econ test 2
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
*1. Suppose that 1983 is the base year for the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and in 2019 the CPI is 254. What does
this "254" mean?
a. What cost $100 in 1983 on average cost 254 times as
much in 2019.
c. What cost $100 in 1983 on average cost 100/254 (or 0.39)
times as much in 2019.
b. What cost $100 in 1983 on average cost
$254 more in 2019.
d. What cost $100 in 1983 on average cost
$154 more in 2019.
What cost $100 in 1983 on average cost
$154 more in 2019.
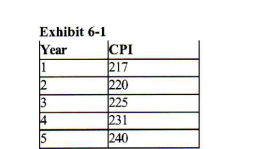
Refer to Exhibit 6-1. Prices rose by _____ percent from Year 1 to Year 2.
a. 1.38 b. 0.14
c. 1.29 d. 1.94
1.38
If the CPI is 100 in the base year and 106 in the current year, how much did prices rise between the base year
and the current year?
a. 6 percent b. 106 percent
c. 1.06 percent d. 0.06 percent
6 percent
The inconvenience associated with reducing money holdings to avoid the inflation tax is called:
a. menu costs b. shoeleather costs
c. variable yardstick costs d. fixed costs
shoeleather costs
The movie "Return of the Jedi" earned $264 million in 1983 when it was released. The CPI in 1983 was 97.8 and the CPI in 2012 was 226.665. Approximately how much did the movie earn in 2012 dollars?
a. $590 million b. $612 million
c. $2.12 million d. $123 million
$612 million
2012 dollars = 264 × (226.665 / 97.8)
226.665 / 97.8 ≈ 2.318
264 × 2.318 ≈ 612
Answer: b. $612 million
The value of the consumer price index (CPI) is always equal to _____ in the base year
a. 7 b. 10
c.100 d. 1,000
100
In a hyperinflation
a. people hold as little money as possible
c. people continue to hold the same
amount of money
b. people hold as much money as possible because financial
assets lose their value rapidly.
d. some people hold more money and some hold less
people hold as little money as possible
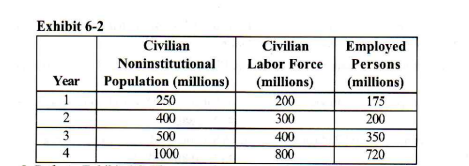
Refer to Exhibit 6-2. The unemployment rate in year 2 is
a. 75 percent. b.33 1/3 percent.
c. 50 percent. d. 66 2/3 percent.
33 1/3 percent
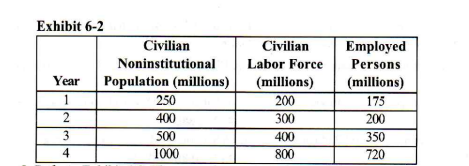
Refer to Exhibit 6-2. The labor force participation rate in year 3 is
a. 12 1/2 percent. b. 70 percent.
c. 80 percent. d. 30 percent.
80 percent
In many large retail stores, price markdowns are now determined by computer. The "middle managers" who used to make these decisions personally became _______ unemployed.
a. frictionally b. structurally
c. naturally d. cyclically
structurally
Jones lost his job in industry A, but he has skills that can be transferred to industry B (which is currently hiring). Smith lost a job in industry C, but his skills cannot be transferred to industry B or to any other industry. Jones is_______ unemployed and Smith is _______unemployed.
a. structurally; frictionally b. structurally; structurally
c. frictionally; frictionally d. frictionally; structurally
frictionally; structurally
Among the ways to be classified as unemployed by the Bureau of Labor Statistics, a person must be not working,
a. have been actively looking for work within the past four weeks, and currently be available for work
b. and currently be available for work, regardless of whether one is actively looking for work or not
c. and be waiting to be called back to work from a permanent layoff
d. and activity looking for work within the past year
have been actively looking for work within the past four weeks, and currently be available for work
The unemployment rate equals the
a. number of employed persons divided by the number of unemployed persons
b. number of unemployed persons divided by the civilian non-institutional population.
c. number of unemployed persons divided by the civilian labor force.
d. sum of unemployed persons and discouraged workers divided by the civilian labor force.
number of unemployed persons divided by the civilian labor force.
Unemployment that arises as a result of the time it takes for unemployed people to locate a job utilizing their transferable skills is called ________ unemployment.
a. structural b. cyclical
c. natural d. frictional
frictional
Persons in the civilian labor force fall into one of two categories:_______ or ________
a. job leaver; job loser
c. employed; unemployed
b. entrant; reentrant
d. discouraged workers; encouraged workers
employed; unemployed
Persons who are retired or engaged in own-home housework are considered to be in which of the following
categories?
a. in the civilian labor force
c. employed
b. not in the labor force
d. unemployed
not in the labor force
*Some economists believe that because the government the unemployment rate is biased _____ discouraged workers as unemployed, the unemployment rate is biased _______.
a. counts; upward
b. counts: downward
c. does not count; upward
d. does not count; downward
does not count; downward
The expenditure approach to measuring GDP sums
a. consumption, investment, government purchases, and net exports.
b. sales, revenues, income, and wages.
c. profits, compensation of employees, consumption, and investment.
d. net exports, consumption, wages, and
salaries.
consumption, investment, government purchases, and net exports.
*Real GDP is GDP
a. in current-year prices.
b. in base-year prices.
c. in GDP-prices.
d. in that year's prices.
in base-year prices
Disposable income is
a. equal to GDP minus the capital consumption allowance.
b. that portion of personal income that can be used for consumption and saving.
c. the sum of all payments to suppliers of the factors of production.
d. equal to national income.
that portion of personal income that can be used for consumption and saving.
