Clinical Psych
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/109
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:21 PM on 3/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1
New cards
Psychological Disorders
a syndrome marked by a clinically significant disturbance in a individual’s cognition, emotion regulation, or behavior
2
New cards
insanity degree
legal term- when someone pleads insanity they are trying to prove they could not recognize right or wrong at the time of the crime
3
New cards
Intern’s Syndrome
condition among medical/psychology students to see symptoms they are studying in themselves
4
New cards
Etiology
causes and progress of a disease or disorder
\-signs and symptoms
\-why does it happen
\-signs and symptoms
\-why does it happen
5
New cards
Biopsychosocial model
diagnosis and treatment of disorders is not only biological, but also must consider the environment, a person’s interpretation of events, bad habits and or bad social skills
6
New cards
Biomedical Model
the concept that diseases or psychological disorders have physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases cured through treatment in a hospital
7
New cards
Diathesis Stress Model
explains behavior/disorder as the result of biological and environmental factors
Diathesis- hereditary disposition
Stress- environmental load put on us by as people
Diathesis- hereditary disposition
Stress- environmental load put on us by as people
8
New cards
Labeling disorders
classifications attempt to describe a disorder, predict its course, apply treatment, and stimulate research
* patients can be viewed differently or treated differently with labels
* patients can be viewed differently or treated differently with labels
9
New cards
DSM-V
system of diagnosis under which a person will be compared to criteria in the manual and if they meet those criteria, they can be diagnosed
10
New cards
Thomas Szaz
theorist who believed that mental illness was a myth because there are no biological, chemical, or physical traces of most mental illnesses
\-thought labels associated with mental illnesses were political
\-thought labels associated with mental illnesses were political
11
New cards
posttraumatic growth
positive psychological changes as a result of struggling with extremely challenging circumstances and life crises
12
New cards
Social Anxiety Disorder
intense fear of social situations, have intense fear of being scrutinized by others, avoids potentially embarrassing situations
13
New cards
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
person is continually tense, apprehensive, and in state of automatic nervous system arousal
* often jittery, agitated, sleep deprived
* often accompanied by depressed mood
* often jittery, agitated, sleep deprived
* often accompanied by depressed mood
14
New cards
Panic disorder
anxiety disorder marked by unpredictable minutes of long intense dread in which a person experiences terror and accompanying chest pain, choking, etc.
15
New cards
Phobias
anxiety disorders marked by a persistent irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object, activity, or situation
* incapacitated by efforts to avoid fears
* incapacitated by efforts to avoid fears
16
New cards
Obsessive compulsive disorder
characterized by unwanted repetitive thoughts (obsessions) and actions (compulsions)
* person will often know their thoughts are irrational, which increases anxiety surrounding behaviors and they continue to take up more and more time
* person will often know their thoughts are irrational, which increases anxiety surrounding behaviors and they continue to take up more and more time
17
New cards
Hoarding Disorder
persistent difficulty discarding or parting with possessions because of perceived need to save them
* distress at thought of getting rid of things
* distress at thought of getting rid of things
18
New cards
Body Dysmorphic disorder
person can’t stop thinking about one or more perceived flaws in appearance
* can feel ashamed or anxious in social situations
* can feel ashamed or anxious in social situations
19
New cards
Post Traumatic stress disorder
characterized by haunting memories, nightmares, social withdrawal, jumpy anxiety, numbness of feeling, insomnia for over 4 weeks after a traumatic experience
20
New cards
Major Depressive Disorder
when a person experiences (in the absence of drugs or other medical conditions) two or more weeks with 5 or more symptoms of depression, one of must be depressed/loss of interest or pleasure
21
New cards
Symptoms of Major Depressive Disorder
* significant weight loss
* insomnia or hypersomnia
* lethargy or physical agitation
* fatigue/ loss of energy
* feeling worthless
* excessive guilt
* problems in thinking/ concentrating
* recurrent thoughts of death/suicide
\
* insomnia or hypersomnia
* lethargy or physical agitation
* fatigue/ loss of energy
* feeling worthless
* excessive guilt
* problems in thinking/ concentrating
* recurrent thoughts of death/suicide
\
22
New cards
Persistent depressive disorder
mildly depressed mood more often than not for at least 2 years
23
New cards
Symptoms of Persistent depressive disorder
* low self esteem
* problems with sleep
* low energy
* hopelessness
* problems with appetite
* problems with decision making
* problems with sleep
* low energy
* hopelessness
* problems with appetite
* problems with decision making
24
New cards
Bipolar disorder
periods of deep depression and mania
* phases alternate week to week/ month to month
* phases alternate week to week/ month to month
25
New cards
mania
hyperactive, euphoric, wildly optimistic
26
New cards
Cyclothymia
shifts between milder depression and hypomania (milder mania)
27
New cards
Seasonal Affective Disorder
people who have normal mental health through most of the year exhibit depressive symptoms at the same time each year (mostly winter)
28
New cards
Dissasociative Amnesia
memory disorder characterized by sudden autobiographical memory loss
* forget name, address, family, friends, etc.
