Neuroscience final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
110 Terms
1
New cards
what is the main idea of the Neuron Doctrine?
a. the nervous system is comprised of individual neurons that signal across gaps
b. neurons are the building block of the nervous system that communicate primarily through cytoplasmic connections
c. neural networks are the structural units of all living matter
d. neurons are a syncytium of neurons that work together
e. all of the above
a. the nervous system is comprised of individual neurons that signal across gaps
b. neurons are the building block of the nervous system that communicate primarily through cytoplasmic connections
c. neural networks are the structural units of all living matter
d. neurons are a syncytium of neurons that work together
e. all of the above
a
2
New cards
which value would give you the best estimate of the relative number and complexity of synaptic inputs to a given neuron?
a. the number of axons that neuron has
b. the extent and complexity of that neuron’s dendritic branches and spines
c. the number of neurotransmitter vesicles in the neuron’s axon terminal
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
a. the number of axons that neuron has
b. the extent and complexity of that neuron’s dendritic branches and spines
c. the number of neurotransmitter vesicles in the neuron’s axon terminal
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
b
3
New cards
according to the principle of dynamic polarity, which of the following best describes the flow of information in a neuron?
a. axon to cell body to axon terminal to dendrites
b. axon to dendrites to cell body to axon terminal
c. axon terminal to axon to dendrites to cell body
d. dendrites to axon terminal to axon to cell body
e. dendrites to cell body to axon to axon terminal
a. axon to cell body to axon terminal to dendrites
b. axon to dendrites to cell body to axon terminal
c. axon terminal to axon to dendrites to cell body
d. dendrites to axon terminal to axon to cell body
e. dendrites to cell body to axon to axon terminal
e
4
New cards
put the following cerebrospinal fluid flow in order:
i. enters the subdural sinuses through arachnoid cilli/granulations
ii. enters the subarachnoid space
iii. derived from choroid plexus on the walls of ventricles
iv. leaves ventricles via formina
v. cycles back to blood circulation
\
a. iii, iv, ii, i, v
b. ii, i, iv, iii, v
c. iv, iii, i, ii, v
d. iii, i, ii, iv, v
e. none of the above
i. enters the subdural sinuses through arachnoid cilli/granulations
ii. enters the subarachnoid space
iii. derived from choroid plexus on the walls of ventricles
iv. leaves ventricles via formina
v. cycles back to blood circulation
\
a. iii, iv, ii, i, v
b. ii, i, iv, iii, v
c. iv, iii, i, ii, v
d. iii, i, ii, iv, v
e. none of the above
a
5
New cards
you are examining a motor neuron from the peripheral nervous system of a rat. Which of the following would you expect to be true for the axon under view?
a. it has a continuous sheath of insulation (myelin) wrapped around the entire axon without any gaps
b. it has segments of myelin provided by oligodendrocytes
c. action potential propagation in this axon is faster than in an unmyelinated axon
d. none of the above
e. b and c only
a. it has a continuous sheath of insulation (myelin) wrapped around the entire axon without any gaps
b. it has segments of myelin provided by oligodendrocytes
c. action potential propagation in this axon is faster than in an unmyelinated axon
d. none of the above
e. b and c only
c
6
New cards
which of the following is false about the structure of the Meninges?
a. the sub-arachnoid space is a fluid filled space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater
b. the three main layers of the meninges from outside to inside are the Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
c. the meninges are tissue layers which protect the brain from toxins in the blood
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
a. the sub-arachnoid space is a fluid filled space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater
b. the three main layers of the meninges from outside to inside are the Dura mater, arachnoid mater, and pia mater
c. the meninges are tissue layers which protect the brain from toxins in the blood
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
c
7
New cards
you have suffered an injury to the brain which has led to cell damage and death. Which type of nervous system cell is most important in clearing away the accumulated cellular debris?
a. neurons
b. oligodendrocytes
c. Schwann cells
d. microglia
e. endothelial cells
a. neurons
b. oligodendrocytes
c. Schwann cells
d. microglia
e. endothelial cells
d
8
New cards
in what region do sensory inputs enter the spinal cord and in what region do motor signals leave?
a. sensory information travels in through the ventral side, and motor signals go our through the dorsal side of the spinal cord
b. sensory information travels in through the dorsal side and motor signals go out through the ventral side of the spinal cord
c. sensory and motor signals often travel in both directions so that both the front and the back of the periphery can give/receive stimuli
d. sensory and motor signals both go through the dorsal side of the spinal cord
e. sensory and motor signals both go through the ventral side of the spinal cord
a. sensory information travels in through the ventral side, and motor signals go our through the dorsal side of the spinal cord
b. sensory information travels in through the dorsal side and motor signals go out through the ventral side of the spinal cord
c. sensory and motor signals often travel in both directions so that both the front and the back of the periphery can give/receive stimuli
d. sensory and motor signals both go through the dorsal side of the spinal cord
e. sensory and motor signals both go through the ventral side of the spinal cord
b
9
New cards
a 23 year old female presents complaining of hearing changes and balance issues. Which cranial nerve is most likely involved with her problems?
a. V
b. VII
c. VIII
d. IX
e. XI
a. V
b. VII
c. VIII
d. IX
e. XI
c
10
New cards
which of the following cranial nerves is paired with its correct function and number?
a. Vagus (X) nerve is a motor and sensory nerve that controls autonomic functions of the gut
b. abducens (VI) nerve is a motor nerve that controls papillary constriction and accommodation (shape of the lens)
c. hypoglossal (XIII) nerve is a sensory nerve of the larynx and pharynx
d. trigeminal (V) nerve is a motor and sensory nerve that controls eye movement and sense of balance
e. none of the above are correct
a. Vagus (X) nerve is a motor and sensory nerve that controls autonomic functions of the gut
b. abducens (VI) nerve is a motor nerve that controls papillary constriction and accommodation (shape of the lens)
c. hypoglossal (XIII) nerve is a sensory nerve of the larynx and pharynx
d. trigeminal (V) nerve is a motor and sensory nerve that controls eye movement and sense of balance
e. none of the above are correct
a
11
New cards
hippocampus function
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a
12
New cards
limbic system function
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
b
13
New cards
basal ganglia function
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
c
14
New cards
cerebellum function
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
d
15
New cards
medulla function
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
a. involved in memory formation and consolidation
b. group of structures involved in the regulation of emotions and emotional interpretation of environmental stimuli
c. group of structures that controls smooth, voluntary movements
d. important for motor planning and learning
e. coordinated basic life support systems such as respiration
e
16
New cards
which of the following conditions is met when the cell is at its resting membrane potential?
a. the concentration of sodium inside the cell must be equal to the concentration of sodium outside of the cell
b. the concentration of potassium inside the cell must be equal to the concentration of potassium outside the cell
c. both a and b are true at resting potential
d. there are no ions moving across the membrane
e. none of the above are true at rest
a. the concentration of sodium inside the cell must be equal to the concentration of sodium outside of the cell
b. the concentration of potassium inside the cell must be equal to the concentration of potassium outside the cell
c. both a and b are true at resting potential
d. there are no ions moving across the membrane
e. none of the above are true at rest
e
17
New cards
the Na+/K+ ATPase…
a. moves Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradients
b. makes the resting membrane potential more negative
c. is a homogenizing force contributing to the resting membrane potential
d. all of the above
e. a and be only
a. moves Na+ and K+ against their concentration gradients
b. makes the resting membrane potential more negative
c. is a homogenizing force contributing to the resting membrane potential
d. all of the above
e. a and be only
e
18
New cards
which layer of the cerebral cortex would be largest in the somatosensory cortex and the motor cortex respectively?
