ap macro unit one - basic economic concepts
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
scarcity
something that is LIMITED and WANTED.
ex: resources
four factors of production
Land
Labor
Capital
Entrepreneurship
(LLCE - Let’s Laugh Cus Economics!)
types of capital
physical capital (machinery, tools)
human capital (skills, training, education)
financial capital (money)
PPC
Production Possibilities Curve. Illustrates opportunity cost.
every point is a combination of output level
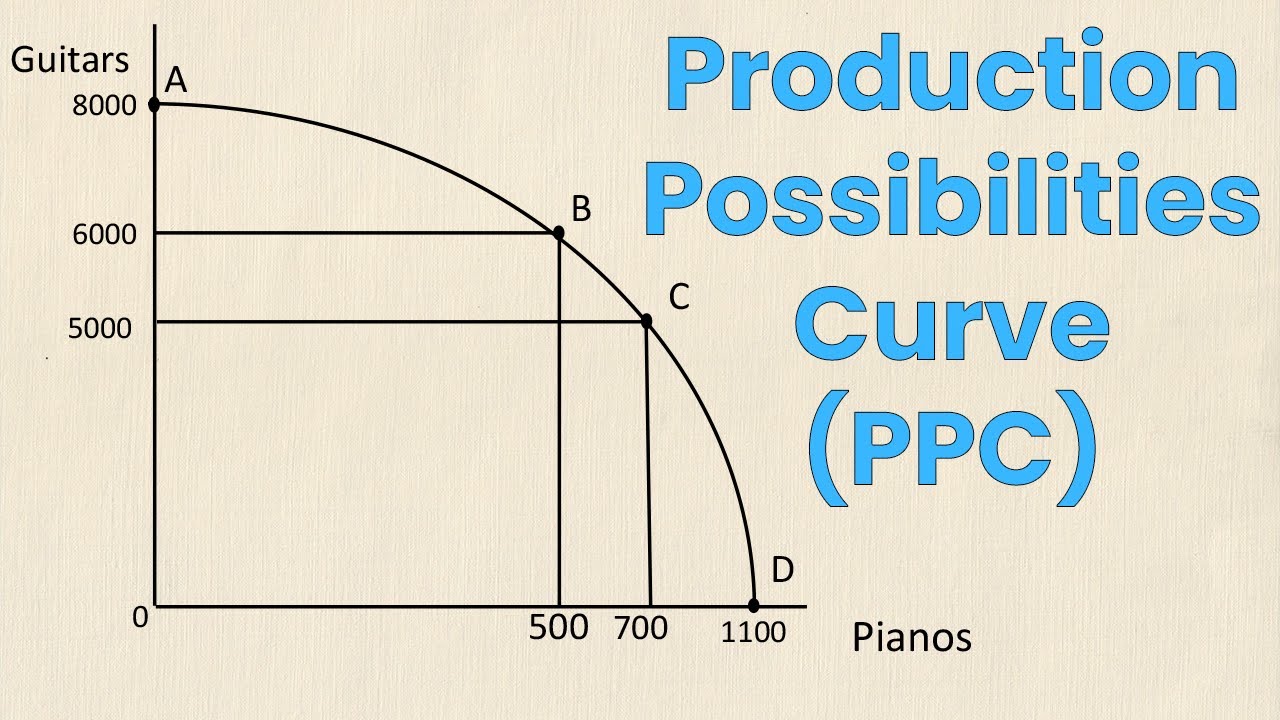
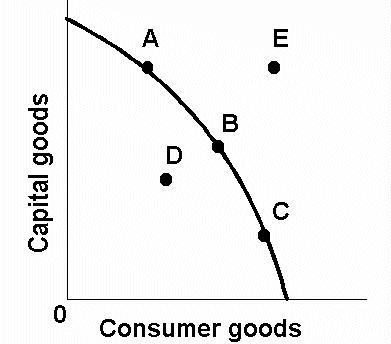
PPC Curve - A, B, C
Full Employment - Efficient
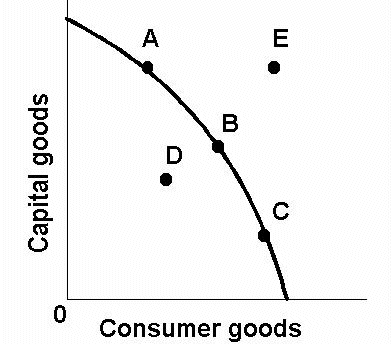
PPC Curve - D
Not efficient production, has not reached full employment
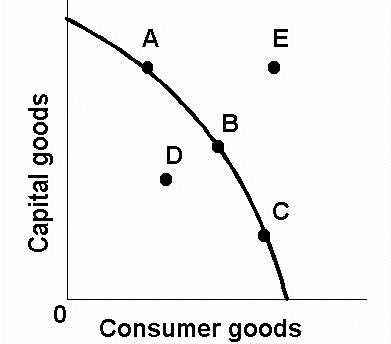
PPC Curve - E
Beyond production possibilities, unattainable
Movement along the PPC Curve
Demonstrates trade offs
Outward shift of the PPC Curve
Demonstrates economic growth
Inward shift of the PPC Curve
Demonstrates economic contraction
Comparative Advantage
When a producer can create a given amount of product at a lower opportunity cost.
Ex: Producer 1 can make it while giving up less than Producer 2
Output problems, calculating comparative advantage
OOO
Output: Other goes Over
Input problems, calculating comparative advantage
IOU
Input: Other goes Under
Demand Shifters
MERIT
Market Size (number of consumers)
Expectations about the product
Related Prices (Prices of Complementary or Substitute products)
Income (normal and inferior goods)
Tastes
Complementary Products in Consumption
Products that go well with each other. Like burger buns and burger patties. If the price for one goes down, demand for that item goes down, and so the demand for the complementary products also goes down.
