Exam II
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/132
Last updated 4:10 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
1
New cards
How many times more viscous is blood than water?
5x
2
New cards
**Whole** **Blood**
**Formed Elements** **+** **Plasma**
3
New cards
pH of blood
7\.35-7.45
4
New cards
How many L of blood in male?
\~5-6L
5
New cards
How many L of blood in female?
\~4-5L
6
New cards
Temperature of Blood
38 C or 100.4 F
7
New cards
What color is deoxygenated blood?
deep red- burgandy
8
New cards
What color is oxygenated blood?
bright red
9
New cards
What are the 3 types of plasma protein? (FAG)
Fibrinogen, Albumin, and Globulin
10
New cards
Blood Plasma consists of how many percent of whole blood?
\~55%
11
New cards
Which of these are NOT produced by the liver?
a. Albumin
b. Alpha and Beta Globulin
c. Immunoglobulin
d. Fibrinogen
a. Albumin
b. Alpha and Beta Globulin
c. Immunoglobulin
d. Fibrinogen
Immunoglobulin aka Antibodies
12
New cards
Cellular component makes how many % of the blood?
45%
13
New cards
Megakaryocytes produce?
platelets
14
New cards
Erythropoiesis
process of forming erythrocytes
15
New cards
Leukopoiesis
process of forming leukocytes
16
New cards
Thrombopoiesis
process of forming platelets
17
New cards
small proteins or peptides that have a specific effect or effects when they bind to receptors on their target cells
Cytokines
18
New cards
What is the lifespan of an erythrocyte?
120 days
19
New cards
Does hemoglobin irreversibly binds with oxygen?
no- reversibly
20
New cards
Each heme’s central iron (Fe2+) binds with?
O2 molecule
21
New cards
O2 binds to Hb
oxyhemoglobin (bright red)
22
New cards
Hemoglobin without oxygen
deoxyhemoglobin (dark red)
23
New cards
CO2 bound to Hb
carbaminohemoglobin
24
New cards
How long does it take to form erythropoiesis and where does it form?
15 days and in red bone marrow
25
New cards
How many RBCs are made per second?
\~2-3 million
26
New cards
Too few RBCs lead to?
hypoxia
27
New cards
Too many RBCs lead to?
increased blood viscosity
28
New cards
Hypoxia
inadequate availability of oxygen
29
New cards
What breaks down dying RBCs?
Macrophages in lymph organs
30
New cards
How can leukocytes leave capillaries?
doapedesis (emigration)
31
New cards
Neutrophils form spears that pierce holes in membrane of ingested microbe.
32
New cards
What do eosinophils attack?
parasites- parasitic worms
33
New cards
How do eosinophils attack?
release enzymes and digest their surface
34
New cards
Histamine
DILATES blood vessels
35
New cards
Heparin
anti-coagulant; prevents blood clotting
36
New cards
Where are lymphocytes mostly found?
lymphoid tissue
37
New cards
What shape do RBCs become when O2 levels are low?
crescent
38
New cards
**Thromboembolic Disorders**
undesirable clot formation
39
New cards
Bleeding Disorders:
abnormalities that prevent normal clot formation
40
New cards
**Thrombus**
blood clot that develops and persists or remains in blood vessel
41
New cards
**Embolus**
thrombus freely floating in bloodstream
42
New cards
**Embolism**
embolus obstructing a vessel
43
New cards
**Anticoagulant Drugs**:
used to prevent undesirable clotting- blood thinners
44
New cards
**Anticoagulant Drugs**: Aspirin
inhibits thromboxane A2
45
New cards
**Anticoagulant Drugs**: Heparin
anticoagulant used clinically for pre-operative and post-operative cardiac care
46
New cards
**Anticoagulant Drugs**: Warfarin
used for people prone to atrial fibrillation
47
New cards
**Anticoagulant Drugs**: Dabigatran
directly inhibits thrombin
48
New cards
**Thrombocytopenia**
deficient number of circulating platelets
49
New cards
**Lymph**
interstitial fluid that has entered the lymphatic vessels (lymphatics)
50
New cards
**Lymphatic** **vessels** (**Lymphatics**)
carry lymph from peripheral tissues to the venous system
51
New cards
**Lymphatic** (**Lymphoid)** **tissues** and **Lymphatic (Lymphoid)** **organs**
* houses lymphocytes, phagocytes, and other immune cells
* structures include ***spleen***, ***thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes***, other ***lymphoid tissues***
* structures include ***spleen***, ***thymus, tonsils, lymph nodes***, other ***lymphoid tissues***
52
New cards
Lacteals
lymphatic capillaries that absorb digested fat and deliver fatty lymph (**chyle**) to the blood
53
New cards
**Lymphangitis**
condition in which lymphatic vessels appear as painful red lines under the skin
54
New cards
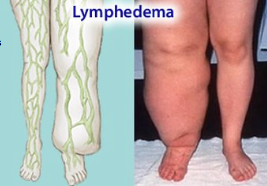
**Lymphedema**
accumulation of interstitial fluid due to interference with lymphatic drainage
Most caused by blockage of lymph vessel
Most caused by blockage of lymph vessel
55
New cards
NK cells attack?
cancerous and virally infected cells
56
New cards
***T cells*** function
manage immune response, and attack and destroy infected cells
57
New cards
B cells
become **plasma** **cells →** secrete **antibodies**
58
New cards
**Macrophages**
phagocytic cells found in various tissue to __help activate lymphocytes__
59
New cards
**Dendritic Cells**
phagocytic cells found in connective tissue and epidermis to __help activate lymphocytes__
60
New cards
What do Lymphoid Nodule Germinal Centers contain?
