AP Psychology Unit 2: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/137
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
138 Terms
Sensory Neurons
Afferent Neurons
Carry messages from body's tissues & sensory organs. Inward TO the brain and spinal cord.
Interneurons
Process information between thee sensory input and motor input.
Motor Neurons
Efferent Neurons
Carries outgoing information FROM the brain and spinal cord TO the muscles and glands.
Sensory Neurons --> Interneurons --> Motor Neurons
Dendrites
Receives messages from other cells. Grabs messages initially.
Cell Body/Soma
Processes messages, the cell's life support center.
Axon
Passes messages away FROM the cell body TO other neurons, muscles, or glands. (Sent through the axon.)
Terminal Buttons
Transmits messages to the next dendrites/neurons. Message is sent out through the axon terminals.
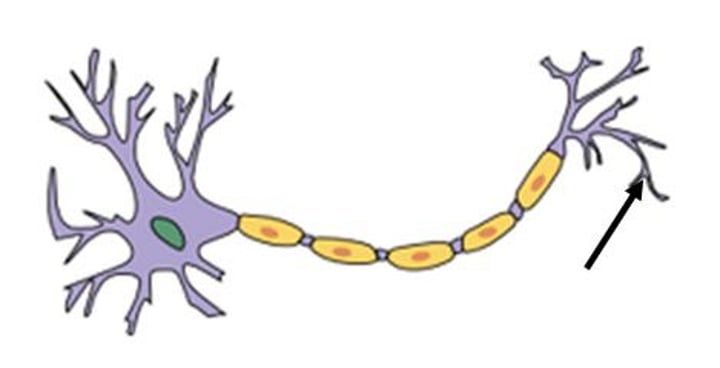
Myelin Sheath
Insulates and protects the axon and speeds transmission of the neural impulse. (Overall speeds up message.)
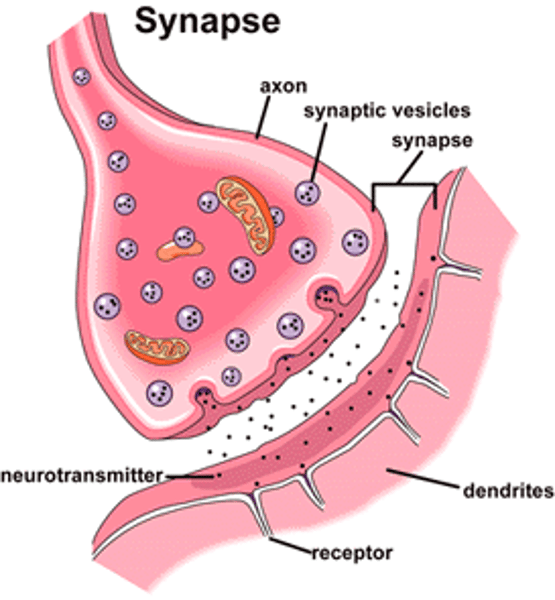
Synapse
The space between terminal buttons and dendrites of the next neuron receiving the signal.
Schwann cells
Helps axons regenerate, surrounded by myelin. (Found in peripheral nervous system).
Resting Potential
Neuron at rest, prior to the neuron being fired.
- Positively charged ions on the outside.
- Negatively charged ions on the inside.
Action Potential
Neuron is sent.
- Positively charged ions flood inside, DEPOLARIZING that part of the axon.
- Negatively charged ions flood outside the axon.
Refractory Period
During a resting pause, neuron returns to its original state.
- Positively charged ions pump back out.
- Negatively charged ions return back inside the axon.
Excitatory Signals
Excites and encourages the next neuron cell to fire. Message CONTINUES to fire through other neurons.
Inhibitory Signals
Stops and discourages the next cell to fire. STOPS message from going through other neurons.
The Threshold
When excitatory signals ARE MORE THAN the inhibitory signals, then the signal passes though the threshold. Action potential is created, the next neuron fired. Once passed through the threshold, the signal/message cannot stop.
All-or-none-Principal
A neuron either fires completely, or not at all.
Neurotransmitters
Held in terminal buttons, fit into receptors uniquely. Like a key in a lock.
Excess Neurotransmitters
Reabsorbed by sending the neurons in a process called reuptake.
Endorphins
"Morphine within", natural optiate-like neurotransmitters linked to pain control & pleasure.
- All pain is taken away due to endorphins, ex: Runners' High, or no initial pain upon being injured.
Acetylcholine: too much, too little.
Enables learning and memory, and muscle action.
(If ACh is blocked, muscles cannot contract).
Too much: Muscle spasms, possible OCD.
