DNA, genes and protein synthesis
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
what is a gene?
a section of DNA that contains the coded information for making polypeptides and functional RNA
what is the coded information in the form of?
a specific sequence of bases along the DNA molecule
what do polypeptides make up and what does this mean?
they make up proteins, so genes determine the proteins of an organism
what are enzymes?
proteins
why are enzymes responsible for an organisms development and activites?
they control chemical reactions
what do genes (and other environmental factors) therefore determine?
the nature and development of all organisms
what is a gene? (location based)
a section of DNA located at a particular position (locus) on a DNA molecule
what does a gene (base sequence of DNA) code for?
the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide
or a functional RNA, including rRNA and tRNA
what did scientists suggest when trying to discover how DNA bases code for amino acids?
there must be a minimum of 3 bases that coded for each amino acid
what was their reasoning?
only 20 amino acids regularly occur in proteins
each amino acid must have its own code of bases on the DNA
only 4 different bases are present in DNA
if each base coded for a different amino acid, only 4 different amino acids could be coded for
using a pair of bases, 16 different codes are possible (still inadeuqate)
3 bases produce 64 different codes, more than enough to satisfy the requirements of 20 amino acids
what is each set of 3 bases for each amino acid called?
a triplet
what is the case as there are 64 possible triplets and only 20 amino acids?
some amino acids are coded for by more than one triplet
what have further experiments revealed about the features of the genetic code?
a few amino acids are coded for by only 1 triplet
the remaining amino acids are coded for by 2-6 triplets
the code is known as a degenerate code as most amino acids are coded for by more than one triplet
a triplet is always read in one particular direction along the DNA strand
the start of a DNA sequence that codes for a polypeptide is always the same triplet. this codes for the amino acid methionine. if this first methionine molecule doesnt form part of the final polypeptide, it is later removed
3 triplets dont code for any amino acid. these are called stop codes and mark the end of a polypeptide chain. they act in much the same way as a full stop
the code is non overlapping - each base is only read once (eg. 123456, 123, 456, not 123 234 345 …)
the code is universal, with few exceptions each triplet codes for the same amino acid in all organisms - indirect evidence for evolution
what does much of the DNA in eukaryotes do?
not code for polypeptides
within genes…
only certain sequences code for amino acids
what are these coding sequences called?
exons
what are the non coding sequences called?
introns
what do some genes code for?
rRNA and tRNA
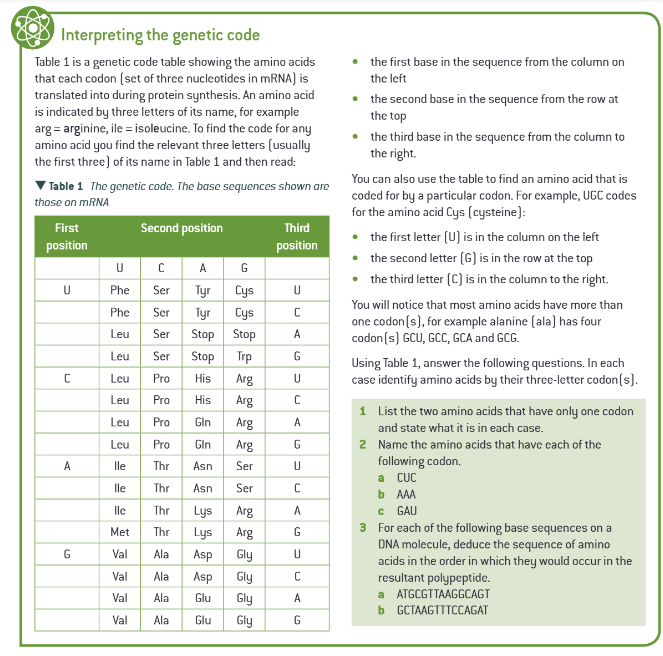
extra info: interpreting the genetic code