Substitute Products in Consumption
Products that can be substituted for one another. If the price of one product goes up, the demand for that product goes down, and instead the demand for the substitute goes up.
Market Size
number of consumers
Normal goods
Goods whose demand increases as one’s income increases.
Ex: The richer you are, the more demand for clothes.
Inferior goods
Goods whose demand decreases as one’s income increases. You don’t have to settle for these goods anymore.
Ex: The richer you are, the less you need to buy a used car.
Shifters of Supply
TRICE
Technology
Related Prices (Complements and substitutes)
Complements in production: by-products of something. For example you can sell cow meat from cows but also their milk. If the price of one complement increases, the supply of it will increase and thus the supply of the other complement will also increase.
Substitutes in production: Co-produced goods, so producers can choose to produce either. If the price of one substitute goes up, suppliers will supply more of that.
Input Prices (ex: wages)
Competition (number of producers)
Expectations (ex: if a farmer feels soybeans will be expensive next season, they will supply more soybeans next year)
Complements in Production
By-products of something. For example you can sell cow meat from cows but also their milk.
If the price of one complement increases, the supply of it will increase and thus the supply of the other complement will also increase.
Substitutes in Production
Co-produced goods, so producers can choose to produce either. If the price of one substitute goes up, suppliers will supply more of that.
