Bio: Macromolecules
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Carbohydrate
contains carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; oxygen and carbon number are close
proteins
contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and nitrogen
lipids
contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and sometimes a phosphate group; oxygen and carbon number are not close at all
nucleic acids
contain carbon, hudrogen, oxygen, phosphate, and nitrogen
monomer
small, single unit, basic building block
dimer
2 monomers bonded
polymer
many monomers joined together with a covalent bond
different polymers
different sequences of monomers →
anabolic, endergonic reactions
reactions that build up macromolecules
catabolic, exergonic reactions
reactions that break down macromolecules
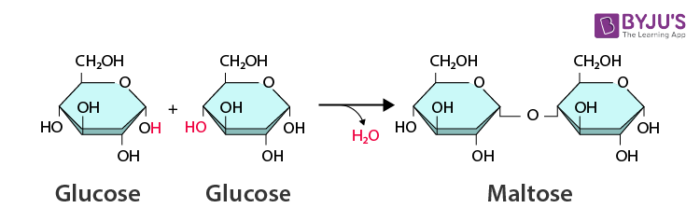
dehydration synthesis (condensation reaction)
builds molecules up, requires energy. results in the formation of a large molecule out of smaller molecules forming covalent bonds.
water is formed and released each time a covalent bond is formed
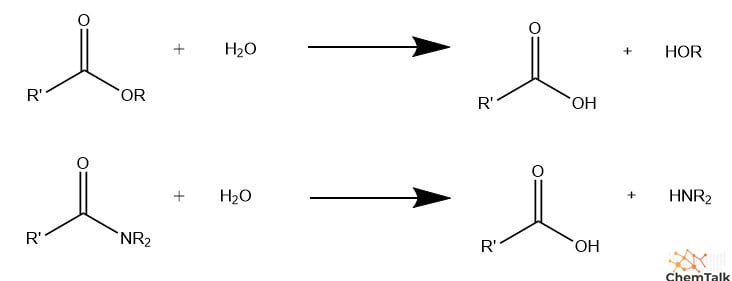
hydrolysis reaction
breaks molecules down, releases energy. results in formation of smaller molecules out of a large molecules breaking covalent bonds
water is broken doen and its parts are added to form the products
monosaccharide
monomer of a carbohydrate
1C: 2H: 1O ratio
glucose, fructose, and galactose
6- carbon sugars
C6: H12: O6
ribose and deoxyribose
5- carbon sugars
disaccaharide
dimer of carbohydrates- double sugar
sucrose, maltose, lactose
disaccharides
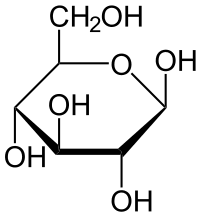
alpha glucose
1-hydroxyl and 4- hydroxyl on the same side
hydroxyl group below
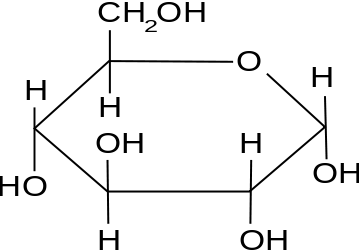