Too little: Alzheimers Disease
SSRI
Serotonin drugs stay in the synapse gap.
Dopamine: too much, too little.
Voluntary movement, attention, pleasure. (Ex: Addiction)
Too much: Schizophrenia
Too little: Parkinson's Disease
Serotonin: too much, too little.
Controls mood, appetite, and sleep.
Too much: Mania
Too little: Depression. (Ex: SSRI Drugs)
Norepinephrine: too much, too little.
Extends. adrenaline levels. (Epinephrine's reserve tank).
Too much: Increase in adrenaline
Too little: Depressed mood
GABA: too little.
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibits neuron from firing.
Too little: Seizures, tremors, and insomnia.
Glutamate: too much.
A major excitatory neurotransmitter. Encourages neuron to fire.
Too much: Migraines/seizures.
Antagonists
BLOCKS the receptor sites so neurotransmitters cannot fit. Decreases impulses, and can cause too much reuptake.
Agonist
Mimics the neurotransmitter, increases/raises impulses and overstimulating the neuron.
Ex: Meth, cocaine, etc.
Central Nervous System
The brain and the spinal cord.
Spinal cord connects peripheral nervous system to the brain.
The Peripheral Nervous System
Consists of autonomic and somatic nervous system.
Somatic Nervous Sustem
Voluntary control of skeletal muscles. (Actions we intentionally make).
Autonomic Nervous Sustem
Nerves that control out responses to stress and threats. Actions we cannot control, works by themselves.
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic in an emergency.
Sympathetic: Arouses and expands energy.
Parasympathetic: Calms energy.
EEG
- Detects brain waves.
- what different types of waves the brain produces during different stages of consciousness.
CT/CAT
- Camera's rotate around ones' head.
- Creates a detailed 3D picture of it's structure. (A sophisticated X-Ray).
- Uses radiation.
- Shows structure, NOT function.
PET
- What areas of the brain are most active during certain tasks.
- Measures how much of a certain chemical the brain is using in different situations. Overall brain and chemical activity.
- Shows function, NOT structure.
MRI
- Uses magnetic field to measure the density and location of brain material.
- Patient is NOT exposed to radiation.
- Only shows structure, NOT activity of the brain/function.
fMRI
- Combines elements of the MRI and PET scans.
- Shows BOTH brain structure AND brain activity/function.
Hindbrain
Life Support System
Medula, pons, cerebellum
Medulla
Controls heartbeat & Breathing
Pons
Coordinates movement, plays a role in sleep & breathing.
Cerebellum
Controls voluntary movement & balance.
Midbrain
Controls simple movements with sensory information.
Reticular Formation
Reticular Formation
Relays important information to other areas of the brain.
Promotes & regulates arousal & consciousness.
Limbic System (The Forebrain)
Emotion & Drives
Thalamus, hypothalamus, pituitary glands, amygdala, hippocampus, corpus callosum.
Thalamus
Receives all information from senses (Except smell), and routes to the higher brain.
Hypothalamus
Regulates behavior & hormones.
Pituitary Gland
Sexual/reproductive development & function.
Amygdala
Controls rage & fear, and the perception of these emotions.
Hippocampus
Controls learning & memory. Damage to right/left hippocampus can lead to different types of memory loss.
Corpus Callosum
Connects the to brain hemispheres & carries messages between them.
The Cerebral Cortex
A thin layer of interconnected neural cells, with complex systems of thinking & processing.
Association Areas
Parts of the cerebral cortex NOT involved in primary motor & sensory functions.
The Four Lobes
Frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital.
Frontal Lobe
Speaking, muscle movements, making plans & Judgements.
Premotor cortex, motor cortex, prefrontal cortex, Broca's Area.
Premotor Cortex
Involved in sensory guidance of movement.
Motor Cortex
Controls voluntary movements.
Prefrontal Cortex
Expression of personality & expression of appropriate social behavior.
Broca's Area
Controls language expression & muscle movements involved in speech.
Parietal Lobe
Processes sensory information like touch & pain.
Somatosensory Cortex
Somatosensory Cortex
Constructs understanding of what is being gelt. The more sensitive the body region, the larger the sensory cortex area is.
Occipital Lobe
Involved in vision & vision processing.
Visual Cortex
Visual Cortex
Recognizes patterns.
Temporal Lobe
Processes sounds.
Auditory cortex, Wernicke's area.
Auditory Cortex
Processes speech sounds.
Wernicke's Area
Controls language reception.
Split Brain
A condition that isolates the brain hemispheres (by cutting the corpus callosum).
