Unit Five Econ Test
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:09 PM on 5/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
E- both B and C
What happens in the case of a product that has elastic supply when the price decreases?
A. existing producers expand production
B. existing producers produce less
C. some producers drop out of the market
D. both A and C
E. both B and C
A. existing producers expand production
B. existing producers produce less
C. some producers drop out of the market
D. both A and C
E. both B and C
2
New cards
A- cargo ships
For which of the following products or services is supply likely to be inelastic in the short term whether prices rise or fall?
A. cargo ships
B. haircuts
C. newspapers
D. staples
A. cargo ships
B. haircuts
C. newspapers
D. staples
3
New cards
D- positive incentive
When a price increases and producers increase the production of goods, this is an example of?
A. negative externality
C. negative incentive
B. positive externality
D. positive incentive
A. negative externality
C. negative incentive
B. positive externality
D. positive incentive
4
New cards
D- law of supply
This develops from the choices of both current and new producers of a good, and is the tendency of suppliers to offer more of a good at a higher price?
A. law of demand
B. supply curve
C. supply schedule
D. law of supply
A. law of demand
B. supply curve
C. supply schedule
D. law of supply
5
New cards
E- both B and C
This displays the relationship between prices and the total quantity supplied by all firms in
the market?
A. law of demand
B. supply curve
C. supply schedule
D. law of supply
E. both B and C
the market?
A. law of demand
B. supply curve
C. supply schedule
D. law of supply
E. both B and C
6
New cards
D- time
The key factor in determining the elasticity of supply is?
A. price
B. goods
C. demand
D. time
A. price
B. goods
C. demand
D. time
7
New cards
C.- inelastic
What is the term for supply of a product that cannot easily or quickly expand or reduce its production in response to price?
A. profit
B. elastic
C. inelastic
D. time
A. profit
B. elastic
C. inelastic
D. time
8
New cards
A- quantity supplied
The amount a supplier is willing and able to supply at a certain price is the?
A. quantity supplied
B. elastic supply
C. supply schedule
D. quantity demand
A. quantity supplied
B. elastic supply
C. supply schedule
D. quantity demand
9
New cards
D- both A and C
What happens in the case of a product that has elastic supply when the price increases?
A. existing producers expand production
B. existing producers produce less
C. new producers enter the market
D. both A and C
E. both B and C
A. existing producers expand production
B. existing producers produce less
C. new producers enter the market
D. both A and C
E. both B and C
10
New cards
B- a supply curve
A graph of the data points in the supply schedule creates which of the following?
A. demand curve
B. a supply curve
C. quantity of goods demanded
D. supply of goods available
A. demand curve
B. a supply curve
C. quantity of goods demanded
D. supply of goods available
11
New cards
B- when additional workers increase output at a decreasing rate
When do diminishing marginal returns occur?
A. when workers increase output but others decrease it
B. when additional workers increase output at a decreasing rate
C. when extra workers will have to wait their turn to be productive
D. when additional workers will get in each other's way
A. when workers increase output but others decrease it
B. when additional workers increase output at a decreasing rate
C. when extra workers will have to wait their turn to be productive
D. when additional workers will get in each other's way
12
New cards
B- fixed cost plus variable cost
How is the total cost of a factory or other production site determined?
A. marginal cost plus fixed cost
B. fixed cost plus variable cost
C. fixed cost minus marginal cost
D. marginal cost plus variable cost
A. marginal cost plus fixed cost
B. fixed cost plus variable cost
C. fixed cost minus marginal cost
D. marginal cost plus variable cost
13
New cards
D- variable cost
A cost that rises or falls depending on the quantity produced is called a (n)?
A. total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
A. total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
14
New cards
C- largest gap between total cost and total revenue
A manufacturer sets their total output to maximize profit by setting production so?
A. that total revenue plus costs is greatest
B. marginal revenue is smallest
C. largest gap between total cost and total revenue
D. marginal cost is higher than profit
A. that total revenue plus costs is greatest
B. marginal revenue is smallest
C. largest gap between total cost and total revenue
D. marginal cost is higher than profit
15
New cards
B- marginal product of labor
The change in output that results having one more worker is called the?
A. marginal revenue
C. marginal cost
B. marginal product of labor
D. marginal labor
A. marginal revenue
C. marginal cost
B. marginal product of labor
D. marginal labor
16
New cards
C- fixed cost
A cost that does not change depending quantity produced is called a(n)?
A. total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
A. total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
17
New cards
B- marginal cost
The additional cost of producing one more unit is called a(n)?
A total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
A total cost
B. marginal cost
C. fixed cost
D. variable cost
18
New cards
D- revenue from the goods being manufactured exceeds the operating cost
When would it make sense for a factory that is losing money to remain in operation if?
A. marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
B. total cost of the goods exceeds operating cost
C. marginal product of labor becomes negative
D. revenue from the goods being manufactured exceeds the operating cost
A. marginal revenue is equal to marginal cost
B. total cost of the goods exceeds operating cost
C. marginal product of labor becomes negative
D. revenue from the goods being manufactured exceeds the operating cost
19
New cards
B- diminishing marginal returns
When the addition of another worker causes production to decrease is called?
A. marginal cost
B. diminishing marginal returns
C. negative marginal returns
D. increasing marginal return
A. marginal cost
B. diminishing marginal returns
C. negative marginal returns
D. increasing marginal return
20
New cards
A- marginal revenue
The additional income from selling one more unit of a good is called?
