Pediatric Orthopedics and Rheumatology
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine (coronal plane) due to idiopathic, congenital, neuromuscular causes
PE: Shoulder height, Waist/scapular asymmetry, Adams forward bend test, trunk shift, Rib prominence, Neuro exam
Dx: XRAY (first line): Cobb angle>10º (diagnostic);
MRI (atypical curve, neuro concerns, surgical planning)
Tx: Cobb Angle on imaging:
10-25º observation
25-45º bracing in skeletally immature to prevent progression
>45-50º: consider surgical intervention
Curves>90º associated with cardiopulmonary dysfunction, pain, decreased self image
Congenital Torticollis
most common cause due to abnormal contraction of sternocleidomastoid muscle
Risk Factors: oligohydraminios, first pregnancy, traumatic delivery, breech position
S/S: persistent head tilt and rotation toward involved side; can cause plagiocephaly (flat head syndrome); hip dysplasia (20%)
PE: check for palpable SCM muscle tightening, passive ROM, neuro exam, hip exam
Tx: passive stretching and physical therapy (95% improved by 1yo); collar, surgery (rare)
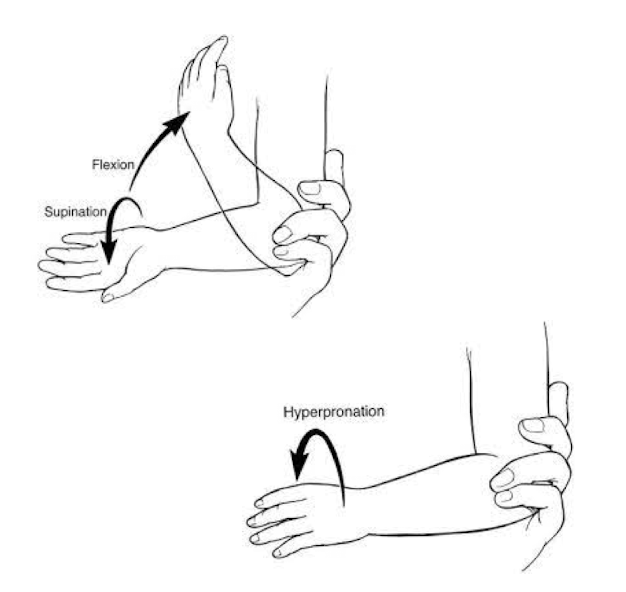
Nursemaid’s elbow
radial head subluxes with axial traction due to underdeveloped annual ligament w/ pull to lift, grabbing to catch fall, tantrums
very common 1-4yo, less common>5yo
PE: arm in slight flexion, pronated with no swelling; pain with any flexion or supination; r/o bony tenderness or deformity (supracondylar fracture)
