ANS 431 - Reproductive Physiology Exam 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:45 AM on 2/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
158 Terms
1
New cards
female reproductive system
production and development of oocytes
provide an environment for the growth and nourishment of the developing embryo/fetus after fertilization
synthesis of hormones
provide an environment for the growth and nourishment of the developing embryo/fetus after fertilization
synthesis of hormones
2
New cards
cow
female bovine
3
New cards
bull
male bovine
4
New cards
ewe
female ovine
5
New cards
ram
male ovine
6
New cards
sow
female porcine
7
New cards
boar
male porcine
8
New cards
hen
female avian
9
New cards
rooster
male avian
10
New cards
broad ligament
connective tissue sheet which supports and suspends the reproductive tract
11
New cards
mesometrium
the broad ligament that suspends the uterus
12
New cards
mesovarium
the broad ligament that suspends the ovaries
13
New cards
mesosalpinx
the broad ligament that suspends the oviducts
14
New cards
estrogen
a steroid hormone produced by the ovary:
regulates growth
enhances and maintains the mucous membrane that lines the uterus
stimulates the growth of the follicle
maintains thickness of vaginal wall and promotes lubrication
helps stop milk flow after weaning
regulates growth
enhances and maintains the mucous membrane that lines the uterus
stimulates the growth of the follicle
maintains thickness of vaginal wall and promotes lubrication
helps stop milk flow after weaning
15
New cards
gilt
young female porcine
16
New cards
barrow
castrated male pig
17
New cards
hiefer
young female bovine
18
New cards
progesterone
a steroid hormone produced by the ovary:
prepares the endometrium for the potential of pregnancy after ovulation
supports pregnancy
prepares the endometrium for the potential of pregnancy after ovulation
supports pregnancy
19
New cards
inhibin
protein hormone produced by the ovary:
produced by the granulosa cell
regulation of pituitary FSH secretion
reduces the hypothalamic LH releasing hormone content
produced by the granulosa cell
regulation of pituitary FSH secretion
reduces the hypothalamic LH releasing hormone content
20
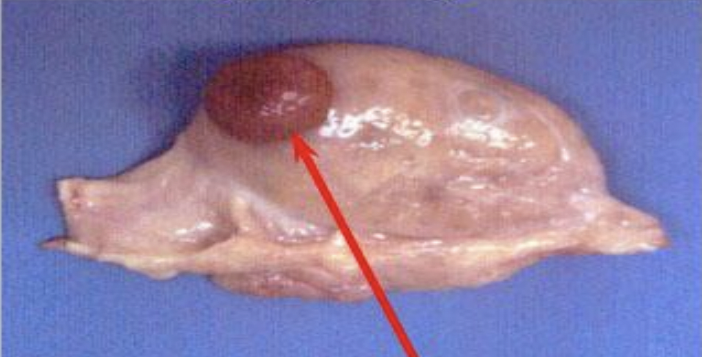
New cards
corpus luteum
produces progesterone
21
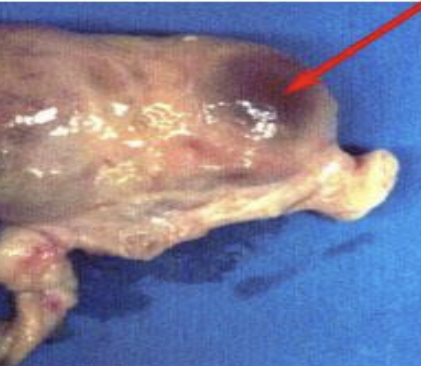
New cards
follicle
a small fluid filled sac in the ovary that contains an immature oocyte
22
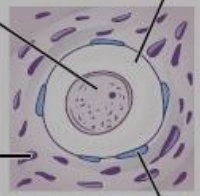
New cards
primordial follicle
one layer of flattened granulosa cells around the oocyte
23
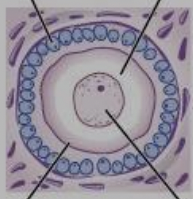
New cards
primary follicle
one layer of cuboidal granulosa cells around an oocyte
24
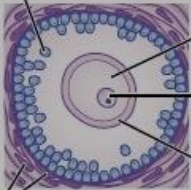
New cards
secondary follicles
two or more layers of cuboidal granulosa cells around the oocyte and no sign of antrum formation
25
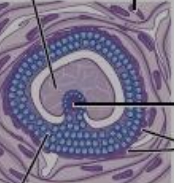
New cards
tertiary follicle
follicle forms a fluid filled cavity; differentiation of cell layers in the follicle wall
26
New cards
antrum
follicular fluid
27
New cards
theca cells
a group of endocrine cells in the ovary made up of connective tissue surrounding the follicle
28
New cards
granulosa cells
the cells on the innermost layer of the follicle
29
New cards
oviducts
gamete transport
fertilization site
supports early embryo development
transport of embryo to uterus
fertilization site
supports early embryo development
transport of embryo to uterus
30
New cards
infundibulum
the section of the oviduct closest to the ovary
31
New cards
ampullary
the mid-section of the oviduct
32
New cards
isthmus
the section of the oviduct closest to the uterus
33
New cards
uterotubal junction
the site of fertilization
34
New cards
fimbriae
finger-like projections on the end of the oviduct closest to the ovary
35
New cards
ostium
the opening of the oviduct
36
New cards
uterus
muscle contraction to transport sperm and expel fetus and placenta
absorption and phagocytosis
partially prepares sperm for fertilization
provide environment for embryo and fetal growth
hormone production
absorption and phagocytosis
partially prepares sperm for fertilization
provide environment for embryo and fetal growth
hormone production
37
New cards
prostaglandin F2a
produced by the uterus
stimulates the contraction of uterine and bronchial smooth muscle and produces vasoconstriction in some blood vessels
stimulates the contraction of uterine and bronchial smooth muscle and produces vasoconstriction in some blood vessels
38
New cards
bicornuate
what type of uterus do cows have?