beta glucose
1 hydroxyl and 4 hydroxyl, on opposite sides
hydroxyl group above
linear
polymers made out of beta glucose
linear polysacchrides
allows for hydrogen bonds creating a strong building material such as cellulose
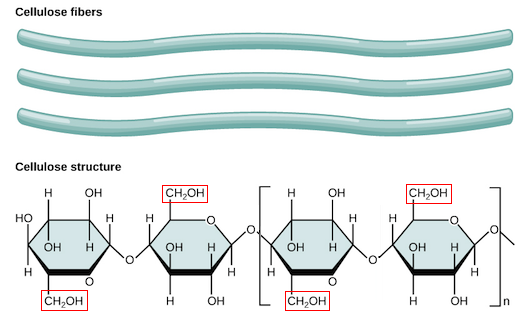
helical
polymers made out of alpha glucose
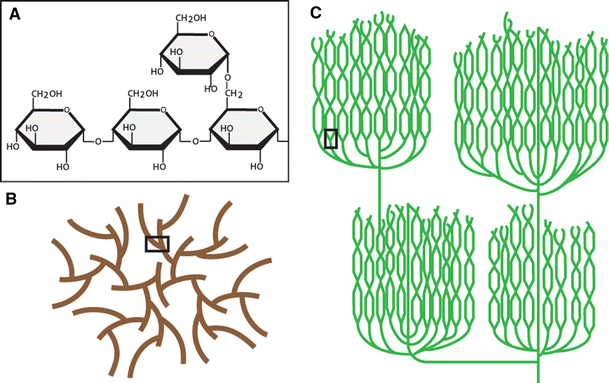
alpha glucose (starch and glycogen)
energy storage polysaccharides
beta glucose( cellulose and chitin)
structural polysaccharides
starch
energy storage polysaccharide found in plants (plastids)
glycogen
energy storage polysaccharide found in animals
short term energy storage in liver + muscle
extensively branched
cellulose
structural polysaccharide found in plants, in the cell wall
most abundant on earth
insoluble fiber
chitin
structural polysaccharide found in animals and fungus, makes up exoskeleton in animals
makes up cell wall in fungus and found in exoskeletons
amylose
simple starch, unbranched
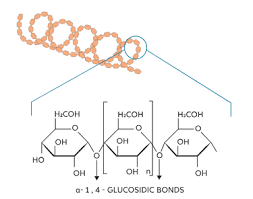
amylopectin
complex starch, branched
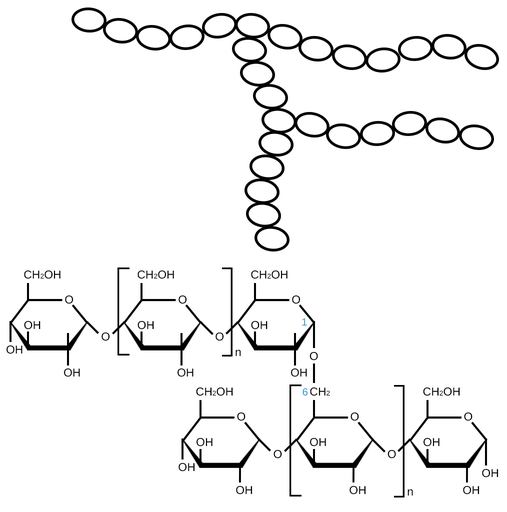
glycosidic bond
covalent bond; holds monomers together to make polymers in sugars C-O-C
polysaccharide
polymer of carbohydrates
C:H bond
non-polar covalent bond; insoluble in water
hydrocarbon tails
causes lipids to repel water
adipose
long term energy storage, insulation, cushion/ protects organs
2x more than carbs
how much energy does a lipid store
fatty acid and glycerol
what are the two “monomers” of a lipid
fatty acid
carboxyl group bonded to long hydrocarbon chain
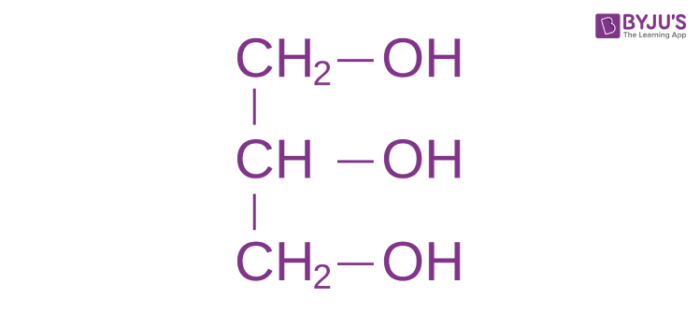
glycerol
3-C backbone, sugar alcohol
ester linkage
covalent bond between glycerol and fatty acid; O-C-O
triglyceride (fat molecule)
glycerol + 3 fatty acids