Dx: clinical diagnosis, imaging unnecessary unless concern for fracture/atypical
Tx: reduce in clinic (hyperpronation or flexion/supination), pt ed. for high recurrence rate
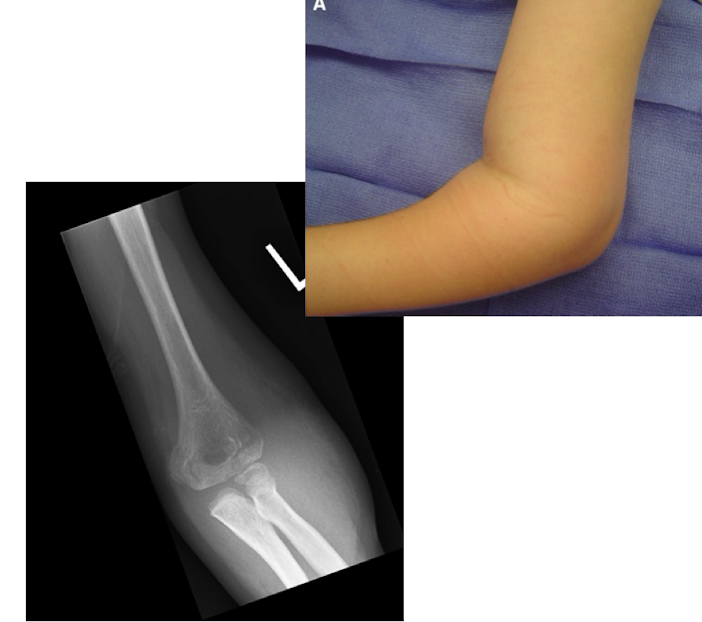
Supracondylar fracture of the distal humerus
one of the most common traumatic fractures in kids 5-7yo
S/S: pain, swollen elbow, limited motion; associated with anterior interosseous nerve, median or radial nerve neurapraxia, can be urgent (pulseless, check with Doppler)
Dx: XRAY AP/Lat view of elbow
Tx: Casting (minimally displaced); surgery (complicated)
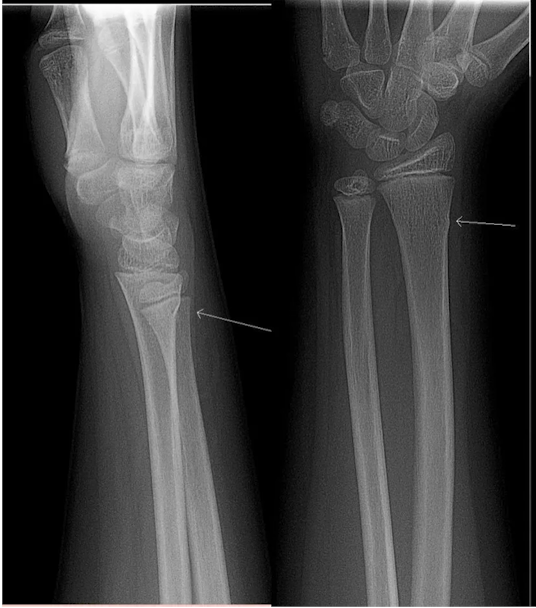
Torus (buckle) fracture
bony cortex is compressed and bulges without extension of the fracture or breach of cortex, distal radius is most common site due to FOOSH injury
-50% of all pediatric fractures
S/S: wrist pain after fall with limited swelling or loss of motion
Dx: XRAY AP/Lateral shows bulging ‘buckle’ of bony cortex of wrist
Tx: conservative: splint vs short arm cast, can be managed by PCP, minimal follow up, no surgery
Greenstick fracture
partial thickness fracture of one cortex, a pediatric fracture <10yo
-forearm (most common), can occur in other long bones, tibia/fibula
MOI: FOOSH injury is most common cause
S/S: loss of motion, pain to palpation, +/- ecchymosis, deformity
Dx: XRAY (first line) shows ‘bowing’ of bones
Tx: conservative: depending on angulation, ± reduction with casting
