Biology Florida EOC
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
121 Terms
Independent Variable
- what is being changed or tested during experiment; cause
Dependent Variable
-what is being measured or observed during experiment; effect
Control Variable
-use as the comparison "group" in an experiment
What makes an experiment reliable?
-has been tested numerous times by more than one scientist
-it follows steps of scientific method
-no bias
-information came from third party
-study been retested
-results are published in scientific journal
Theory
-are subject to revision and modification over time
Laws
-developed when observations around the world are tested and retested until there is a consensus in a scientific community; not changed over time
Dissection Light Microscope
-lowest magnification for microscopes
-views organs and tissues during dissection
-views 3D specimens
Compound Light Microscope
-40x to 400x
-views tissue samples, blood, microorganisms, and larger details of some cells
-common classroom microscope
Transmission Electron Microscope
-passes a beam of electrons through a thin specimen
-mainly used to study internal structures of cells that cannot be viewed under light microscopes
Scanning Electron Microscope
-electron beam passes over specimens surface that is coated with thin layer of gold metal
-studies details of specimen's surface
-3D and black&white
Polar Molecules
-have an end that is slightly positive and an end that is lightly negative
-water
Hydrogen Bonding
-attraction between the slightly positive hydrogen of one molecule and the slightly negative oxygen of another water molecule
Surface tension
elastic-like forces existing on the surface of a liquid caused by asymmetry in the attractive forces between the liquid molecules
Cohesion
when two like substances attract to one another
Adhesion
when two unlike substances attract
universal solvent
water can dissolve into many substances: ionic compounds and polar molecules dissolve easily in water
water____ when it freezes
expands
frozen water is ____ dense
less
high specific heat
can absorb a lot of energy before changing temperature
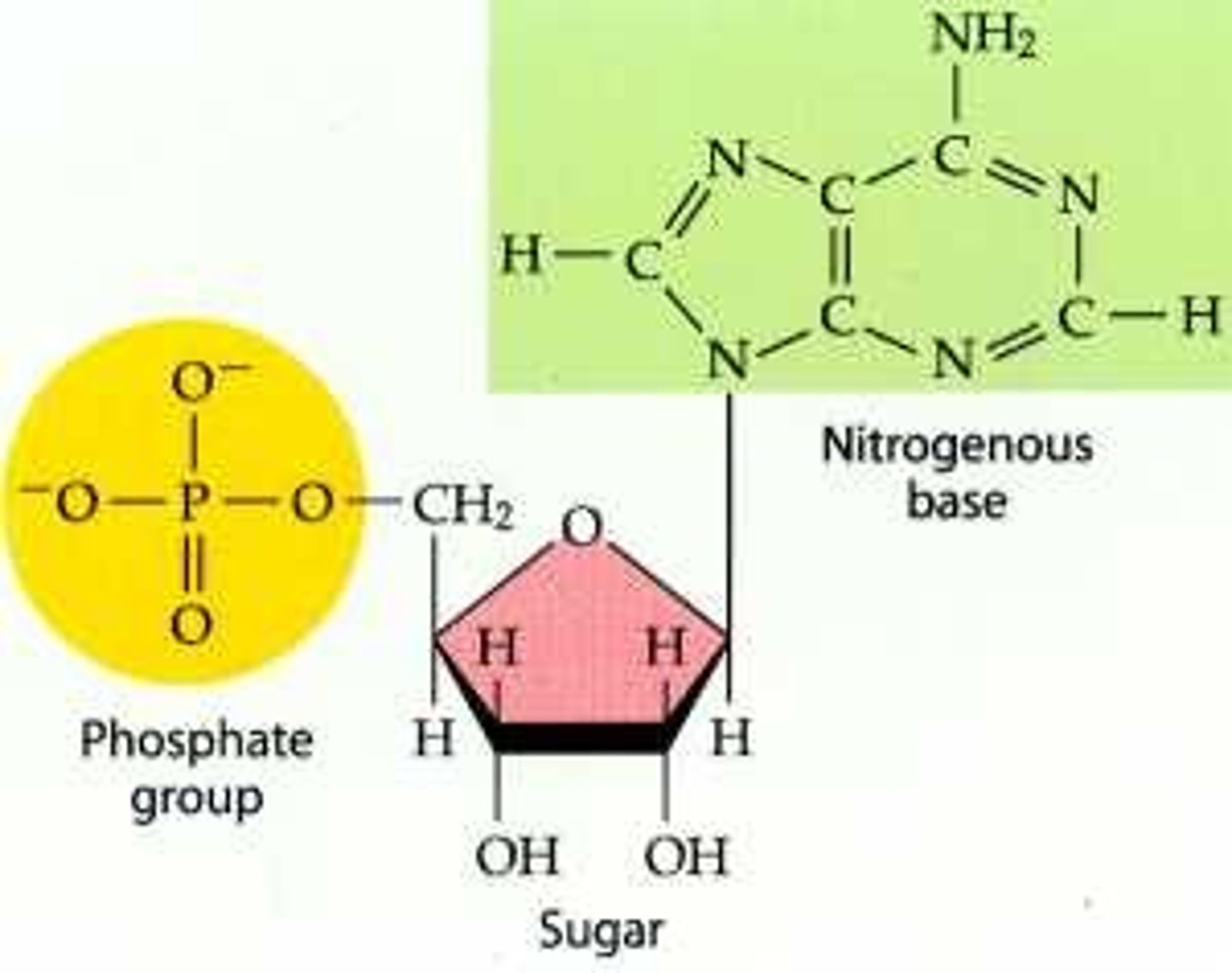
nucleic acids
-made of nucleotides
-codes to make protein
-ex: DNA and RNA
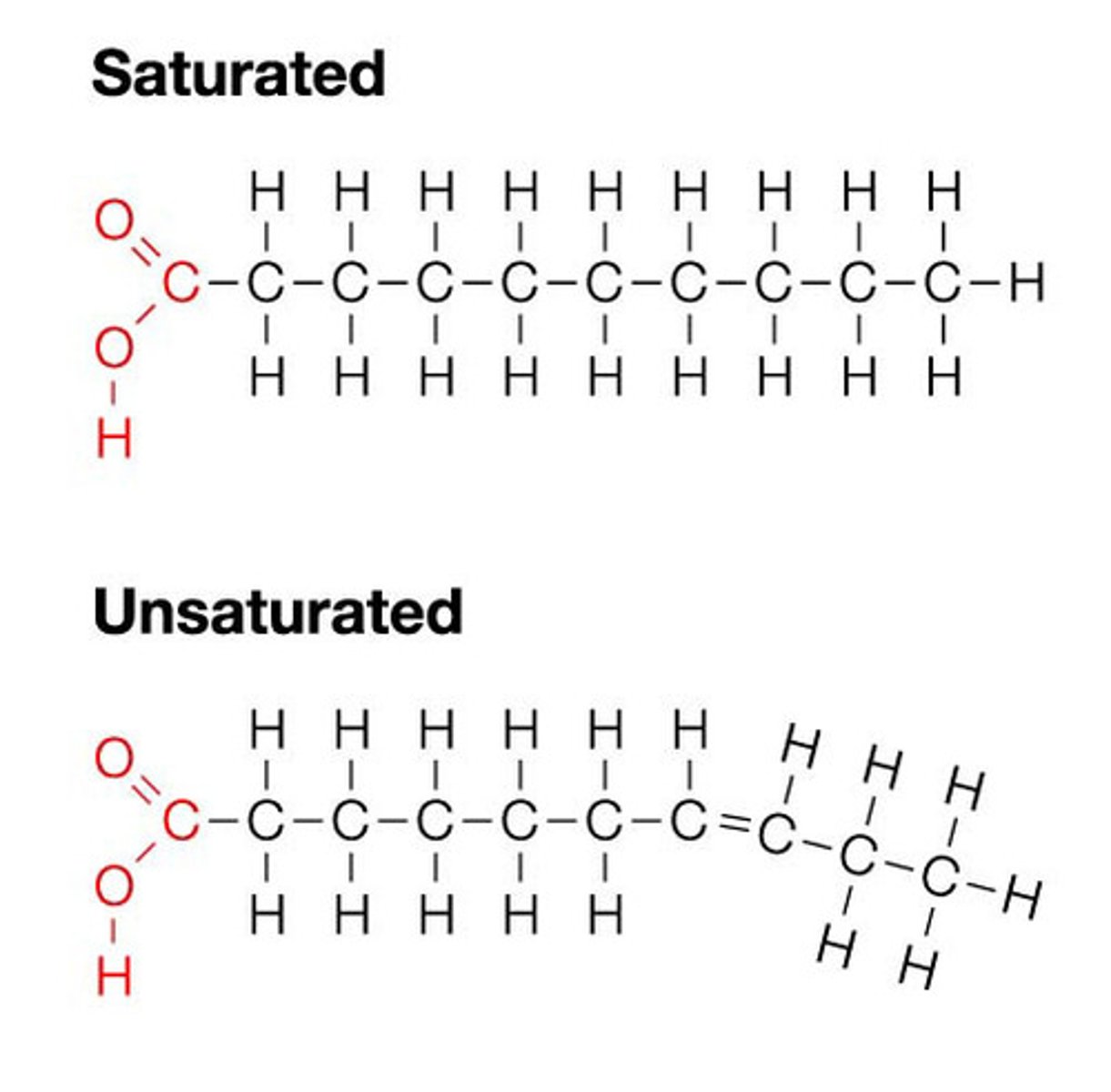
lipids
-fats that store energy and insulation
-phospholipids are cell membrane
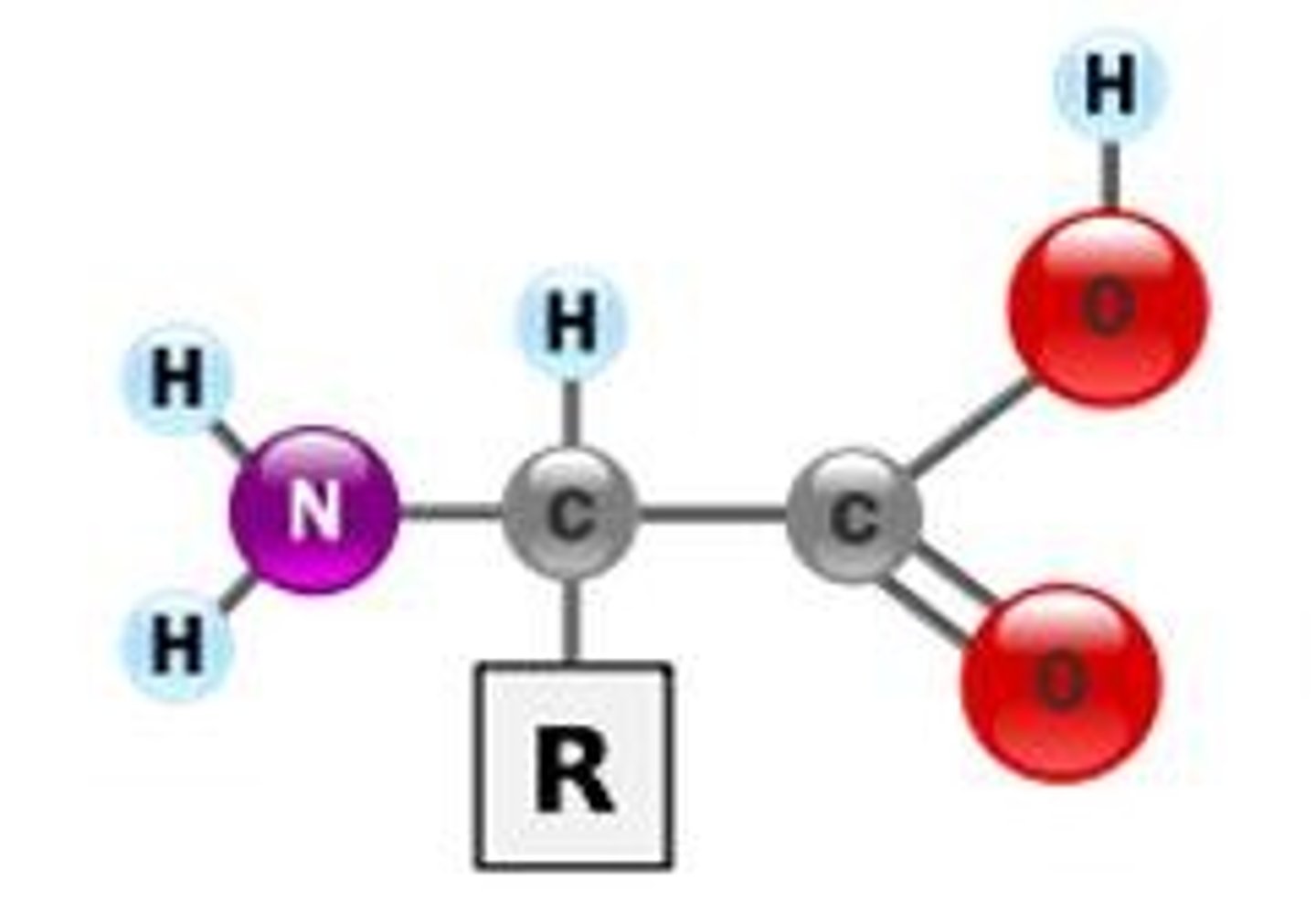
proteins
-made of amino acids
-structure, movement defense,signaling,etc
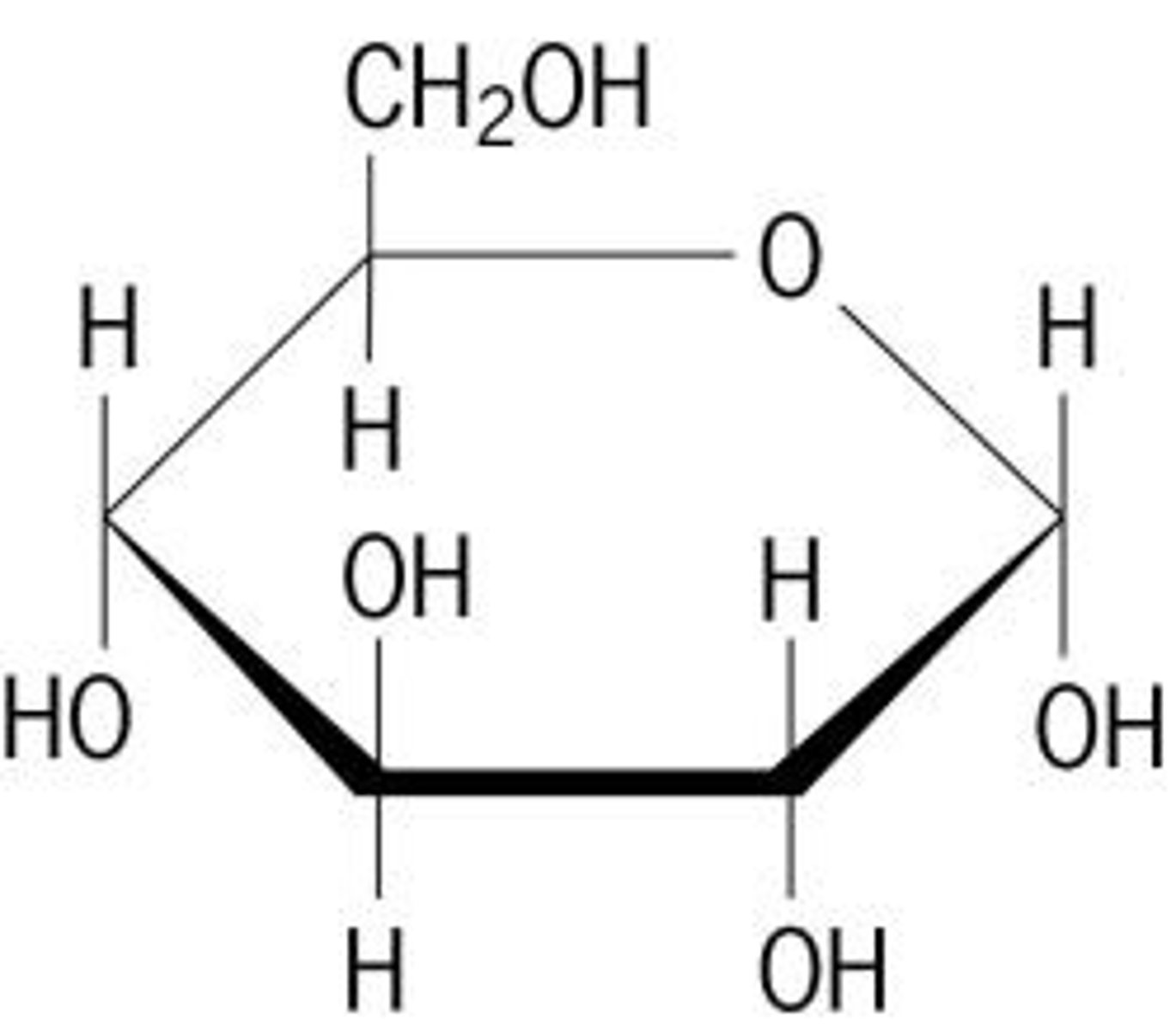
carbohydrates
-made of monosachharides
-energy,structure
enzymes
-biological catalyst that speeds up rate of reactions by lowering activation energy
-not used up during reaction
-are affected by environmental factors, like pH and temp.