a. V, II
b. IV, V
c. II, IV
d. V, IV
e. II, III
a. V, II
b. IV, V
c. II, IV
d. V, IV
e. II, III
b
19
New cards
which of the following does not contribute to the resting membrane potential of neurons?
a. negatively charged proteins inside the neuron
b. the sodium/potassium pump
c. potassium flow through leak channels
d. opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels
e. neither c nor d contribute to the resting membrane potential
a. negatively charged proteins inside the neuron
b. the sodium/potassium pump
c. potassium flow through leak channels
d. opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels
e. neither c nor d contribute to the resting membrane potential
d
20
New cards
which of the following does NOT happen at the threshold potential?
a. an action potential is triggered
b. the membrane is depolarized relative to resting potential
c. voltage-gated sodium channels are opened
d. potassium ions enter the cell
e. all of the above happen at the threshold potential
a. an action potential is triggered
b. the membrane is depolarized relative to resting potential
c. voltage-gated sodium channels are opened
d. potassium ions enter the cell
e. all of the above happen at the threshold potential
d
21
New cards
which of the following is TRUE regarding small molecule neurotransmitters and neuropeptides?
a. small molecule neurotransmitters are packages into large dense-core vesicles
b. the final step of neuropeptide synthesis occurs in vesicles in axon terminal
c. for small molecule neurotransmitter, both the enzyme and the neurotransmitter are synthesized in the axon terminal before being transported into vesicles
d. all of the above are true
e. only a and b are true
a. small molecule neurotransmitters are packages into large dense-core vesicles
b. the final step of neuropeptide synthesis occurs in vesicles in axon terminal
c. for small molecule neurotransmitter, both the enzyme and the neurotransmitter are synthesized in the axon terminal before being transported into vesicles
d. all of the above are true
e. only a and b are true
22
New cards
as a neurologist, you are treating a patient with Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by a decreased concentration and decreased effect of acetylcholine. Which of the following answer choices is the best therapy option for your patient?
a. prescribe a drug that inhibits monoamine oxidase (MAO)
b. increase the concentration of glutamate in these neurons
c. decrease the concentration of choline transferase in those cholinergic neurons
d. prescribe a drug that causes synaptotagmin in those cholinergic neurons to have a decreased sensitivity for calcium
e. prescribe a drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterases (AChE)
a. prescribe a drug that inhibits monoamine oxidase (MAO)
b. increase the concentration of glutamate in these neurons
c. decrease the concentration of choline transferase in those cholinergic neurons
d. prescribe a drug that causes synaptotagmin in those cholinergic neurons to have a decreased sensitivity for calcium
e. prescribe a drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterases (AChE)
e
23
New cards
if a neuron expresses the enzymes Tyrosine Hydroxylase, Dopa-Carboxylase and Dopamine B-Hydroxylase what type(s) of neurotransmitter(s) will it release from its vesicles?
a. dopamine
b. norepinephrine
c. epinephrine
d. a and b
e. b and c
a. dopamine
b. norepinephrine
c. epinephrine
d. a and b
e. b and c
b
24
New cards
which of the following is true regarding sensory transduction in machnoreceptors?
a. receptor potentials are graded with respect to the strength of stimulation
b. deformation or stretching of the skin or muscle causes mechano-sensitive ion channels to open
c. Na+ and Ca++ are responsible for depolarization of receptor afferents
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
a. receptor potentials are graded with respect to the strength of stimulation
b. deformation or stretching of the skin or muscle causes mechano-sensitive ion channels to open
c. Na+ and Ca++ are responsible for depolarization of receptor afferents
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
d
25
New cards
which of the following statements accurately describes cortical mapping?
a. the representation of the body in the somatosensory map is proportional to body surface area
b. somatosensory are fixed and cannot change as results of experience
c. the better the spatial accuracy, the larger the representation of that area in the somatosensory cortex
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a. the representation of the body in the somatosensory map is proportional to body surface area
b. somatosensory are fixed and cannot change as results of experience
c. the better the spatial accuracy, the larger the representation of that area in the somatosensory cortex
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
c
26
New cards
a sensory “receptor” potential is usually due to…
a. resting or “leak” currents in the cell body
b. the activation of voltage-gated ion channels
c. the activation of ligand-gated ion channels
d. an external stimulus impinging upon sensory nerve endings
e. an internal stimulus modifying a synaptic signal between two interneurons
a. resting or “leak” currents in the cell body
b. the activation of voltage-gated ion channels
c. the activation of ligand-gated ion channels
d. an external stimulus impinging upon sensory nerve endings
e. an internal stimulus modifying a synaptic signal between two interneurons
d
27
New cards
Somatosensory neurons in the DRG normally transmit information..
a. from the cell body to the spinal cord
b. from the cell body to the skin
c. from the spinal cord to the skin
d. from the skin to the spinal cord
e. transmission would depend on which synapses in the DRG were active
a. from the cell body to the spinal cord
b. from the cell body to the skin
c. from the spinal cord to the skin
d. from the skin to the spinal cord
e. transmission would depend on which synapses in the DRG were active
28
New cards
sharp pain is known as ____ pain involving _______ and _______ fibers. Longer diffused pain is as ____ pain involving __ and ____ fibers
a. second, unmyelinated and C; first, myelinated and A-delta
b. first, myelinated and A-delta; second, unmyelinated and C
c. first, myelinated and A-delta; second, myelinated and C
d. first, unmyelinated and A-delta; second, unmyelinated and C
e. second, myelinated and a-delta; first, unmyelinated and C
a. second, unmyelinated and C; first, myelinated and A-delta
b. first, myelinated and A-delta; second, unmyelinated and C
c. first, myelinated and A-delta; second, myelinated and C
d. first, unmyelinated and A-delta; second, unmyelinated and C
e. second, myelinated and a-delta; first, unmyelinated and C
b
29
New cards
when you stub your toe, you feel a sharp pain immediately but may also feel a throbbing, persistent pain for hours or days afterwards. Which of the following statements is/are true regarding how these pain signals are transduced?
i. transmission through A-delta fibers is responsible for the initial sharp pain
ii. transmission by C fibers is responsible for the initial sharp pain
iii. TRP channels in free nerve endings are depolarized after activation by the mechanical stimulus
iv. myelination of C fibers allows for fast communication after receiving a stimulus
\
a. i only
b. ii only
c. i and iii
d. ii and iii
e. i, iii and iv
i. transmission through A-delta fibers is responsible for the initial sharp pain
ii. transmission by C fibers is responsible for the initial sharp pain
iii. TRP channels in free nerve endings are depolarized after activation by the mechanical stimulus
iv. myelination of C fibers allows for fast communication after receiving a stimulus
\
a. i only
b. ii only
c. i and iii
d. ii and iii
e. i, iii and iv
c
30
New cards
True or False: all neurons that contain glutamate in the nerve terminal will be a glutamatergic neuron
false
31
New cards
which of the following is true for a sensory receptor potential but not true for a postsynaptic potential
a. it is always excitatory
b. it can be excitatory or inhibitory
c. it is a graded potential, therefore proportional to the intensity of the stimulus
d. if it is large enough to reach threshold it will trigger an action potential in the neuron
e. all of the above are true only for sensory receptor potentials
a. it is always excitatory
b. it can be excitatory or inhibitory
c. it is a graded potential, therefore proportional to the intensity of the stimulus
d. if it is large enough to reach threshold it will trigger an action potential in the neuron
e. all of the above are true only for sensory receptor potentials
a
32
New cards
which of the following is (are) a way that opioids can relieve pain?