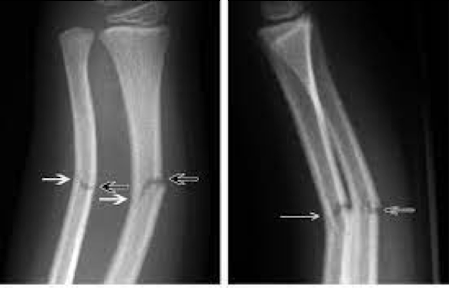
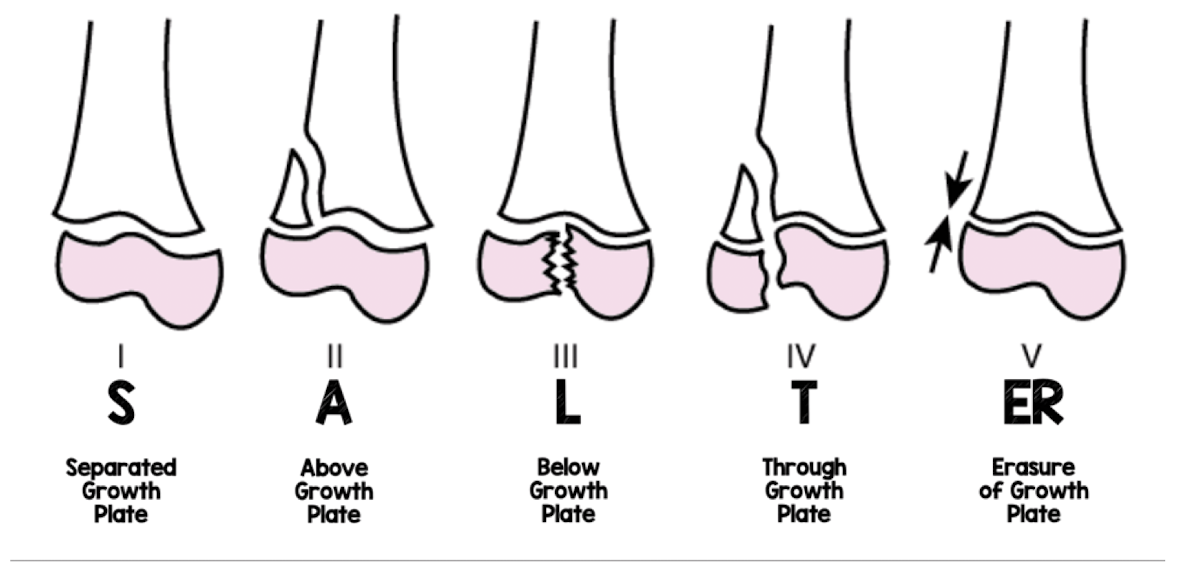
Salter-Harris classification
What classification system is used to classify any fracture that extends to the articular surface (growth plate) of pediatric patients?
Non Accidental Trauma (NAT)
RED FLAGS History:
Delays in seeking treatment
Inconsistent stories between historians
Caregivers who have an inappropriate affect
A pattern of injury that does not match what caregivers say happened
A child with a history of injuries
RED FLAG Orthopedic Injuries:
Long bone fractures in a child who is not walking yet
Fractures of ribs, skull, scapulae or sternum (shaken baby)
Metaphyseal corner fractures***
Multiple fractures at different stages of healing
Use due diligence and follow guidelines for your institution
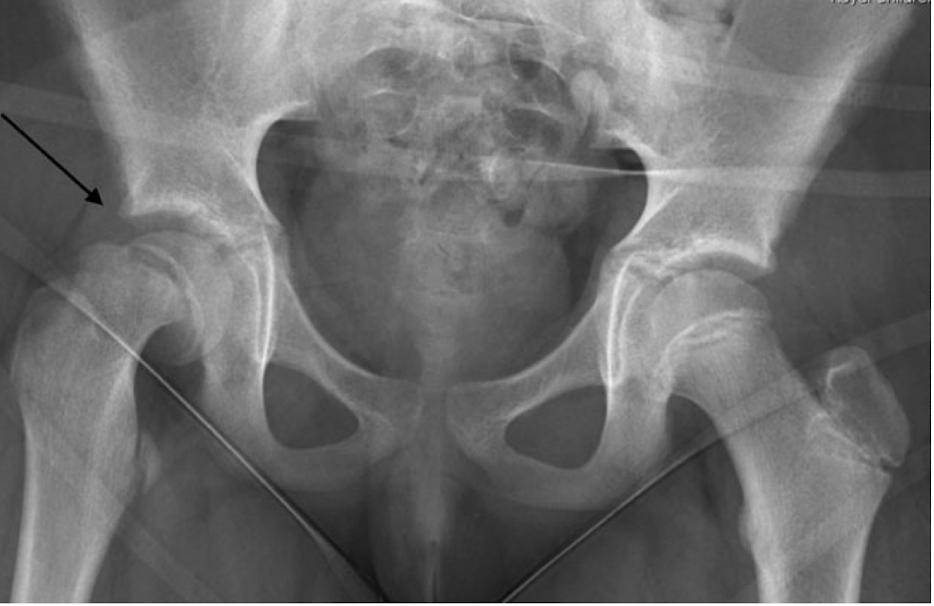
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
disorder of proximal femoral physis causing slippage of the metaphysis relative to epiphysis, most commonly affecting adolescent hips 10-15yo in periods of frequent growth
Risk Factors: AMAB>AFAB, obesity, underlying endocrine disorders (hypothyroid)
S/S: knee pain due to activation of medial obturator nerve, pain in hip, groin, thigh, abnormal gait/limp, hip held in external rotation
Dx: XRAY (“ice cream scoop off cone”)
Tx: percutaneous in situ fixation (surgery)
Complications: contralateral slip, early osteoarthritis, osteonecrosis of head in unstable