cell theory
-all living things are made of cells
-cell is basic unit of structure and living things
-new cells are produced from existing cells
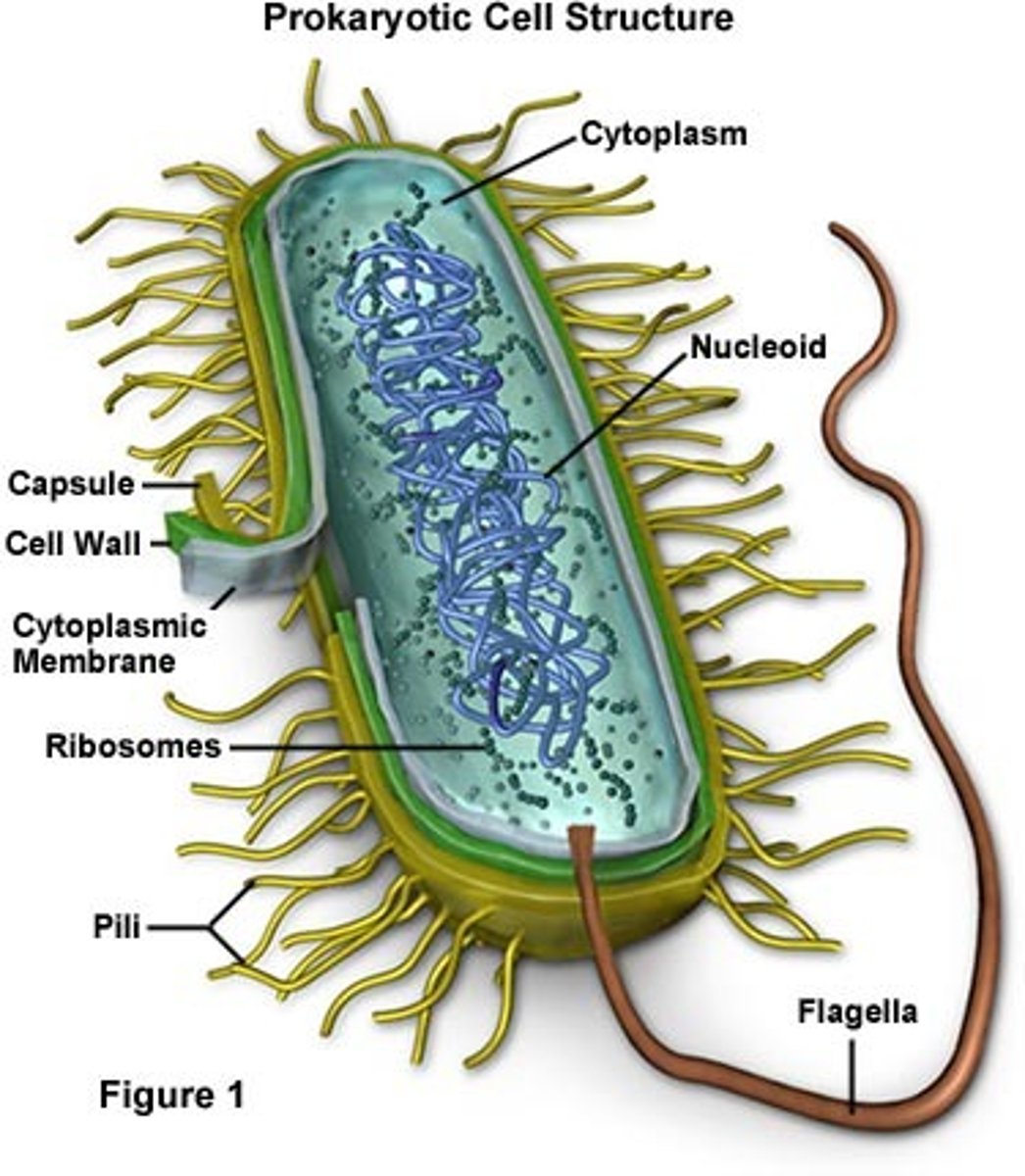
prokaryotes
-contain DNA
-no nucleus
-only single-celled
-few organelles
-basic
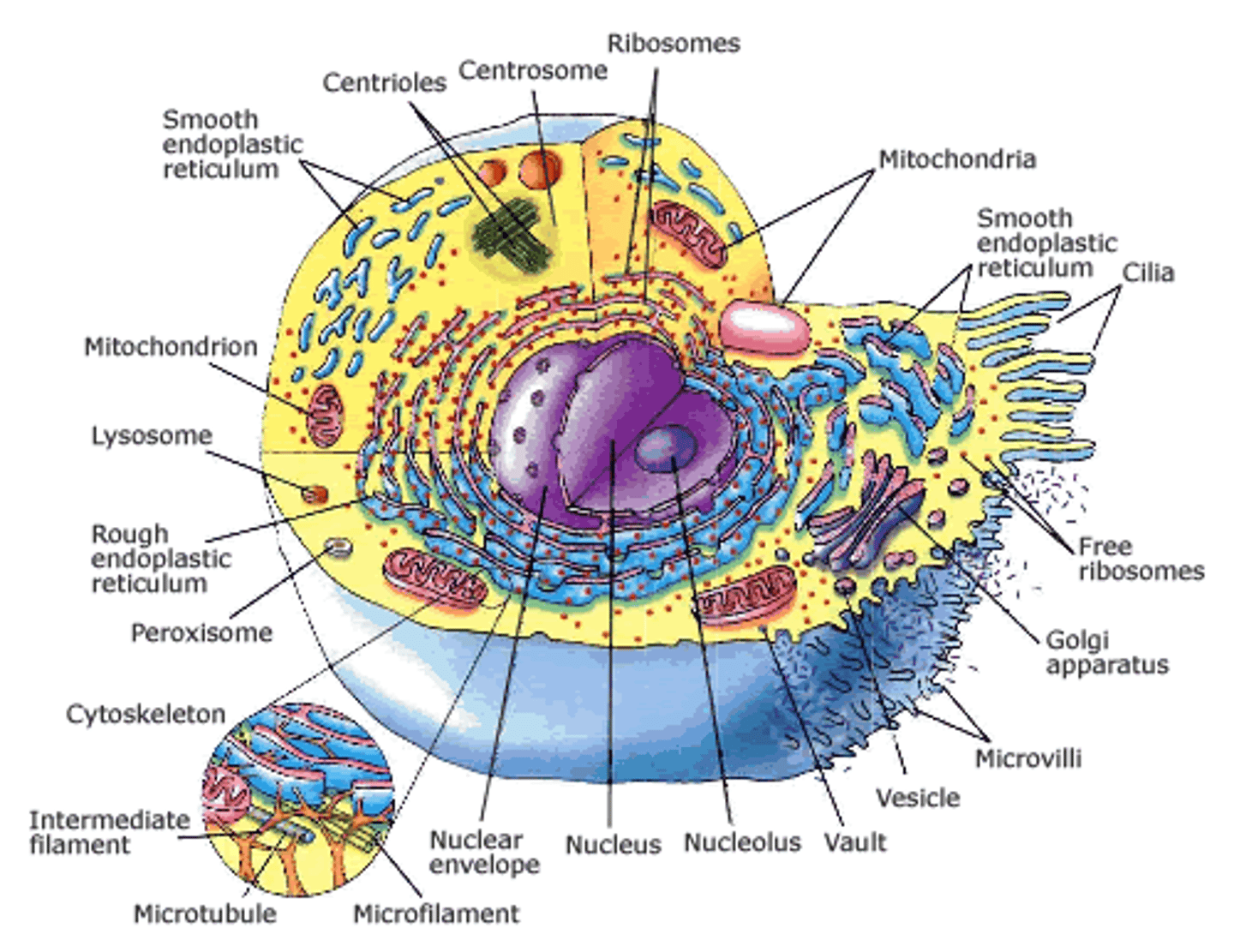
eukaryotes
-animal and plant cells
-contain DNA
-nucleus
-membrane bound organelles
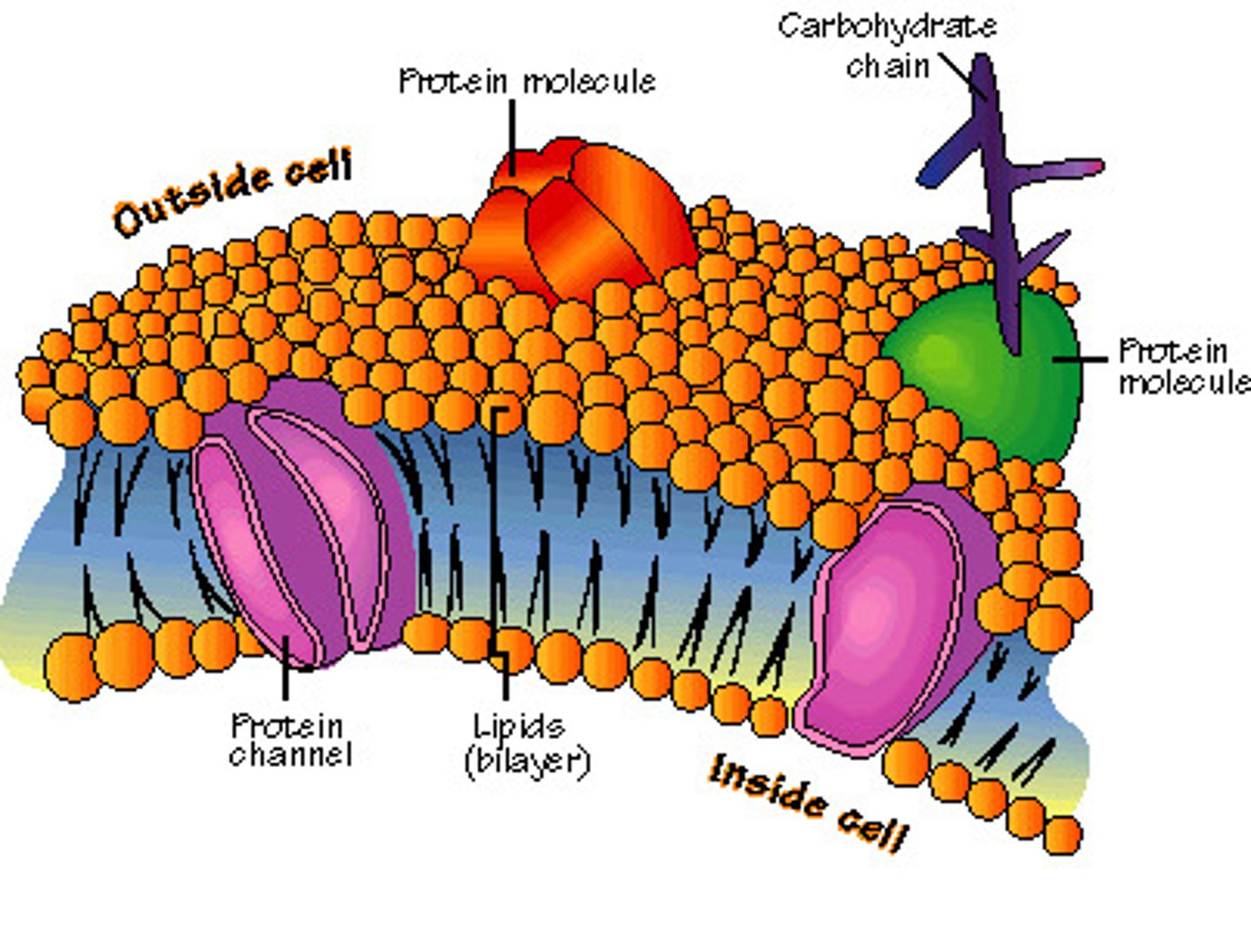
cell membrane
-selective barrier for the cell, allows some things to pass and others to not
-made of carbohydrates, phospholipids, and proteins
-selectively permeable
nucleus
-center of cell that contains most genetic information
cytoplasm
-thick fluid that fills up a cell and surrounds all other organelles
ribosomes
-found in cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum, responsible for protein synthesis
rough endoplasmic reticulum
-covered with ribosomes, responsible for making and storing proteins, and creates vesicles to carry new proteins to the Golgi apparatus