**proliferating B cells** + **Antigen Presenting Cells**
61
New cards
**MALT**
**m**ucosa-**a**ssociated **l**ymphatic **t**issue
62
New cards
***Primary*** **Lymphatic (Lymphoid) Organs**
**Red Bone Marrow** and **Thymus**
63
New cards
***Secondary*** **Lymphatic (Lymphoid) Organs**
**Lymph Nodes, Appendix, Spleen**, **Tonsils, MALT**
64
New cards
How many lymph nodes are found throughout the body?
600
65
New cards
Lymph **Macrophages**
remove and destroy microorganisms and debris that enter lymph
66
New cards
Cortex contains
T and B cells
67
New cards
Medulla contains
B cells, plasma cells, macrophages
68
New cards
***Buboes***
inflamed, swollen, tender lymph nodes that result when nodes are overwhelmed by what they are trying to destroy
69
New cards
True/False: Lymph nodes can become ***secondary cancer sites*** if metastasizing cancer cells become trapped in node
True
70
New cards
True/False: spleen filters lymph
True
71
New cards
Where are MALT found?
in lamina propria throughout body
72
New cards
*Phagocytes*
white blood cells that ingest and digest (eat) foreign invaders
73
New cards
**Neutrophils**
most abundant phagocytes, but die fighting become phagocytic on exposure to infectious material
74
New cards
**Eosinophils**
phagocytic cells; attack parasitic worms
75
New cards
**Macrophages**
develop from **monocytes** and are the chief and most robust phagocytic cells
76
New cards
**Opsonization (cup handles)**
immune system uses __antibodies__ or __complement proteins__ as **opsonins- Antibody (IgG or IgM) or complement protein (C3B)** that coat pathogens
77
New cards
Cytolysis
cell burst
78
New cards
Apoptosis
programmed cell death
79
New cards
Natural Killer
nonphagocytic that programmed cell death
80
New cards
What cells do Natural Killer attack?
cells that lack “self” cell-surface antigens
81
New cards
Is fever a cardinal sign of inflammation?
no
82
New cards
Is Prostaglandin an inflammatory mediator?
Yes
83
New cards
TRUE/FALSE: C3B binds to the pathogen while C3A goes stimulate masts and basophils
TRUE
84
New cards
During a fever, what is secreted?
pryrogens
85
New cards
What are pyrogens?
Pyrogens are fever-chemical producing agent reset body’s thermostat is hypothalamus- raised body temperature.
86
New cards
Is humoral immunity, antibody or cell mediated?
Antibody
87
New cards
Is cellular immunity, antibody or cell mediated?
Cell mediated
88
New cards
Helper T cell
activates other lymphocytes (B lymphocytes and cytotoxic T cells) and macrophages
“help by activate”
“help by activate”
89
New cards
**Cytotoxic T Cell**
directly kills virus-infected cells and tumor cells
90
New cards
Antigens
substances that can mobilize adaptive defenses and provoke an immune response
91
New cards
**MHC Class I protein**
displayed by all NUCLEATED cells except RBCs
92
New cards
**MHC Class II protein**
displayed by ***Antigen Presenting Cells*** (APCs) (dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells)
93
New cards
Cytokines
Chemical messengers of immune system
94
New cards
T Lymphocyte Activation:
1. Antigen binding
2. Co-stimulation
3. Clonal selection
1. Antigen binding
2. Co-stimulation
3. Clonal selection
T cell antigen receptors (**TCRs**) bind to antigen-MHC complex on APC surface
95
New cards
**Co-stimulation**
The release of cytokines (IL-1)
The binding of cell surface proteins:
CD4 binds with MHC II
CD8 binds with MHC I
CD28 binds with B7
The binding of cell surface proteins:
CD4 binds with MHC II
CD8 binds with MHC I
CD28 binds with B7
96
New cards
Do Helper Th cells activate both humoral and cellular immunity?
yes
97
New cards
Cells that are cloned become?
plasma cells- antibody-secreting cells
98
New cards
Cells that do not become plasma cells become?
memory cells
99
New cards
What happens once a specific antigen is recognized by a B cell receptor?
cross-linking
100
New cards
**Autoimmune disease**
results when immune system loses ability to distinguish self from foreign