MCAT Organic Chemistry - Aldehydes and Ketones II: Enolates
1/14
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
α-carbon
adjacent to the carbonyl carbon
α-hydrogens
hydrogens connected to the α-carbon, very acidic and easily deprotonated, leaving negative charge
ketones < aldehydes (steric hinderance)
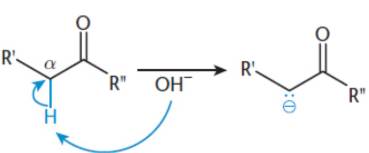
carbanion
molecule with a negatively charged carbon atom
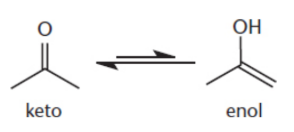
enol
presence of a carbon–carbon double bond (the en– component) and an alcohol (the –ol component)
tautomers
isomers which differ in the placement of a proton and the double bond
enolization/tautomerization
interconverting from the keto to the enol tautomer
equilibrium: ketone < < < enol
α-racemization
any aldehyde or ketone with a chiral α-carbon will rapidly become a racemic mixture as the keto and enol forms interconvert
Michael addition
the carbanion attacks an α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound, a molecule with a multiple bond between the α- and β-carbons next to a carbonyl
kinetic product
formed more rapidly but is less stable; double bond to the less substituted α-carbon; formed by the removal of the α-hydrogen from the less substituted α-carbon because it offers less steric hindrance
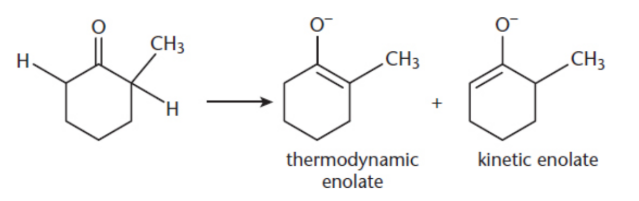
thermodynamic product
formed more slowly, but is more stable and features the double bond being formed with the more substituted α-carbon; formed by the removal of the α-hydrogen from the more substituted α-carbon
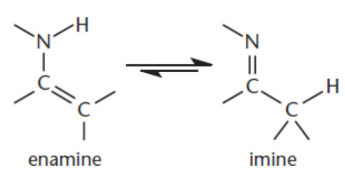
Enamines
tautomers of imines; interconvertible
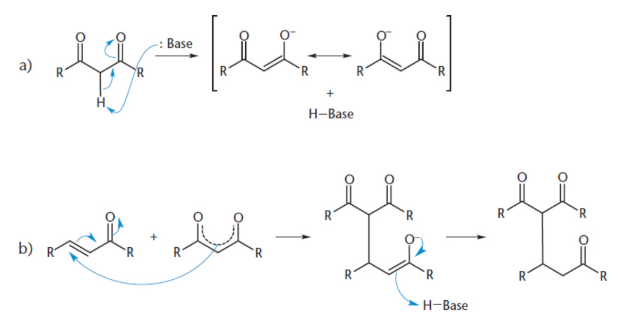
aldol condensation
nucleophilic addition to a carbonyl; aldehyde or ketone acts both as an velectrophile (in its keto form) and a nucleophile (in its enolate form); end result is the formation of a carbon–carbon bond
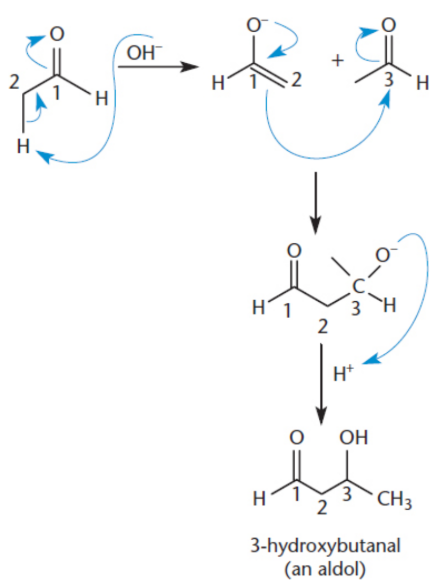
aldol
a molecule that contains both aldehyde and alcohol functional groups
Dehydration of aldol
E1 or E2 mechanism
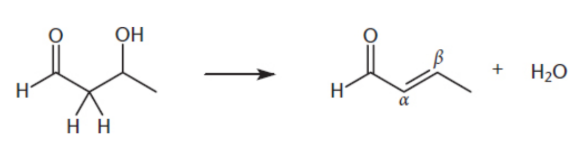
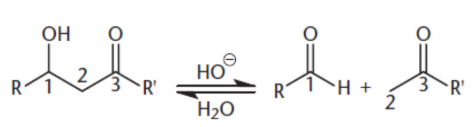
retro-aldol reaction
reverse of aldol condensation; aqueous base is added and heat is applied