smooth ER
-detoxifies harmful substances
golgi apparatus
- responsible for modifying and storing proteins
lysosomes
-contain enzymes which break down large molecules to be used by the cell
vacuoles
-store food, water, and minerals
mitochondria
powerhouse of cell
cell wall
surrounds membrane and provides additional layer of protection
chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll and uses energy from sun to make glucose
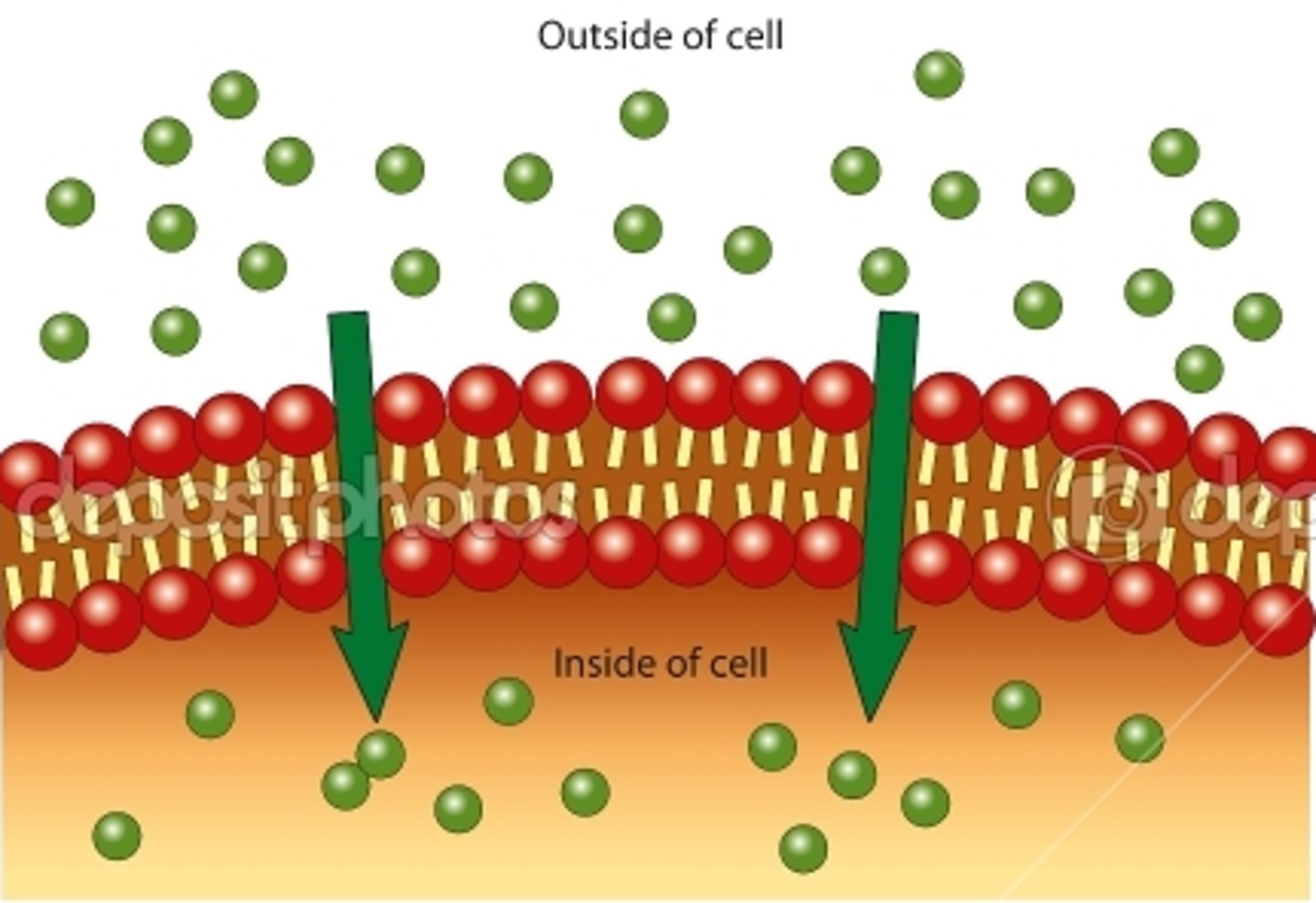
passive transport
-no energy needed, moves with concentration gradient (ex: simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion )
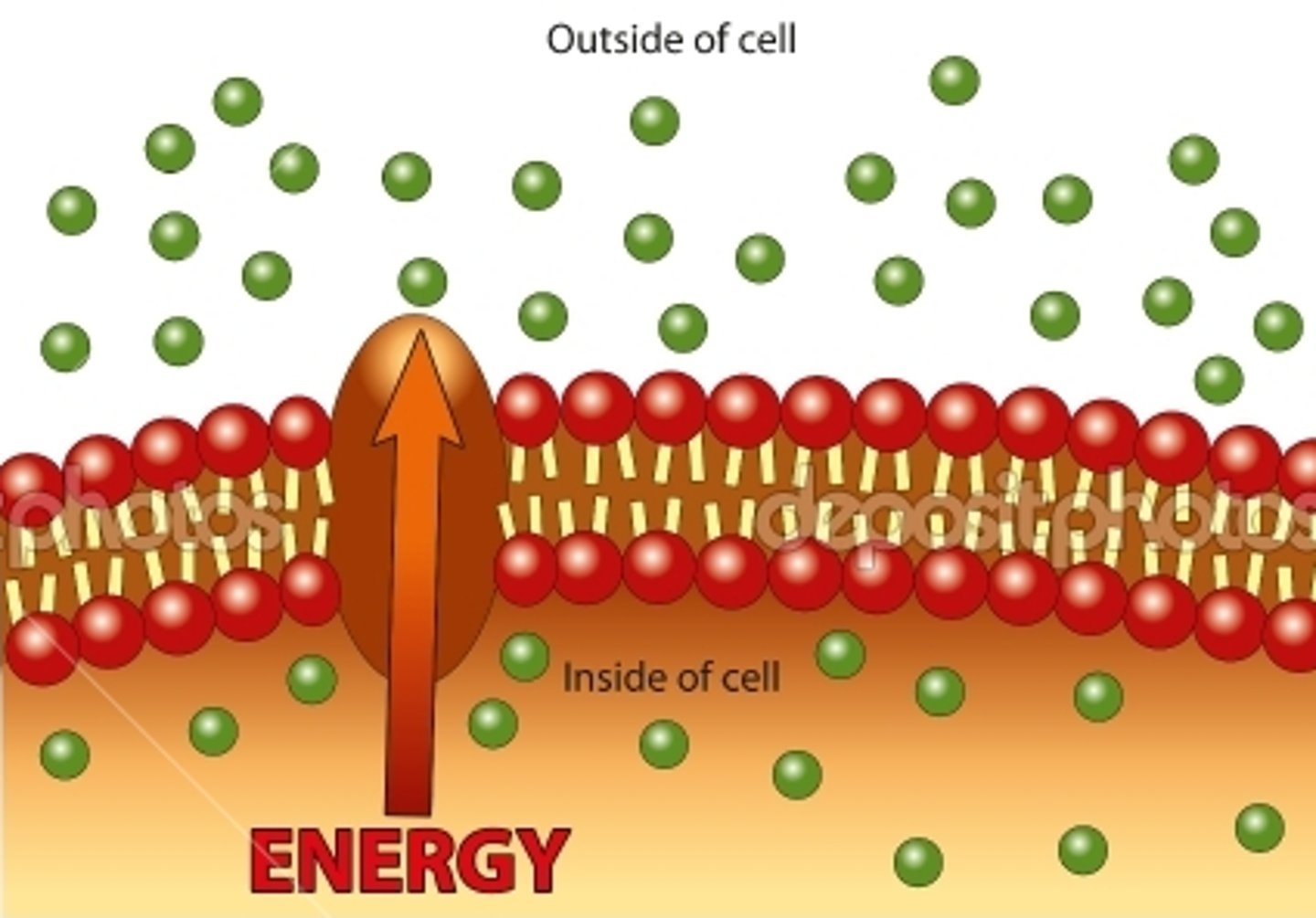
active transport
uses energy against concentration gradient
osmosis
movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane (passive transport)
Interphase
DNA duplicates (G1, S, G2 phase)
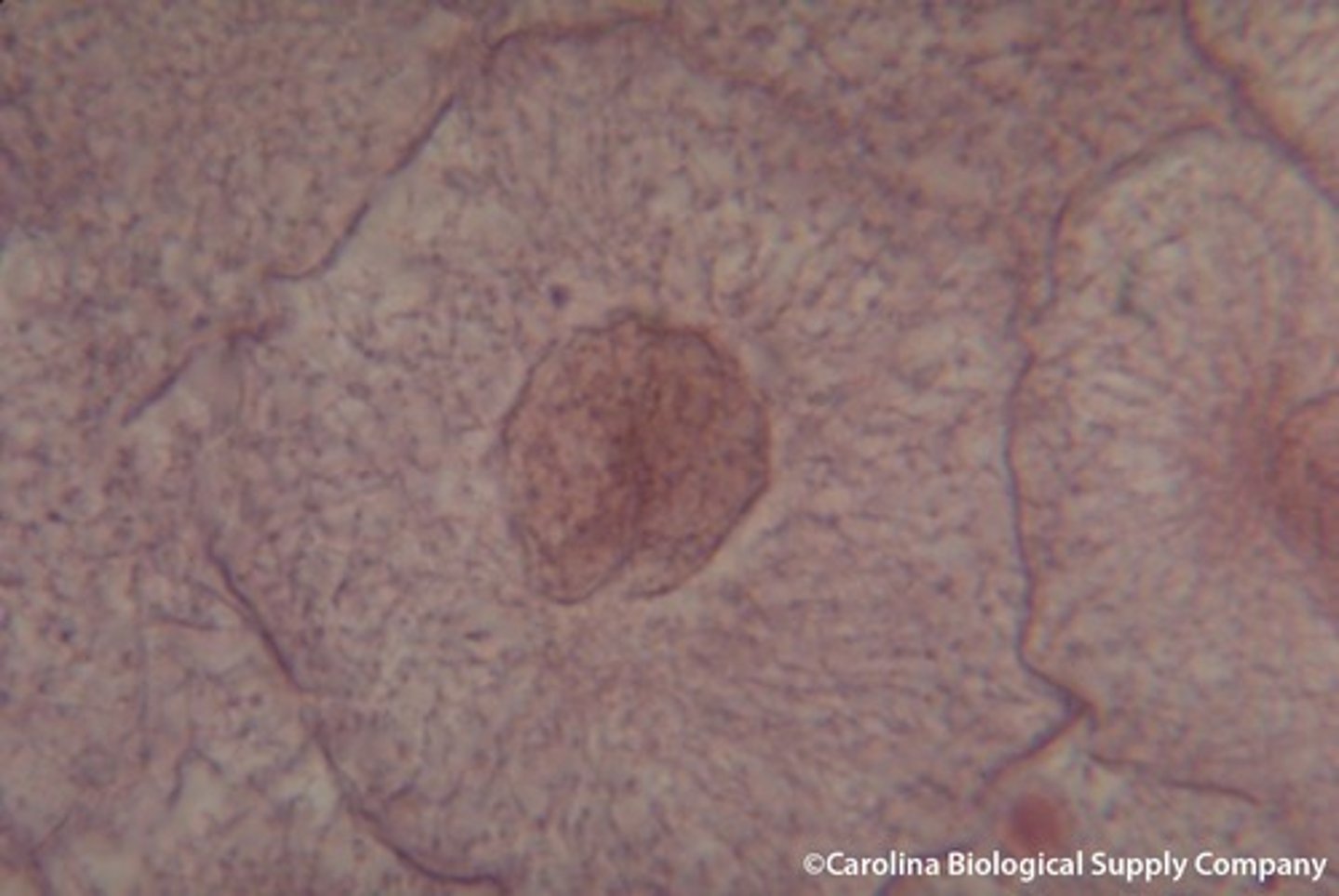
Prophase
