Antiprotozoal: Malaria ~ PDA
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
protozoa causing malaria in humans & form hypnozoites in the liver and cause relapse even after years
plasmodium vivax
plasmodium ovale
life cycle of plasmodium
Gametocytes from an infected human are transferred to a mosquito during a blood meal
In mosquito stomach, a zygote forms & matures = oocyst on the outside stomach wall
Sporozoites released from the oocyst migrate to salivary glands. During next blood meal, the mosquito transfers Plasmodium spp. sporozoites from its saliva to another human.
Sporozoites enter the host’s bloodstream and travel to the liver. Sporozoites replicate in the liver and then lyse infected hepatocytes, releasing merozoites.
Merozoites infect erythrocytes, undergoing asexual cycles of erythrocytic infection & lysis
Some merozoites differentiate into gametocytes, which can be ingested by another mosquito and thereby continue the cycle of infection. P. vivax and P. ovale can form dormant hypnozoites, which can remain in infected hepatocytes for months to years before release into the circulation
Quinine Structure
1st known antimalarial
is a blood schizonticide = targets something in malial life cycle
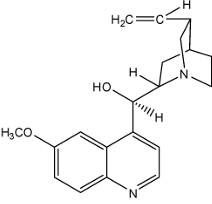
Quinine Properties
t1/2 = 18h
hepatic metabolism
70% protein binding
88% absorption
Quinine SE
CV: prolong QT
CNS: dizzy, fatigue, HA, disturbed sleep, nervous, ataxia [lack coordination]
Neuromuscular & skeletal: weakness & tremors
Ophthalmic: visual disturbances
Quinine MOA
disrupt the erythrocytic stage by interfering w/ parasitic hemoglobin metabolism & increasing intracellular pH
bind to heme in hemoglobin [ food source] and plasmodium can’t feed on erythrocytes
proposed mechanisms of drug action include inhibition of heme polymerization, enhancement of oxidant production, and reaction with heme to form cytotoxic metabolites.
Chloroquine Structure
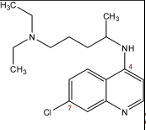
Chloroquine Properties
one weekly dose
drug of choice [even tho resistant infections common]
Hydroxychloroquine Structure
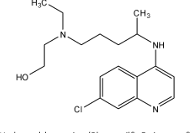
Hydroxychloroquine Properties
tx uncomplicated malaria caused by all EXCEPT P. knowlesi
prophylaxis of malarias where chloroquine resistance NOT reported
Mefloquine Structure
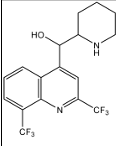
Mefloquine Properties
tx & prevent malaria
one weekly dose
begin 1 week before travel [continue till 4 weeks after travel]
if area has chloroquine resistant P. falciparum, use this as alternative or halofantrine
Primaquine Structure
tx relapsing p. vivax or p. ovale → activity towards hypnozoites
create reactive oxidative species [ROS]
Perform testing for glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency prior to tx
![<p>tx relapsing p. vivax or p. ovale → activity towards hypnozoites</p><p>create reactive oxidative species [ROS]</p><p>Perform testing for glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency prior to tx</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/63d80061-21cf-49dd-b0ab-58cca2bb1ae0.png)
Tafenoquine Structure
prevent relapse of malaria in pt >16yo who is recieving antimalial tx for acute p. vivax [hypnozoites]
create reactive oxidative species [ROS]
Perform testing for glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency prior to tx
![<p>prevent relapse of malaria in pt >16yo who is recieving antimalial tx for acute p. vivax [hypnozoites]</p><p>create reactive oxidative species [ROS]</p><p>Perform testing for glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency prior to tx</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/9a4d928a-5957-420d-b373-4a16521c0b5a.png)
Atovaquone Structure