saturated and unsaturated
what are the two types of fatty acids
saturated fatty acid
all single C-C bonds, linear, and maxium hydrogen
packed together tightly and solidify at room temperature
unsaturated fatty acid
contain at least one C-C double bond in the fatty acid; double bong creates a kink in the chain, not max hydrogen
kinks make the fats unable to pack together closely, thus remaining a liquid at room temperature
phospholipid
1 glycerol, 2 fatty acids, and a phosphate group (PO4) that can have other molecules attached to it
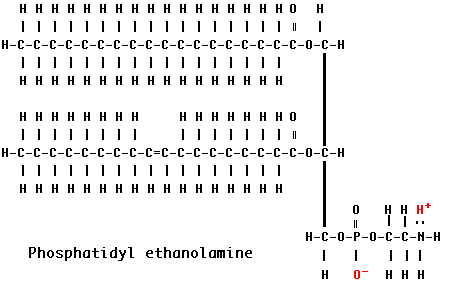
head of phospholipid
phosphate group (negative charge) that is hydrophilic (interacts with polar molecules aka water= H-bond with water)
tail of phospholipid
2 fatty acid (hydrocarbon) tails are hydrophobic
protected by the heads in a phospholipid bilayer
steroid
4 fused carbon rings with different functional groups attached giving different properties
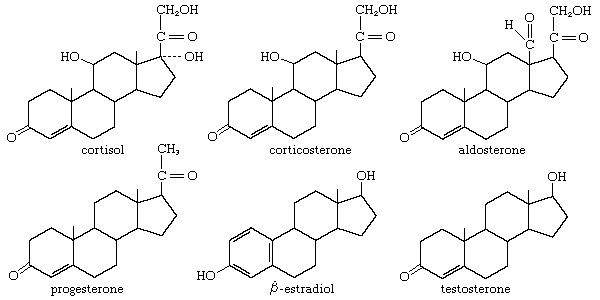
cholesterol
the basis for forming all other steroids
found in cell memebranes - fluidity
synthesized by the liver, also obtained in diet
high levels lead to cardiovascular disease
differences in fuction and structure
differences in saturation determine what in a lipid
amino acid
monomer of proteins
20 total, that differ at the R group
carboxyl (COOH) and amino acid (-NH2)
what 2 functional groups are present in an amino acid
dipeptide
dimer of proteins
polypeptide
polymer of proteins
glycoprotein
protein + carbohydrate: found in cell membrane, helps cells with recognition
peptide bond
covalent bond that holds proteins together, C-N
enzymatic, defensive, hormones, transport, receptors, structure, contractile, and storage
what are the 8 functions of proteins