* forget name, address, family, friends, etc.
29
New cards
Dissociative Fugue
amnesia for personality, identity, individuality, with unplanned traveling/wandering
* usually short lived
* usually short lived
30
New cards
Dissociative Identity Disorder
rare dissasociative disorder in which a person exhibits two or more distinct and alternating personalities
* each personality has own voice/mannerisms
* original personality denies awareness of others
* each personality has own voice/mannerisms
* original personality denies awareness of others
31
New cards
Antipyschotic drugs
drugs used to treat schizophrenia and other severe forms of thought disorders
\-dampen responsiveness to irrelevant stimuli
\-occupy receptor sites for dopamine
\-dampen responsiveness to irrelevant stimuli
\-occupy receptor sites for dopamine
32
New cards
Psychoactive drugs
drugs that physically change the brain’s functioning by altering its chemistry
33
New cards
Antidepressants
drugs used to treat anxiety disorders, depression, OCD, and PTSD
* act as agonists, working to increase availability of neurotransmitters such as norepinphrine and serotonin
* take abt a month to go into full effect
* act as agonists, working to increase availability of neurotransmitters such as norepinphrine and serotonin
* take abt a month to go into full effect
34
New cards
Antianxiety drugs
* used to control anxiety and agitation
* typically used along with psychotherapy
* work to depress the nervous system
* can be addictive
* typically used along with psychotherapy
* work to depress the nervous system
* can be addictive
35
New cards
Mood Stabilizers
* used to treat the emotional highs and lows of bipolar or schizophrenia
36
New cards
Lithium Carbonate
* helps stabilize mood and decreases risk of suicide
* most common drug for this is lithium carbonate
* becomes distributed in the central nervous system and causes various changes there
* most common drug for this is lithium carbonate
* becomes distributed in the central nervous system and causes various changes there
37
New cards
Electroconvulsive Therapy
biomedical therapy for severely depressed (or manic) patients in which a brief electric current is sent through the brain of an anesthetised patient
* will seize and be unconcious for abt 30 min
* done 3 times a week for 2-4 weeks
* will seize and be unconcious for abt 30 min
* done 3 times a week for 2-4 weeks
38
New cards
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
procedure that includes application of repeated pulses of magnetic energy to the brain
* used to treat depressed moods
* patients are awake during procedure, and there are no serious side effects
* assumed to stimulate depressed areas of the brain
* used to treat depressed moods
* patients are awake during procedure, and there are no serious side effects
* assumed to stimulate depressed areas of the brain
39
New cards
Deep Brain Stimulation
* relatively new technique that involves use of an implanted device that will stimulate the neural hub that connects the frontal lobe and the limbic system
* used to attempt to treat depression
* has appeared to create relief for some
* used to attempt to treat depression
* has appeared to create relief for some
40
New cards
Psychosurgery
surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to change behavior
* most famous of this is lobotomy
* most famous of this is lobotomy
41
New cards
Lobotomy
* procedure that was used to calm uncontrollably emotional or violent patients
* during procedure, nerves connecting the frontal lobe to the emotion controlling centers of the brain were cut
* during procedure, nerves connecting the frontal lobe to the emotion controlling centers of the brain were cut
42
New cards
Schizophrenia
* delusions- false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur that may accompany psychotic disorders
* hallucinations- false sensory experience
* disorganized speech
* diminished or innapropriate emotional expression
* disturbed perceptions
* caused by genetics and having larger ventricles
* hallucinations- false sensory experience
* disorganized speech
* diminished or innapropriate emotional expression
* disturbed perceptions
* caused by genetics and having larger ventricles
43
New cards
Delusions
* false beliefs, often of persecution or grandeur that may accompany psychotic disorders
44
New cards
Chromic Process Schizophrenia
schizophrenia that develops slowly over time
* more likely to have negative symptoms
* more likely to have negative symptoms
45
New cards
Acute/ Reactive Schizophrenia
when schizophrenia develops suddenly
* more likely to have positive symptoms
* more likely to have positive symptoms
46
New cards
Negative symptoms of schizophrenia
remove appropriate behavior
* catatonic state
* expressionless faces
* toneless voices
* catatonic state
* expressionless faces
* toneless voices
47
New cards
Positive symptoms of schizophrenia
* disorganized speech
* hallucination
* delusion
* hallucination
* delusion
48
New cards
Neurodevelopmental disorders
impairments in the growth and development of the brain or cerebral nervous system
49
New cards
Autism Spectrum disorder
marked by significant defecincies in communication and social interactions and by rigidly fixed interests and repetitive behaviors
50
New cards
Attention defecit hyperactivity disorder
extreme innattention hyperactivity and impulsitivity
* caused by genetics
* diagnosed 3x more in boys than girls
* caused by genetics
* diagnosed 3x more in boys than girls
51
New cards
Tourette’s Syndrome
characterized by multiple motor tics and at least one vocal tic
* also includes coprolalia- type of vocal tic which you say taboo/ innapropriate words (only 10% with tourettes have this)
* cause by genetic factors
* also includes coprolalia- type of vocal tic which you say taboo/ innapropriate words (only 10% with tourettes have this)
* cause by genetic factors
52
New cards
Impulse and conduct disorders
problems with self control or emotions or behaviors
\
\
53
New cards
Conduct Disorder
behavioral and emotional disorder found in children which is characterized by
* agressive behavior- fighting, bullying, violating rules, running away
* destructive behavior- arson, vandalism, etc.