Brain Plasticity
Allows our brain to modify itself after different types of change. Our brain can rewire & reorganize in response to damage. (Adapt).
Genes
Biochemical units of heredity that makes up our chromosomes, which are made up of DNA.
46 Chromosomes (23 from Mom, 23 from Dad).
Identical Twins
- Same fertilized egg split in half.
- Don't always share the same copy of genes.
Fraternal Twins
- Two fertilized eggs that share the same womb.
Genes vs. Environment
Genes influence personality traits. Environment influences attitudes, values, manners, faith & politics.
Molecular Genetics
Studies function & structure of genes. Also looks in. mechanisms that control gene expression.
Positive vs. Negative characteristics of molecular genetics.
Positive: Looks for risks of genetic disorders, explore mechanisms that control gene expression. (Weight, height, sexual orientation, etc).
Negative: Potential discrimination in prenatal, genetic screening, are we "playing god" with something that's supposed to be natural?
We process information...
Subconsciously at the same time, or even before we're consciously aware of things.
(We are awake, we are here).
Daydreaming & Fantasies
- Sexual Fantasies
- Escapist Fantasies
- Most often daydreams are realistic, typical day-to-day situations.
Daydreaming Benefits
- Allow us to mentally prepare for future situations, job interviews, etc.
- Essential for children's social & cognitive development.
- Can substitute for impulsive behavior.
Biological Rythms
- Annual Cycles (Bird migration, hibernation, etc).
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD).
28 Day Cycles
Female menstrual/ovulation cycle, the moon cycles.
24 Hour Cycles
Humans/mammals vary in alertness, body temp, and growth hormone secretion.
(Low body temp in the morning, increases and peaks in the afternoon, lowers in the evening).
90-Minute Cycles
Sleep stages.
Circadian Rhythm
Our Biological Clock
- A 24 hour cycle that affects our body temp, wakefulness, and blood pressure.
- A consistent natural human cycle.
- Light heavily affects our rhythm (both natural light and artificial light).
- Artificial light delays sleep, creates the necessity for bedtimes and alarm clocks.
Suprichiasmatic Nucleus (SCN)
Located in the hypothalamus, causes brain's pineal gland to decrease production of melatonin (sleepy hormone) in the morning, and increase production in the evening.
Awake just before sleep
- Alpha waves, slow waves in a relaxed awake state.