a. binding to mu, delta and kappa receptors on a 1st order afferent neuron’s terminal to reduce calcium influx
b. opening a potassium channel to produce an IPSP in the 2nd order pain neuron
c. increasing the duration of the action potential in the 1st order afferent neuron
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a. binding to mu, delta and kappa receptors on a 1st order afferent neuron’s terminal to reduce calcium influx
b. opening a potassium channel to produce an IPSP in the 2nd order pain neuron
c. increasing the duration of the action potential in the 1st order afferent neuron
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
e
33
New cards
during a softball game, Anna gets hit in the thigh by a bad pitch, and she immediately grabs her leg and starts rubbing it. She discovers that this helped to reduce the amount of pain that she experienced. Why is this the case?
a. C fibers from her skin are directly inhibited by touch and no longer transmit a pain signal to the brain
b. skin mechanoreceptors have excited an interneuron that inhibited second order pain neurons in the spinal cord
c. the C fibers on her skin are activated and directly inhibit second order neurons so no pain signal is transmitted
d. the inhibitory neurons that synapse onto second order pain neurons are firing less and reducing transmission of the pain signal to the brain
a. C fibers from her skin are directly inhibited by touch and no longer transmit a pain signal to the brain
b. skin mechanoreceptors have excited an interneuron that inhibited second order pain neurons in the spinal cord
c. the C fibers on her skin are activated and directly inhibit second order neurons so no pain signal is transmitted
d. the inhibitory neurons that synapse onto second order pain neurons are firing less and reducing transmission of the pain signal to the brain
34
New cards
what statement is true about on and off coding?
a. on cells hyperpolarize with increasing light intensity
b. off cells hyperpolarize with decreasing light intensity
c. on bipolar cells fire more action potentials with increasing light intensity
d. off ganglion cells fire more action potentials with decreasing light intensity
e. none of the above are true
a. on cells hyperpolarize with increasing light intensity
b. off cells hyperpolarize with decreasing light intensity
c. on bipolar cells fire more action potentials with increasing light intensity
d. off ganglion cells fire more action potentials with decreasing light intensity
e. none of the above are true
35
New cards
you are falling asleep while watching TV, so your pillow ends up covering you right eye since you have laid down. If you can only see the TV with your left eye, what is true about your visual field?
a. only the right side of your visual cortex is receiving input from the TV
b. only the left side of your visual cortex is receiving input from the TV
c. your left eye sends all of its visual input across the optic chiasm to the right side of the visual cortex
d. both a and c are true
e. none of the above are true
a. only the right side of your visual cortex is receiving input from the TV
b. only the left side of your visual cortex is receiving input from the TV
c. your left eye sends all of its visual input across the optic chiasm to the right side of the visual cortex
d. both a and c are true
e. none of the above are true
e
36
New cards
which statement about bipolar cells is true
a. increasing light intensity activates mGluRs on ON bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
b. increasing light intensity decreases activation of mGluRs on ON bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
c. increasing light intensity activates AMPA receptors on OFF bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
d. increasing light intensity decreases activation of AMPA receptors on OFF bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
e. A and C are true
f. B and D are true
a. increasing light intensity activates mGluRs on ON bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
b. increasing light intensity decreases activation of mGluRs on ON bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
c. increasing light intensity activates AMPA receptors on OFF bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
d. increasing light intensity decreases activation of AMPA receptors on OFF bipolar cells, resulting in their depolarization
e. A and C are true
f. B and D are true
b
37
New cards
which statement is true?
a. the role of the lens is to narrow or widen the light path into the eye
b. myopia is a result of light focusing behind the retina instead of focusing directly on the retina
c. the role of retinal pigmented epithelium cells is to absorb light to prevent backscatter and remove and recycle photoreceptor discs
d. photoreceptors throughout the retina have the same size receptive fields
e. damage to the “what” pathway results in optic ataxia
a. the role of the lens is to narrow or widen the light path into the eye
b. myopia is a result of light focusing behind the retina instead of focusing directly on the retina
c. the role of retinal pigmented epithelium cells is to absorb light to prevent backscatter and remove and recycle photoreceptor discs
d. photoreceptors throughout the retina have the same size receptive fields
e. damage to the “what” pathway results in optic ataxia
c
38
New cards
as light intensity changes, the receptor potentials of cells within the retina also change. which of the following pathways is true with decreased light intensity?
a. off bipolar cells hyperpolarize as mGluR receptors are activated by glutamate and cause the conversion of cGMP to GMP
b. channel rhodopsin has a conformational change from cis-retinal to trans-retinal, resulting in activation of the G protein transducin
c. horizontal cells are directly stimulated to suppress action potentials from photoreceptor cells
d. voltage-gated Ca++ channels in photoreceptors open and stimulate the release of glutamate into the synapse
e. phosphodiesterase converts cGMP to GMP in the rods and causes cGMP-gated Na+/Ca++ channels to close
a. off bipolar cells hyperpolarize as mGluR receptors are activated by glutamate and cause the conversion of cGMP to GMP
b. channel rhodopsin has a conformational change from cis-retinal to trans-retinal, resulting in activation of the G protein transducin
c. horizontal cells are directly stimulated to suppress action potentials from photoreceptor cells
d. voltage-gated Ca++ channels in photoreceptors open and stimulate the release of glutamate into the synapse
e. phosphodiesterase converts cGMP to GMP in the rods and causes cGMP-gated Na+/Ca++ channels to close
d
39
New cards
which of the following cell types in the visual system express AMPA receptors?
i. photoreceptors
ii. ON bipolar cells
iii. OFF bipolar cells
iv. ganglion cells
\
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iii
d. ii and iv
e. iii and iv
i. photoreceptors
ii. ON bipolar cells
iii. OFF bipolar cells
iv. ganglion cells
\
a. i and ii
b. i and iii
c. ii and iii
d. ii and iv
e. iii and iv
e
40
New cards
which sensory receptor(s) produce action potentials?
a. cones
b. rods
c. both a and b
d. bipolar cells
e. ganglion cells
f. horizontal cells
a. cones
b. rods
c. both a and b
d. bipolar cells
e. ganglion cells
f. horizontal cells
e
41
New cards
the auditory hair cell bodies are embedded in the _____
a, tectorial membrane
b. basilar membrane
c. tunnel of corti
d. spiral ganglion
e. oval window
a, tectorial membrane
b. basilar membrane
c. tunnel of corti
d. spiral ganglion
e. oval window
b
42
New cards
what gives rise to tonotopy (the frequency ‘map’) along the cochlea?
a. the changing width and stiffness of the basilar membrane
b. the changing width and stiffness of the tectorial membrane
c. the speed at which sound waves propagate along the length of the cochlea
d. the changing mechanical properties of the cochlear wall along the length of the cochlea
e. the increasing density of the cochlear fluid along the length of the cochlea
a. the changing width and stiffness of the basilar membrane
b. the changing width and stiffness of the tectorial membrane
c. the speed at which sound waves propagate along the length of the cochlea
d. the changing mechanical properties of the cochlear wall along the length of the cochlea
e. the increasing density of the cochlear fluid along the length of the cochlea
a
43
New cards
in the lab, you identify a hair cell from a mouse that is releasing glutamate at rest, only produces graded potentials, hyperpolarizes when prodded, and is depolarized by potassium. What kind of hair cell have you isolated?