by making sure the amino acid is in the right direction
how do enzymes speed up the reaction in the protein
hydrophobic
carbon + hydrogen
electornegative/ hydrophilic
oxygen + nitrogen
primary structure of proteins
linear chain (a change here will cause a change in all other levels)

secondary structure
polypeptide backbone is folded and stabilized by hydrogen bonds
hydrogen bond formed between oxygen of carboxyl group and hydrogen of amino group
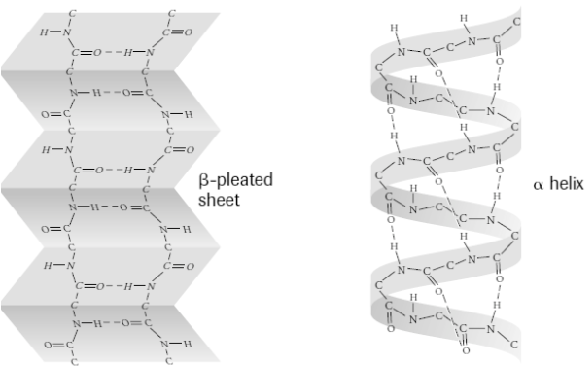
alpha helix
colied regions of a secondary structure amino acid
beta pleated sheet
flat/ folded regions of a secondary structure amino acid
tertiary structure
3d protein shape is stabilized by side chain interactions (R groups)
hydrogen bonds from between polar side chains
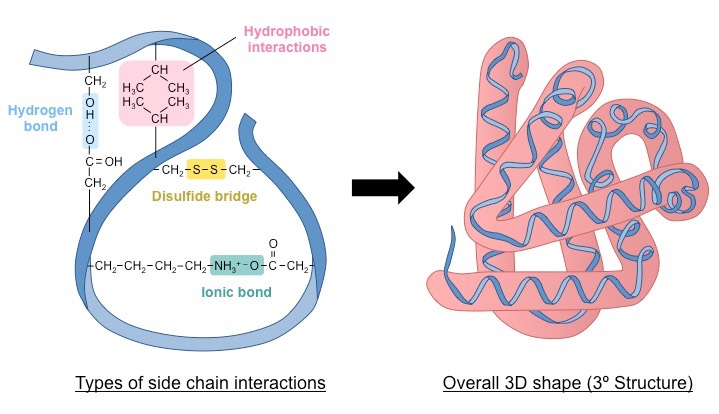
disulfide bridges
covalent bonds between sulfhydryl (-SH) groups
quaternary structure
multiple polypeptide chains combine to form one protein

denature
change in protein shape due to breakdown of interactions/ bonding causing it to unravel/ unfold and no longer function
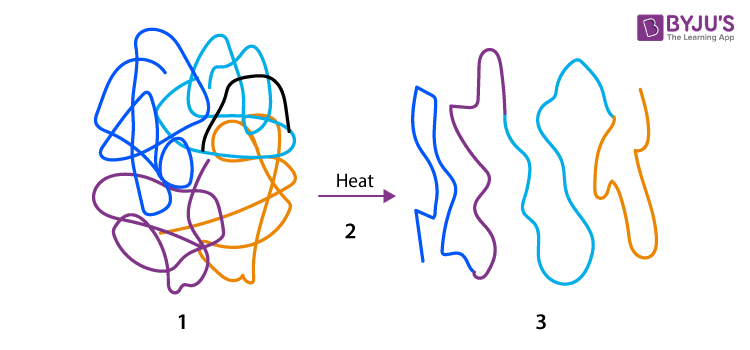
chaperonin
proteins that assit in the process of folding other proteins
large interior spaces that provide the polypeptide chain a “safe place” to fold away from outsid/ environmental influence of the cell
diseases such as alzheimer’s, parkinson’s, and mad cow can be caused
what can happen in a protein misfolds
the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide
what determines the overall shape and function of the protein
the carboxyl (C) terminus of the growing peptide chain
where do the covalent bonds form in a linear chain of amino acids
nucleotide
the monomer of a nucleic acid
pentose (5C) sugar, Phosphate group (PO4), and a nitogen