*To macroeconomists, investment is mainly the purchases of goods and services
a. by businesses.
b. to hold as wealth, such as gold coins or art.
c. to hold as wealth, such as stocks and bonds.
d. by the government.
by businesses
Interest is the return to
a. land b. entrepreneurship
c. labor d. capital
capital
*According to Okun's rule of thumb, if the economy produces at an annual rate of $10 trillion, then an increase in the rate of unemployment from 5.5 percent to 6 percent would be expected to cause income in the economy
to:
a. rise by $200 billion b. fall by $200 billion
c. fall by $100 billion d. rise by $100 billion
fall by $100 billion
Okun’s rule of thumb:
A 1 percentage point increase in unemployment → 2% decrease in GDP.
Unemployment increases from 5.5% to 6.0% = 0.5 percentage point increase
→ GDP decreases by 1%.
GDP = $10 trillion
1% of $10 trillion = $0.1 trillion = $100 billion
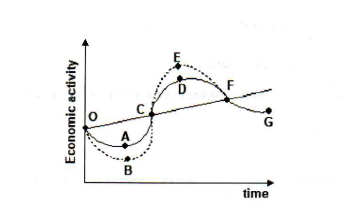
Refer to Figure 1. A movement from D to G represents
a. trough b. peak
c. recession d. expansion
recession
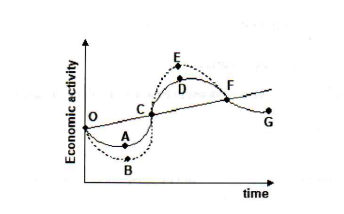
Refer to Figure 1. Which point represents a peak:
a. A b. B
c. C d. D
D
The circular flow diagram shows:
a. the movement of expenditures and factor payments through the economy.
b. how national income is distributed to individuals.
c. how national income changes over time.
d. the movement of goods from one business to another.
the movement of expenditures and factor payments through the economy.
Two ways of measuring Gross Domestic Product are the _______ approach and the _______ approach.
a. expenditure; income
b. expenditure; national product
c. national product; income
d. net national product; personal income
expenditure; income
Net exports equals
a. exports divided by imports
b. the sum of exports and imports
c. exports minus imports
d. exports during the year
exports minus imports
The standard definition of "recession" is
a. a period of a positive frictional unemployment rate.
b. two consecutive quarters of falling Real GDP.
c. the lowest point in a business cycle. approach and the
d. a period of negative inflation.
two consecutive quarters of falling Real GDP
When computing national income, which of the following is not included in compensation of employees?
a. wages and salaries paid to employees
b. employers' contributions to Social Security and employee benefit plans
c. the monetary value of fringe benefits, tips, and paid vacations
d. income earned by self-employed individuals
income earned by self-employed individuals
*** The typical U.S. business cycle, measured peak to peak, lasts approximately
a. 4 to 5 years. b. 8 to 10 years.
c. 1 to 3 years. d. 6 months to 2 years.
4 to 5 years
For a neo Malthusian model, the key is that _________ keeps being added to a fixed amount of ______
a. population; natural resources b. natural resources; land
c. population; land d. capital; natural resources
population; natural resources
Growth usually leads to decreased birth rates because:
a. pollution reduces the fertility of the population.
c. immigration crowds out endogenous population growth
b. men and women are too tired to have kids.
d. the opportunity cost of having children rises.
the opportunity cost of having children rises
According to the Solow (or Neoclassical or Classical) growth model, poorer countries should:
a. grow at the same rate as richer countries b. grow at an ever increasing rate
c. grow faster than richer countries d. grow slower than richer countries
grow faster than richer countries
The Solow or Neoclassical growth theory emphasized how ______ contribute to growth.
a. capital b. technological changes
c. government policies d. factors limiting population growth
capital
_______ occurs when the presence of a less efficient technology blocks the adoption of a more efficient
technology.
a. Network externalities. b. Positive externalities
c. Learning by doing d. Technological lock-in
Technological lock-in
*The range of laws, rules, and regulations that define the allowed forms of use and transfer of resources is called structure of the economy. the
a. monetary b. property rights
c. microeconomic d. macroeconomic
property rights
Neoclassical or Solow growth theory treats technology as an_______variable, and new growth or endogenous growth theory treats technology as an ________
a, exogenous; endogenous variable
b. endogenous; exogenous variable
c. endogenous; endogenous variable, as well
d. exogenous; exogenous variable, as well
exogenous; endogenous variable
The key idea of the Malthusian model of economic growth was:
a. technological development b. diminishing marginal product of labor
c. diminishing marginal product of capital d. diminishing marginal product of land
diminishing marginal product of labor
Which of the following is an example of a network externality?
a. Pollution
b. Your neighbor using deodorant
c. Others owing a telephone making it more useful to other people owing them
d. Others benefiting from technological breakthrough
Others owing a telephone making it more useful to other people owing them
The fact that _________ is the only movie ever made in Esperanto is good evidence that English is a superior language in terms of culture. The reason Prof. Davis gave for thinking that Esperanto/English was not a good example of technological lock-in was ________________.
a. Dungeons and Dragons; that English is easier b. Incubus; that English is easier grammatically
grammatically.
c. Dungeons and Dragons; English has a history allowing greater cultural opportunities
d. Incubus; English has a history allowing greater cultural opportunities
Incubus; English has a history allowing greater cultural opportunities
All of the following were periods of recession or depression except:
a. 1930s b. 1893
c. Late 1990s d. The two months at the start of COVID
Late 1990s
The Nobel Prize in Economics this year was awarded to researchers who studied:
a growth b. the minimum wage
c. econometrics d. recessions and depressions
growth