chromosomes become visible, nuclear membrane breaks down, and centrioles organize spindle fibers
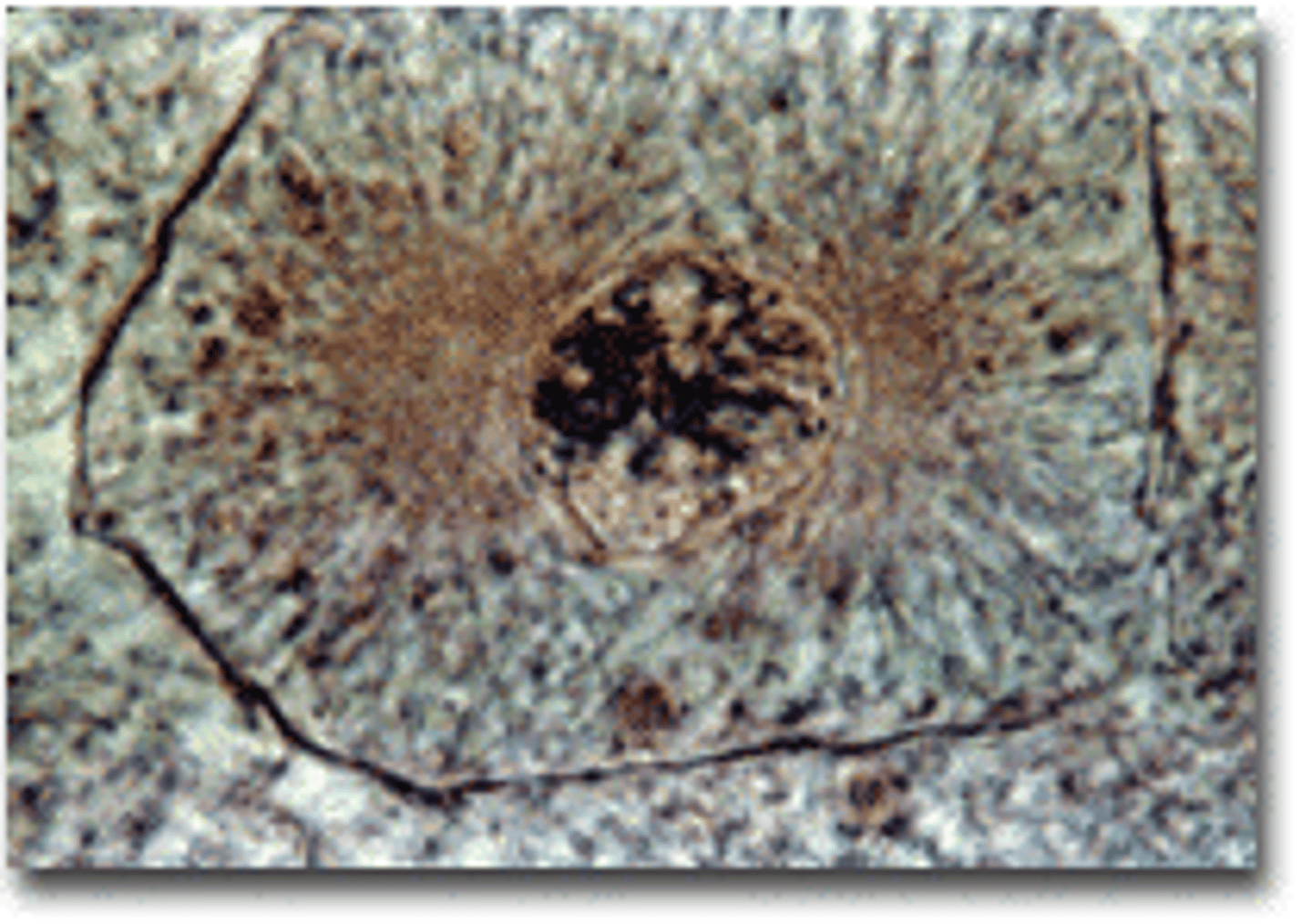
Metaphase
sister chromatids pairs line up in middle of cell and spindle fibers attach at middle of each pair
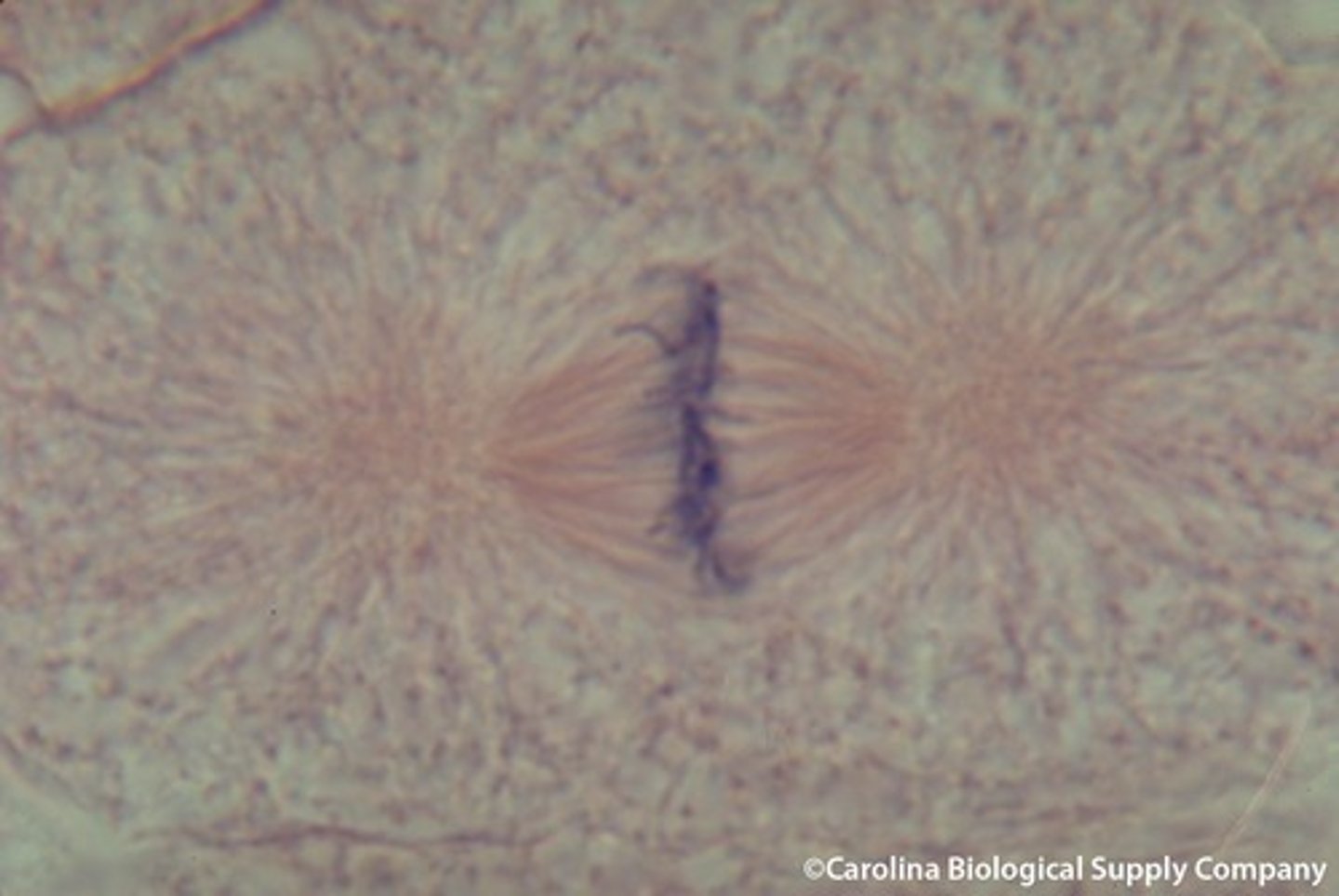
Anaphase
individual chromosomes are pulled apart and move to opposite sides of the cell
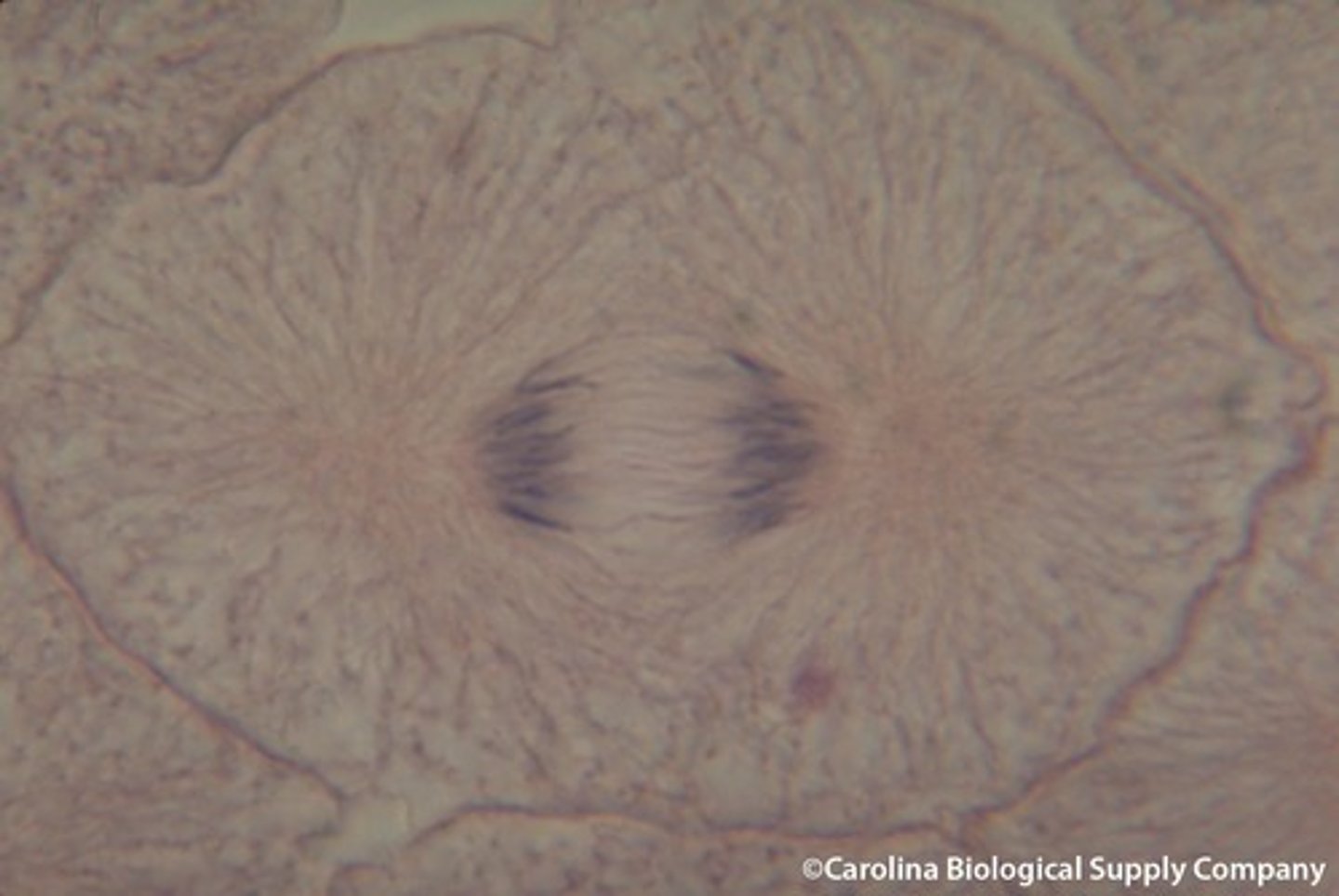
Telophase
chromosomes stretch out and become tangled chromatin again. nuclear envelope form, and spindle breaks apart
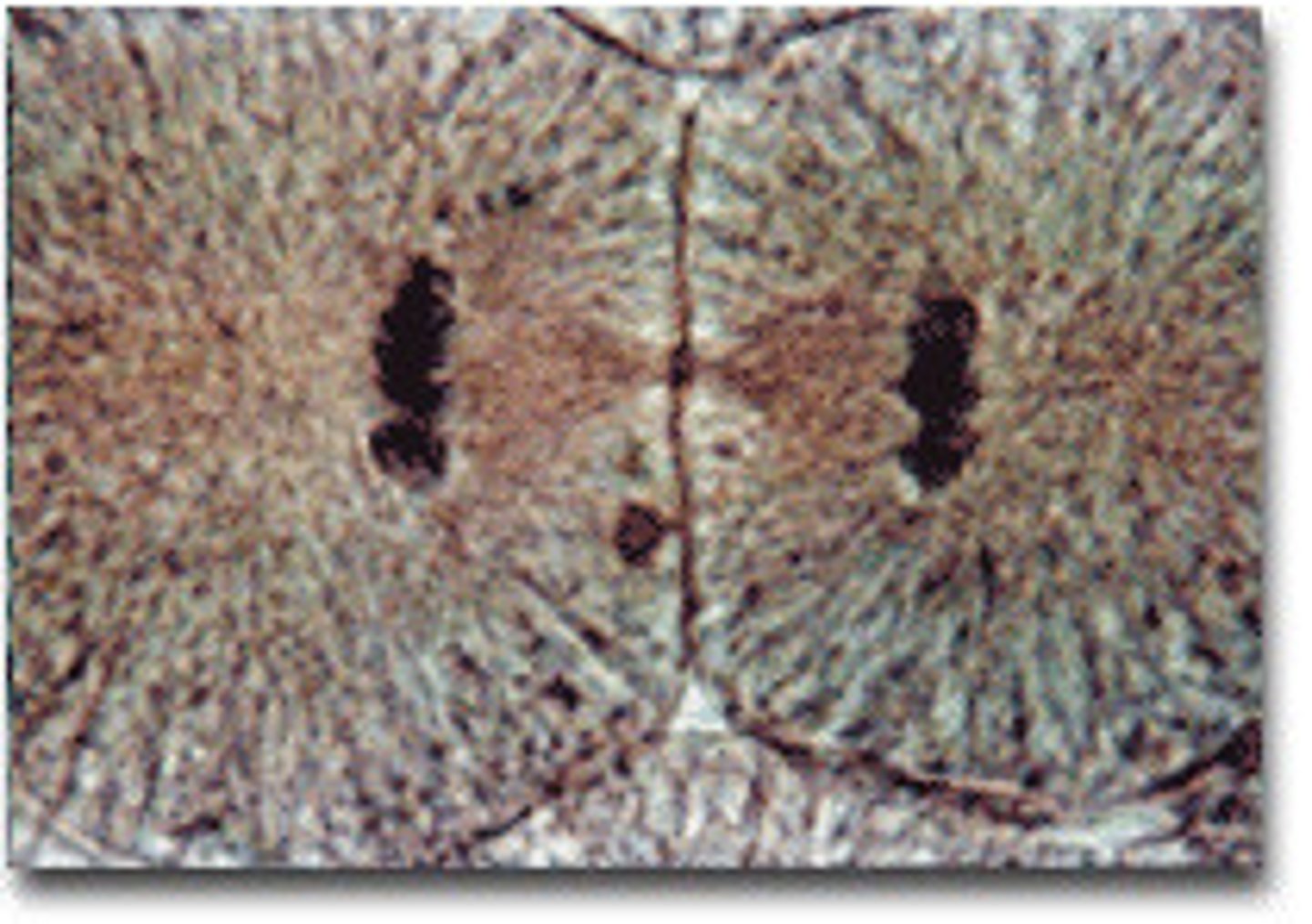
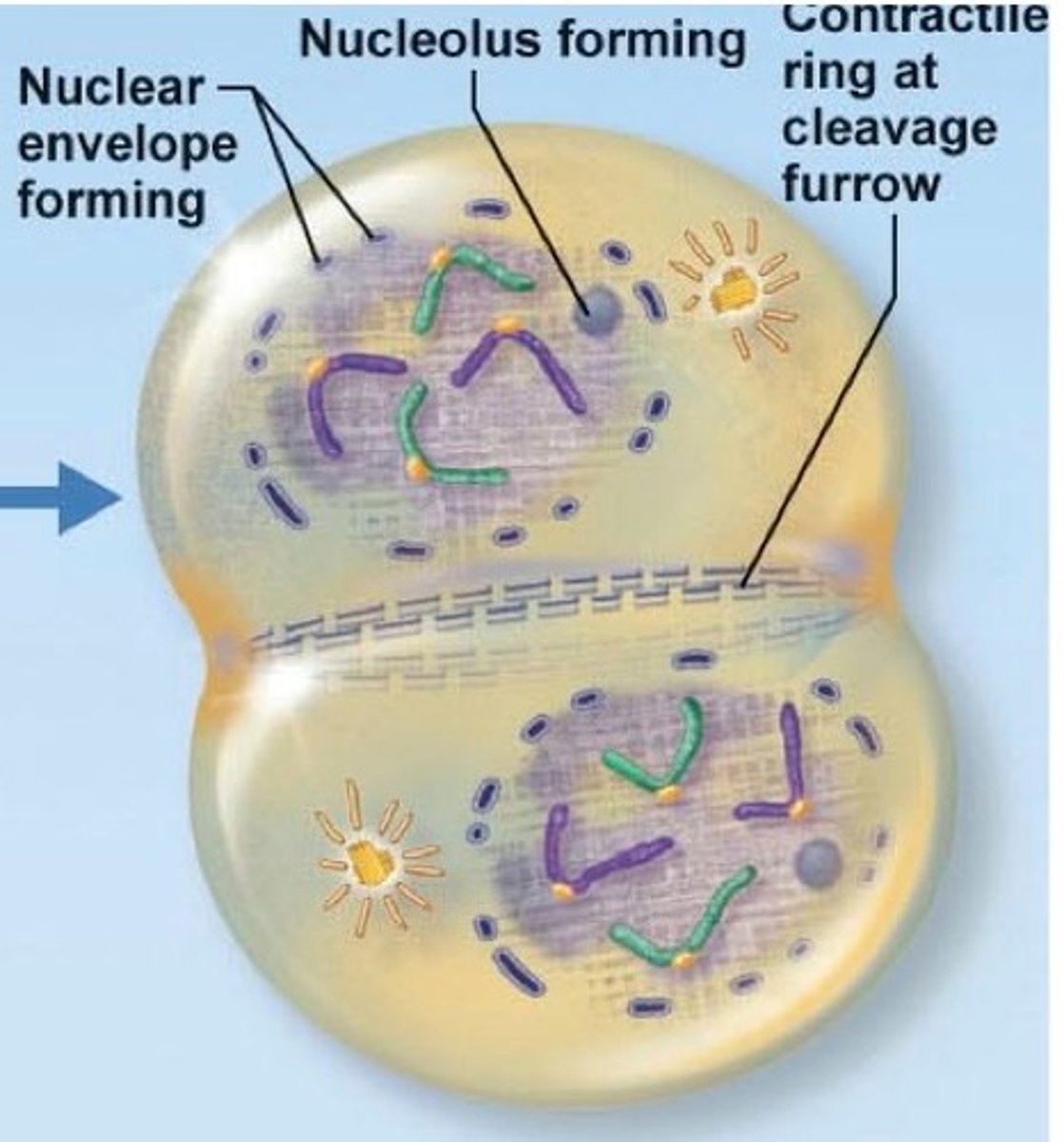
cytokinesis
cell divides into two separate cells: in plansts a cell plate forms
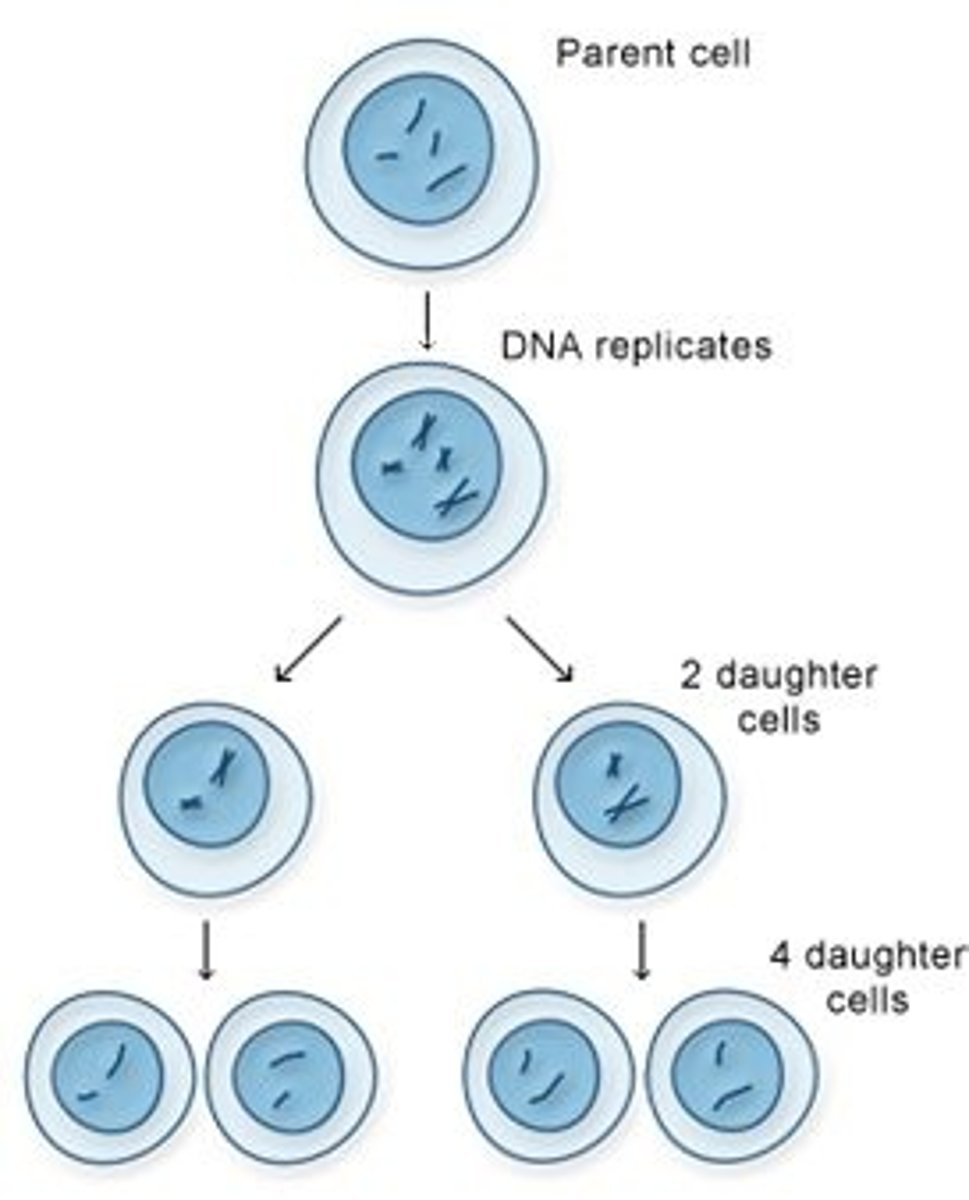
Meiosis
-makes four haploid daughter cells that are gametes
-each offspring gets one gamete from each parent
phenotype
-physical expression
genotype
organisms inherited genes
homozygous
having identical alleles for a trait
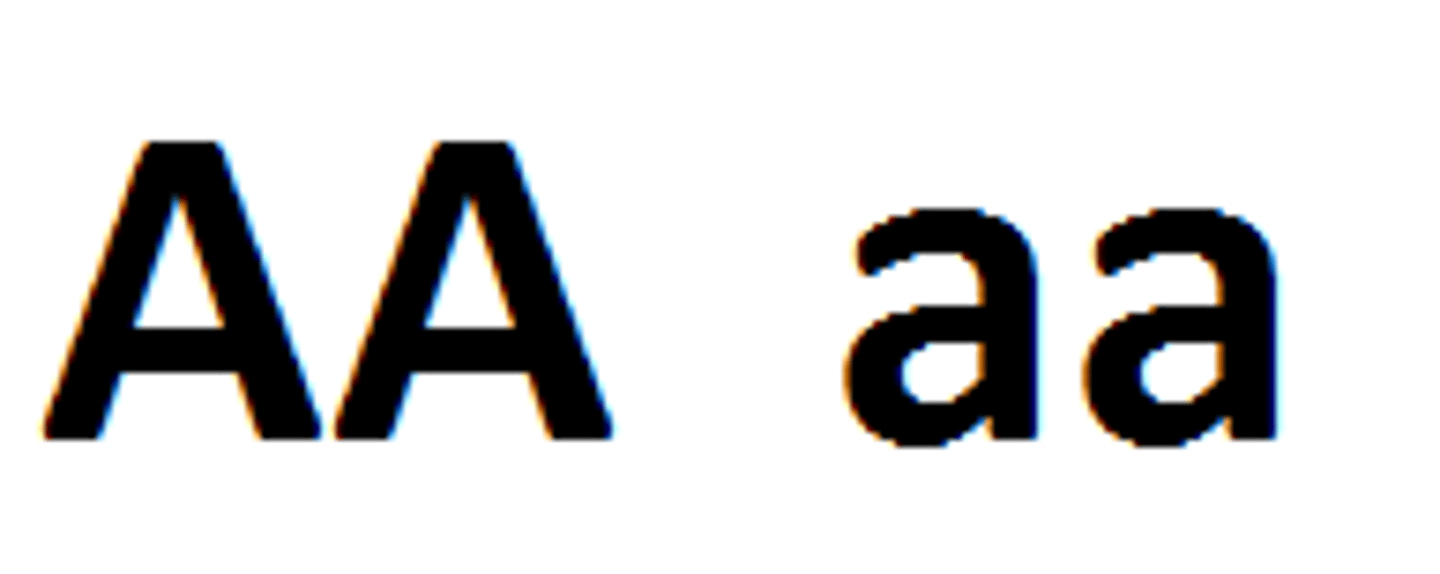
