Natural Disasters
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Final Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Storm stages
tropical wave
tropical depression or disturbance
tropical storm (gets named from here)
hurricane (74 mph winds)
What is fire?
rapid combustion
combination of O2 with carbon, hydrogen, and other elements in a chemical reaction that produces light, heat, and flame
exothermic reaction (releases heat) o can think of it as the opposite of photosynthesis
Fire stages: pre-heating
water is expelled from wood/fuel
this is accomplished through:
flames (nearby fires)
long periods of dryness (lack of rain, drought)
Fire stages: pyrolysis
thermal degradation of wood cellulose (stable to about 615 F)
gives off flammable gasses and water vapor
ash
gas movement causing cracks in the wood
can BECOME flames
Fire stages: flaming combustion
pyrolyzed wood burns hot and fast
greatest energy released
highly efficient; predominates in windy environments
heat transfer through:
radiation
convection
conduction
Fire stages: glowing combustion
after the active flames die off; coals
wood slowly consumed in oxidation reaction
lower temperature!
Fire burn direction
Up!
up slope
heat rises
2005 hurricane season
Worst season on record until 2020
27 names storms
7 considered major
Hurricane seasonal average
10 named storms, 6 hurricanes, 2 major
Pacific Ocean name for hurricane
Typhoon
Indian Ocean name for hurricane
Cyclone
tropical wave
initial low pressure disturbance
unorganized
moving west
winds < 20 mph
tropical depression or disturbance
moving mass of thunder storms
starting to organize
assigned a number
winds < 39 mph
tropical storm
gets named
alternating male/female names starting with "A"
distinct rotary/cyclonic motion
winds 39 – 74 mph
Hurricane
well-defined circular structure with large rain bands
central "eye" of low pressure first forms
winds > 74 mph (increasing to > 150 mph)
Northern Hemisphere hurricane turn which way??????
Counterclockwise
Cat 2 hurricane in terms of energy from hydrogen bombs???
Hundreds
Hurricane conditions in the beginning
calm wind patterns
for several days and 100s of miles
warm ocean surface (80 degrees)
as well as 200 feet below
vertical disturbance in the atmosphere
Saffir Simpson scale
measured in categories (1 through 5)
function of wind speed and storm surge
potential damage
potential damage is not linear with category
Saffir Simpson scale: cat 1
wind: 74-95 mph
effects: No real damage to building structures
Saffir Simpson scale: cat 2
wind: 96-110 mph
effects: Minor damage to buildings. Considerable damage to vegetation
Saffir Simpson scale: cat 3
wind: 111-130 mph
effects: Some structural damage to small residences. Mobile homes are destroyed. Flooding near the coast.
Saffir Simpson scale: cat 4
wind: 131-155 mph
effects: Complete roof structure failure on small residences. Major erosion of beach. Major damage to lower floors of structures.
Saffir Simpson scale: cat 5
wind: >155 mph
effects: Complete roof failure and major damage to all structures located less than 15 feet ASL
Storm surge
large volume of rain/runoff prior to landfall of the hurricane
90% of all fatalities in a hurricane caused by storm surge
large amounts of erosion
Storm surge from 3 factors:
force of the waves (including debris in the water)
hydraulic lift (upward force) under structures
reflected wave energy from man-made structures
Factors in storm surge SEVERITY
wind speed
tide stage
low pressure
two types of surge:
flood surge: water brought onto the land by the storm
ebb surge: water floods off the land to the sea
Where is wind moving fastest on that there hurricane moving north?
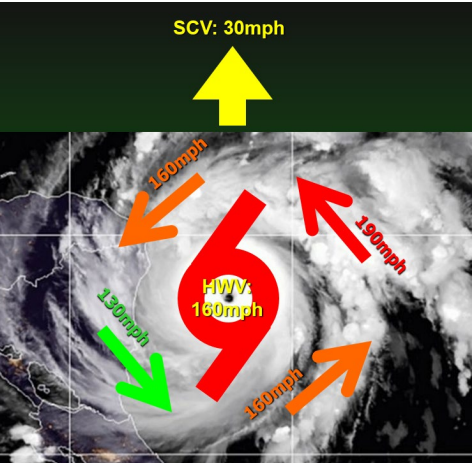
Doppler radar
Examines final movements prior to landfall
hours to days timescale
visible and infrared satellite images
Every 30 minutes on average
can be acquired pretty fast
Planes flying through hurricane storm center
measure vertical structure, wind speeds, pressure, and temperatures
use drop-sonde instruments to relay information regarding the change with height
Hurricane Andrew
Category 4-5
Bahamas —> Florida —> Louisiana
COSTLIEST IN U.S. History (UNTIL KATRINA)
COULD have been worse if it landed a bit more north
Hurricane Katrina
Costliest Atlantic hurricane in history!!!
costliest damage at eye wall
mini swirls did happen!