**DO NOT MISS!
<4 years old
-Infection (septic arthritis)
-Transient synovitis
-Legg-Calve-Perthes “Perthes” Disease (avascular necrosis)
-Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)
-Fracture (occult)
Causes of limping/refusal to walk in ______
8-16 years old
-Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE)
-Septic arthritis
-Osteomyelitis
-Sever’s calcaneal apophysitis
-Osgood-Schlatter’s disease (tibial tubercle apophysitis)
Causes of limping in ______
Septic Arthritis
joint infection caused by virus, fungus, or bacteria most commonly in childhood <5yo
-typically lower extremity (80%), hip most common in kids
S/S: acute and febrile, irritable, poor appetite, favoring a limb, limited ROM with pain
Septic Arthritis
Most common pathogen:
S. aureus most common cause in all age groups
Group B Strep in neonates
N. gonorrhoeae in adolescents
Dx: synovial analysis (gold standard): Cloudy, WBC >50k, neutrophils >75%; XRAY, US, MRI
Tx: Hospital admission for prompt treatment to avoid cartilage damage: ortho surgery: drainage/lavage, joint arthrotomy, arthroscopy, f/u imaging, pediatric infectious disease consult, empiric antibiotics initially until pathogen is identified, parental IV antibiotics → PO x3 weeks
Transient Synovitis
transient inflammation of joint capsule
S/S: nontoxic/afebrile, insidious onset of limp, groin/thigh pain
hip held in flexion, ABduction/external rotation with mild pain internal rotation, pain/guarding with “log rolling”
Dx: XR, US/labs (WBC, ESR, CRP) - must r/o septic hip!
Tx: conservative, rest, limited weight bearing, NSAIDS, close follow up
**should see marked improvement in 24-48 hours, resolution in 1-2 weeks
Red flag: if worsening or febrile (Septic Arthritis of Hip)
Kocher’s Clinical Criteria
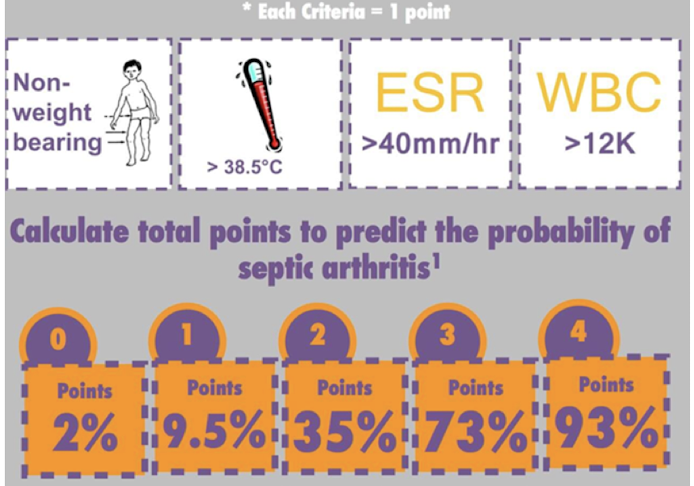
Transient Synovitis vs. Septic Arthritis of Hip
Legg Calve Perthes Syndrome (Perthes)
idiopathic pediatric avascular necrosis the proximal femoral epiphysis of hip due to disruption of blood supply
