G4: Synthetic DNA Assembly and Genome Editing
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
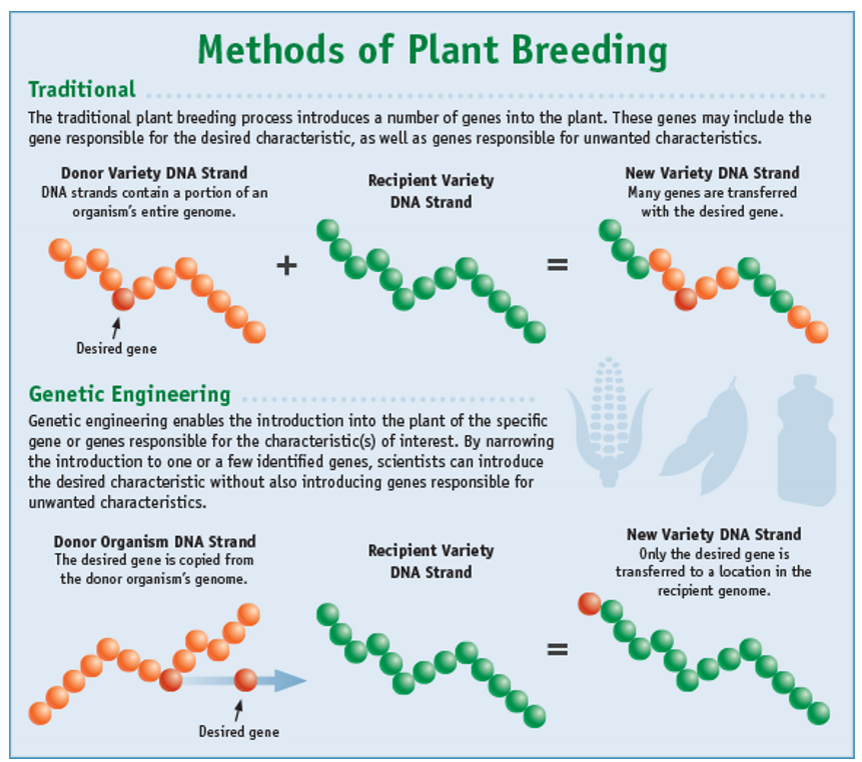
Methods of plant breeding
Traditional
Genetic Engineering
Synthetic Biology
Application of engineering principles to the fundamental components of biology.
Aims for creating useful functions in diverse areas:
Therapeutics
Biosensors
Bioenergy
Bioremediation
Chemicals and materials production
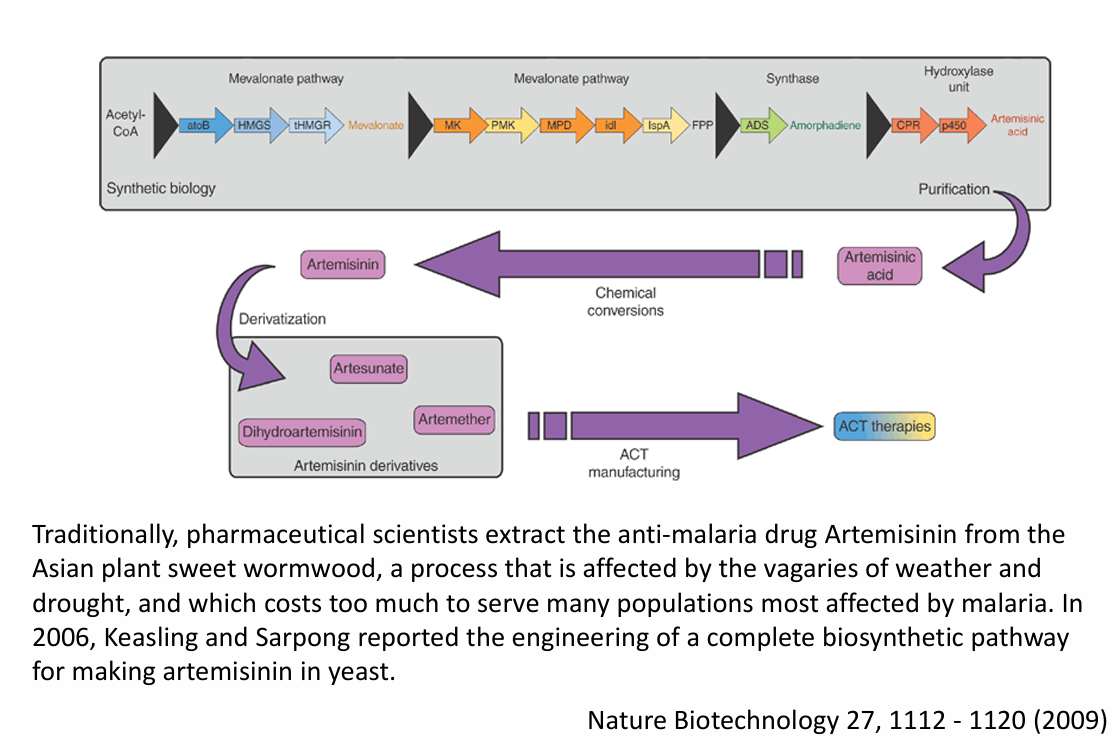
Why was the synthesis of artemisinin in yeast a milestone in synthetic biology?