a. auditory
b. vestibular
c. a and b are both possible
d. olfactory receptor neuron
e. photoreceptor
a. auditory
b. vestibular
c. a and b are both possible
d. olfactory receptor neuron
e. photoreceptor
b
44
New cards
place the following events in the correct order
i. the basilar membrane vibration causes the tectorial membrane to move
ii. stretch activated tip links on the stereocilia cause an influx of K+ ions
iii. vibrations through the cochlea begin at the base and travel to the appropriate frequency on the tonotopic map for maximum vibration
iv. K+ ions depolarize hair cells, causing voltage-gated calcium channels to open and transmitter to be released
v. the movement of the tectorial membrane causes shearing force of the hair cells against the membrane
\
a. iii, i, iv, ii, v
b. i, iii, ii, v, iv
c. iii, i, v, ii, iv
d. i, v, iii, iv, ii
e. iii, i, v, iv, ii
i. the basilar membrane vibration causes the tectorial membrane to move
ii. stretch activated tip links on the stereocilia cause an influx of K+ ions
iii. vibrations through the cochlea begin at the base and travel to the appropriate frequency on the tonotopic map for maximum vibration
iv. K+ ions depolarize hair cells, causing voltage-gated calcium channels to open and transmitter to be released
v. the movement of the tectorial membrane causes shearing force of the hair cells against the membrane
\
a. iii, i, iv, ii, v
b. i, iii, ii, v, iv
c. iii, i, v, ii, iv
d. i, v, iii, iv, ii
e. iii, i, v, iv, ii
c
45
New cards
which of these statements regarding the gustatory system is false?
a. each taste bud can contain multiple types of taste receptors
b. taste buds produce graded potentials that trigger serotonin release
c. taste regions for each kind of taste receptor have significant overlap when mapped on the tongue
d. taste buds line the walls of the papillae which are small bumps in the tongue
e. gustatory cortex is located in the frontal lobe
a. each taste bud can contain multiple types of taste receptors
b. taste buds produce graded potentials that trigger serotonin release
c. taste regions for each kind of taste receptor have significant overlap when mapped on the tongue
d. taste buds line the walls of the papillae which are small bumps in the tongue
e. gustatory cortex is located in the frontal lobe
e
46
New cards
the semicircular canals are largely insensitive to linear acceleration because…
a. the forces produced by linear acceleration are the same on both sides of each cupula
b. the different hair cell orientations in the cupula cancel out any linear acceleration responses
c. forces generated by linear acceleration are never strong enough to bend hair cell bundles
d. linear acceleration does not exert a force on the fluid in the semicircular canal
e. none of the above; semicircular canals are, in fact, highly sensitive to linear acceleration
a. the forces produced by linear acceleration are the same on both sides of each cupula
b. the different hair cell orientations in the cupula cancel out any linear acceleration responses
c. forces generated by linear acceleration are never strong enough to bend hair cell bundles
d. linear acceleration does not exert a force on the fluid in the semicircular canal
e. none of the above; semicircular canals are, in fact, highly sensitive to linear acceleration
a
47
New cards
your pet dog puts his head out the window of the your car as you speed down Fifth Avenue. How does the dog’s vestibular system encode this experience?
a. his otolithic organs would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron continuously until the owner stops the car
b. his otolithic organs would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron rate only during acceleration
c. his otolithic organs would not change the firing rate of the afferent neuron because they no not code linear acceleration
d. his semicircular canals would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron only during acceleration
e. his semicircular canals would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron continuously till the owner stops the car
a. his otolithic organs would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron continuously until the owner stops the car
b. his otolithic organs would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron rate only during acceleration
c. his otolithic organs would not change the firing rate of the afferent neuron because they no not code linear acceleration
d. his semicircular canals would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron only during acceleration
e. his semicircular canals would produce an increased firing rate in the afferent neuron continuously till the owner stops the car
b
48
New cards
listed below are the various components of the olfactory transduction process
1\. G-protein
2. Voltage-gated sodium channel
3. calcium-activated chloride channel
4. cAMP-gated ion channel
5. Adenylyl cyclase III
\
a. 5; 1; 4; 3; 2
b. 1; 5; 4; 2; 3
c. 5; 4; 1; 3; 2
d. 1; 5; 4; 3; 2
e. 2; 1; 5; 4; 3
1\. G-protein
2. Voltage-gated sodium channel
3. calcium-activated chloride channel
4. cAMP-gated ion channel
5. Adenylyl cyclase III
\
a. 5; 1; 4; 3; 2
b. 1; 5; 4; 2; 3
c. 5; 4; 1; 3; 2
d. 1; 5; 4; 3; 2
e. 2; 1; 5; 4; 3
d
49
New cards
Harry has a medical condition where he has endolymph in his Tympanic canal. Will his hearing be affected?
a. yes, his hair cells will stop firing action potentials
b. yes, his hair cell will not depolarize
c. yes, his hair cell will not repolarize
d. no, endolymph is normally found in the Tympanic canal
e. no, endolymph is found only in the vestibular system
a. yes, his hair cells will stop firing action potentials
b. yes, his hair cell will not depolarize
c. yes, his hair cell will not repolarize
d. no, endolymph is normally found in the Tympanic canal
e. no, endolymph is found only in the vestibular system
c
50
New cards
true or false: in auditory and vestibular hair cells, potassium is responsible for both depolarization (due to influx) and repolarization (due to efflux)
true
51
New cards
you are not relaxing in you dorm after your neuroscience exam. Which part of your autonomic system is activated and what effects occur?
a. parasympathetic; your pupils dilate, you digestion begins, your heart rate increases
b. sympathetic; you pupils dilate, your digestion stops, you heart rate increases
c. parasympathetic; your pupils constrict, your digestion begins, your heart rate decreases
d. sympathetic; your pupils constrict, your digestion stops, your heart rate increases
e. parasympathetic; your pupils dilate, you digestion begins, your heart rate decreases
a. parasympathetic; your pupils dilate, you digestion begins, your heart rate increases
b. sympathetic; you pupils dilate, your digestion stops, you heart rate increases
c. parasympathetic; your pupils constrict, your digestion begins, your heart rate decreases
d. sympathetic; your pupils constrict, your digestion stops, your heart rate increases
e. parasympathetic; your pupils dilate, you digestion begins, your heart rate decreases
c
52
New cards
which of the following is a correct distinction between the sympathetic (SNS) and parasympathetic (PNS) branches of the ANS?
a. postganglionic fibers of the PNS release acetlycholine, whereas those of the SNS release norepinephrine
b. the SNS postganglionic cell bodies are present in the spinal cord, whereas the PNS ganglia are located in the dorsal root ganglion
c. the PNS has short preganglionic fibers, whereas the SNS has long preganglionic fibers
d. the PNS is activated during times of stress, whereas the SNS is active during rest and relaxation
e. all of the above are correct
a. postganglionic fibers of the PNS release acetlycholine, whereas those of the SNS release norepinephrine
b. the SNS postganglionic cell bodies are present in the spinal cord, whereas the PNS ganglia are located in the dorsal root ganglion
c. the PNS has short preganglionic fibers, whereas the SNS has long preganglionic fibers
d. the PNS is activated during times of stress, whereas the SNS is active during rest and relaxation
e. all of the above are correct
c
53
New cards
which of the following would not be expected to result from sympathetic nervous system activation?
a. increased heart rate
b. increased air intake due to bronchodilation
c. decreased activity of the gastrointestinal tract
d. increased blood pressure
e. increased uptake (storage) of glucose by the liver
a. increased heart rate
b. increased air intake due to bronchodilation
c. decreased activity of the gastrointestinal tract
d. increased blood pressure
e. increased uptake (storage) of glucose by the liver
e
54
New cards
which of the following accurately describes the visceral motor system, but NOT the somatic motor system?
i. highly organized muscle endplates
ii. contains a myelinated lower motor neuron
iii. contains an unmyelinated lower motor neuron
iv. contains neurons that release norepinephrine
v. has only iontropic postsynaptic receptors
\
a. i, ii, iii, iv, v
b. i, ii, iii, v
c. iii, iv
d. iii, v
e. iii, iv, v
i. highly organized muscle endplates
ii. contains a myelinated lower motor neuron
iii. contains an unmyelinated lower motor neuron
iv. contains neurons that release norepinephrine
v. has only iontropic postsynaptic receptors
\
a. i, ii, iii, iv, v
b. i, ii, iii, v
c. iii, iv
d. iii, v
e. iii, iv, v
c
55
New cards
which of the following is false about a motor neurons?
