Enolate Anions & Enamines
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
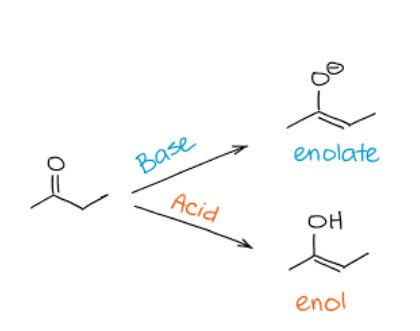
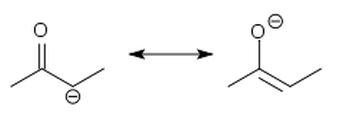
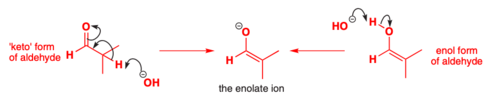
structure of an enolate
2
New cards
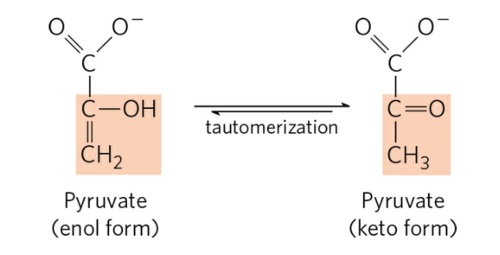
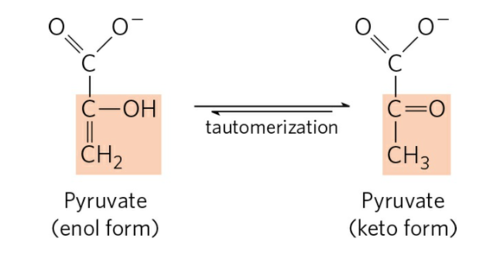
structure of the keto form
3
New cards
structure of the enol form
4
New cards
symmetrical ketone + strong base (⁻OH)
results in the same enolate
5
New cards
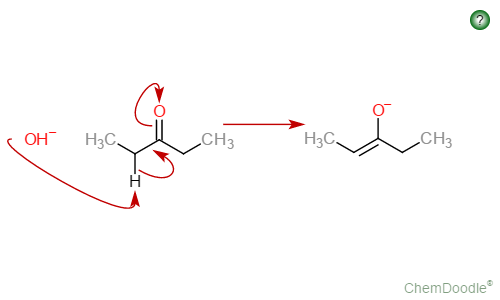
ketone w/a single alpha carbon + strong base (⁻OH)
results in an enolate
6
New cards
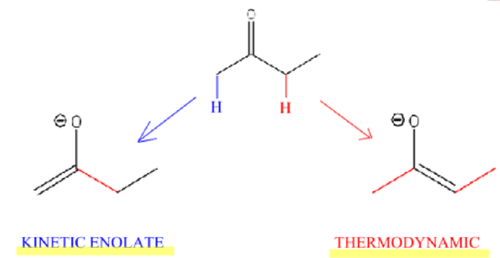
ketone w/two different alpha carbons + strong base (⁻OH)
results in two different enolates (thermodynamic is more stable, but kinetic forms faster)
7
New cards
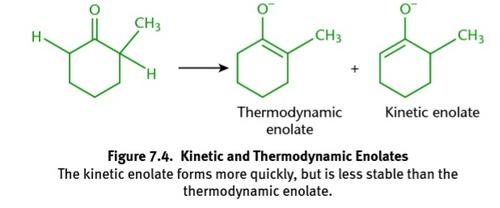
thermodynamic enolate
8
New cards
kinetic enolate
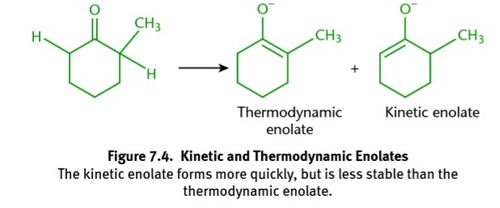
9
New cards
aldehyde/ketone + ⁻OH, X₂
(α-halogenation) all α hydrogens are replaced by X
10
New cards
aldehyde/ketone + H⁺, X₂
(α-halogenation) only one α hydrogen is replaced by X, resulting in a chiral center
11
New cards
aldehyde/ketone + ⁻OH, X₂ (xs)
(haloform formation) results in a carboxylate anion and a haloform
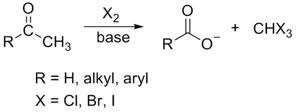
12
New cards
enolate + aldehyde/ketone
results in a hydroxyl ketone with α-β orientation
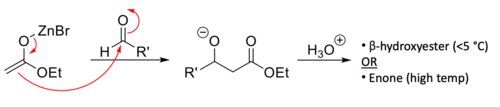
13
New cards
LDA, and KOt-butyl needs __ conditions and forms a __ product
LDA, KOt-butyl needs kinetic conditions (-78°C) and forms a kinetic product
14
New cards
NaOH, KOH, and MeOH needs __ conditions and forms a __ product