Traditionally, artemisinin, an anti-malaria drug, was extracted from sweet wormwood, a costly and weather-sensitive method. Engineering yeast to produce artemisinin enabled a more reliable, scalable, and affordable production method, showcasing the power of synthetic biology to address global health issues.
Key enabling technologies of synthetic biology
Computational modelling and quantitative measurement: modelling of the design to predict system performance prior to fabrication.
DNA sequencing: provides genetic building blocks and verifies constructs.
DNA synthesis:
Chemical synthesis of fragments up to 1000 bp.
Molecular biology tools to assemble final synthesis constructs.
DNA assembly methods
DNA synthesis
By restriction/ligation
Traditional cloning in multiple cloning sites
BioBrick approach
Golden Gate shuffling
By homologous recombination
Sequence and ligation independent cloning (SLIC)
Gibson assembly
Circular polymerase extension cloning (CPEC)
In-fusion cloning
DNA shuffling
DNA synthesis as a DNA assembly method (with advantages and limitations)
DNA synthesis enables the de novo construction of genetic sequences without a template. It's typically achieved through solid-phase chemical synthesis of oligonucleotides (short DNA fragments, current limit is around 200 nts, but increasing), which are then assembled into longer constructs using overlapping oligonucleotides of 40-20 nts via molecular techniques.
Advantages
Complete freedom for the DNA sequence.
Codon optimization possible to tailor to host expression system.