a. each a motor neuron can innervate multiple fibers in the same muscle
b. a motor neurons innervate extrafusal muscle fibers for muscle contraction
c. a muscle fiber can receive input from only one a motor neuron
d. all the a motor neurons and their postsynaptic fibers are collectively called the motor unit
e. all of the above are true
a. each a motor neuron can innervate multiple fibers in the same muscle
b. a motor neurons innervate extrafusal muscle fibers for muscle contraction
c. a muscle fiber can receive input from only one a motor neuron
d. all the a motor neurons and their postsynaptic fibers are collectively called the motor unit
e. all of the above are true
56
New cards
what is the best definition of a mEPP?
a. synaptic potential that is evoked by an action potential in the motor neuron
b. synaptic potential that occurs spontaneously in the motor cortex
c. synaptic potential that is very small
d. synaptic potential that crosses threshold
e. synaptic potential that corresponds to the release of a single vesicle
a. synaptic potential that is evoked by an action potential in the motor neuron
b. synaptic potential that occurs spontaneously in the motor cortex
c. synaptic potential that is very small
d. synaptic potential that crosses threshold
e. synaptic potential that corresponds to the release of a single vesicle
e
57
New cards
all of the following are true about short term synaptic facilitation except…
a. it can happen in response to a burst of action potentials at the neuromuscular junction
b. extra intracellular calcium cannot bind with synaptotagmin so there is less vesicle fusion
c. it is caused by increased Ca++ in the presynaptic bouton
d. short-term facilitation is temporary
e. short-term facilitation increases the probability that the muscle fiber will contract
a. it can happen in response to a burst of action potentials at the neuromuscular junction
b. extra intracellular calcium cannot bind with synaptotagmin so there is less vesicle fusion
c. it is caused by increased Ca++ in the presynaptic bouton
d. short-term facilitation is temporary
e. short-term facilitation increases the probability that the muscle fiber will contract
b
58
New cards
which of the following is true regarding EPPs and/or action potentials
a. EPPs and APs both decay with distance in the skeletal muscle
b. EPPs cause an action potential, by opening voltage-gated sodium channels in the muscle
c. EPPs are caused by glutamate binding to ligand-gated ion channels receptors to depolarize the postsynaptic membrane
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
a. EPPs and APs both decay with distance in the skeletal muscle
b. EPPs cause an action potential, by opening voltage-gated sodium channels in the muscle
c. EPPs are caused by glutamate binding to ligand-gated ion channels receptors to depolarize the postsynaptic membrane
d. all of the above are true
e. none of the above are true
59
New cards
which of the following is responsible for the initial depolarization of the skeletal muscle fiber?
a. ligand gated acetylcholine receptors
b. metabotropic acetylcholin receptors
c. voltage gated calcium channels
d. voltage gated sodium channels
e. both a and b
a. ligand gated acetylcholine receptors
b. metabotropic acetylcholin receptors
c. voltage gated calcium channels
d. voltage gated sodium channels
e. both a and b
60
New cards
you’re sitting in the woods. There’s no one around and you phone is dead. Out of the corner of your eye, you spot him: Shia LaBeouf. What is the correct order of motor unit activation when you go from sitting still to sprinting away?
a. slow, FFR, FF
b. slow, FF, FFR
c. FFR, FF, slow
d. FFR, slow, FF
e. FF, slow, FFR
a. slow, FFR, FF
b. slow, FF, FFR
c. FFR, FF, slow
d. FFR, slow, FF
e. FF, slow, FFR
a
61
New cards
which of the following is true about the visceral (autonomic) motor system, but not the somatic nervous system
i. uses norepinephrine as one of its neurotransmitters
ii. uses acetylcholine as one of its neurotransmitters
iii. has 2 lower motor neurons
iv. targets skeletal muscle
v. targets cardiac and smooth muscle
\
a. i, iii
b. ii, iii
c. i, ii, iii
d. i, iii, iv
e. i, iii, v
f. ii, iii, iv
g. ii, iii, v
h. i, ii, iii, v
i. uses norepinephrine as one of its neurotransmitters
ii. uses acetylcholine as one of its neurotransmitters
iii. has 2 lower motor neurons
iv. targets skeletal muscle
v. targets cardiac and smooth muscle
\
a. i, iii
b. ii, iii
c. i, ii, iii
d. i, iii, iv
e. i, iii, v
f. ii, iii, iv
g. ii, iii, v
h. i, ii, iii, v
e
62
New cards
which of the following describes evidence that upper motor neurons can be associated to create circuits that evoke an organized behavior when stimulated?
a. higher AP frequency in motor neurons increases the force of muscle contraction
b. stimulating one site of the motor cortex causes contraction of multiple fibers, but only in a single muscle
c. a particular movement such as bringing hand to mouth, can be triggered by stimulation of separate sited in motor cortex
d. contraction of one muscle group creates activity in two or more different areas of the motor cortex
e. stimulation of one upper motor neurons results in contraction of a single muscle fiber
a. higher AP frequency in motor neurons increases the force of muscle contraction
b. stimulating one site of the motor cortex causes contraction of multiple fibers, but only in a single muscle
c. a particular movement such as bringing hand to mouth, can be triggered by stimulation of separate sited in motor cortex
d. contraction of one muscle group creates activity in two or more different areas of the motor cortex
e. stimulation of one upper motor neurons results in contraction of a single muscle fiber
c
63
New cards
which of the following statements is true concerning Betz cells?
a. they are a defining feature of the basal ganglia
b. they are present in layer 3 of the motor cortex
c. they are large lower motor neurons
d. they are specialized subset of interneurons in the spinal cord
e. none of the above are true
a. they are a defining feature of the basal ganglia
b. they are present in layer 3 of the motor cortex
c. they are large lower motor neurons
d. they are specialized subset of interneurons in the spinal cord
e. none of the above are true
e
64
New cards
both upper and lower motor neurons are involved in controlling the activity of your right bicep. Where do the cell bodies of these motor neurons live?
a. upper motor neuron - left motor cortex; lower motor neuron - left spinal cord
b. upper motor neuron - left motor cortex; lower motor neuron - right spinal cord
c. upper motor neuron - right motor cortex; lower motor neuron - right spinal cord
d. upper motor neuron - right motor cortex; lower motor neuron - left spinal cord
e. none of these are correct
a. upper motor neuron - left motor cortex; lower motor neuron - left spinal cord
b. upper motor neuron - left motor cortex; lower motor neuron - right spinal cord
c. upper motor neuron - right motor cortex; lower motor neuron - right spinal cord
d. upper motor neuron - right motor cortex; lower motor neuron - left spinal cord
e. none of these are correct
b
65
New cards
the TA’s are celebrating the end of the year and have gotten together for a few drinks. Sean holds out his mug for a refill and when Joe starts to pour soda in, the mug slips down slightly but Sean quickly recovers to prevent his mug from spilling. Which of the following does not occur in this reflex circuit?