39
New cards
endometrium
mucous membrane lining the inside of the uterus
40
New cards
myometrium
the smooth muscle tissue of the uterus
middle-tissue layer
middle-tissue layer
41
New cards
perimetrium
the outer serous layer of the uterus
42
New cards
cervix
transport of sperm
barrier to sperm
reservoir for sperm
blocking bacterial invasion during pregnancy
birth canal
barrier to sperm
reservoir for sperm
blocking bacterial invasion during pregnancy
birth canal
43
New cards
4-5
the cow has how many cervical rings?
44
New cards
connective
the cervix is composed of thick ______ tissue
45
New cards
mucus
_____ is secreted from the cervix near time of breeding and ovulation
46
New cards
vagina
copulatory organ
has glands that secrete lubrication
glands secrete pheromones
birth canal
has glands that secrete lubrication
glands secrete pheromones
birth canal
47
New cards
anterior vagina
portion of the vagina closest to the uterus
has columnar epithelium submucosa
has columnar epithelium submucosa
48
New cards
posterior vagina
portion of the vagina closest to the vulva
has stratified squamous epithelium
has stratified squamous epithelium
49
New cards
labia
closes the entrance to the vagina
50
New cards
clitoris
female sensory organ
51
New cards
mare
has kidney bean-shaped ovary
52
New cards
cow
has almond shaped ovary
53
New cards
sow
has grape-like shaped ovary
54
New cards
non-equine ovary
cortex on outside of ovary
ovulation can occur on any point of the ovary
ovulation can occur on any point of the ovary
55
New cards
Mare ovary
medulla on the inside of the ovary, cortex on the outside
ovulation occurs at the ovulation fossa
ovulation occurs at the ovulation fossa
56
New cards
germinal epithelium
what part of the ovary is responsible for 85% of ovarian cancers?
57
New cards
corpus albicans
scar tissue on the ovary from past ovulations
58
New cards
cow
4-5 cervical rings
short uterine body
medium uterine horns
short uterine body
medium uterine horns
59
New cards
mare
large uterine body
short uterine horns
longitudinal folds along the cervix
short uterine horns
longitudinal folds along the cervix
60
New cards
sow
long uterine horns
interdigitating pads
no vaginal fornix
interdigitating pads
no vaginal fornix
61
New cards
cat and dog
small uterine body
long uterine horns
long uterine horns
62
New cards
human
what species has a simplex reproductive tract?
63
New cards
simplex
large uterine body with no horns
64
New cards
bicournate
uterine body with horns
65
New cards
duplex
in opossum, rabbit, and mouse
2 uterine horns with 2 cervixes
2 uterine horns with 2 cervixes
66
New cards
opossum
what species has 2 vaginas?
67
New cards
vulva
most caudal part of the genital tract
12 - 15cm
labia or lips
protects the entrance of the vagina
situated approx. 7 cm below the anus
12 - 15cm
labia or lips
protects the entrance of the vagina
situated approx. 7 cm below the anus
68
New cards
commissures
dorsal and ventral are the sites of the union of the labia
69
New cards
perineum
area surrounding the vulva and anus
conformation is critical
conformation is critical
70
New cards
pneumovagina
“Windsucking”
the anus is too deep, pulling the labia tight allowing wind to enter the vulva.
the anus is too deep, pulling the labia tight allowing wind to enter the vulva.
