Applied Anatomy Exam 2
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Okstate Dr. J
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
resistance training, stretching (to a lower degree), steroids (muscles grow fast but not tendons; and premature growth plate closure)
The correct order in a muscle structure analysis
In descending order, Whole muscles, Fascicles containing muscle fibers (cells), Muscle fibers (cells) containing myofibrils, Myofibrils containing myofilaments, Myofilaments = Actin & Myosin, Actin contains Troponin & Tropomyosin, Myosin with cross bridges
Which part of the nervous system is rest and digest?
Parasympathetic
age related loss of strength and muscle mass
sarcoplasmic reticulum.
transmit action potentials into muscle fibers.
What is the terminal cisternae?
(ends of sr that touches t tube)- contains ca ions used in muscle contractions
ability to receive and respond to stimuli
The ability of a muscle to stretch beyond normal length
When 2 or more muscles act to produce a movement that 1 cannot perform alone
fan shaped muscles
What is another name for an efferent neuron?
Motor neuron
In walls of hollow organs and blood vessels
transported along nerves the skin then to the cell body, where it becomes latent and reside lifelong.
Sodium is outside the cell; calcium is in the SR
Fiber arrangement; Number of fibers/ type/ size of fibers
breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Dense irregular connective tissue surrounding a fascile (bundle) of muscle fibers
Dense irregular connective tissue surrounding individual muscle fibers.
muscle biopsy
In muscle fibers; caused by resistance training (2-6 reps)
In the peripheral nervous system; they develop myelin.
Type II (fast-twitch) fibers
Stretch of the quadriceps muscle, patellar tendon
Survival question about stuck in snowy tent
If flame goes orange
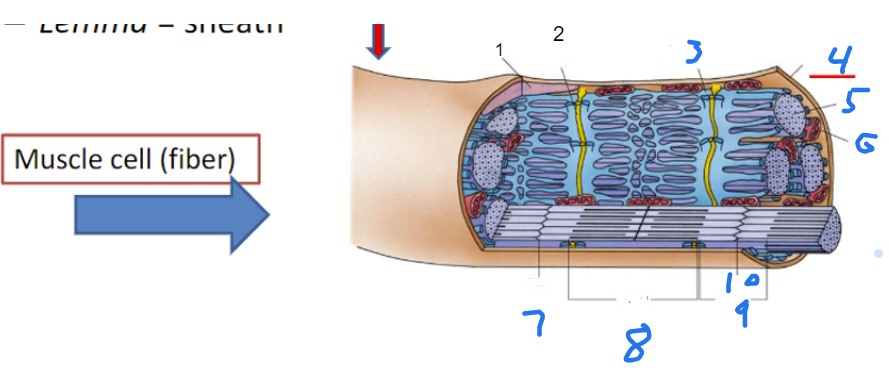
Identify the Muscle cell (fiber)
In order, nucleus, transverse tubule, terminal cisterane of SR, sarcolemma, myofilbril, mitochondria, z line, a band, I band
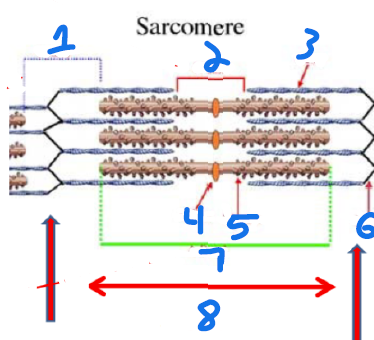
Identify the Sarcomere
In order, I band, H zone, actin, M line, myosin, Z line, A band, Z to Z
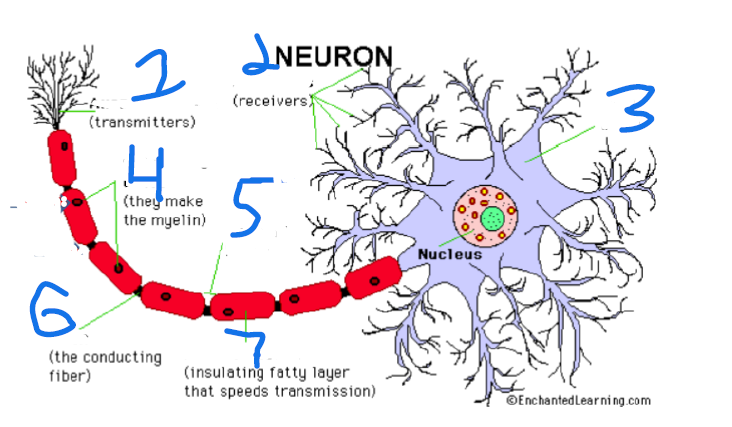
Identify the Neuron
In order, axon terminal, dendrites, cell body, schwann’s cells, node of ranvier, axon, myelin sheath