a. the added load of the soda stretches the intrafusal muscle fibers of the bicep
b. sensory neurons from the muscle spindle synapse onto a motor neuron and interneurons
c. the rate of action potential firing increases in the muscle spindle fiber
d. inhibition of motor neurons innervating the bicep muscle
e. all of the above do occur
a. the added load of the soda stretches the intrafusal muscle fibers of the bicep
b. sensory neurons from the muscle spindle synapse onto a motor neuron and interneurons
c. the rate of action potential firing increases in the muscle spindle fiber
d. inhibition of motor neurons innervating the bicep muscle
e. all of the above do occur
d
66
New cards
which of the following statements accurately describe spinal cord organization
1. a-motor neurons are organized from lateral to medal such that those found towards the medial section of the spinal cord controls the distal muscles
2. lumbar spinal cord enlargement is observed where neurons that innervate the legs and feet are located
3. neuronal cell bodies of neurons that innervate single muscles are only found in a single spinal cord segment
4. muscles of the trunk are represented medially while muscles of arms and hands are represented laterally
\
a. 2, 4
b. 1, 2, 4
c. 2, 3, 4
d. 4
e. 1, 2, 3, 4
1. a-motor neurons are organized from lateral to medal such that those found towards the medial section of the spinal cord controls the distal muscles
2. lumbar spinal cord enlargement is observed where neurons that innervate the legs and feet are located
3. neuronal cell bodies of neurons that innervate single muscles are only found in a single spinal cord segment
4. muscles of the trunk are represented medially while muscles of arms and hands are represented laterally
\
a. 2, 4
b. 1, 2, 4
c. 2, 3, 4
d. 4
e. 1, 2, 3, 4
a
67
New cards
Mark is walking through a corn maze and hears a sudden loud noise coming from the corn stalks. he reflexively turns his head and adjusts his gaze towards the direction of the noise to orient towards the stimulus. Descending input from which brain area most contributed to Mark’s reaction?
a. primary motor cortex
b. premotor cortex
c. reticular formation
d. superior colliculus
e. vestibular nuclei
a. primary motor cortex
b. premotor cortex
c. reticular formation
d. superior colliculus
e. vestibular nuclei
d
68
New cards
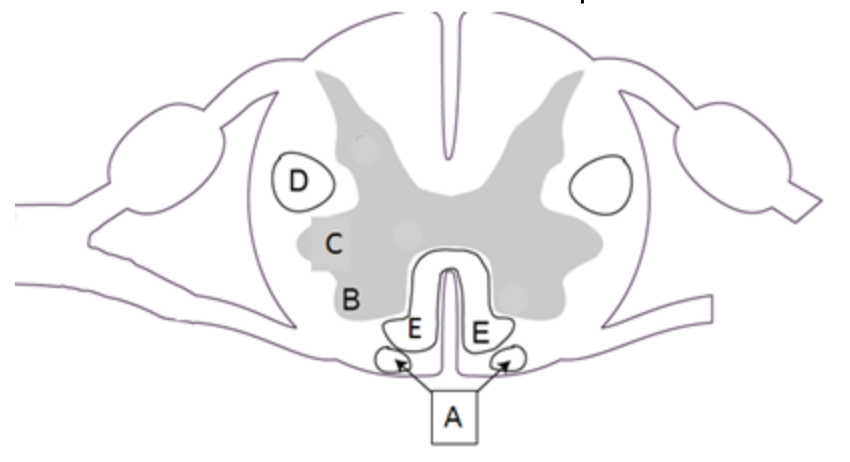
which area contains the cell bodies of alpha lower motor neurons?
b
69
New cards
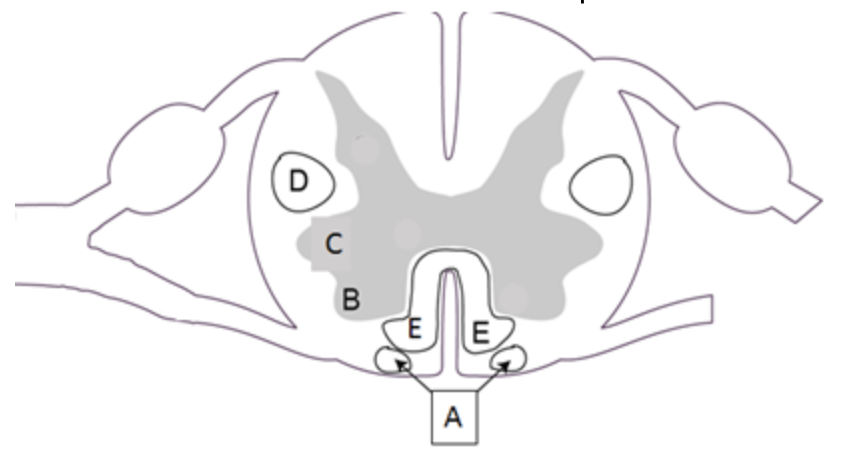
which area contains axons that descended from primary motor cortex, but did NOT cross the midline over at the pyramidal decussation (medulla)?
a
70
New cards
what is true of both the basal ganglia circuit function and cerebellum circuit function?
a. they are both involved in motor learning
b. they both receive input from the spinal cord
c. they both are important for error detection and correction
d. they are both primarily excitatory and must be inhibited for proper movement to occur
e. all of the above are true
a. they are both involved in motor learning
b. they both receive input from the spinal cord
c. they both are important for error detection and correction
d. they are both primarily excitatory and must be inhibited for proper movement to occur
e. all of the above are true
a
71
New cards
which of the following is true regarding connections between medium spiny neurons (MSNs) and globus pallidus neurons (GPNs)?
i. MSNs are excitatory and release glutamate onto GPNs
ii. MSNs contact very few GPNs
iii. GPNs are inhibited by the release of GABA from MSNs
iv. GPNs receive input directly from the cortex that can override the input from MSNs
\
a. i
b. i, iii
c. ii, iii
d. iii
e. i, iii, iv
i. MSNs are excitatory and release glutamate onto GPNs
ii. MSNs contact very few GPNs
iii. GPNs are inhibited by the release of GABA from MSNs
iv. GPNs receive input directly from the cortex that can override the input from MSNs
\
a. i
b. i, iii
c. ii, iii
d. iii
e. i, iii, iv
72
New cards
listed below are the events that occur during basal ganglia funcitoning
1. disinhibition of thalamic nuclei that project to motor cortex
2. inhibition of globus pallidus
3. excitation of corpus striatum
which of the following is the correct sequence of these events?
a. 1; 2; 3
b. 3; 2; 1
c. 1; 3; 2
d. 3; 1; 2
e. 2; 3; 1
1. disinhibition of thalamic nuclei that project to motor cortex
2. inhibition of globus pallidus
3. excitation of corpus striatum
which of the following is the correct sequence of these events?
a. 1; 2; 3
b. 3; 2; 1
c. 1; 3; 2
d. 3; 1; 2
e. 2; 3; 1
b
73
New cards
increased stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus by motor cortex would result in which of the following outcomes?
i. increased firing of internal globus pallidus neurons
ii. decreased firing of internal globus palliduc neurons
iii. increased firing of thalamic neurons
iv. decreased firing of thalamic neurons
v. an overall decrease in movement
vi. an overall increase in movement
\
a. i, iii, v
b. i, iv, v
c. i, iii, iv
d. i, iv, vi
e. ii, iii, v
f. ii, iv, v
g. ii, iii, vi
h, ii, iv, vi
i. increased firing of internal globus pallidus neurons
ii. decreased firing of internal globus palliduc neurons
iii. increased firing of thalamic neurons
iv. decreased firing of thalamic neurons
v. an overall decrease in movement
vi. an overall increase in movement
\
a. i, iii, v
b. i, iv, v
c. i, iii, iv
d. i, iv, vi
e. ii, iii, v
f. ii, iv, v
g. ii, iii, vi
h, ii, iv, vi
74
New cards
which of the following does not accurately describe MSNs?