heterozygous
having different alleles for a trait

incomplete dominance
alleles for the genes are neither dominant nor recessive
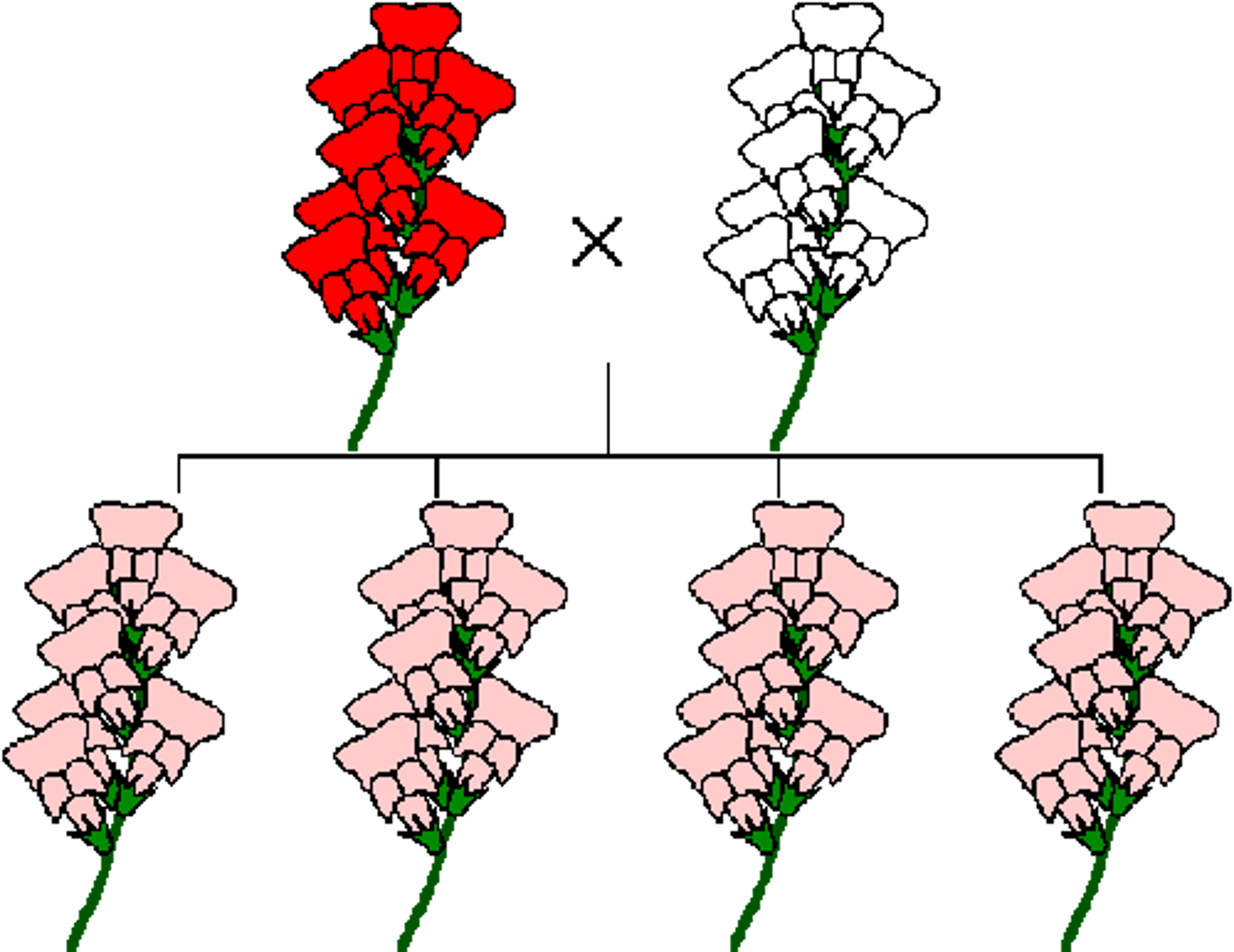
codominance
traits from both alleles are expressed in phenotype of offspring
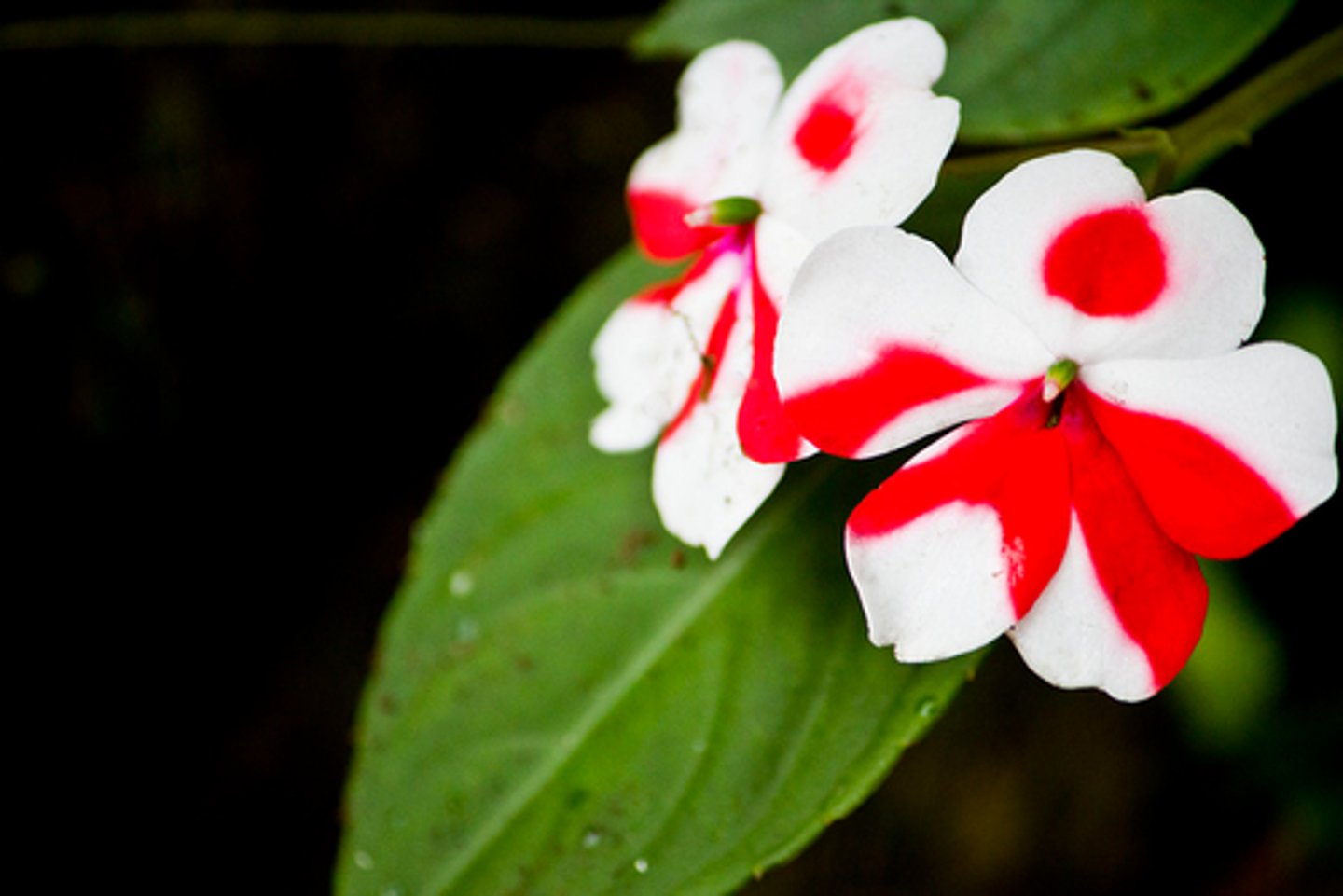

sex-linked traits
genes carried by sex chromosome
independent assortment
genes for different traits segregate independently during gamete production
polygenic inheritance
traits controlled by more than one gene
multiple alleles
more than two alleles for one gene
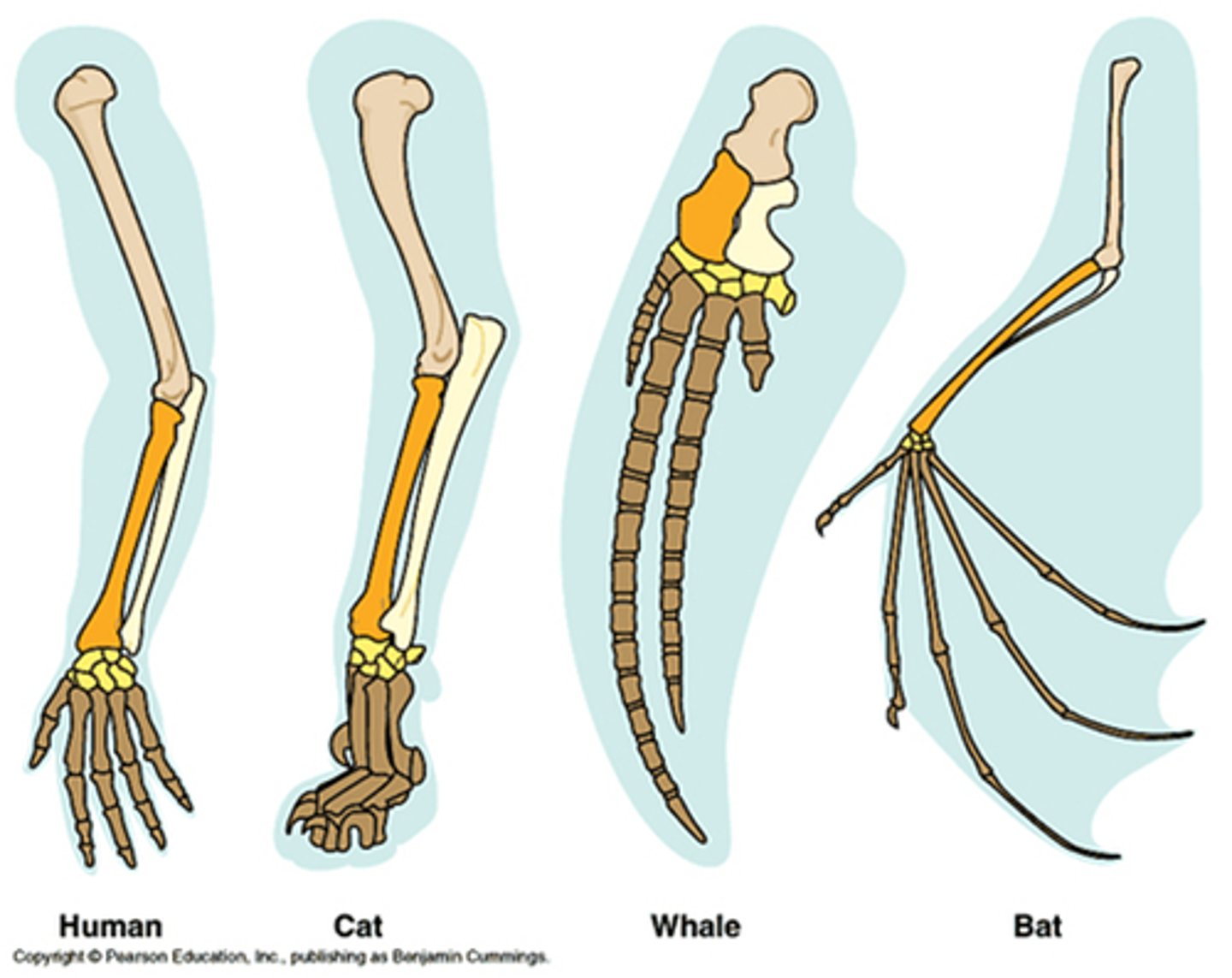
homologous structures
similar structures found in varying animals that evolved from a common ancestor
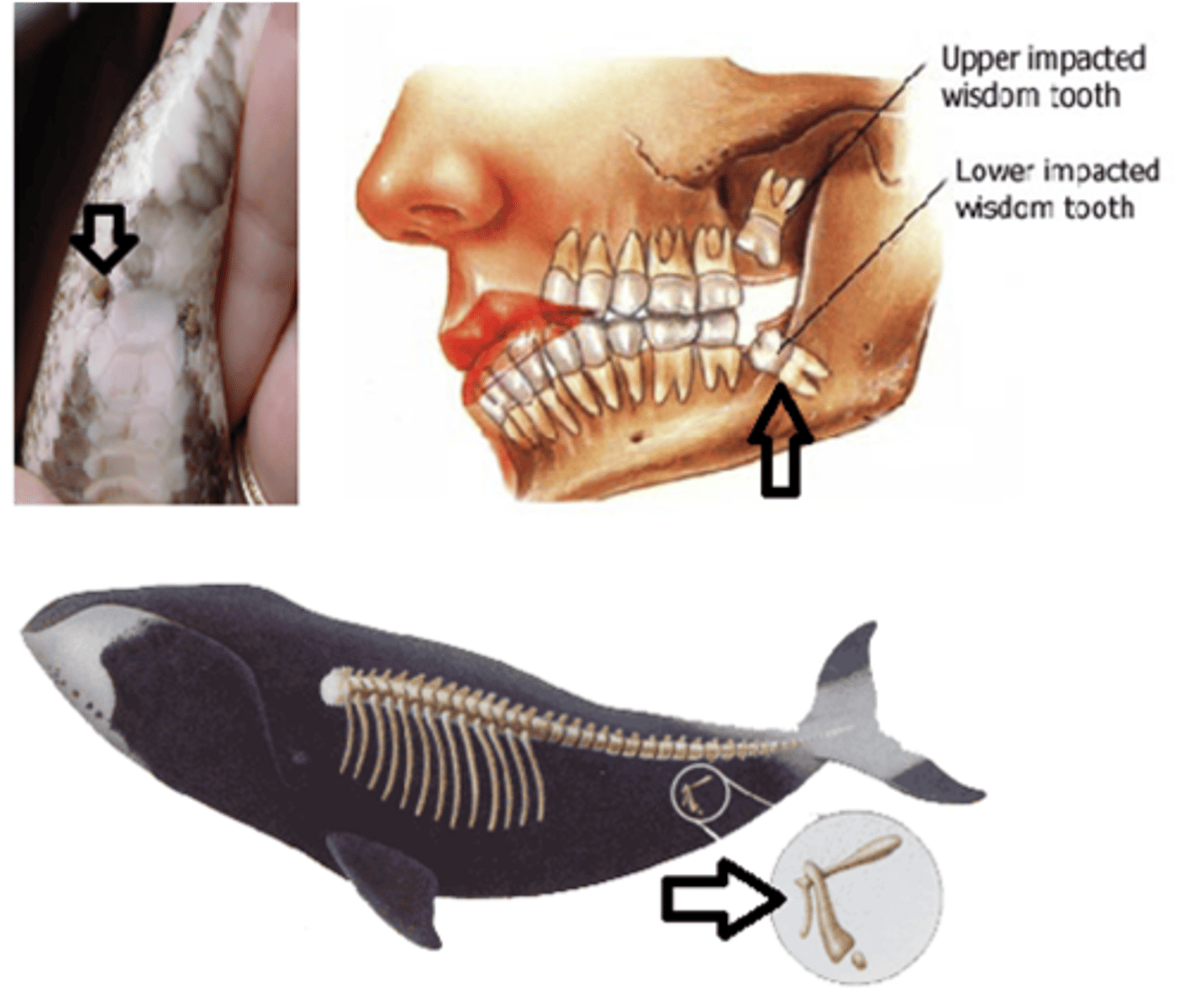
vestigial structures
structure in an organism that no longer serves its original function
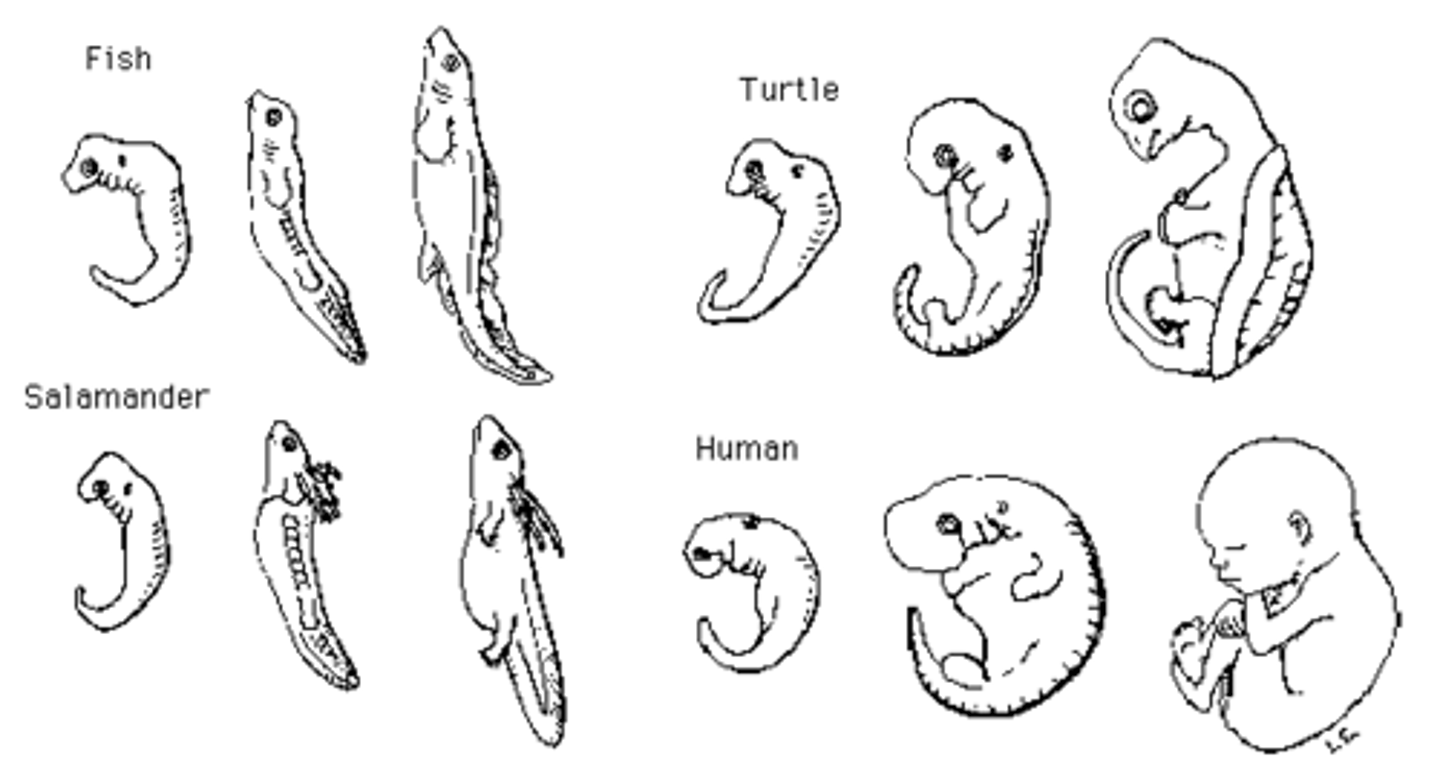
Comparative embryology
closely related organisms go through equivalent stages of embryonic development.