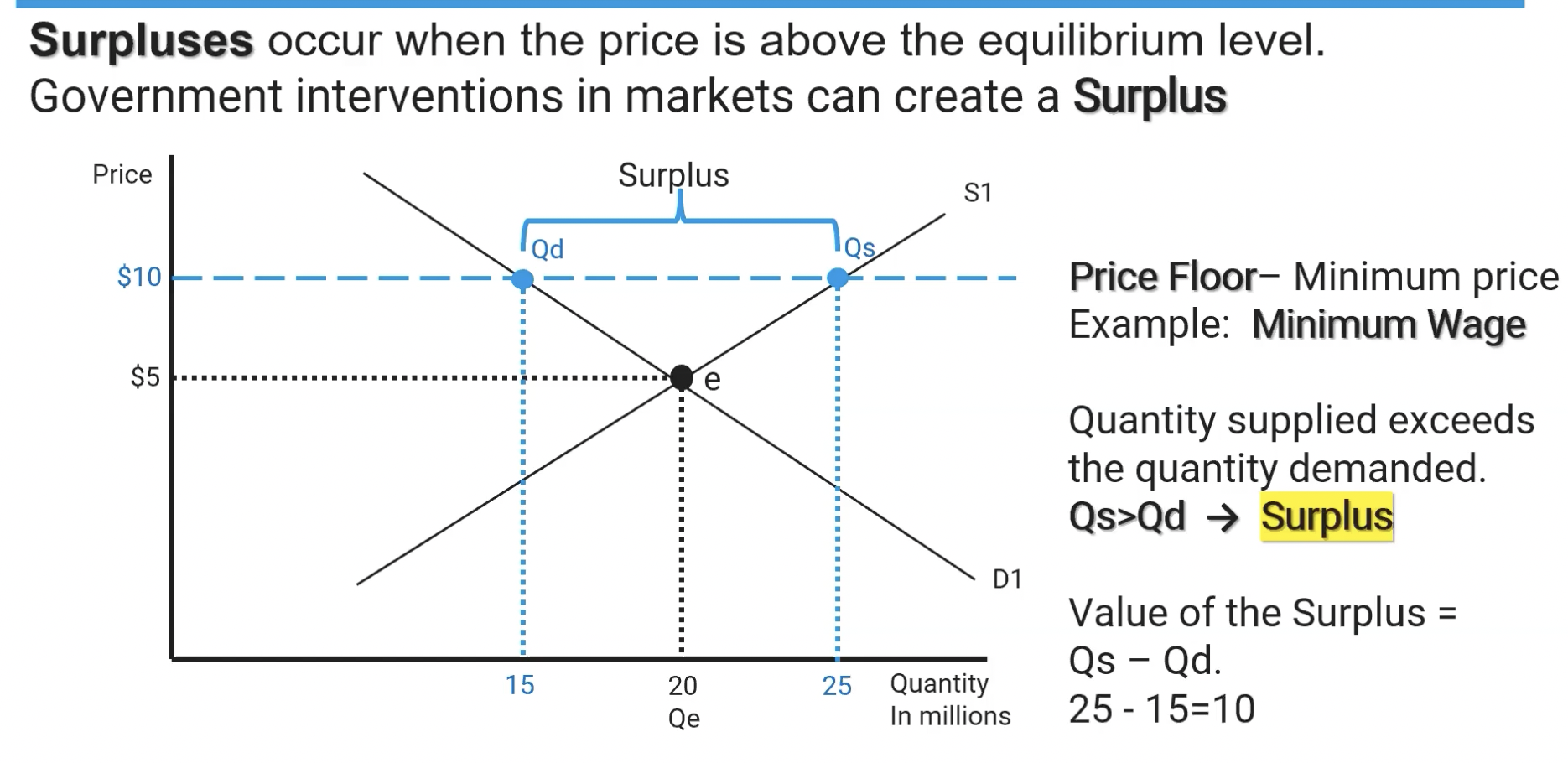
Price Floor
When the government institutes a MINIMUM price value for a product, thereby creating a surplus for the product.