-typically 4-8yo, AMAB:AFAB 5:1, typically unilateral
S/S: insidious onset, can have painless limp or intermittent groin, hip, thigh pain
PE: stiff ROM, loss of internal rotation, ABduction, limp/Trendelenburg gait (dropped hip), limb length inequality (later stages)
Dx: XRAY (initial); MRI with neg XRAY and high suspicion
Tx: observation; NSAIDs, activity restriction (swim/bike), PT for ROM
→good outcomes in 60% (hip is never completely normal, risk for early osteoarthritis) surgical: reserved for severe cases generally after 8yo
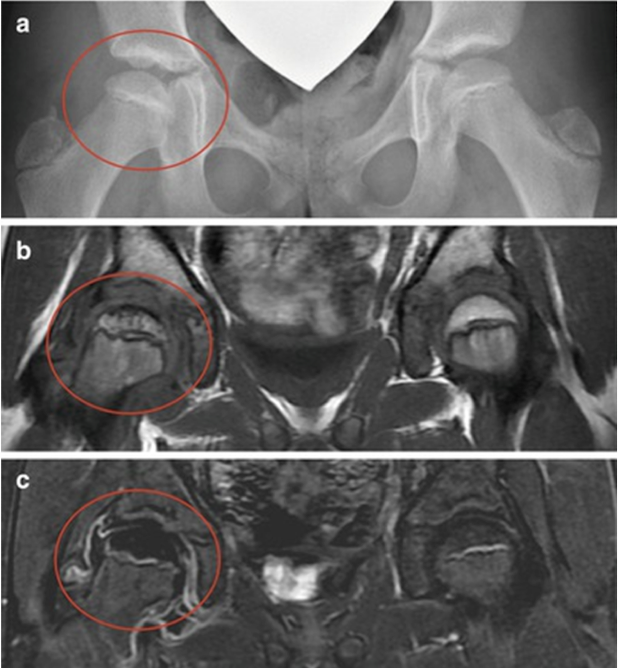
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
abnormal development of the hip joint resulting in instability, subluxation, dislocation and degeneration; the most common orthopedic disorder in newborns
Risk Factors: Female, First born, Family history, Breech (needs US)
Imaging: Ultrasound if risk factors or positive screening test (Barlow, Ortolani, Galeazzi); XRAY if >6 months
**DO NOT MISS!
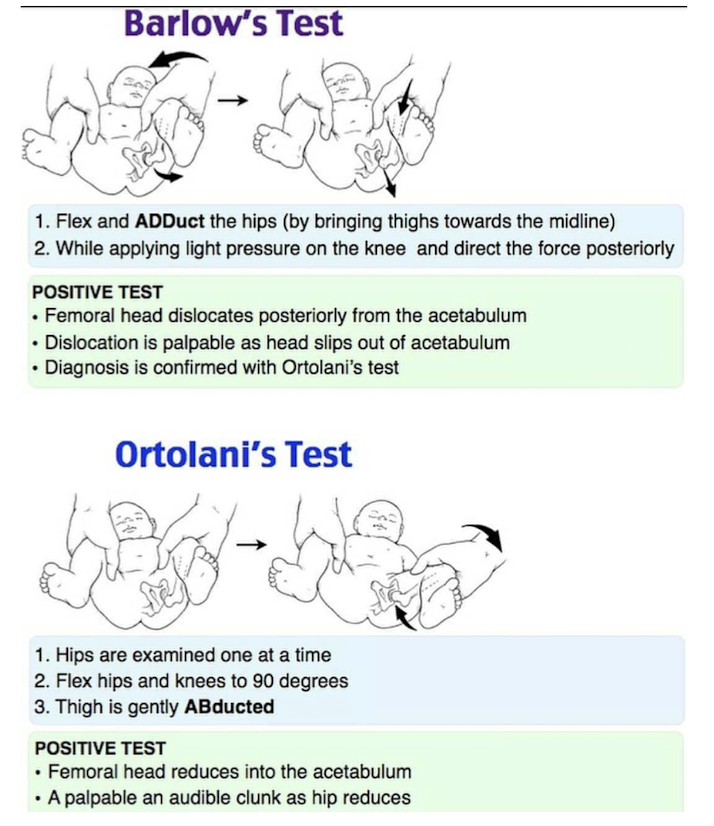
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
newborn screening at 24-72hrs, repeat at every well-child check up 6 months:
Barlow: hip dislocates/subluxes with gentle pressure externally rotated
Ortolani: hip reduces out to in
Galeazzi: limb length discrepancy
Ultrasound if risk factors or positive screening test (XRAY >6 months)
after 1 year: may present as gait abnormality, pelvic obliquity/lumbar lordosis
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
Dx: Ultrasound up to 6 months old with any risk factors (Female, First born, Family history, Breech),XRAY pelvis >6mos old
Tx: Pavlik harness/abduction brace in <6 months; reducible Spica cast in 6-18 mos
operative: open reduction with spica cast, open reduction with femoral or pelvic osteotomy
Early intervention and treatment promotes normal development of hip and prevents dislocation, prevents osteoarthritis and pain in children