- We DO NOT know we've fallen asleep until we wake up.
NREM - 1
- About 5 Minutes
- Alpha waves to theta waves. NOT processing what you're hearing.
Hypnagogic Images
Sensation of falling/floating, hallucinogenic images.
Hypnic Jerk
Suddenly twitching/jerking awake, NO known cause, except our survival instinct to keep from falling.
NREM - 2
- About 20 Minutes
- Can easily be woken, but clearly asleep.
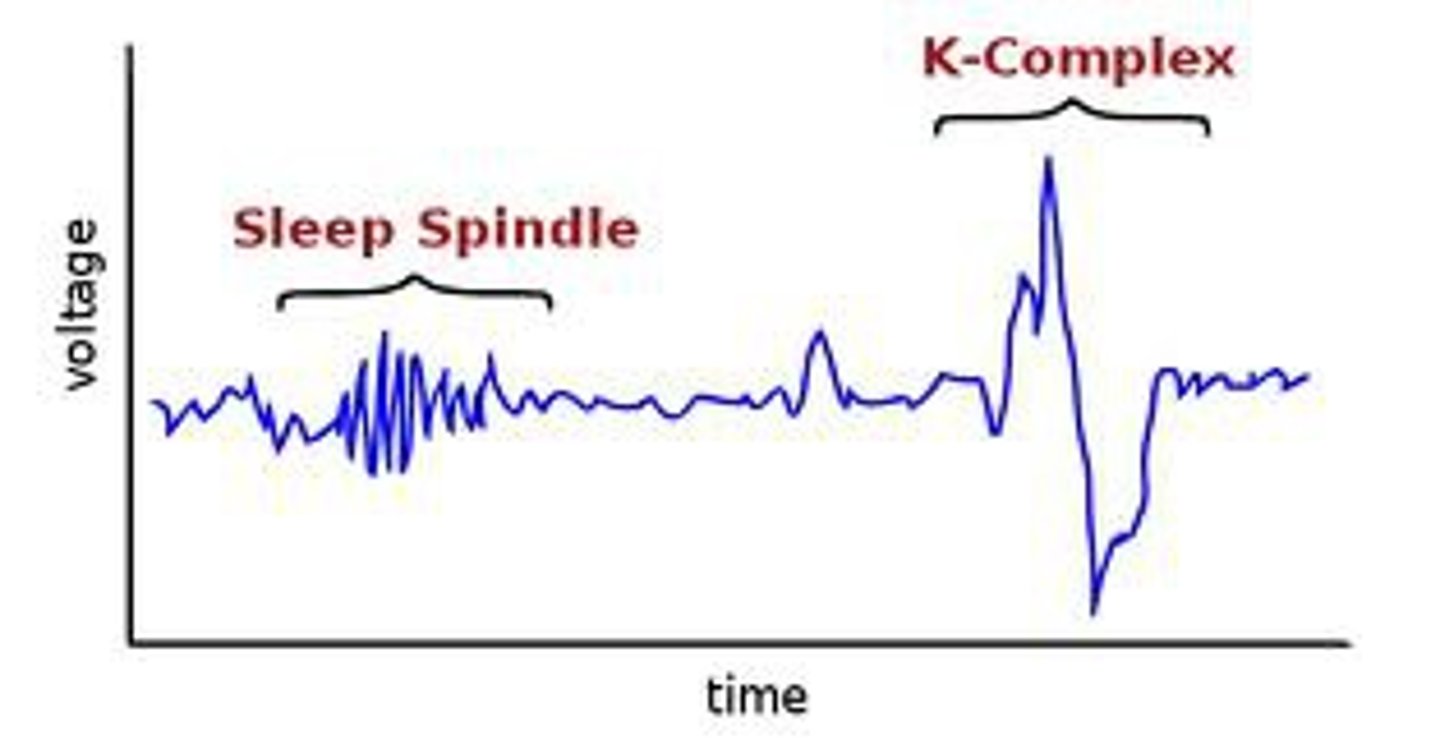
K - Complexes
A long delta wave, lasts for about a second.
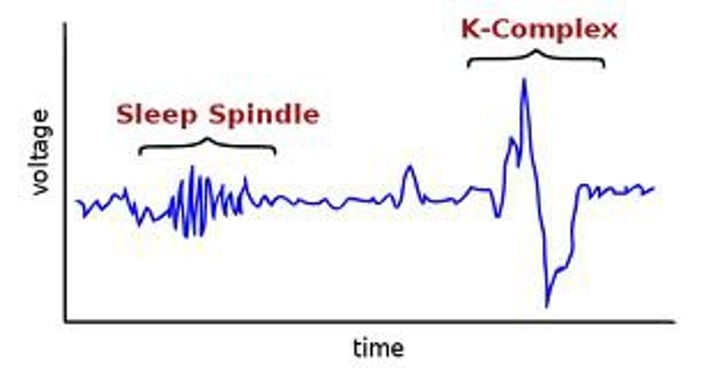
Sleep Spindle
A burst of fast waves that last for less than a second.
NREM - 3 and NREM- 4
- About 30 Minutes, slow wave sleep.
- Delta waves - large and slow waves of deep sleep. Hard to wake up from this sleep.
- Sleep walking/talking occurs NOT when dreaming.
- Growth hormones released.
REM Sleep
- AKA Paradoxical Sleep
- Returns to stage 3, 2, then REM sleep.
- The older we get, the less REM sleep we need.
- Last 10 minutes in the first period, gets longer each time. Alpha AND Beta waves, also a theta rhythm.
- Heart rate rises, breathing is rapid and irregular, genitals are aroused, eyes dart around behind closed lids.
- Muscles are paralyzed (Can't move).
- Motor Cortex: Active but brainstem blocks it's messages.
- Visual & Auditory brain areas are active during REM sleep.
REM Dreams
Emotional & Story Like
Sleep Paralysis
When the immobility lingers as you awaken from REM sleep.
- You wake up, but can't move. Causes anxiety and panic.
REM Rebound
- We dive back into REM sleep quickly and longer after being derived of it. Or woken up repeatedly during REM sleep.
- REM Dreams have been known to inspire literacy, ideas, etc.
Sleep Deprivation
- Brain keeps a record of sleep debt for at least 2 weeks.
- The younger we are, the more sleep we need.
- Lack of sleep increases stress, tiredness, shortens life expectancy, more irritable, lessened productivity, memory impairment, lack of creativity, concentration & communication.
Functions of Sleep
- Protects: We naturally hide awake & tuck ourselves in.
- Heals & Helps Recuperate: Restores body tissues, the brain repairs & reorganizes itself & consolidates memories.
- Helps Us Grow: Pituitary gland releases a growth hormone. As we age, we have less deep sleep and release less growth hormone.
Insomnia
Problems with falling or staying asleep.
Narcolepsy
Directly collapsing into REM sleep. Periodic, overwhelming sleepiness.