* deceitful behavior- lying, shoplifting, etc.
with little to some remorse
* agressive behavior- fighting, bullying, violating rules, running away
* destructive behavior- arson, vandalism, etc.
* deceitful behavior- lying, shoplifting, etc.
with little to some remorse
54
New cards
Oppositional defiant disorder
presents as ongoing pattern of an angry/irritable mood, defiant/argumentative behavior and vindictiveness to those in authority
* temper tantrums
* arguing w/ authority
* blaming others for mistakes
* swearing
* being spiteful
* saying mean and hurtful things when upset
* temper tantrums
* arguing w/ authority
* blaming others for mistakes
* swearing
* being spiteful
* saying mean and hurtful things when upset
55
New cards
Somatic Symptom disorder
psychological disorder in which the symptoms take a somatic (bodily) form without apparent physical cause
* psychological state produces physical results
* psychological state produces physical results
56
New cards
Conversion disorder
disorder in which a person experiences very specific genuine physical symptoms with no physiological basis
* covers area which is covered voluntarily- swallowing, vision, etc.
* covers area which is covered voluntarily- swallowing, vision, etc.
57
New cards
Illness Anxiety disorder
interprets normal physical sensations as symptoms of a disease
* every physical sensation is caused by a disease no matter what doctors say
* every physical sensation is caused by a disease no matter what doctors say
58
New cards
Factitious disorder
acts as if they have an illness by creating or exaggerating symptoms
* creates medical issues for attention
* purposely creates bodily symtoms as result of a psychological issue
* creates medical issues for attention
* purposely creates bodily symtoms as result of a psychological issue
59
New cards
anorexia nervosa
eating disorder in which a person maintains starvation diet despite being significantly underweight
* anorexic people typically feel fat even though they are underweight and they are afraid of being fat
* anorexic people typically feel fat even though they are underweight and they are afraid of being fat
60
New cards
bullimia nervosa
eating disorder in which a person alternates binge eating with purging (vomiting or laxatives), excessive excercise or fasting
61
New cards
Binge eating disorder
characterized by binge eating episodes accompanied by distress, disgust, or guilt, but without purging associated with bullimia
62
New cards
Personality disorders
characterized by inflexible and enduring behavior patterns that impair social function
63
New cards
Cluster A Personality
(odd, bizzare, eccentric)- paranoid schizoid schizotypical
64
New cards
Cluster B Personality
(dramatic, erratic)- antisocial, histrionic, compulsive
65
New cards
Cluster C Personality
(anxious fearful)- avoidant, dependant, obsessive compulsive
66
New cards
Paranoid Personality disorder
characterized by paranoia, mistrusting people, and are suspicious of others with no reason to be
* unforgiving, hypersensitive, cold/distant in relationships, and cannot see their role in problems
* unforgiving, hypersensitive, cold/distant in relationships, and cannot see their role in problems
67
New cards
Antisocial personality disorder
person exhibits lack of conscious for wrongdoing, even towards friends and family- may be aggressive, ruthless, impulsive
* criminal behavior is common
* genetic and social cause (trauma, poverty, etc.)
* criminal behavior is common
* genetic and social cause (trauma, poverty, etc.)