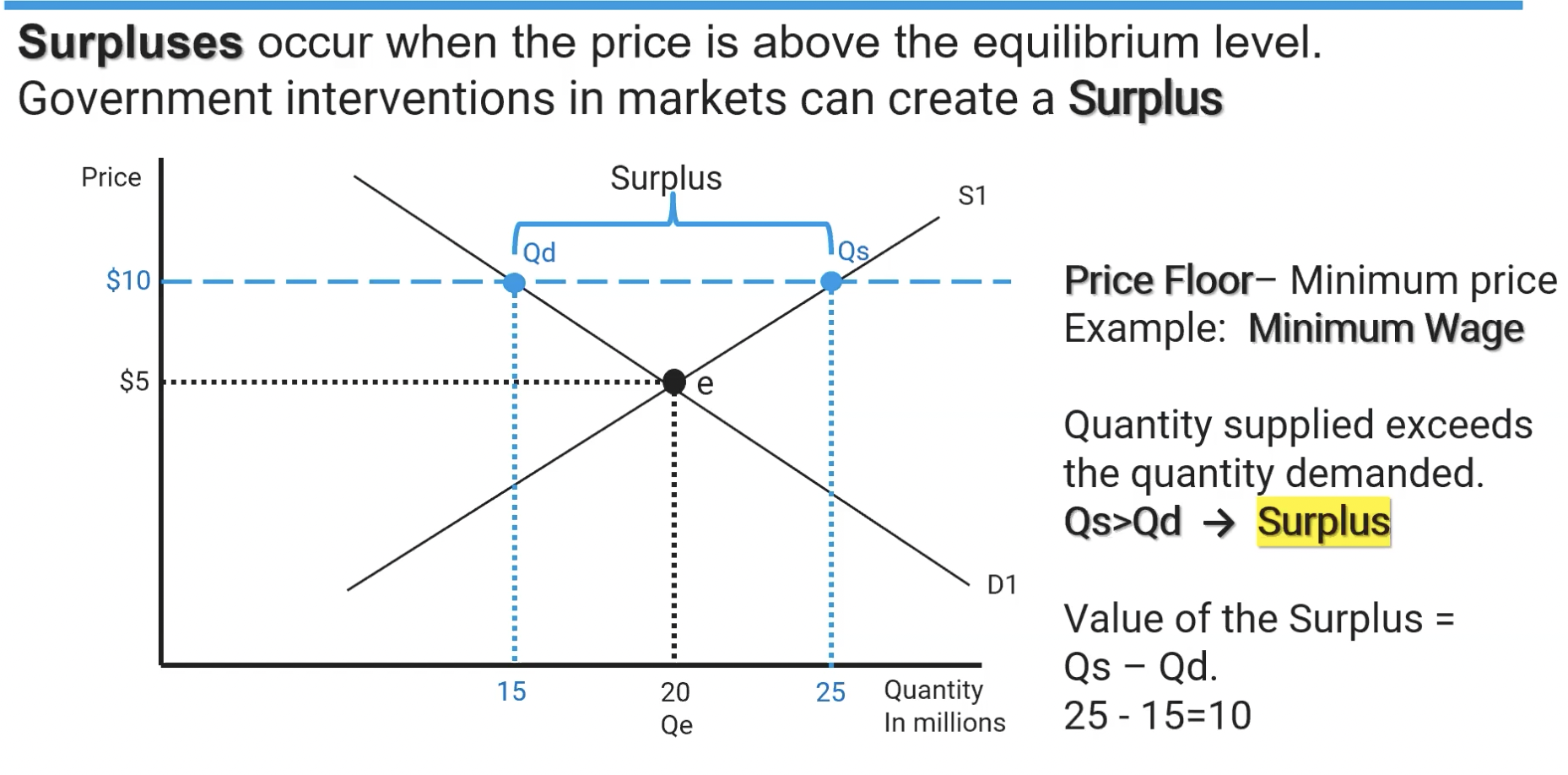
Surplus
Quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. Can be caused by a Price Floor being instituted by the government