Scar free: if overlaps are carefully designed.
Automation: commercial services offer rapid, scalable synthesis.
Limitations
Length constraints
Assembly required
Ligation methods for DNA synthesis
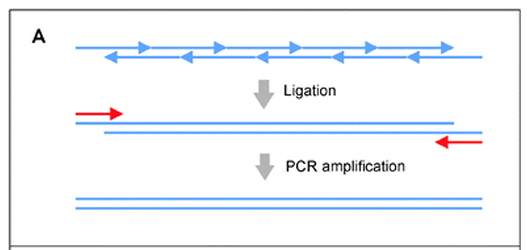
Ligation-based assembly
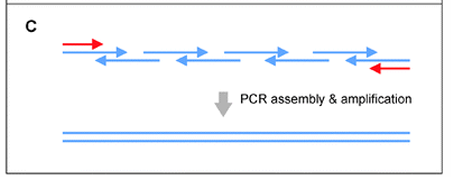
Two-step PCR-driven assembly
One-step PCR gene assembly
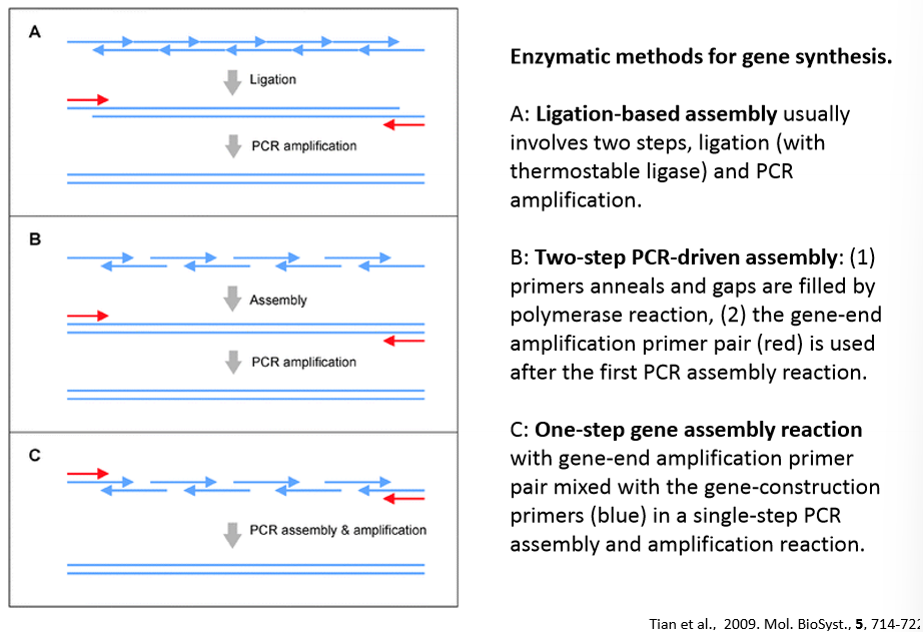
Ligation-based assembly
Ligation: short overlapping oligos are annealed and joined using a thermostable DNA ligase.
Amplification: the ligated fragments are then amplified to create the full length double stranded DNA.
Two-step PCR driven assembly
PCR assembly: overlapping oligonucleotides are mixed, annealed, and extended by a DNA polymerase to fill gaps between overlaps.
Outer primer amplification: a second PCR uses external primers that bind to the ends of the assembled product to amplify the full length gene.
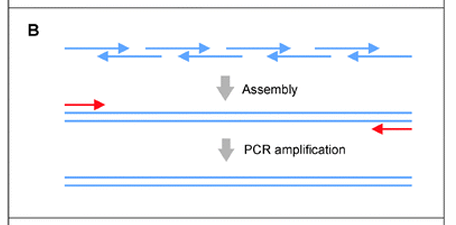
One-step PCR gene assembly
All gene construction primers (blue) and the gene-end amplification primers (red) are combined in a single PCR reaction.
Assembly and amplification occurs simultaneously.
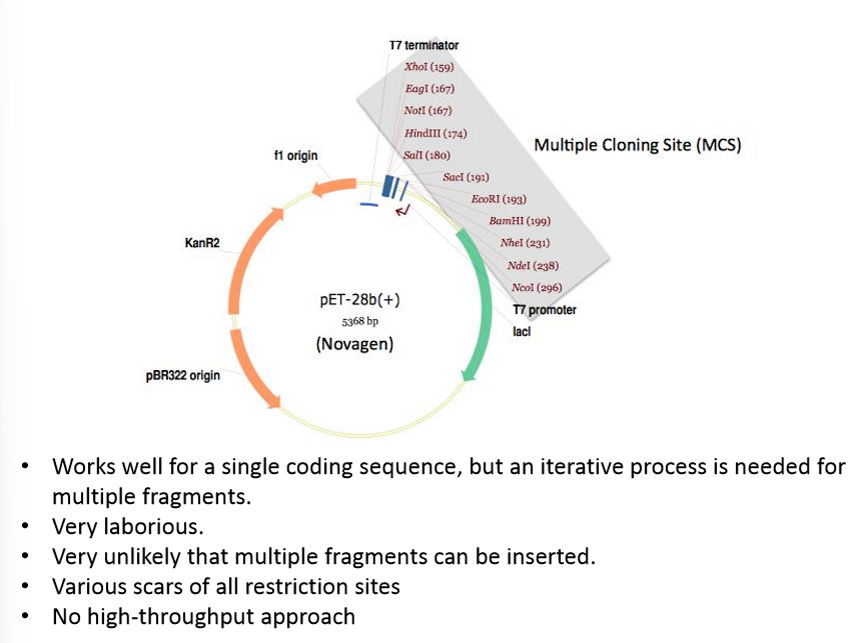
Explain the traditional cloning in multiple cloning sites approach as a DNA assembly method by restriction/ligation
Traditional cloning is a method where a DNA fragment of interest (such as a gene) is inserted into a plasmid vector using restriction enzymes and DNA ligase. This is one of the earliest and most widely used molecular biology techniques.