68
New cards
69
New cards
Narcissistic personality disorder
* person will have inflated sense of their own importance as well as need for admiration
* behind this self-esteem is fragile
* unhappy when they dont get admiration they crave
* genetic/ social factors cause it
* behind this self-esteem is fragile
* unhappy when they dont get admiration they crave
* genetic/ social factors cause it
70
New cards
Avoidant Personality disorder
avoid work, school, events that force them to interact with others, concerned with feelings of inadequacy
71
New cards
Borderline Personality disorder
mood swings, intense episodes of anger, anxiety, etc, which can last a few hours to a few days
72
New cards
Histrionic Personality disorder
characterized by intense unstable emotions and distorted self images
* overly dramatic and concerned with appearance
* often seen as shallow
* overly dramatic and concerned with appearance
* often seen as shallow
73
New cards
Obsessive compulsive personality disorder
person who is preoccupied with orderliness, perfectionism, interpersonal control
* reluctant to delegate tasks and is stubborn
* reluctant to delegate tasks and is stubborn
74
New cards
Phillipe Pinel
helped to establish a more humane approach (moral treatment) to treating the mentally ill that considered emotions and social interactions
* seen as father of modern psychiatry
* seen as father of modern psychiatry
75
New cards
Dorothea Dix
known for touring prisons in massachusetts and advocated for the mentally ill who were imprisoned there
76
New cards
Deinstitutionalization
A movement to shift individuals with mental illness from long-term institutional care to community-based care.
* done to improve their quality of life and reduce the stigma associated with mental illness.
* done to improve their quality of life and reduce the stigma associated with mental illness.
77
New cards
Clinical Psychologist
can provide emotional, mental, and behavioral healthcare but are unable to prescribe medication
78
New cards
Psychiatrist
specializes in treatment of psychotic disorders
* are MDs and can prescribe medication
* are MDs and can prescribe medication
79
New cards
Social Workers
can provide therapy, social rehabilitation, crisis intervention, or outreach services
80
New cards
Counselors
type of social worker that can evaluate and treat mental/ behavioral disorders
81
New cards
Eclectic Approach
An approach to therapy that combines techniques from different theories to fit the client's needs. It aims to be flexible and adaptable to individual cases.
82
New cards
Psychoanalytic Approach
A psychological approach that focuses on the unconscious mind and early childhood experiences to understand and treat mental illness. Developed by Sigmund Freud, this approach emphasizes the role of unconscious conflicts, defense mechanisms, and the importance of the therapist-patient relationship in therapy.
83
New cards
Freud and Jung
believed free association released previously repressed feelings, allowing patient to gain self-insight
84
New cards
Dream Interpretation
analyst’s interpretation noting supposed dream meanings, resistances, and other significant behaviors and events in order to promote insight
85
New cards
Transference
strong positive or negative feelings transferred to the analyst of emotions, linked with other relationships
* leads to insight on current relationships
* leads to insight on current relationships
86
New cards
Catharsis
purging emotions which brings relief
87
New cards
Psychodynamic Therapy
derived from psychoanalytic theory that focuses on themes important in all relationships
* goal is to help people improve relationship skills rather than looking at past hurts
* goal is to help people improve relationship skills rather than looking at past hurts
88
New cards
Insight therapy
aims to improve psychological functioning by increasing a person’s awareness of underlying motives and defenses
89
New cards
Client Centered Therapy
created by Carl Rogers, therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathetic environment to facilitate clients growth
* therapist listens without judging
* therapist listens without judging
90
New cards
Active Listening
when listener echoes, restates, and clarifies feelings of the client
91
New cards
Unconditional Positive Regard
therapist helps client feel unconditionally accepted, so that they express their true feelings, which will be empathetically reflected by therapist
92
New cards
Conditions of Worth
conditions we think we must meet in order for people to accept us as worthy of love or positive regard
93
New cards
Cognitive Therapy
Type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and beliefs to improve mental health.
