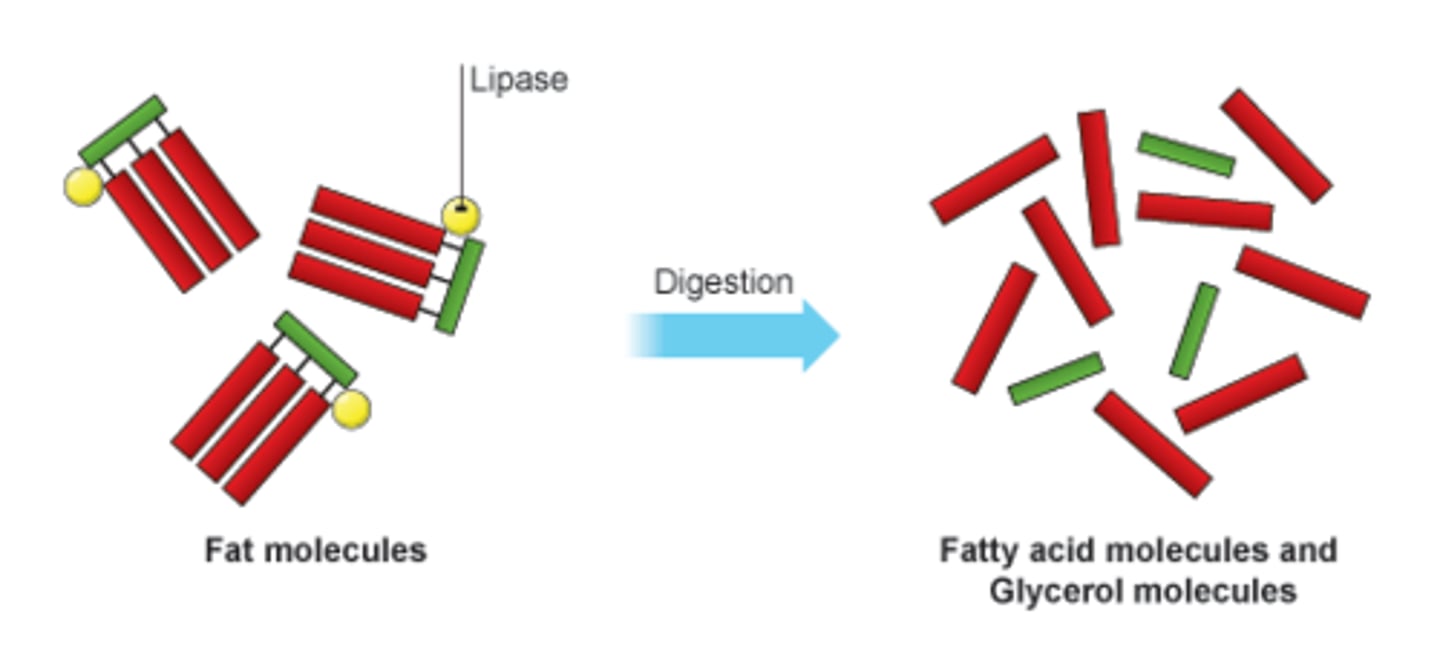
Lipase
Enzyme found in the small intestine that breaks down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids
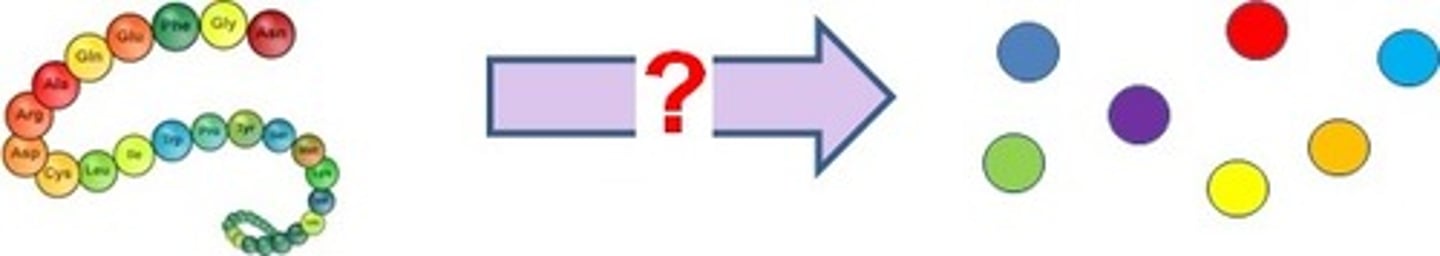
Protease
Enzyme found in the stomach and small intestine that breaks down proteins into amino acids
Commercial and industrial use
Enzymes can be used to improve many products and industrial processes, they are used in detergents, making cheese, making alcohol and bread, making medicines and industrial chemicals
Biological detergents
Washing powders that contain enzymes such as protease and lipase and can save energy by working at lower temperatures

Economical benefit of enzymes in industry
Enzymes can speed up the rates of reaction without being used up, they lower the energy needed for reactions meaning reactions can take place at lower temperatures, overall enzymes make processes quicker and cheaper