**DO NOT MISS!
Genu Valgum/Varum
1. gum- “knock kneed”: evaluate >8-10yo
2. rum - “bow legged”: evaluate >2-3yo
Pathologic conditions: Blounts disease, Rickets, Posttraumatic concerns

Toe walking
common when learning to walk, most walk heel-toe by 2-5yo
Causes
idiopathic: muscle contracture
congenital: clubfoot
neurologic: cerebral palsy
Myogenic: muscular dystrophy
Functional: habitual, common when learning to walk
Tx: stretching and physical therapy, splinting/serial casting, botox injections, surgery (Achilles lengthening)
Clubfoot
most common MSK birth defect, idiopathic deformity of the foot with strong genetic component
S/S: multi contractures: cavus, adductus, varus, equinus
Tx:
-Ponseti method: serial casting + heel cord tenotomy + foot abduction orthosis (avoids comprehensive surgery >90%, compliance is key!)
-Comprehensive surgery
*if untreated, can lead to significant disability
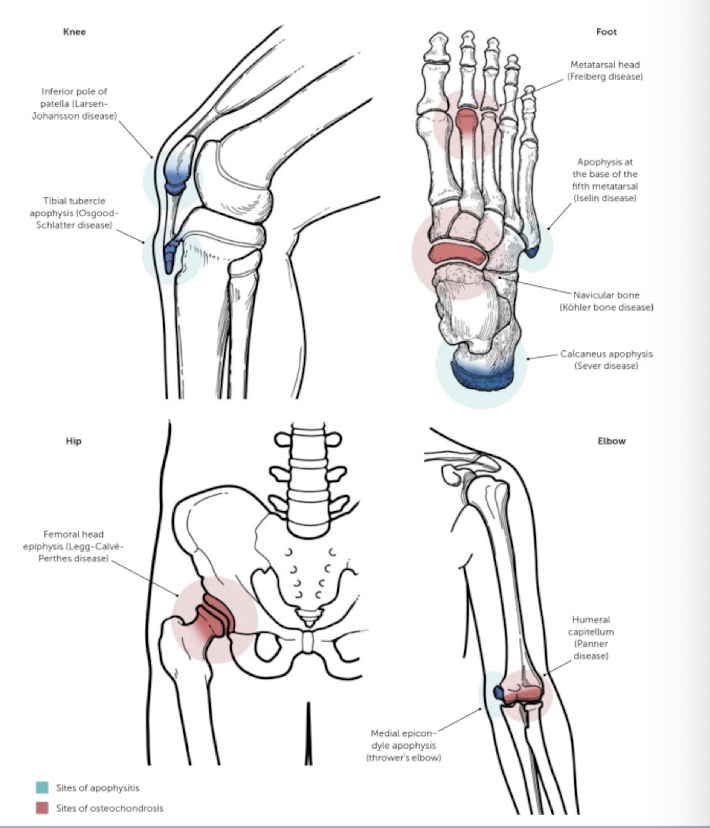
Osgood-Schlatter Disease
tibial tubercle apophysitis (overuse injury) due to repetitive strain and microtrauma from patellar tendon
-typically 10-14yo with recent growth spurt (prior to growth plate closure) and high levels of physical activity
S/S: focal pain, swelling, tenderness to palpation over tibial tubercle; worse with sprinting/jumping, improved with rest
Tx: activity modification x 2-3 months, RICE, NSAIDs, strengthening, supportive measures, surgery for refractory cases

Apophyseal Injury
Part of a spectrum of Osteochondroses often seen during adolescence
Causes: Microtrauma: Repetitive use; Macrotrauma: Avulsion
Risk factors: Rapid growth, general inflexibility, activities with rapid acceleration/deceleration
ie. Osgood-Schlatter Disease
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA)
chronic autoimmune inflammatory arthritis lasting >6 weeks in a patient <16 years old; the most common rheumatic disease in children
-AFAB>AMAB
S/S: synovitis, joint effusion, soft tissue swelling