what are the 3 parts of a nucleotide
ribose (RNA) or deoxyribose (DNA)
what are the pentose sugars in a nucleotide
gives the backbone a negative charge
what does the phosphate group do in a nucleotide
adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine, and uracil
what are the 5 nitrogen bases
thymine
what does adenine bond to in DNA
guanine
what does cytosine bond to
uracil
what does adenine bond to in RNA
thymine, uracil, and cytosine
what are the pyrimidines (base with one 6-carbon ring)
adenine and guanine
what are the purines (base with one 6-carbon ring and one 5-carbon ring)
polynucleotide
polymer of nucleic acid
phosphodiester C-O-P
covalent bond holding nucleic acids together
5-C ribose
Adenine nitrogen base
3 phosphate groups
what does ATP contain
5-C ribose
Adenine nitrogen base
2 phosphate groups
what does ADP contain
5-C sugar (ribose or deoxyribose)
Nitrogen base
what does a nucleoside contain
the 3’ end
where are nucleotides added to a growing DNA/RNA strand
5’
phosphate group in DNA/RNA is where
3’
hydroxyl group in DNA/RNA is where
antiparrel 3’-5’ 5-3’
what is the directionality of DNA strands
close evolutionary relationship
similar DNA/proteins→
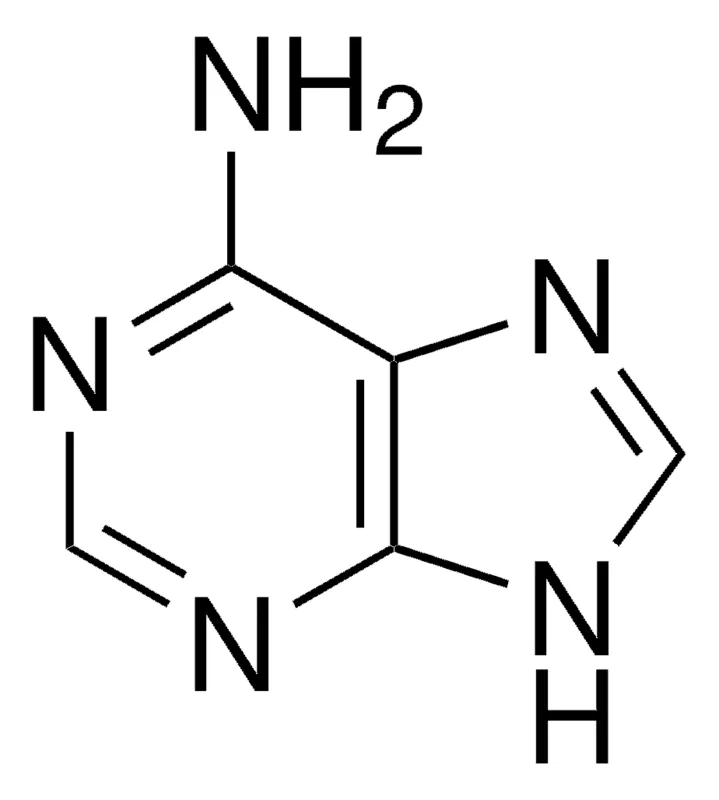
adenine
what is this nitrogen base
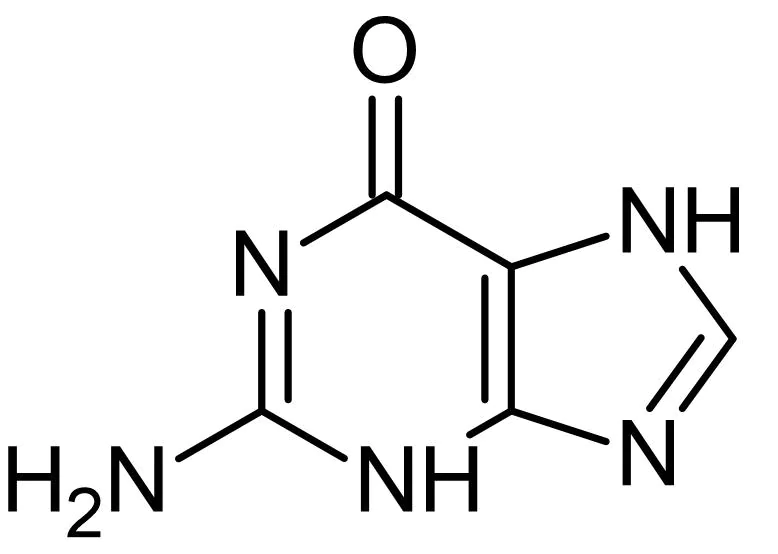
guanine
what is this nitrogen base
cytosine
what is this nitrogen base
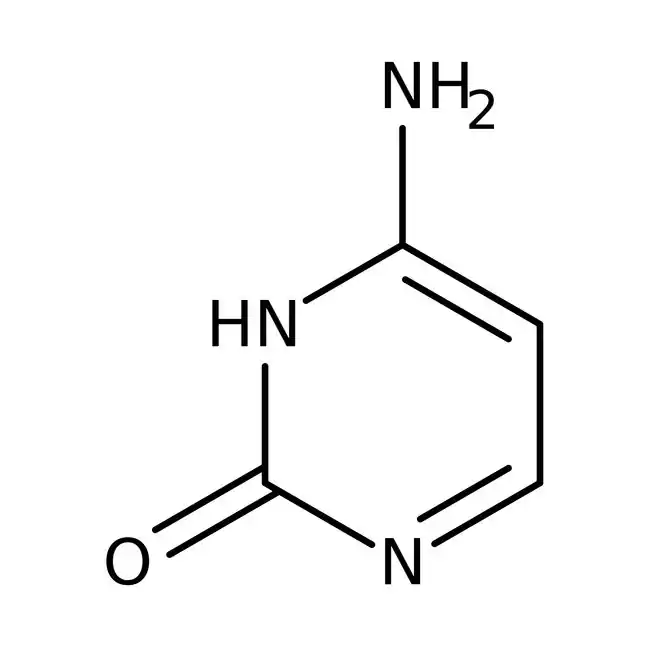
thymine
what is this nitrogen base
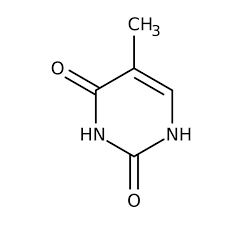
uracil
what is this nitrogen base
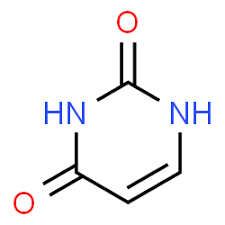
hydrogen bonds
what type of bonds allow for base pairing
3 hydrogen bonds
how many hydrogen bonds do guanine and cytosine have
2 hydrogen bonds
how many hydrogen bonds do adenine and thymine have