Florida, to the gulf, to Louisiana after it regained energy
Cat 5 in the Gulf
NOVA: Flood! (The Great flood of 1993)
Flooding in the Midwest! (Mississippi River)
unusually wet Summer
JETSTREAM stayed over the Midwest month after month (storm highway)
weakening levees
all out war against nature
bringing in more dam/levee supplies
multiple levee breaks/multiple crests
St. Louis
big ass floodwall broke!
broken levee on the Columbia side relieve pressure on St. Louis and the propane tanks
9 state area
costliest flood in U.S. hisotry
Mini swirls
small localized swirls within the eyewall
Flood
damaging floods result when the volume of river/stream flow exceeds natural barriers and/or the levels of flood preparedness
because flow is greater or longer than expected
because of an incomplete understanding of local hazards
Natural flood causes
heavy rain
dam failure
rapid snowmelt / ice jams
deforestation
steep slopes
storm surges during tropical storms / hurricanes
Deadliest flood disaster
Johnstown floods
Infiltration capacity
capacity of a soil to absorb water
High infiltration rates
coarse soil
well-vegetated land
low soil moisture
porous topsoil
poor infiltration rates
impermeable crusts in the soil
salt layers
cold weather (frozen soil has poor infiltration)
compaction
paved (impervious) surfaces
Hydrograph
discharge rate (Q) in m3/s (plus rainfall amount) versus time
measured by a stream gauge
varies with infiltration capacity and rainfall amount
Case Study: Pittsburgh flood 1936
Flood Control Act 1936 and 1938
primary causes
prolonged precipitation (snow & rain)
high intensity, shorter duration rains
certain areas had large flash floods
steep slopes, thin soil cover, low vegetation
Power and water cut off; contamination by sewage
Flood Control Act 1936 and 1938
Flash flooding of Washington Blvd. in Pittsburgh
Aug. 19, 2011 at 4:30pm (rush hour) o 1.79 inches of rain in 30 min
volume = 208 Olympic sized swimming pools
10 feet of water rapidly rose on the roadway
sewer capacity was exceeded
killed 4 people
Miramichi Fire
October 1825 (Maine & New Brunswick)
a summer of sparse rain
strong winds spread smaller camp and settler’s fires
among the worst wildfires in North American history Page 2/6
burned 3.9 million acres
killed 160 - 500 people
left 15,000 homeless
Bad trees for fires D:
Ponderosa Pines
western U.S.
cones don’t open until a certain temperature is reached
Eucalyptus
high oil content
Riskiest area in the world for wildfires
the Mediterranean
Northern California: Mendocino complex fire
burned more than 459,000 acres
the largest complex fire in the state's history
Diablo winds
Originate inland in areas of high pressure
air becomes hotter and drier as it heads west towards the low pressure coast
speed up as they are forced through narrow spaces (canyons and mountainsides)
if they hit already dry area, they can fan the flames and carry the wildfire overland
Early earth
was more similar to present-day Venus than what we have today
extreme volcanic activity
high CO2 in atmosphere (we talking 98% yo) and hotter temperatures
Where that early earth CO2 go??
Its in the limestone and other organic material!!! (80% of it)
resulting from plate tectonics and rock cycle
rest went to oceans and living material
Oxygen isotopes
we can examine changes in rock and fossil composition over time for example: O2 isotope ratio in shells (think back to those early lectures!) there are three isotopes of O2 (16O, 17O, 18O) - 16O is the most common Page 2/6 evaporation from the oceans favors lighter isotopes therefore, precipitation concentrates 16O and 17O on land (in ice/snow) and 18O gets concentrated in the sea if the amount of 18O/16O is measured in shells, scientists know about the conditions of the water at the time they were formed - lower 18O meant warmer conditions
Greenhouse gasses
allow solar energy in but trap the radiant heat from the Earth from escaping
water vapor (H2O)
carbon dioxide (CO2)
methane (CH4)
nitrous oxide (N2O)
ozone (O3)
CFC’s
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC)
100’s of scientists meeting and reporting their findings on climate change
assess current models/predictions
report areas of uncertainty
High level findings from IPCC
warming of climate is not in question
90% of all warming since 1950 is due to human activity
all greenhouse gases are at their highest amount in the past 650,000 years
the probability that this is all from natural causes is < 5%
average world temperatures could rise from 1 to 6° F by 2100
> 60% chance of increased droughts, hurricanes, and extreme tides
> 90% chance of more frequent heat waves and heavy rainfall
a rise in sea level of between 7 – 23 inches
levels now will continue to affect the climate for the next 1,000 years!
Climate mitigation options
changes in technology o carbon-free or carbon-neutral energy technologies for power plants, cars, etc.
takes time (politics) o cap and trade
limit CO2 emissions through a market-based trading system
CO2 producers pay more for emissions credits
non-CO2 producers gain by selling credits
air scrubbing
possible but VERY expensive right now o
fertilizing the oceans with FeSO4 to grow algae (similar to massive tree planting)
algae would take up CO2
effects on the ocean’s biosphere unknown?
weathering of rocks
pulls CO2 out of atmosphere and makes carbonic acid
also, very slow
geoengineering
inject large amounts of particles into the atmosphere to reflect solar energy
similar to a volcanic eruption
risks unknown?
carbon sequestration
capturing CO2 and injecting it deep underground in a liquid form
Taxonomy order
kingdom phylum class order family genus species