Natural Selection
evolution of a population to become better adapted to their local environment over many generations
Cladogram
organizes organisms based on the physical traits of their ancestors and descendants
6 major kingdoms
Bacteria, Archaebacteria, Protista, Plantae, Fungi, and Animalia
Bacteria
-prokaryotic
-unicellular
-binary fission
-cell walls with peptidoglycan
-found everywhere
Plantae
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-autotrophic
-cell walls made of cellulose
-sexual or asexual
fungi
-eukaryotic
- mostly multicellular
-heterotrophic
-decomposers and cell walls made of chitin
Animalia
-eukaryotic
-multicellular
-heterotrophic
-sexual reproduction
-complex organ system
Structure of DNA
Double helix
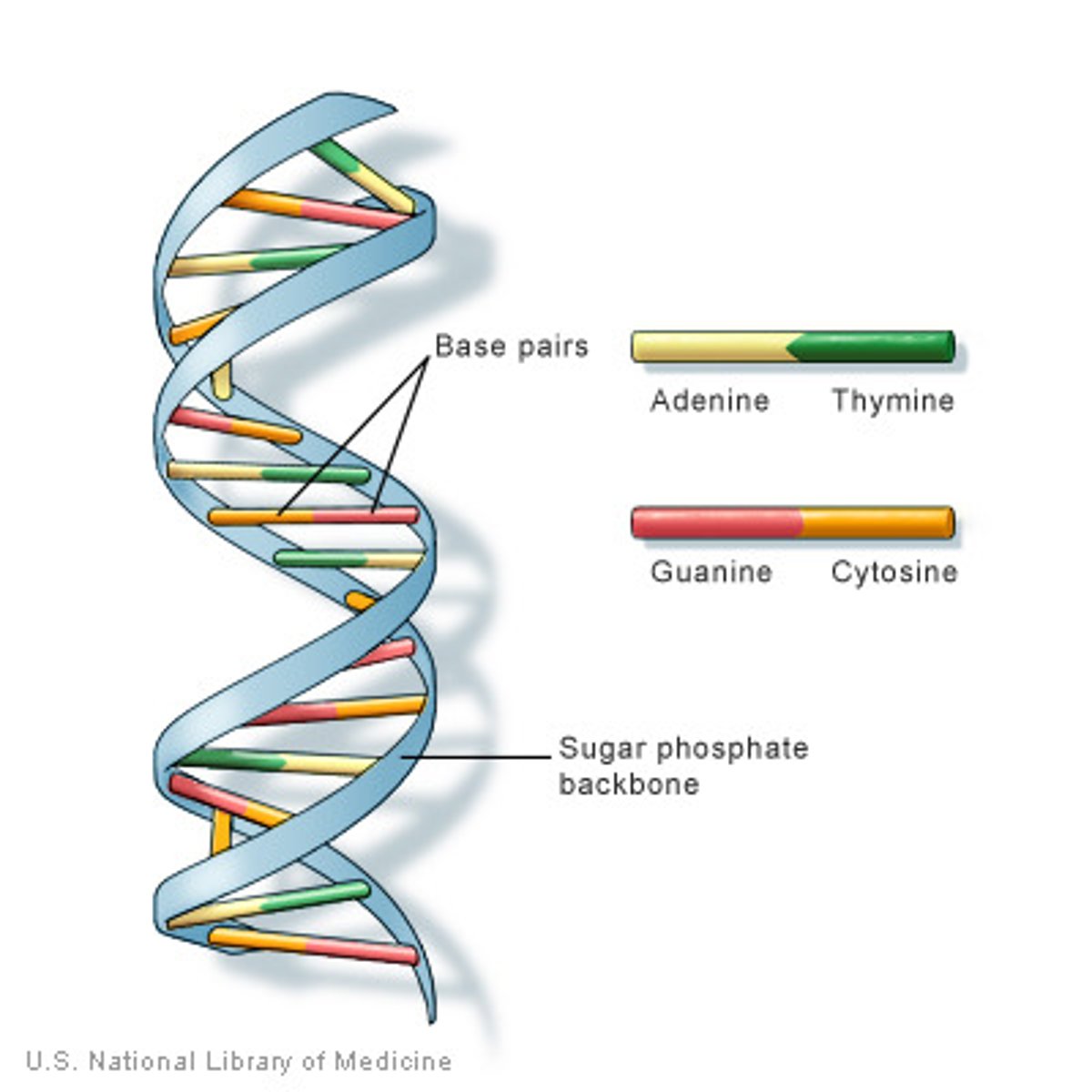
Hydrogen bonding
Form between the nitrogenous bases of each strand, providing just enough attraction to hold the two strands together
DNA is copied in
replication, during the S phase of interphase
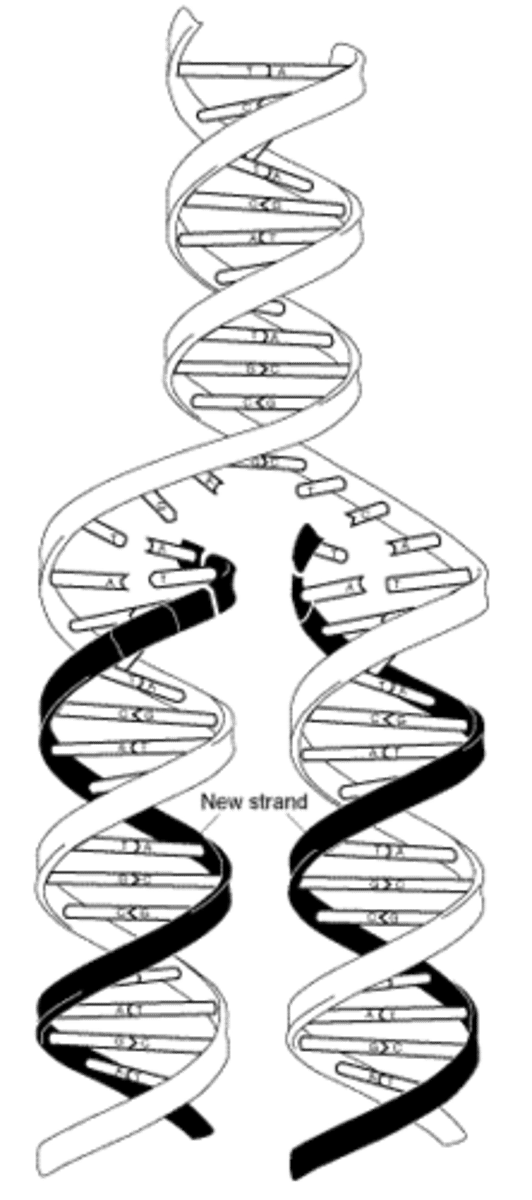

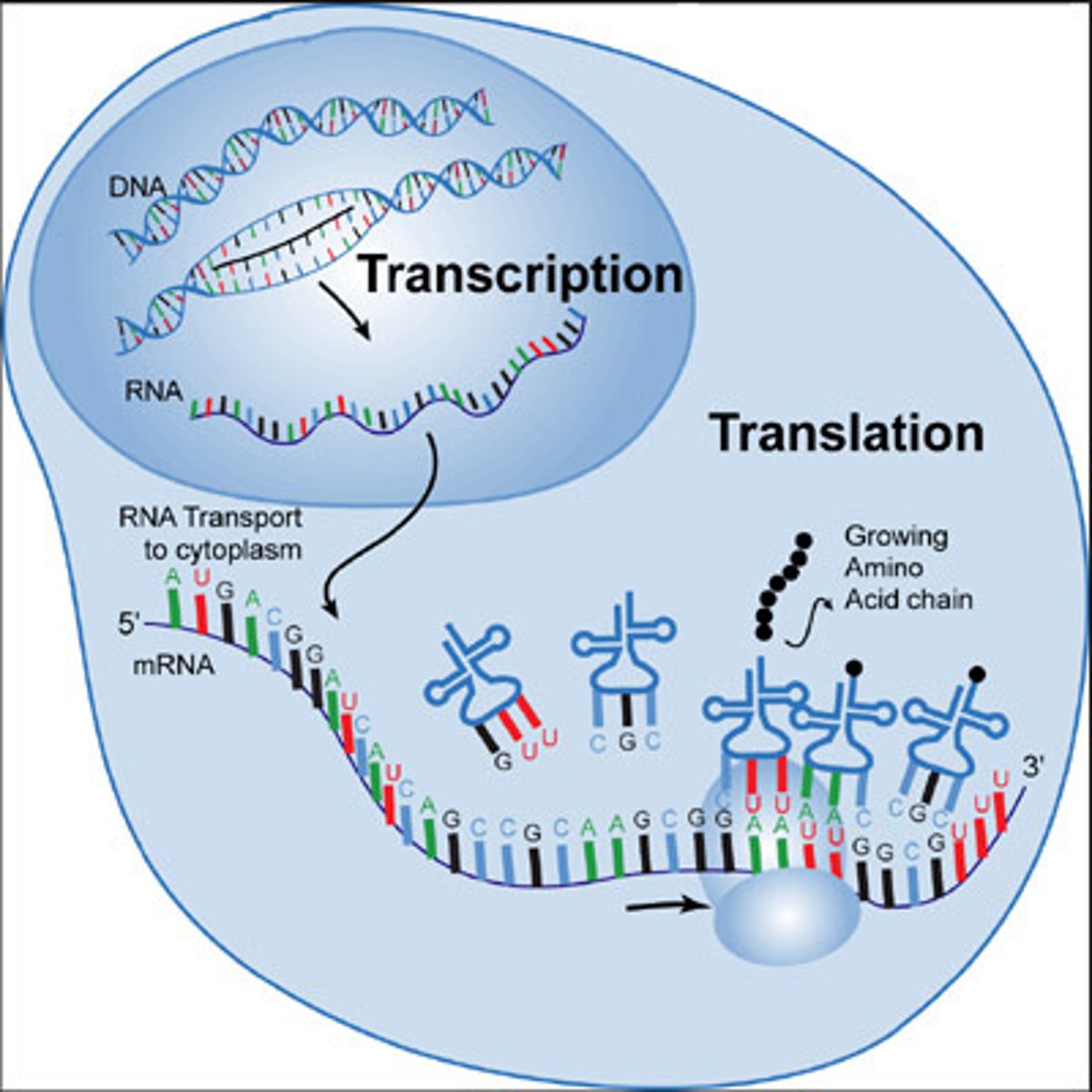
Transcription
-Occurs in the nucleus
- RNA polymerase bonds to the DNA molecule
- DNA molecule unzips as RNA polymerase moves down the DNA molecule.
-Free floating nucleotides will bond to one side of the DNA molecule creating a messenger RNA (mRNA)
-DNA rezips behind the RNA polymerase molecule.
-continues until the creation of the RNA molecule is complete
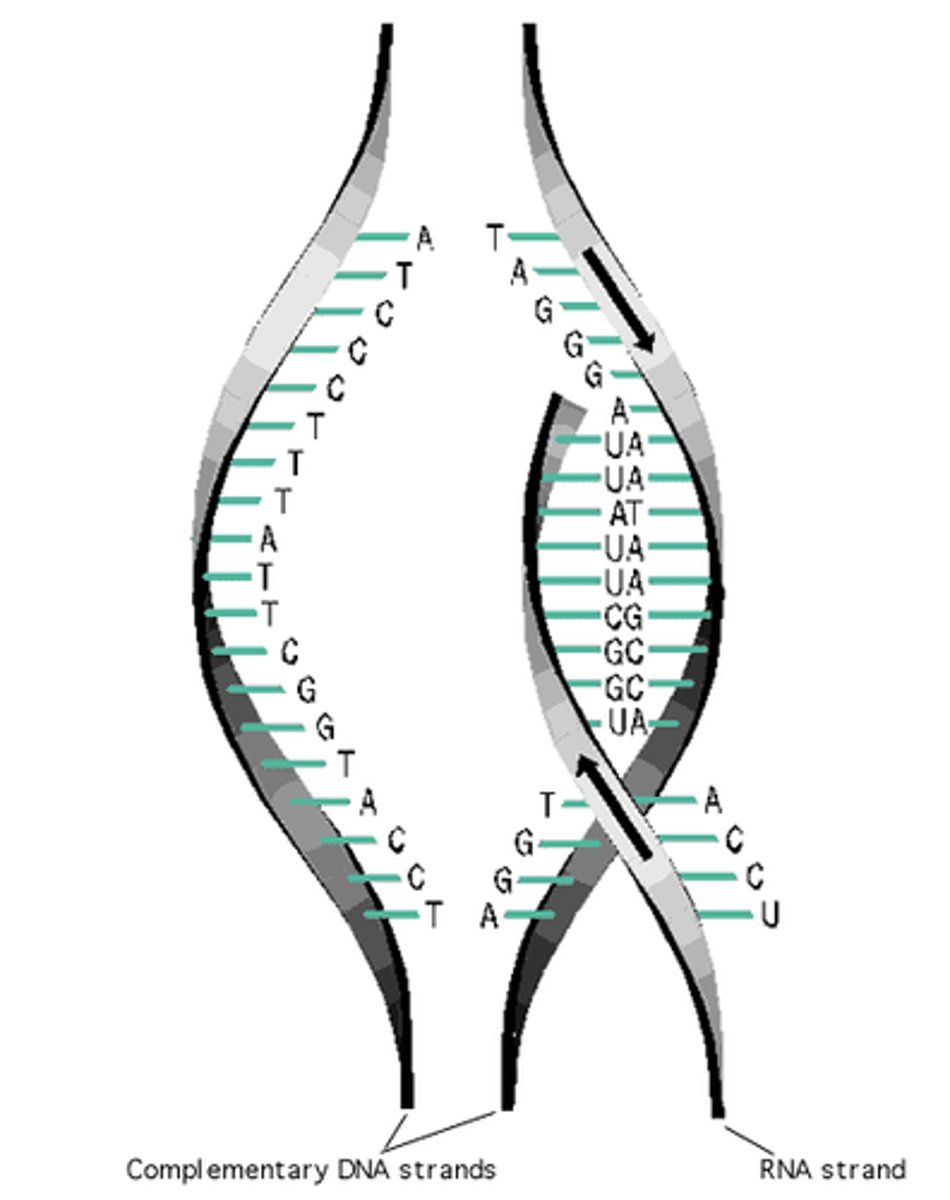
Translation
-Occurs in the cytoplasm
- mRNA attaches to the ribosomes.
-ribosomes and rRNA read the mRNA molecule three nitrogen bases at a time
-A tRNA is signaled to bring a specific amino acid that correlates to the specific codon
- tRNA attaches long enough for the amino acid to be attached to the growing protein chain, and it is then released.