A. marginal revenue
B. marginal product of labor
C. marginal cost
D. operating cost
A. marginal revenue
B. marginal product of labor
C. marginal cost
D. operating cost
21
New cards
D- operating cost
The cost of operating a facility is called?
A. marginal revenue
C. marginal cost
B. marginal product of labor
D. operating cost
A. marginal revenue
C. marginal cost
B. marginal product of labor
D. operating cost
22
New cards
B- diminishing marginal returns
When the addition of another worker causes production to decrease in production below the addition of previous worker?
A. marginal cost
B. diminishing marginal returns
C. negative marginal returns
D. increasing marginal returns
A. marginal cost
B. diminishing marginal returns
C. negative marginal returns
D. increasing marginal returns
23
New cards
C- a decrease in supply
The graph displays a(n)?
A. increase in demand
B. an increase in supply
C. a decrease in supply
D. a rise in price
A. increase in demand
B. an increase in supply
C. a decrease in supply
D. a rise in price
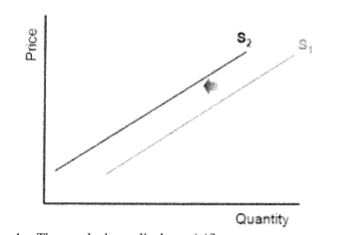
24
New cards
A- subsidies
One method used by governments to affect supply is to give payments that support businesses or the market these payments are called?
A. subsidies
B. welfare
C. taxes
D. regulations
A. subsidies
B. welfare
C. taxes
D. regulations
25
New cards
D- Shift to the right
If more suppliers enter into a market, the supply of a good (car stereos) will increase and the supply curve will?
A. stay the same
B. shift to the left
C. shift up
D. Shift to the right
A. stay the same
B. shift to the left
C. shift up
D. Shift to the right
26
New cards
B- store the goods until a later time
If a seller expects that the price o/ a hood (corn) will rise in the future (winter), they may?
A. sell the goods now
B. store the goods until a later time
C. dump the goods
D. keep the goods forever
A. sell the goods now
B. store the goods until a later time
C. dump the goods
D. keep the goods forever
27
New cards
B- an increase in supply
The graph displays?
A. increase in demand
B. an increase in supply
C. a decrease in supply
D. a rise in price
A. increase in demand
B. an increase in supply
C. a decrease in supply
D. a rise in price
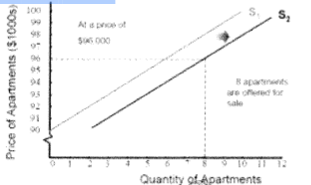
28
New cards
D- regulations
\
An indirect means that governments use to influence the supply of goods in the market through laws this is called?
A. subsidies
B. welfare
C. taxes
D. regulations
An indirect means that governments use to influence the supply of goods in the market through laws this is called?
A. subsidies
B. welfare
C. taxes
D. regulations
29
New cards
A- sell goods
During times of inflation (the value of money declines causing prices to increase), suppliers will?
A. sell goods
B. store goods to sell later
C. destroy stored goods
D. demand a bailout from the government
A. sell goods
B. store goods to sell later
C. destroy stored goods
D. demand a bailout from the government
30
New cards
C- to the right
Since suppliers set output at the most profitable level (price is equal to marginal cost), if the cost of inputs rises, the supply curve will shift?
A. down
B. up
C. to the right
D. to the left
A. down
B. up
C. to the right
D. to the left
31
New cards
E- both A and C
New technologies will cause?
A. decline in the cost of inputs
B. the supply curve to shift to the left
C. the supply curve to shift to the right
D. both A and B
E. both A and C
A. decline in the cost of inputs
B. the supply curve to shift to the left
C. the supply curve to shift to the right
D. both A and B
E. both A and C
32
New cards
B- protect companies from foreign competition
One reason government subsidize manufacturers is to?
A. promote free trade
B. protect companies from foreign competition
C. to raise taxes
D. to outsource jobs to overseas firms
A. promote free trade
B. protect companies from foreign competition
C. to raise taxes
D. to outsource jobs to overseas firms
33
New cards
A- excise tax
The government can reduce the supply of some goods, such as cigarettes, by placing this type of tax on these goods?
A. excise tax
B. sin tax
C. death tax
D. tariff
A. excise tax
B. sin tax
C. death tax
D. tariff
34
New cards
E- both B and C
Regulations cause supply curves to the shift to the left because of which of the following reasons?
A. increased cost of manufacturing
B. increased cost of in inputs
C. decrease in price of goods
D. both A and B
E. both B and C
A. increased cost of manufacturing
B. increased cost of in inputs
C. decrease in price of goods
D. both A and B
E. both B and C
35
New cards
A- sell the goods now
If a soybean farmer know that by Summer, the price per bushel will drop by $2.00, they will?
A. sell the goods now
C. dump the goods
B. store the goods until a later time
D. keep the goods forever
A. sell the goods now
C. dump the goods
B. store the goods until a later time
D. keep the goods forever
36
New cards
C- shift to the right
The US imports oil from Venezuela, the discovery of new oil fields will cause the supply curve to?
A. down shift
B. shift up
C. shift to the right
D. shift to the left
A. down shift
B. shift up
C. shift to the right
D. shift to the left
37
New cards
A- number of suppliers declines
Which of the following would cause the supply curve to shift to the left?
A. number of suppliers declines
B. the number of suppliers increase
C. cost of inputs decreases
D. government deregulates the market
A. number of suppliers declines
B. the number of suppliers increase
C. cost of inputs decreases
D. government deregulates the market