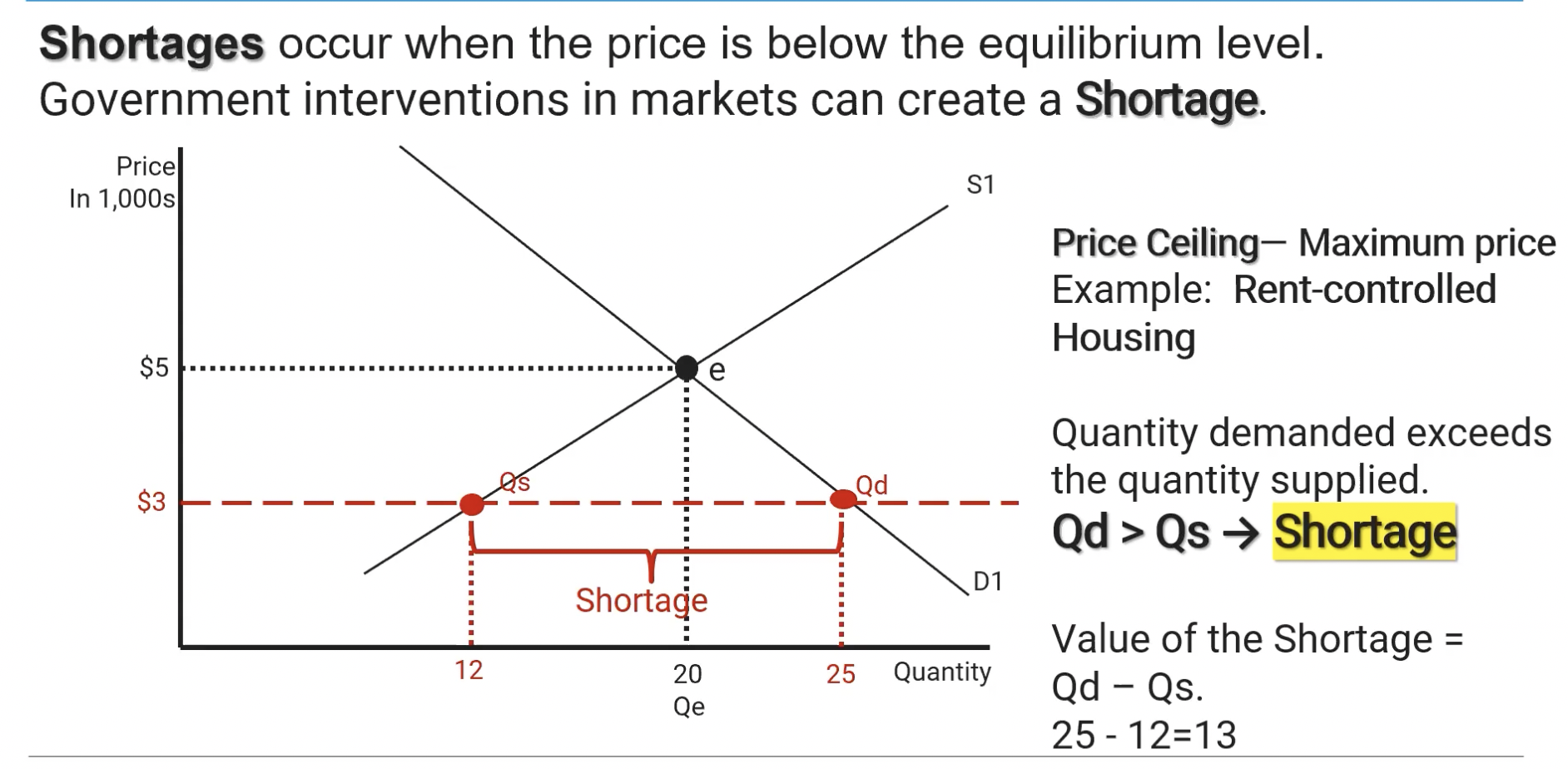
Price Ceiling
Government instituted MAXIMUM price value for a product, creating a shortage in the product.