interfere w/ pyrimidine synthesis
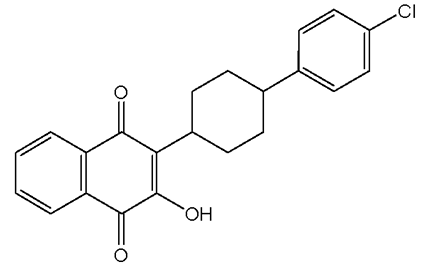
Proganil Structure
prodrug [metabolized to cyclogaunil [active dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor]
daily use
used for 1 week after leaving malaria zone [instead of 4 weeks]
![<p>prodrug [metabolized to cyclogaunil [active <strong>dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor</strong>]</p><p>daily use</p><p><strong>used for 1 week after leaving malaria zone</strong> [instead of 4 weeks]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/96c06e86-0a66-4ba7-9b2b-851c5d9246e9.png)
Atovaquone/Proganil Combo [Malarone] MOA
effective against P. falciparum including strains resistant to chloroquine and mefloquine
P ~ active against hepatic stage of malaria
A ~ inhibits coenzyme Q electron transfer to Cytochrome bc1
no electron transfer = oxidized DHOD can’t be regenerated [DHOD needed for pyrimidine synthesis]
Artemisinin Structure
makes free radicals
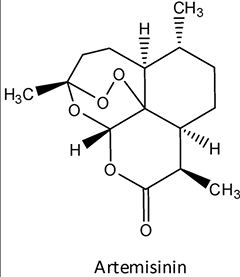
Artemisinin Properties
used in artemisinin=based combo therapy [ACT]
WHO reccomend tx for malaria
Artemisinin MOA
alkylation of macromolecules such as heme & proteins = __ = toxic to plasmodia
Artemether Structure
prodrug
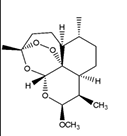
Artemether Properties
tx acute, uncomplicated malaria due to P. falciparum
prodrug [right is active metabolite]
both cmpd are blood schizonticides
effective against chloroquine-sensitive & resistant P. falciparum
![<ul><li><p>tx acute, uncomplicated malaria due to P. falciparum</p></li><li><p>prodrug [right is active metabolite]</p></li><li><p>both cmpd are blood schizonticides</p></li><li><p>effective against <strong>chloroquine-sensitive & resistant</strong> P. falciparum</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/87048004-7402-488b-9e55-1609e2f67366.png)
Lumefantrine Structure
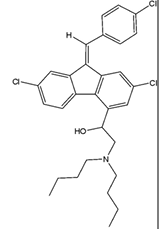
Lumefanterine Properties
inhibits formation of B-hematin by forming complex w/ hemin → ferripoto porphyrin w/ Cl
Artesunate Structure
makes free radicals
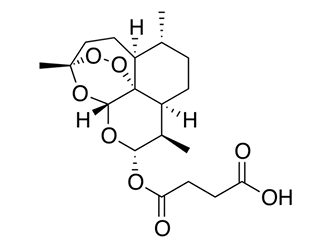
Artesunate Properties
tx severe malaria [1st-line]
given IV, IM, PO, Rectum [CDC recommends IV]
same MOA as artemisinin [toxic to plasmodia]
Doxycycline Structure
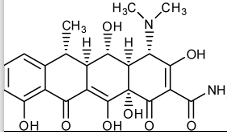
Doxycycline MOA
bind 30S subunit & block bind of tRNA → mRNA
Doxycycline Properties
prophylaxis in short-term travelers [<3 mo] in area w/ chloroquine- resistant P. falciparum
begin 1-2d prior to travel, QD during travel + 4 weeks after returning home
Site of Action of Antimalarial Meds for Short-Term Travel
Schizontes= multinucleated stages of parasites that undergo mitotic division within host cell
Hepatic-stage schizonticides such as atovaquone–proguanil and primaquine kill malaria parasites during the brief period of initial active development within hepatocytes in the liver, and they act on the liver schizonts of all 4 species of organisms that cause human malaria.
Only primaquine and tafenoquine are able to kill quiescent hypnozoites (Plasmodium vivax and P. ovale only), thus preventing secondary attacks (relapses) of clinical malaria.
As compared with other drugs, atovaquone–proguanil and primaquine each act at two separate points in the life cycle. Atovaquone–proguanil acts on hepatic schizonts during initial infection but does not act on hypnozoites, so it does not prevent late-onset relapses of P. vivax and P. ovale.
Blood-stage schizonticides such as atovaquone–proguanil, doxycycline, mefloquine, and chloroquine interrupt schizogony within red cells, preventing clinical manifestations of malaria infection. Not all parasite life-cycle stages are shown in this figure.