NaOH, KOH, and MeOH needs thermodynamic conditions (high temperatures) and forms a thermodynamic product
15
New cards
ester + alkyl oxide
(Claisen condensation) results in an aldol
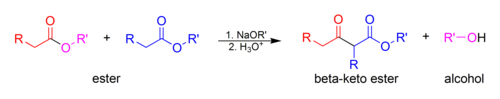
16
New cards
structure of a Claisen product
carbonyls are carbonyl carbon and β-carbon oriented (a β-keto ester)
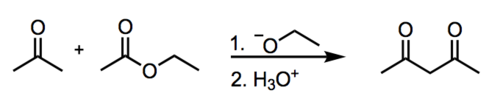
17
New cards
structure of Dieckmann product
carbon ring with carbonyls are carbonyl carbon and β-carbon oriented (a β-keto ester carbonyl ring)
18
New cards
base-catalyzed (⁻OH) α-halogenation
all hydrogens on the α-carbon are converted to halogens
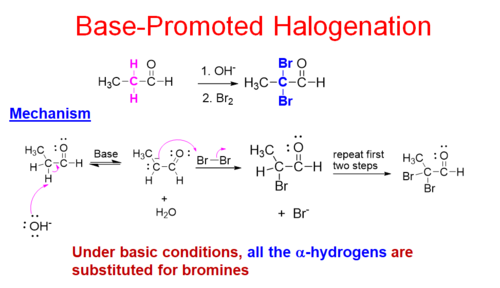
19
New cards
acid-catalyzed (⁺H) α-halogenation
a hydrogen on the α-carbon are converted to the halogens, creating a chiral center
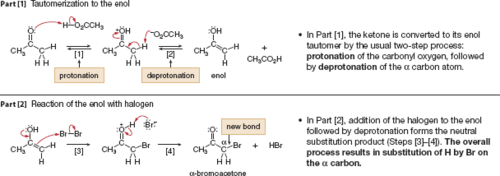
20
New cards
carbonyl with a single α-carbon + acid (⁻OH), X (excess)
haloform formation that results in a carboxylate salt and a CH(X)₃
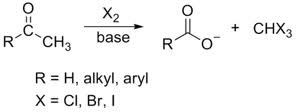
21
New cards
enolate + acid (⁺H), ∆
results in an α-β unsaturated aldehyde/ketone
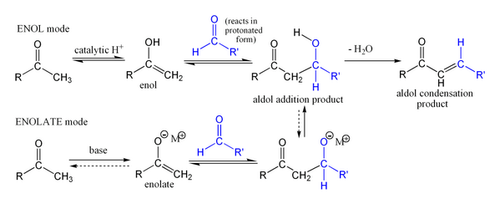
22
New cards
aldehyde/ketone + LDA
results in the corresponding enolate
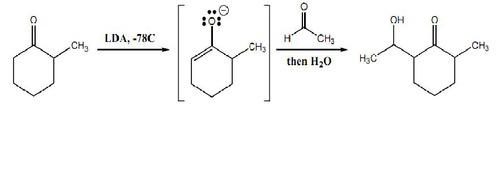
23
New cards
No heat is required in a condensation reaction when:
there is a conjugated system present
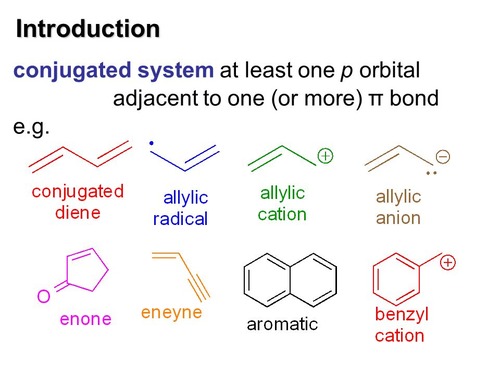
24
New cards
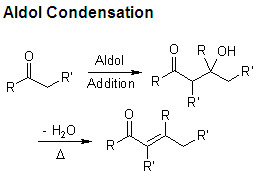
structure of an aldol product
α-β-unsaturated carbonyl
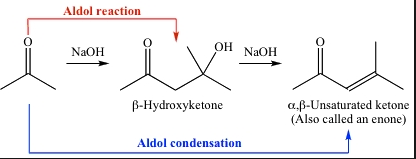
25
New cards
structure of an aldol condensation product
a β-hydroxyl carbonyl
26
New cards
What's the difference between an enol and an enolate?