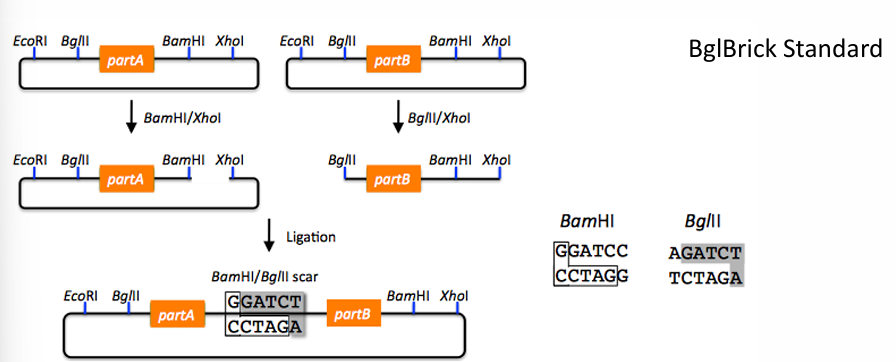
Explain the BioBrick approach as a DNA assembly method by restriction/ligation
BioBricks are DNA sequences standardized according to a specific standard (BioBrick standard, BglBrick standard…), facilitating automatization and re-use.
BglBrick standard
The BglBrick part is carried on a plasmid, flanked by two restriction sites at each side.
It uses four restriction enzymes: EcoRI, BglII, BamHI, and XhoI.
BglII and BamHI have compatible overhangs.
BioBrick limitations and obstacles
Scars: no control over the existence and sequence of intervening scars.
This is problematic when located in the coding sequence.
It can affect mRNA secondary structures.
Iterative process: because only two blocks can be fused at a time, multiple DNA assembly requires an iterative process.
Difficulty of creating a combinatorial library: especially when more than 2 BioBricks are combined.
The first-line BioBricks have to be first created.
Type IIS restriction enzyme
Type of restriction endonucleases that cut DNA outside of their recognition sites, generating user-defined overhangs.
Explain the Golden Gate shuffling approach as a DNA assembly method by restriction/ligation
Method that allow to simultaneously and directionally assemble multiple DNA fragments into a single piece using type IIS restriction enzymes and T4 DNA ligase.
Golden Gate shuffling relies on two unique properties of type IIS restriction enzymes.
Limitations and obstacles of Golden Gate shuffling
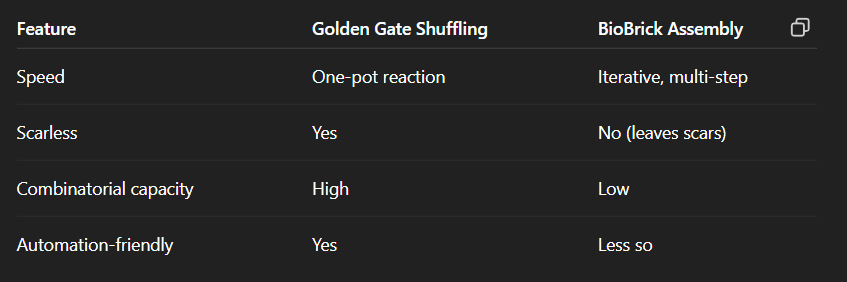
Compare BioBricks assembly and Golden gate assembly
Sequence and Ligation Independent Cloning (SLIC)
Gibson Assembly
Circular Polymerase Extension Cloning (CPEC)
Clonetech In-Fusion Cloning kit
Zinc Finger Nucleases (ZFN)
Fusion of:
DNA binding domain
DNA cleavage domain
Talen
Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nucleases
Fusion of:
DNA binding domain
DNA cleavage domain
CRISPR-Cas