- will continue until a stop codon is read
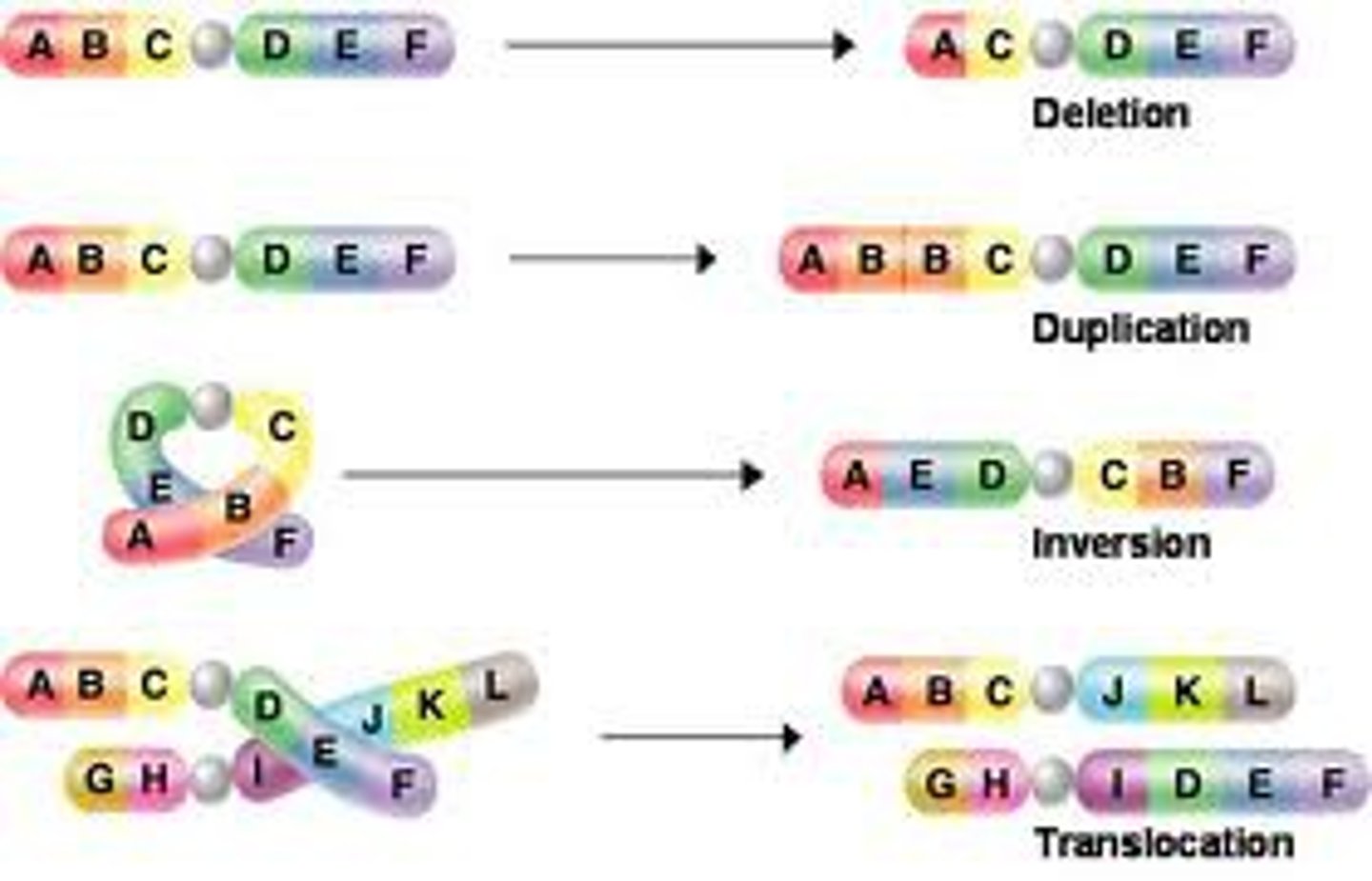
Mutations
A change in a cell's genetic material
Cancer
a disorder in which the body cells lose the ability to control cell growth resulting in uncontrolled cell division
Biotechnology
the use of living systems and organisms to develop or make products
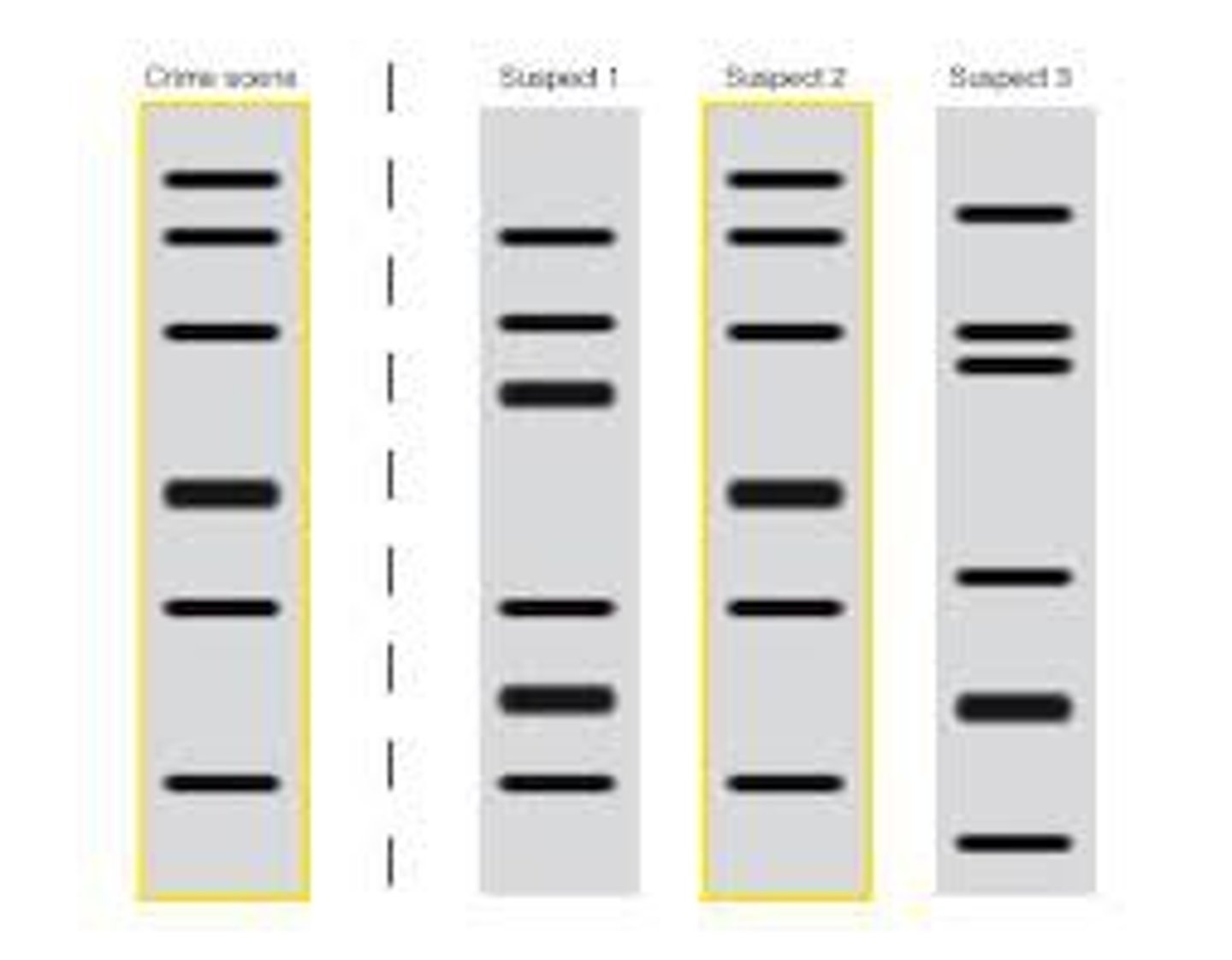
DNA Fingerprinting
tool used by biologists that determines whether two samples of DNA are related by analyzing an individual's unique collection of DNA segments
10%
the amount of energy that passes from one trophic level to the next.
Producers
an organism that produces organic compounds and energy from the environment
Consumers
an organism that feeds on other organisms for food.

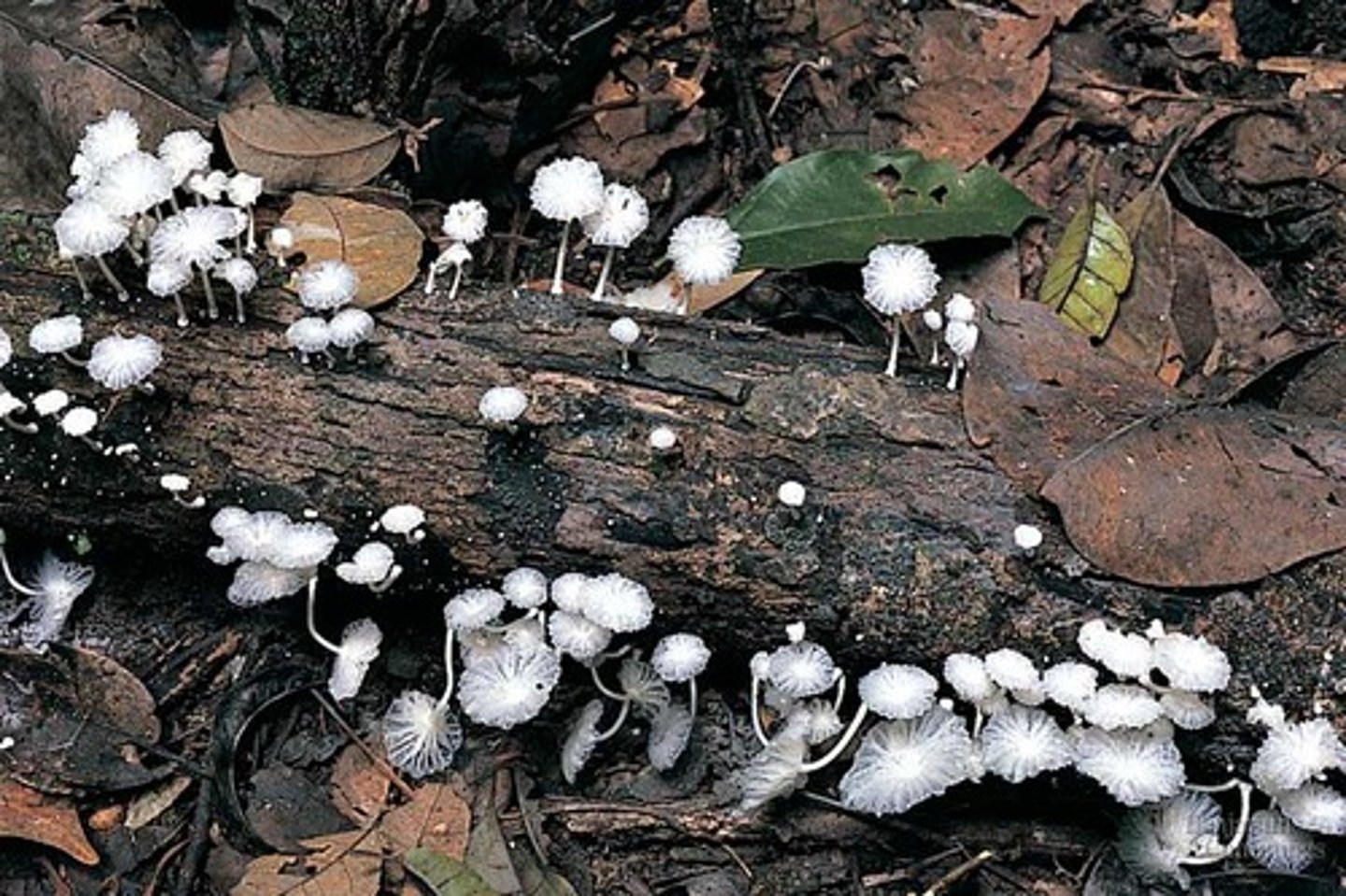
Decomposers
any organism that feeds or obtains nutrients by breaking down organic matter from dead organisms.

Biotic Factors
Factors in an environment relating to, caused by, or produced by living organisms
like dissolved oxygen levels
Abiotic Factors
factor not associated with or derived from living organism like temperature and rain fall amounts
Factors that affect populations
Births & Deaths
Immigration and Emigration
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
Carrying Capacity
Biodiversity
The existence of a wide variety of plant and animal life in a particular environment
Reduces biodiversity
Climate changes
Catastrophic events
Human activities
Introduction of invasive and nonnative species
Affect aquatic systems
-Temperature
-pH
-Dissolved Oxygen
-Salinity
The Water Cycle
-Precipitation (rain)