Labs: CBC, ESR, CRP (must rule out septic joint), ANA, RF, Anti CCP and HLA-B27 to determine subtype
Imaging: XRAY (initial), US (dynamic), MRI (gold standard)
Tx: physical therapy, NSAIDs, biologics (methotrexate, TNF-1) with goal of remission
Refer to Pediatric Rheumatology
Pediatric Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
chronic autoimmune disease, typically teenage onset ~12yo
S/S: prolonged fever + malaise (most common presenting symptoms), malar rash (common in pediatrics); memory loss, psychosis, transverse myelitis, hemoptysis, edema of the lower extremities, headache, and painful mouth sores
Dx: CBC, CMP, ESR, CRP, ANA (95% sens); anti-ds DNA, anti-Smith
Tx: corticosteroids, anti-malarials, biologics (off label)
Refer to Pediatric Rheumatology
Acute Rheumatic Fever
abnormal immunologic response to group A strep 2-4 weeks after initial infection; most common 5-15yo
S/S: may have cardiac, neurologic, MSK, or dermatology manifestations
Dx: Jones criteria, throat culture, CBC, ESR, CRP, ECG/Echo
Tx: antibiotics for strep, NSAIDs for arthralgia, manage carditis
Primary prevention: prompt treatment for all Strep pharyngitis • Secondary prevention: high risk for recurrent attacks with increased risk for Rheumatic Heart Disease, consider long term antimicrobial prophylaxis
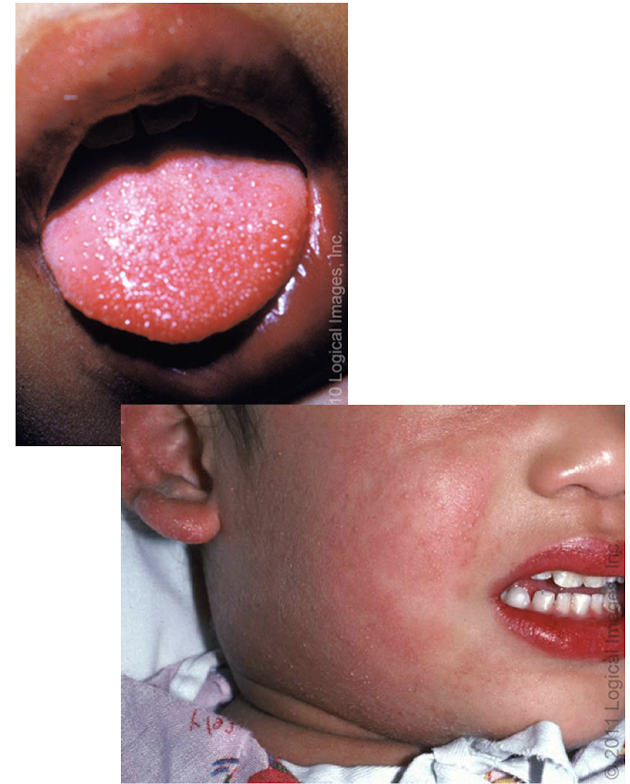
Kawasaki disease
widespread inflammation of small to medium sized arteries, leading cause of heart disease in children
-rare, typically <5yo, AMAB>AFAB, ↑risk in Asian descent
S/S:
-significant prolonged high fever
-bilateral nonexudative conjuctivitis
-erythema of lips and oral mucosa (strawberry tongue)
-extremity changes (swelling, skin peeling)
-cervical lymphadenopathy
Dx: clinical diagnosis; CBC, AST/ALT, CRP, ESR, urinalysis, ECHO
Tx: IVIG +/- glucocorticoids, high dose aspirin (use caution Reyes)
Prognosis: based on cardiac involvement: coronary aneurysm, myocardial infarction, myocarditis