Food Science quiz
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms

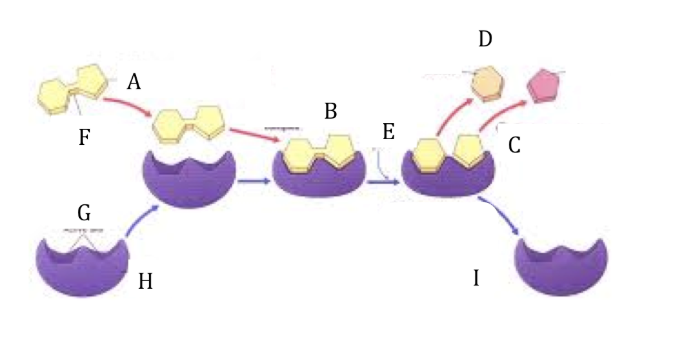
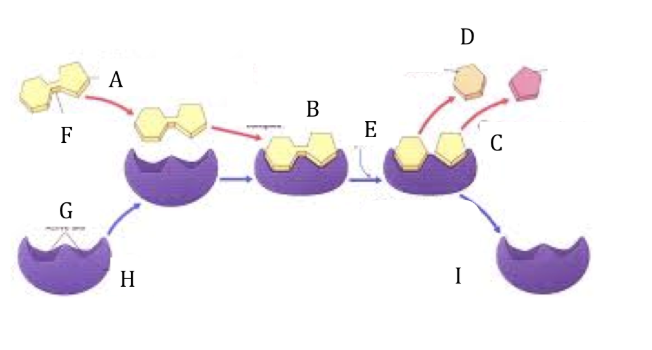
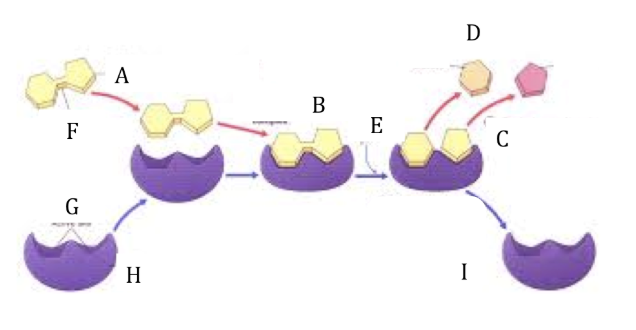
Refer to the lock and key diagram. What letter represents the substrate?
A
D
B
I
A
What happens to the reaction in the diagram?

The reaction slows
The reaction stops
No change to the reaction
The reaction speeds up
The reaction stops
What typically makes up a coenzyme?
Simple sugar
Salt
Vitamin
Mineral
Vitamin
Refer to the lock and key diagram. What letter represents the active sites?
C
A
F
G
G
All of the following are undesirable enzymatic reactions except
Improving yields in fruit juice processing
Microbial spoilage
Oxidation and rancidity
Autolysis
Improving yields in fruit juice processing
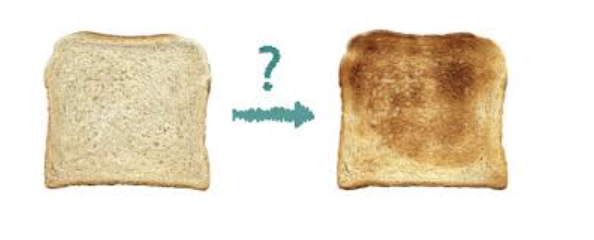
What has happened to the left side of the apple?
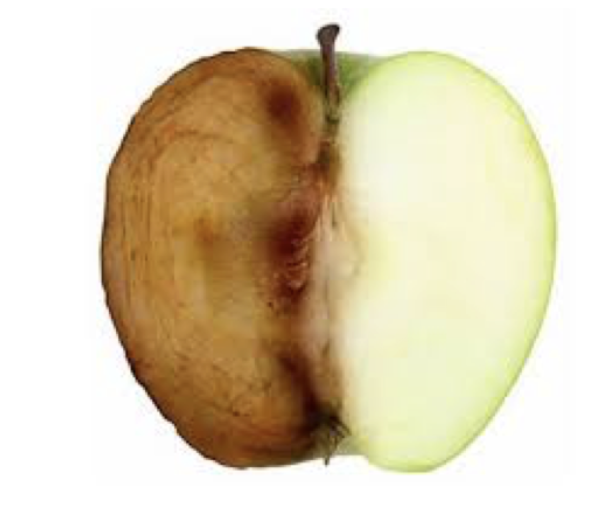

Non - enzymatic browning
Caramelization
Enzymatic browning
Maillard reaction
Enzymatic browning
Refer to the lock and key diagram. What letter represents the enzyme substrate complex?
H
C
A
B
B
What is required for this non enzymatic reaction to occur?
Enzyme
Sugar
Carboxyl and amine both from protein
Carboxyl from carbohydrate and amine from protein
Carboxyl from carbohydrates and amine from protein
What imparts the characteristic dark hue and flavor in coffee, tea, cocoa and raisins?
Papain
Polyphenol oxidase
Bromeline
Glucose oxidase
Polyphenol oxidase
Refer to the lock and key diagram. What does letter D represent?
Active site
Enzyme
Product
Substrate
Product
What controls all chemical reactions in living organisms and acts as an organic catalyst
Enzymes
Proteins
Lipids
Water
Enzymes
What happens to the enzyme once the products are released?
It works only once
It grows larger
It is slowly used up
It is uncharged and repeats the reaction
It is unchanged and repeats the reaction
Caramelizing is an enzymatic reaction
True or false
False
Which of the following is not a function of carbohydrates
* Form Milk Curds
Bleach flour
Retard staling
Improve flour and dough quality
From milk curds
What is the name for the compound that the enzyme works on?
Products
Competitor
Substrate
Active site
Substrate
Which food borne disease is caused by ingesting living infection causing bacteria that produce a toxin in the intenstines?
Intoxication
Toxin-Mediated infection
Infection
Toxin - mediated infection
The CDC only provides information on food borne illness
True or false?
False
Which food borne disease is caused by ingesting preformed toxin (Poison)?
Toxin mediated infection
Intoxication
Infection
Now answer text provided
Intoxication
During which phase of the growth curve is the population adjusting to new conditions and little to no division is taking place?
Log phase
Lag phase
Stationary phase
Death phase
Lag phase
What products are more prone to rancidity
Low in water
High in salt
Low in sugar
HIgh in fat
High in fat
During which phase of the growth curve is the population size decrasing because more cells are dying than are being produced
Lag phase
Death phase
Stationary phase
Log phase
Death phase
Select the microogranisms that are the most important to food
Bacteria
Bacteria and fungi
fungi
Bacteria, fungi (yeast and mold), protozoa and viruses
Bacteria and fungi (Yeast and mold)
Which group of microogramisms would you expect to spoil meat and flesh based foods?
Bacteria
Fungi
Bacteria
The entire population dies during the death phase
True or false
False
Fungi are most likely to cause food spoilage and not cause gastrointestinal distress or short term illness
True or false
True