71
New cards
80%
how much of the vulva should be below the pelvic floor
72
New cards
cloaca
where the vagina and large intestine meet in avian species.
73
New cards
male reproductive system
produce, maintain, and transport sperm and semen
discharge sperm into the female reproductive tract
produce and secrete male sex hormones
discharge sperm into the female reproductive tract
produce and secrete male sex hormones
74
New cards
scrotum
bag of skin that holds and helps to protect the testicles
thermoregulation and support
has sweat glands and thermosensitive nerves
thermoregulation and support
has sweat glands and thermosensitive nerves
75
New cards
tunica dartos
smooth muscle
elevates the testes
androgen dependent (testosterone)
elevates the testes
androgen dependent (testosterone)
76
New cards
tunica albuginea
dense connective tissue
close related with secretory tissues of the testicle
close related with secretory tissues of the testicle
77
New cards
rete testis
a network of small tubes in the testicles that helps move sperm cells from the testicle to the epididymis
78
New cards
seminiferous tubule
tubes in the testicles lined with complex stratified epithelium containing spermatogenic cells and sertoli cells
79
New cards
parenchyma and mediastinum
layers of the testis
80
New cards
testicular capsule
dynamic suborgan that changes in response to hormones and neurotransmitters
comprised of the VVT andTA
has finger-like projections
comprised of the VVT andTA
has finger-like projections
81
New cards
visceral vaginal tunic
thin membrane
provides support
from peritoneum
provides support
from peritoneum
82
New cards
testicular parenchyma
made up of the tubular compartment and interstitial parenchyma
83
New cards
tubular compartment
seminiferous epithelium
sertoli cells
developing germ cells
peritubular cells
sertoli cells
developing germ cells
peritubular cells
84
New cards
interstitial parenchyma
all cells and materials outside the seminiferous (blood vessels, connective tissue, lymphatics, nerve, and the interstitial cells of Leydig
85
New cards
mediastinum
holds the rete testis
86
New cards
germ cells
sperm cells
87
New cards
sertoli cells
surround developing germ cells
provide structural and metabolic support to the developing spermatogenic cells
production: androgen binding protein, sulfated glycoprotein, transferrin, and inhibin
provide structural and metabolic support to the developing spermatogenic cells
production: androgen binding protein, sulfated glycoprotein, transferrin, and inhibin
88
New cards
blood-testes barrier
adjacent sertoli cells are joined together by tight junction through their basal cytoplasmic processes over spermatogonia
prevents entry of harmful substances from blood affecting developing sperms and at the same time preventing sperms related proteins to enter circulation
prevents entry of harmful substances from blood affecting developing sperms and at the same time preventing sperms related proteins to enter circulation
89
New cards
leydig cells
located between seminiferous tubules
produces androgens (testosterone)
produces androgens (testosterone)
90
New cards
epididymis
local where the spermatozoa gain the ability to fertilize an oocyte
91
New cards
caput
at the top of the testes
concentration of sperm fluctuates
sperm is not motile or fertile
proximal cytoplasmic droplet
low disulfide crosslinking
concentration of sperm fluctuates
sperm is not motile or fertile
proximal cytoplasmic droplet
low disulfide crosslinking
92
New cards
proximal head
what part of the epididymis reabsorbes a significant amount of rete fluid?
93
New cards
distal head
what part of the epididymis secretes fluid into the lumen of the epididymal duct?
94
New cards
corpus
lies parallel to the ductus deferens
the concentration of sperm remains constant
sperm has some motility and fertility
translocating cytoplasmic droplet
moderate to high degree of disulfide crosslinking
can bind to oocytes
the concentration of sperm remains constant
sperm has some motility and fertility
translocating cytoplasmic droplet
moderate to high degree of disulfide crosslinking
can bind to oocytes
95
New cards
cauda
located at the bottom of the testes
normal motility and fertile potential
distal droplet
high degree of disulfide crosslinking
can bind to oocytes
normal motility and fertile potential
distal droplet
high degree of disulfide crosslinking
can bind to oocytes
96
New cards
proximal tail
sperm in this section of the epididymis cannot be moved into ejaculatory position following sexual stimulation
97
New cards
distal tail
sperm in this section of the epididymis are eligible for ejaculation, where they move into the ductus deferens and into the pelvic urethra during sexual stimulation
98
New cards
9-14
how many days does sperm transport time take in boars?
99
New cards
12
how many days does sperm transport time take in rams?
100
New cards
14
how many days does sperm transport time take in bulls?