* based on the idea that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and can be changed through identifying and challenging negative patterns
* based on the idea that thoughts, feelings, and behaviors are interconnected and can be changed through identifying and challenging negative patterns
94
New cards
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy
confrontational cognitive therapy that challenges people’s illogical self defeating attitudes and assumptions
* created by Albert Ellis
* created by Albert Ellis
95
New cards
Cognitive Triad
three key elements present in a person’s depressed beliefs
* thought you could reverse the way clients felt abt themselves by gently revealing irrational thinking and persuaded people to see life in a better light
* thought you could reverse the way clients felt abt themselves by gently revealing irrational thinking and persuaded people to see life in a better light
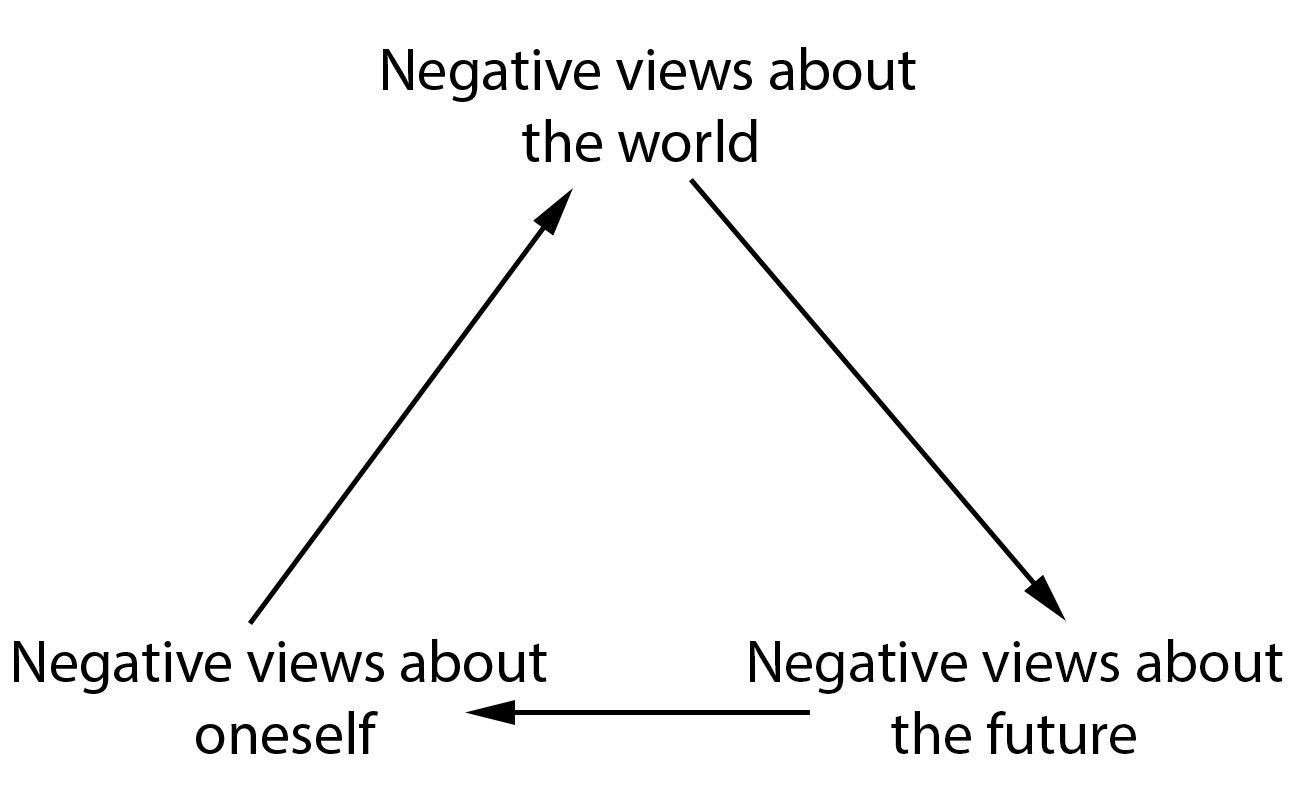
96
New cards
Explanatory styles
created by Seligman
* internal or external causes
* optimist or pessimist
* internal or external causes
* optimist or pessimist
97
New cards
Directive Behavior Therapy
* be mindful and focus on the present
* tolerate crisis with cognitive techniques
* be assertive in relationships
* conditioning to eliminate bad behaviors
* tolerate crisis with cognitive techniques
* be assertive in relationships
* conditioning to eliminate bad behaviors
98
New cards
Counterconditioning
uses classical conditioning to evoke new responses to stimuli that are triggering unwanted behaviors (includes exposure therapy)
99
New cards
Systematic Desensitization
exposure therapy that associates a pleasant, relaxed state with gradually increasing anxiety triggering stimuli
* patients are taught progressive relaxation- therapist has you learn to relax one muscle group at a time until you are completely relaxed-- once releaxed make list of anxiety triggering stimuli and relax and then level up and repeat
* patients are taught progressive relaxation- therapist has you learn to relax one muscle group at a time until you are completely relaxed-- once releaxed make list of anxiety triggering stimuli and relax and then level up and repeat
100
New cards
Flooding
patient subjected to phobia basically immediately
* while exposed, therapist leads them through relaxation techniques to eliminate anxiety
* while exposed, therapist leads them through relaxation techniques to eliminate anxiety