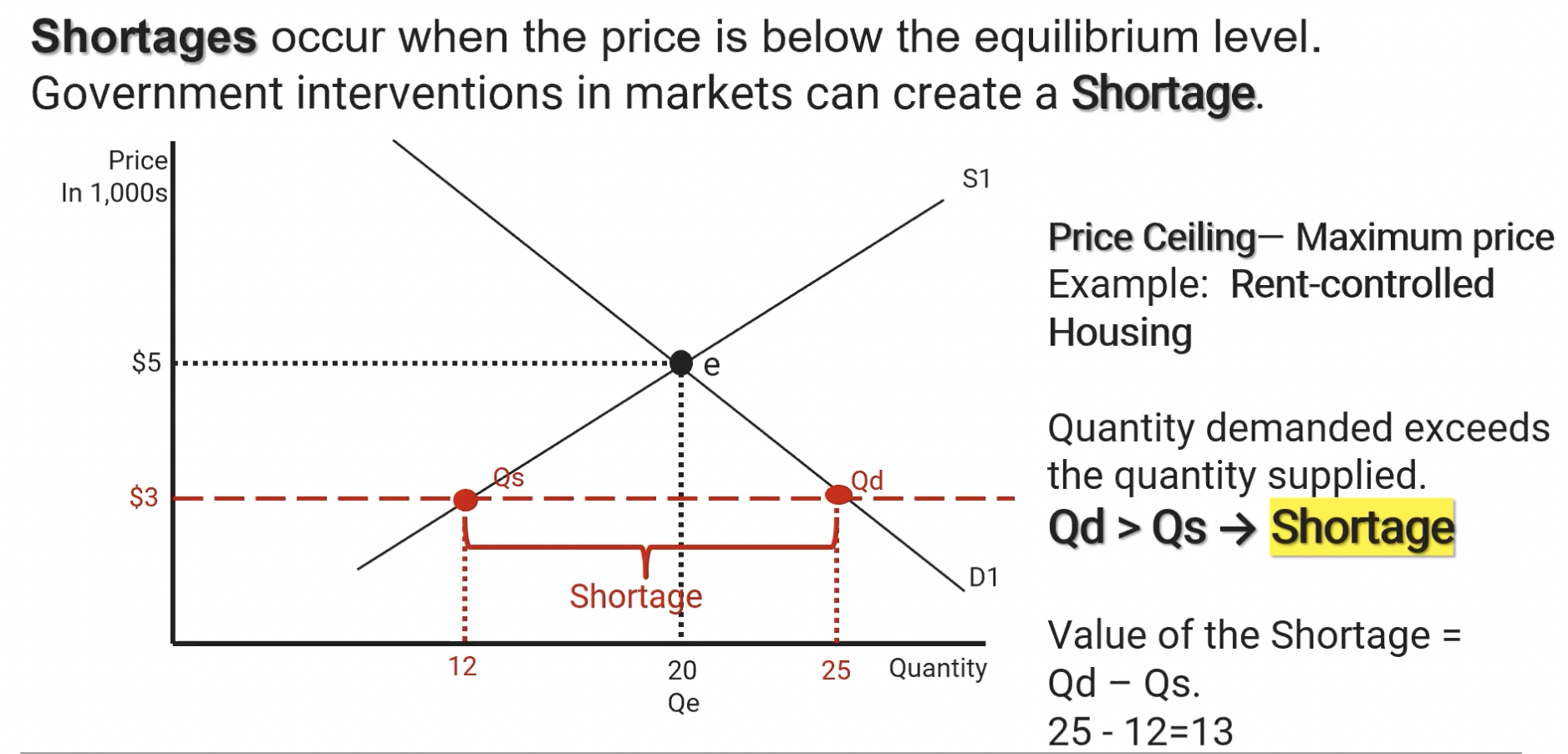
Shortage
Quantity supplied is less than the quantity demanded. Can be caused by a Price Ceiling being instituted by the government.