a. they make a small number of synapses with many GPNs and a large number of synapses with a few GPNs
b. they are GABAergic and therefore inhibitory
c. they are constitutively active to tonically inhibit the thalamus
d. they are activated by inputs from the cortex
e. all of the above are true
a. they make a small number of synapses with many GPNs and a large number of synapses with a few GPNs
b. they are GABAergic and therefore inhibitory
c. they are constitutively active to tonically inhibit the thalamus
d. they are activated by inputs from the cortex
e. all of the above are true
75
New cards
the motor cortex has an (excitatory/inhibitory) connection to the subthalamic nucleus, which (excites/inhibits) the globus pallidus internal, ultimately (promoting/suppressing) movement
a. excitatory, excites, promoting
b. excitatory, excites, suppressing
c. inhibitory, inhibits, promoting
d. inhibitory, inhibits, suppressing
e. excitatory, inhibits, promoting
a. excitatory, excites, promoting
b. excitatory, excites, suppressing
c. inhibitory, inhibits, promoting
d. inhibitory, inhibits, suppressing
e. excitatory, inhibits, promoting
76
New cards
a doctor has just diagnosed a patient with parkinson’s disease. the doctor’s explanation of the disease includes the following:
a. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the corpus striatum cause increased activity of the direct pathway and decreased activity of the indirect pathway
b. the loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra caused increased activity of the direct pathway and decreased activity of the indirect pathway
c. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the corpus striatum caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
d. the loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
e. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the substantia nigra caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
a. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the corpus striatum cause increased activity of the direct pathway and decreased activity of the indirect pathway
b. the loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra caused increased activity of the direct pathway and decreased activity of the indirect pathway
c. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the corpus striatum caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
d. the loss of dopamine neurons in the substantia nigra caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
e. the loss of medium spiny neurons in the substantia nigra caused decreased activity of the direct pathway and increased activity of the indirect pathway
77
New cards
Huntington’s disease causes too much ballistic movement due to which of the following reasons?
a. loss of inhibitory connection between the striatum and the globus pallidus external
b. loss of the inhibitory connection between the straitum and the globus pallidus internal
c. loss of the inhibitory connection between the globus pallidus external and the globus pallidus internal
d. increased activity of the globus pallidus internal neurons
e. both c and d
a. loss of inhibitory connection between the striatum and the globus pallidus external
b. loss of the inhibitory connection between the straitum and the globus pallidus internal
c. loss of the inhibitory connection between the globus pallidus external and the globus pallidus internal
d. increased activity of the globus pallidus internal neurons
e. both c and d
a
78
New cards
dopamine input from the substantia nigra to the striatum results in which of the following?
1. increased firing of globus pallidus internal neurons
2. decreased firing of globus pallidus internal neurons
3. increased firing of globus pallidus external neurons
4. decreased firing of globus pallidus external neurons
5. increased firing of thalamic neurons
6. decreased firing of thalamic neurons
\
a. 1, 3,5
b. 1, 4, 6
c. 1, 3, 6
d. 1, 4, 5
e. 2, 3, 5
f. 2, 4, 6
g. 2, 3, 6
h. 2, 4, 5
1. increased firing of globus pallidus internal neurons
2. decreased firing of globus pallidus internal neurons
3. increased firing of globus pallidus external neurons
4. decreased firing of globus pallidus external neurons
5. increased firing of thalamic neurons
6. decreased firing of thalamic neurons
\
a. 1, 3,5
b. 1, 4, 6
c. 1, 3, 6
d. 1, 4, 5
e. 2, 3, 5
f. 2, 4, 6
g. 2, 3, 6
h. 2, 4, 5
e
79
New cards
which of the following areas compromise the cerebral cortex?
a. vestibulocerebellum
b. spinocerebellum
c. cerebrocerebellum
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
a. vestibulocerebellum
b. spinocerebellum
c. cerebrocerebellum
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
80
New cards
which of the following is true regarding the deep cerebellar nuclei?
a. they provide input to the motor cortex via a relay synapse in the thalamus
b. they are the sole source of input to cerebellar cortex
c. they receive excitatory input from the cerebellar cortex
d. they are comprised on inhibitory medium spiny neurons
e. all of the above are true statements
a. they provide input to the motor cortex via a relay synapse in the thalamus
b. they are the sole source of input to cerebellar cortex
c. they receive excitatory input from the cerebellar cortex
d. they are comprised on inhibitory medium spiny neurons
e. all of the above are true statements
a
81
New cards
which of the following statement about the L-Dopa treatment for Parkinson’s diseases:
a. high doses of L-Dopa cause nausea, vomiting and with long term use, dyskinesias
b. L-Dopa is given as a dopamine precursor because L-Dopa can cross the blood brain barrier but dopamine can not
c. Carbidopa prevents the conversion of L-Dopa to dopamine, but only in the peripheral blood supply
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a. high doses of L-Dopa cause nausea, vomiting and with long term use, dyskinesias
b. L-Dopa is given as a dopamine precursor because L-Dopa can cross the blood brain barrier but dopamine can not
c. Carbidopa prevents the conversion of L-Dopa to dopamine, but only in the peripheral blood supply
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
d
82
New cards
for which disease might gene silencing (of a single gene) be an effective treatment for all patients?
a. Parkinson’s disease
b. Huntington’s disease
c. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
d. all of the above
e. a and b
a. Parkinson’s disease
b. Huntington’s disease
c. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
d. all of the above
e. a and b
b
83
New cards
which of the following is/are involved pathophysiology of ALS?
a. death of upper motor neurons
b. death of lower motor neurons
c. loss of dopamine neurons in the subtantia nigra
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
a. death of upper motor neurons
b. death of lower motor neurons
c. loss of dopamine neurons in the subtantia nigra
d. all of the above
e. a and b only
e
84
New cards
the loss of memories that had been stored before an injury is called ____ amnesia, while the inability to form new memories is called _______ amnesia
a. anterograde, procedural
b. retrograde, procedural
c. anterograde, retrograde
d. retrograde, anterograde
e. both are referred to as declarative amnesia
a. anterograde, procedural
b. retrograde, procedural
c. anterograde, retrograde
d. retrograde, anterograde
e. both are referred to as declarative amnesia
d
85
New cards
study participants are asked to remember a series of 10 words after a variable time delay. After the longes experimental delay of 2 minutes, what effect would be most dominant?
a. primacy but no recency
b. recency but no primacy
c. primacy and recency
d. no primacy or recency
e. impossible to predict since it depends on how good a person’s memory is
a. primacy but no recency
b. recency but no primacy
c. primacy and recency
d. no primacy or recency
e. impossible to predict since it depends on how good a person’s memory is
a
86
New cards
which of the following movement disorders is an auto-immune disorder?
a. tremor
b. Parkinson’s disease
c. Huntington’s disease
d. myasthenia gravis
e. ALS
a. tremor
b. Parkinson’s disease
c. Huntington’s disease
d. myasthenia gravis
e. ALS
d
87
New cards
which of the following statements about the clinical case of H.M. is false?
a. H.M had profound anterograde amnesia
b. H.M.’s non-declarative memory was intact
c. H.M was unable to remember clinicians he met after the surgery, even though they worked with him for many years
d. it demonstrated that the hippocampus is critical for long-term storage of declarative memories
e. H.M’s intellectual functions, as measured by intelligence tests, did not change following the surgery
a. H.M had profound anterograde amnesia
b. H.M.’s non-declarative memory was intact
c. H.M was unable to remember clinicians he met after the surgery, even though they worked with him for many years
d. it demonstrated that the hippocampus is critical for long-term storage of declarative memories
e. H.M’s intellectual functions, as measured by intelligence tests, did not change following the surgery
d
88
New cards
research on spatial learning in rats trained on the Morris water maze task (finding the hidden platform) revealed which of the following?