-Transpiration (water vapor that is released from plants )
-Condensation (when water vapor cools and condenses)
-Evaporation
-Surface water
-Runoff
-Groundwater
The Carbon Cycle
-Plants take carbon out of the air for photosynthesis
-When living things die and decompose the carbon is stored in soil and rocks
-Fossil fuels burned to create energy which releases carbon dioxide
Renewable
a natural resource that is replaceable through biogeochemical cycles or sustainable practices
Non-Renewable
a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced
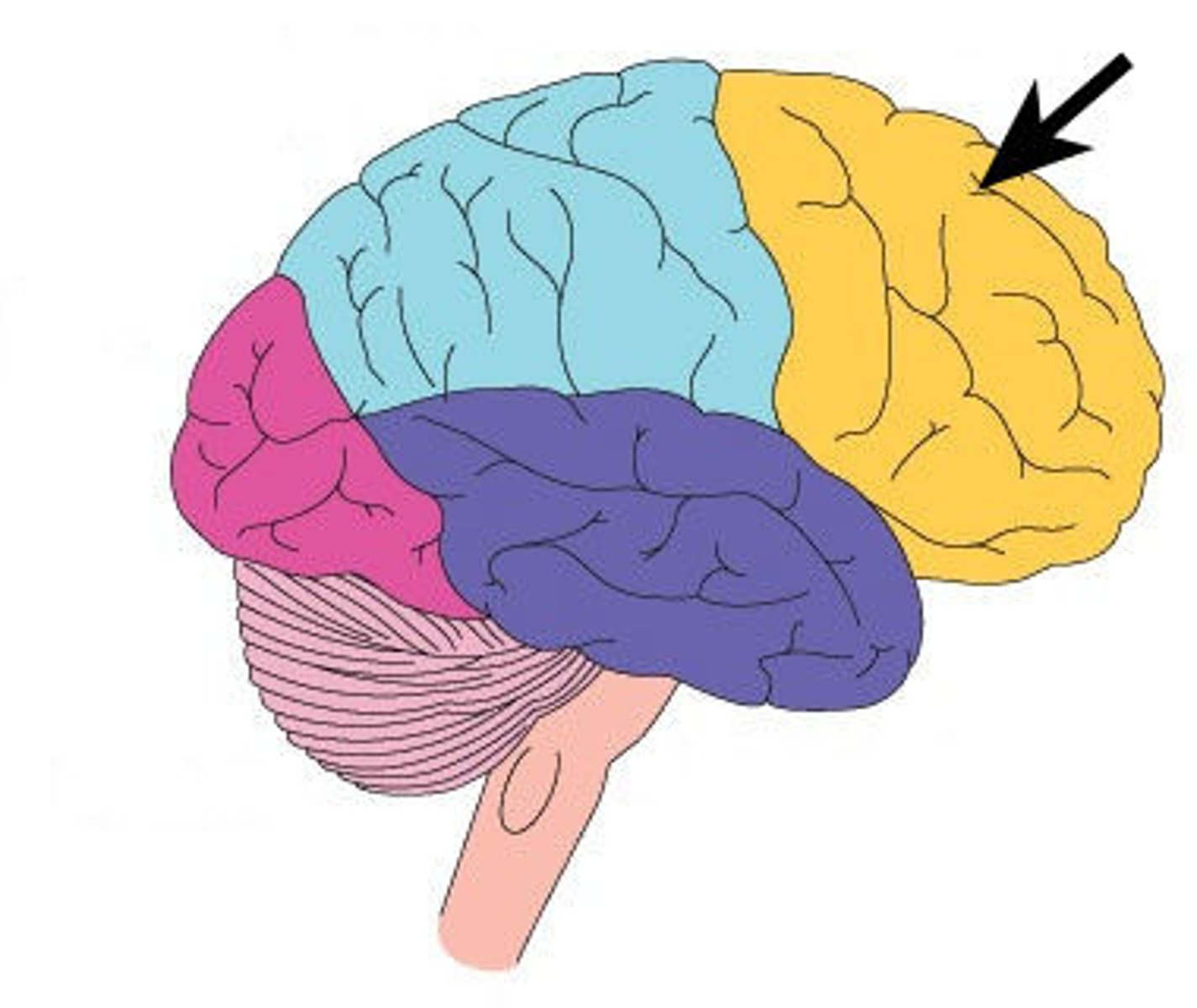
occipital lobe
found at the back of each hemisphere
- area of vision
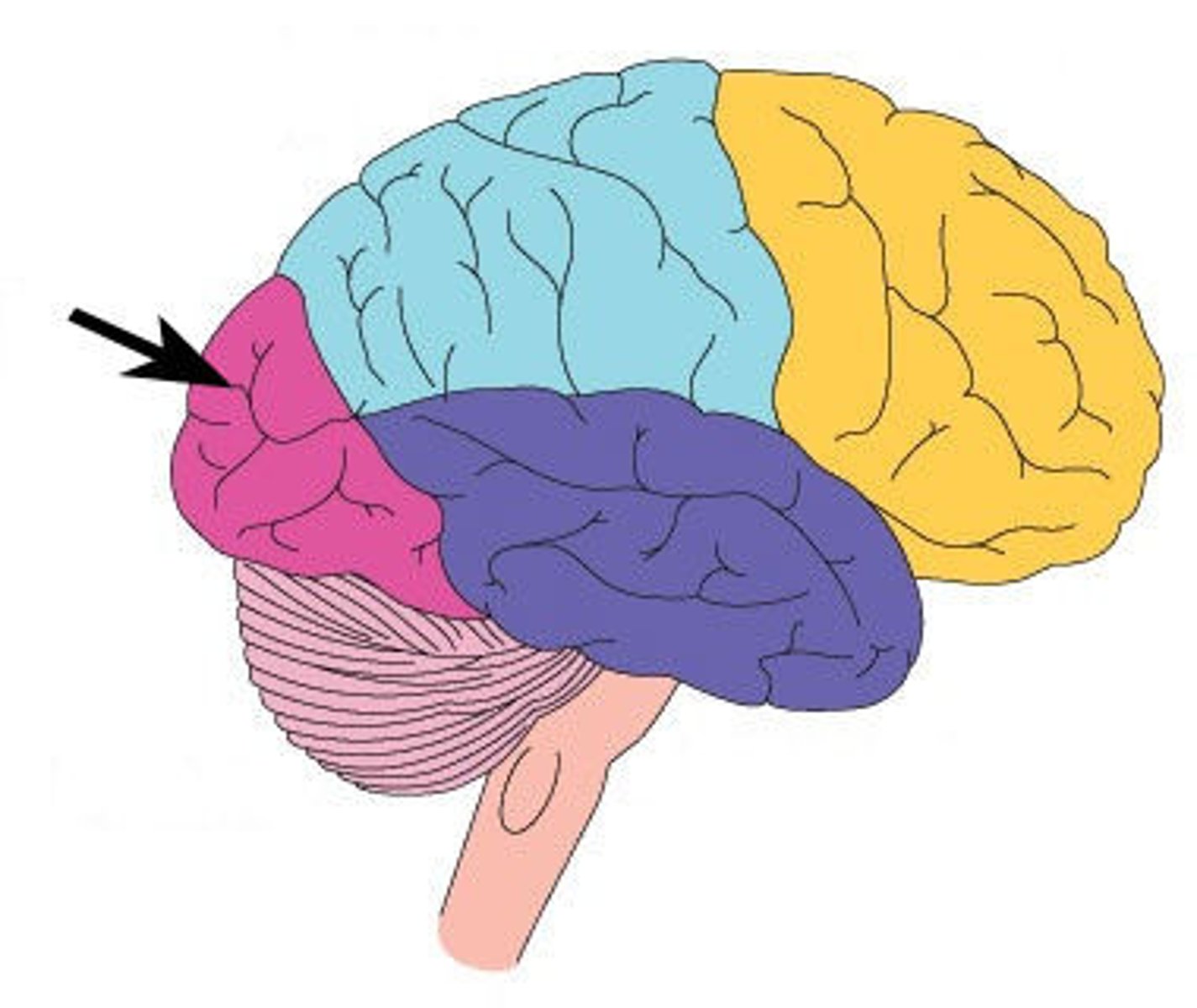
parietal lobe
the middle region of each hemisphere
- sensory and memory areas
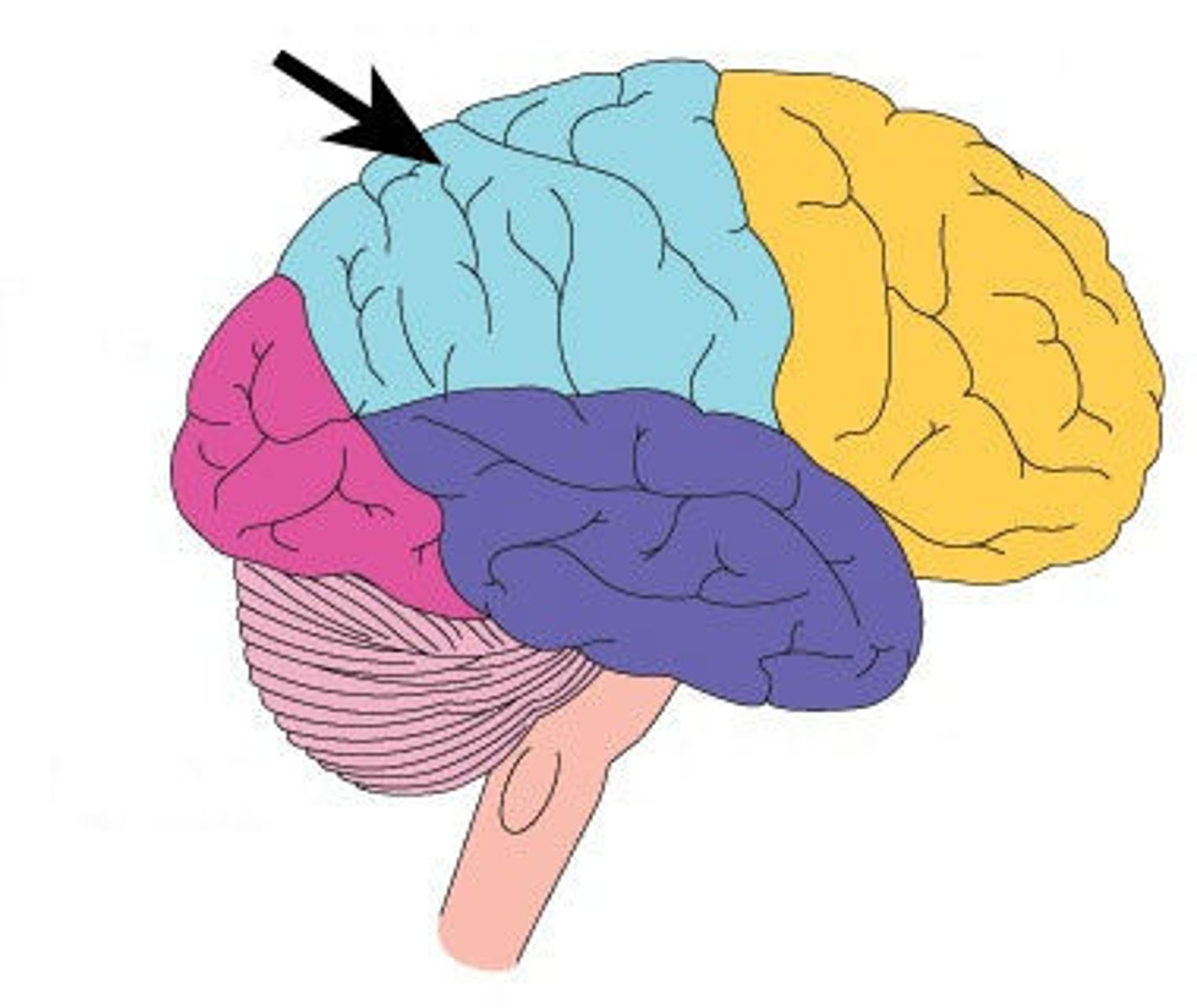
frontal lobe
front part of each hemisphere
- thinking and creative areas
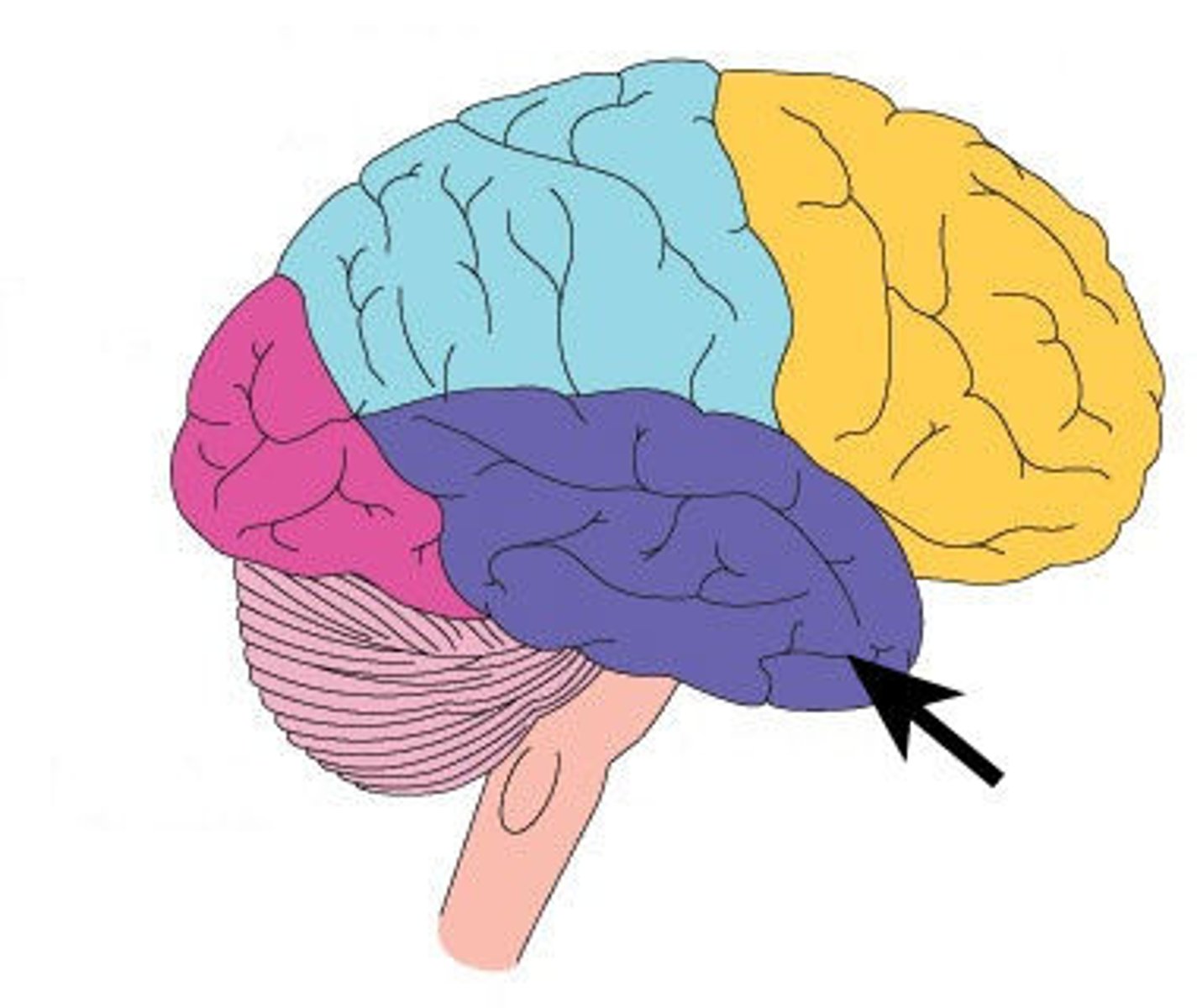
temporal lobe
located on the side of each hemisphere, behind the ears
- controls hearing & speech
Cerebellum
located at the very bottom of the cerebrum.
- controls co-ordination, posture, balance
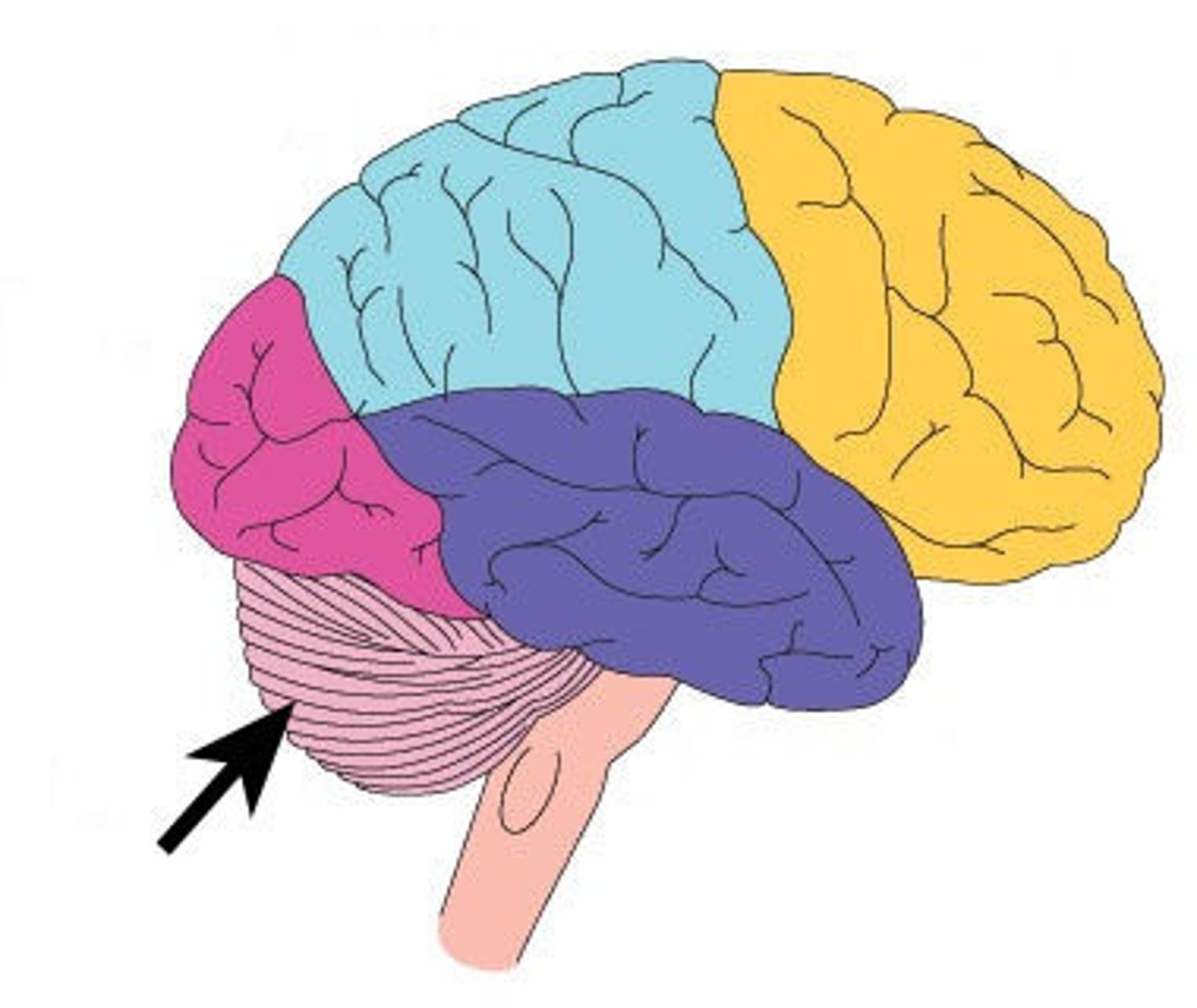
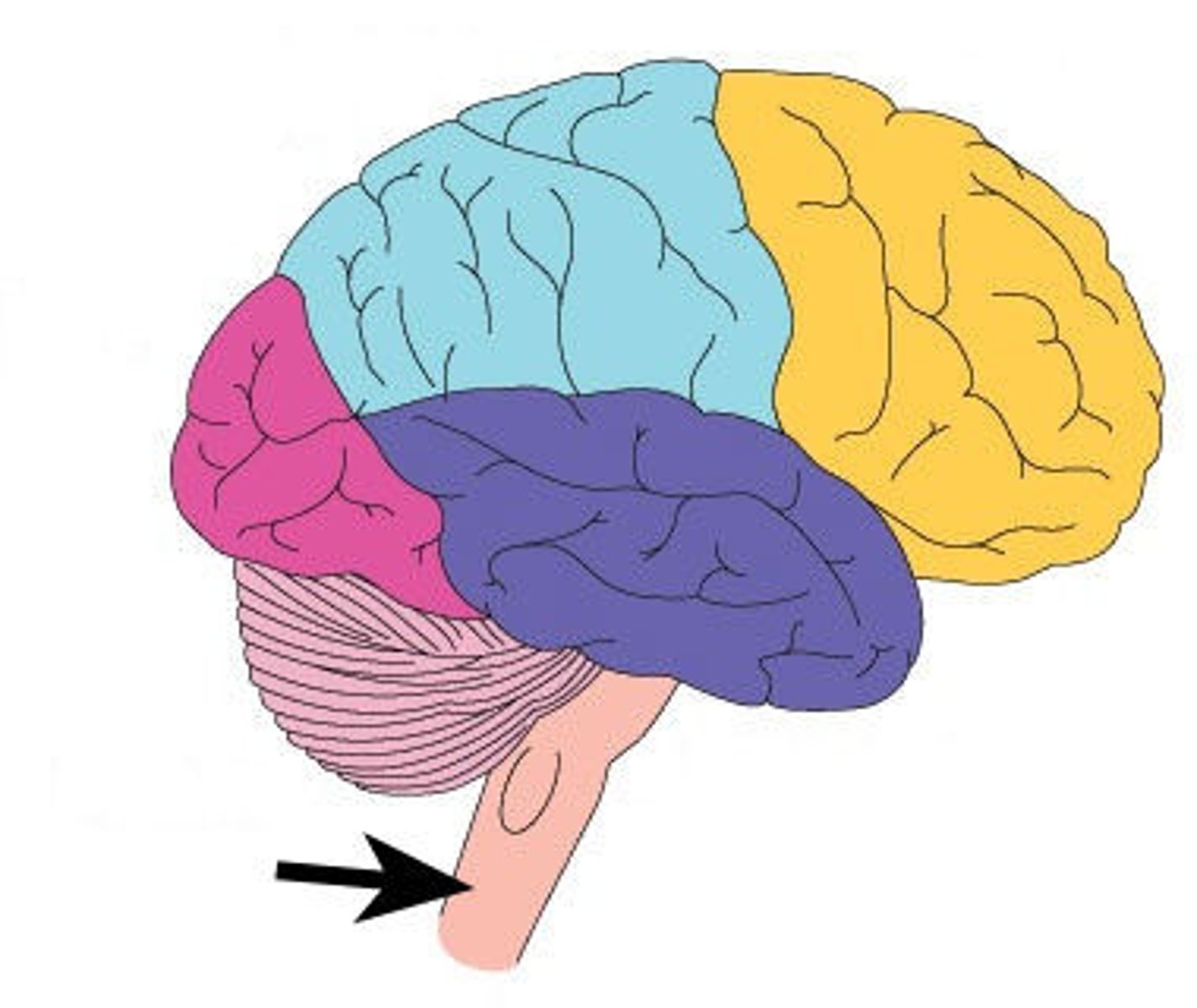
Brain Stem
located below the cerebellum. It connects the brain to the spinal cord.
-controls involuntary movements
High Blood Pressure
also called hypertension; this results when the blood pushing against the walls of the arteries.
Non-Specific Immune Response
the 2nd line of defense. Body does NOT know what is attacking, It protects the body from a wide range of pathogens without distinguishing one infectious agent from another.