Section 2: Environmental Chemistry
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test is Friday, March 10th
Last updated 1:40 AM on 3/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Toxicity
How poisonous a substance is.
2
New cards
Chlorofluorocarbons
chemicals that have been the result of our thinning ozone layer, they move up into the atmosphere & have been breaking down the ozone layer.
3
New cards
PPM (parts per million)
indicator of the concentration of chemicals in the environment.
4
New cards
LD50 (Lethal Dose 50)
amount of a substance that causes 50 % of a group of test subjects to die if they are given a specified dose of the substance all at once.
5
New cards
Acidity
how acidic a water body is.
6
New cards
Pesticides
substances used to kill pests that are unwanted for the growth of certain organisms.
7
New cards
Scrubbers
Devices that remove Sulfur Dioxide & convert it into C02 & Gypsum. (using limestone)
8
New cards
Heavy Metals
mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium and nickel.
9
New cards
Nitrogen Oxide
forms when nitrogen combines with oxygen as a result of fuel combustion.
10
New cards
Sulfur Dioxide
forms when sulfur combines with oxygen in the air.
11
New cards
Biological Indicators
organisms that help determine water quality.
12
New cards
Carbon Dioxide
a greenhouse gas because its releases in large amounts into the atmosphere (human activities)
13
New cards
Carbon Monoxide
a colorless & odorless gas. Its produced by incomplete combustion of chemicals containing carbon (e.g. hydrocarbons) It mainly comes from motor vehicles
14
New cards
Ozone Layer
a natural formation of ozone above Earths surface that protects s against UV rays.
15
New cards
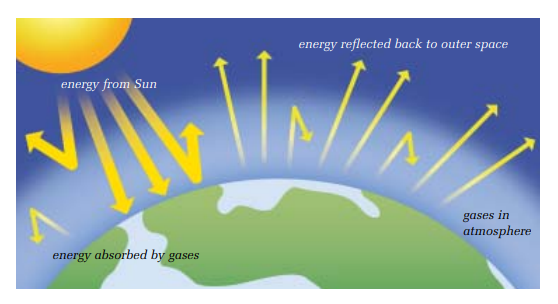
Greenhouse Effect
certain gasses trap heat from the sun & it regulates the earths temperature.
16
New cards
Ground Level Ozone
When ozone combines with gas emissions, it gets closer to the earths surface and becomes harmful for us to breathe in.
17
New cards
Dissolved Oxygen
how much oxygen from the air is dissolved into a water source
18
New cards
Phosphorus & Nitrogen Content
amount of Nitrogen and Phosphorus in a water source (can cause algal blooms)
19
New cards
Heavy Metals
mercury, lead, copper, zinc, cadmium and nickel
20
New cards
Spring acid shock
concentration of acid that can dramatically lower the pH of the water for a short period of time
21
New cards
How to calculate ppm
Divide solute from solvent then take the answer and multiply by 1,000,000
22
New cards
How to calculate LD50
Divide number of deaths from sample size then multiply the answer by 100 to turn into a percent (Remember to round)
23
New cards
Sulfur Dioxide
forms when sulfur combines with oxygen in the air
24
New cards
Nitrogen Oxide
forms when nitrogen combines with oxygen as a result of fuel combustion
25
New cards
Ozone
(O3) makes up a layer in the atmosphere
26
New cards
Ozone Layer
a natural formation of ozone above Earths surface that protects s against UV rays
27
New cards
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse effect made greater by human activities that add greenhouse gasses to the atmosphere (this can create global warming)
28
New cards
Monitor
keeping track of something for a specific purpose
29
New cards
5 Categories of water quality
* Human drinking
* Recreation
* Livestock drinking
* Irrigation
* Protection of Aquatic Life
* Recreation
* Livestock drinking
* Irrigation
* Protection of Aquatic Life
30
New cards
Chemical Factors that affect organisms
* Dissolved oxygen
* Plant nutrients
* Pesticides
* Salts
* Acidity
* Heavy Metals
* Plant nutrients
* Pesticides
* Salts
* Acidity
* Heavy Metals
31
New cards
Levels of dissolved oxygen depends on
* Temperature
* Turbulence (due to wind or rapids)
* The amount of photosynthesis taking place by water plants and algae
* The number of organisms using up the oxygen in the water
* Turbulence (due to wind or rapids)
* The amount of photosynthesis taking place by water plants and algae
* The number of organisms using up the oxygen in the water
32
New cards
Acidic Deposition
when the soil or water does not have the natural bases to neutralize the acidic precipitation
33
New cards
With every breath we inhale:
78% nitrogen
21% oxygen
some traces of argon, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and neon.
21% oxygen
some traces of argon, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and neon.
34
New cards
Air quality can be measured by:
* measuring the levels of pollutants in the air
* estimating the amount of emissions from pollution sources
* estimating the amount of emissions from pollution sources
35
New cards
How do Chlorofluorocarbons affect ozone?
by having products move more slowly through the upper atmosphere, and broken down by the UV radiation. Upon breakdown, chemicals such as chlorine and bromine are produced, which can destroy ozone.
36
New cards
Acute Toxicity
Serious harm after 1 dose
37
New cards
Chronic Toxicity
Effects noticed after substance builds up