a. some strains of rats are able to swim directly to a submerged platform without training
b. after training, rats remember the location of a submerged platform for just a hours
c. the principal effect of hippocampal lesions is that rats require many more trials to learn the location of a submerged platform
d. healthy rats are able to make associations between visual cues outside the water tank and the location of a submerged resting platform
e. all of the above
a. some strains of rats are able to swim directly to a submerged platform without training
b. after training, rats remember the location of a submerged platform for just a hours
c. the principal effect of hippocampal lesions is that rats require many more trials to learn the location of a submerged platform
d. healthy rats are able to make associations between visual cues outside the water tank and the location of a submerged resting platform
e. all of the above
d
89
New cards
according to the ‘mass action principle’ loss of learning and memory storage depends on which of these?
a. the specific type of cortex that is damaged
b. the location of cortex that is damaged
c. the total amount of cortex that is damaged
d. whether the cortical damaged is unilateral or bilateral
e. all of the above
a. the specific type of cortex that is damaged
b. the location of cortex that is damaged
c. the total amount of cortex that is damaged
d. whether the cortical damaged is unilateral or bilateral
e. all of the above
c
90
New cards
which of the following is true about dementia?
a. memory deficits are the only symptoms of dementia
b. dementia is mostly due to the natural process of aging
c. Alzheimer’s disease accounts for about 10% of dementia cases
d. unlike Alzheimer’s disease, it is fairly common for dementia to begin to develop before age 50
e. dementia is characterized by memory impairment along with another intellectual deficit such as aphasia or executive functioning
a. memory deficits are the only symptoms of dementia
b. dementia is mostly due to the natural process of aging
c. Alzheimer’s disease accounts for about 10% of dementia cases
d. unlike Alzheimer’s disease, it is fairly common for dementia to begin to develop before age 50
e. dementia is characterized by memory impairment along with another intellectual deficit such as aphasia or executive functioning
e
91
New cards
which of the following is not an example of declarative memory?
a. remembering what you had for dinner
b. remembering how to ride a bike
c. remembering that a wrench is a tool
d. remembering your friend’s phone number
e. remembering the scene of an accident
a. remembering what you had for dinner
b. remembering how to ride a bike
c. remembering that a wrench is a tool
d. remembering your friend’s phone number
e. remembering the scene of an accident
b
92
New cards
which of the following deficits do you think might cause Alzheimer’s disease patients to not encode their environment, therefore wander around and get lost?
a. loss of place cell neurons in the hippocampus
b. loss of grey matter in the parietal cortex
c. loss of grey matter in the frontal cortex
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
a. loss of place cell neurons in the hippocampus
b. loss of grey matter in the parietal cortex
c. loss of grey matter in the frontal cortex
d. all of the above
e. none of the above
a
93
New cards
which of the following does not contribute to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease?
a. extracellular beta amyloid plaques
b. neurofibrillary tangles comprised of tau protein
c. excess activity in the hippocampus
d. loss of acetylcholine containing neurons
e. all of the above contribute
a. extracellular beta amyloid plaques
b. neurofibrillary tangles comprised of tau protein
c. excess activity in the hippocampus
d. loss of acetylcholine containing neurons
e. all of the above contribute
c
94
New cards
drugs used to alleviate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease attempt to enhance cholinergic transmission by…
a. blocking acetylcholine reuptake
b. blocking acetylcholine receptors
c. increasing acetylcholine syntheses
d. inhibiting the degradation enzyme acetylcholinesterase
e. directly increasing acetylcholine release from the presynaptic neuron inhibiting the degradation enzyme acetylcholinesterase
a. blocking acetylcholine reuptake
b. blocking acetylcholine receptors
c. increasing acetylcholine syntheses
d. inhibiting the degradation enzyme acetylcholinesterase
e. directly increasing acetylcholine release from the presynaptic neuron inhibiting the degradation enzyme acetylcholinesterase
d
95
New cards
which of the following changes occurs in the brain of a person with Alzheimer’s disease?
a. decreased brain weight and volume
b. enlarged ventricles
c. atrophy of the cortex
d. loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis
e. all of the above
a. decreased brain weight and volume
b. enlarged ventricles
c. atrophy of the cortex
d. loss of neurons in the nucleus basalis
e. all of the above
e
96
New cards
which type(s) of synaptic change(s) is(are) thought to underlie learning?
a. formation of axon collaterals to increase the number of synapses in existing circuits
b. increased strength of the synapse resulting in larger post-synaptic potentials
c. neurogenesis - birth and development of new neurons in the hippocampus and cortex
d. all of the above
e. a and b
a. formation of axon collaterals to increase the number of synapses in existing circuits
b. increased strength of the synapse resulting in larger post-synaptic potentials
c. neurogenesis - birth and development of new neurons in the hippocampus and cortex
d. all of the above
e. a and b
e
97
New cards
you observe your pet dog while it is sleeping. You note that she is making muffles braking noises and is moving with small muscle twitches. You conclude that she must be dreaming. What stage of sleep is your dog most likely in?
a. stage 1
b. stage 2
c. stage 3
d. stage 4
e. REM sleep
a. stage 1
b. stage 2
c. stage 3
d. stage 4
e. REM sleep
e
98
New cards
which of the following is true of EEG recording as a person passes into progressively deeper stagers of non-REM sleep?
a. wave frequency decreases, wave amplitude decreases
b. wave frequency decreases, wave amplitude increases
c. wave frequency increases, wave amplitude increases
d. wave frequency increases, wave amplitude decreases
e. wave frequency and amplitude remain unchanged until the onset of REM sleep
a. wave frequency decreases, wave amplitude decreases
b. wave frequency decreases, wave amplitude increases
c. wave frequency increases, wave amplitude increases
d. wave frequency increases, wave amplitude decreases
e. wave frequency and amplitude remain unchanged until the onset of REM sleep
b
99
New cards
in humans and other mammals, the biological clock is found in the:
a. reticular activating system
b. pineal gland
c. superchiasmatic nucleus
d. paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
e. arcuate nucleus
a. reticular activating system
b. pineal gland
c. superchiasmatic nucleus
d. paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus
e. arcuate nucleus
c
100
New cards
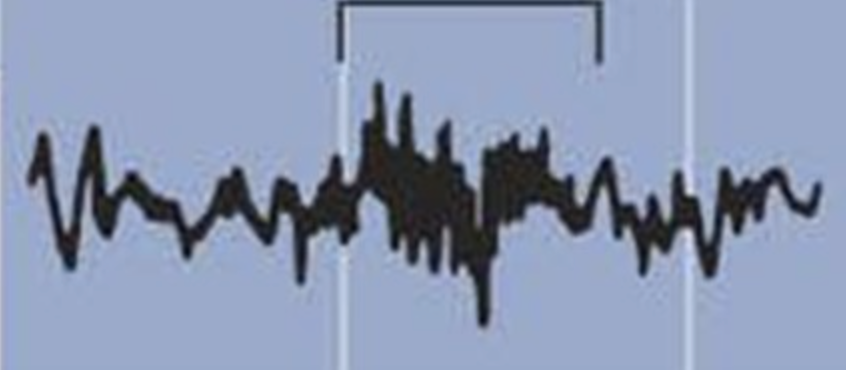
the EEG waveform indicated by the bracket in the figure below is called a ______ and is a characteristic of ______ sleep
a. sleep spindle, stage 2
b. sleep spindle, stage 3
c. slow wave, stage 2
d. slow wave, stage 3
e. slow wave, stage 4
a. sleep spindle, stage 2
b. sleep spindle, stage 3
c. slow wave, stage 2
d. slow wave, stage 3
e. slow wave, stage 4
a