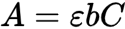AP Chemistry - Unit 3BC
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Kinetic Molecular Theory
A gas consists of particles in constant, random motion.
The combined volume of the particles is negligible compared to the total volume in which the gas is contained.
The particles exert no attractive or repulsive forces on each other EXCEPT when they collide.
Collisions between particles are completely elastic.
The average kinetic energy of the particles is proportional to the Kelvin temperature.
KE = ½mv²
Gas Law Conversions
1000mL = 1L
K = C + 273
1 atm = 760 mmHg = 760 torr = 101.3 KPa
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
T = 0°C or 273K
P = 1 atm or 101.3KPa or 760 torr or 760 mmHg
Mole Fraction Equations
PA = XA * Ptotal
PA/Ptotal =XA
Root mean square speed equation
urms =√3RT/MM
R = 8.314 J
Most probable speed bc the longer tail pulls the average speed slightly to the right
Boltzmann graphs - distribution of molecular speeds & changing the temperature affects the SHAPE of the curve NOT the area beneath it
Effusion
Tendency of gas molecules to move through a tiny hole
rate of ef1 / rate of ef2 = √MM2 / MM1
Solute
What IS dissolved (lesser concentration)
Solvent
What DOES the dissolving (greater concentration)
Solubility
“Like dissolves like”
Ionic compounds tend to dissolve in polar solvents because they form ion-dipoles
Saturated solution
maximum amount of solute dissolved for that temperature and pressure
Unsaturated solution
less than maximum amount of solute is dissolved
Supersaturated solution
temporarily holds more than maximum solute
Molarity equation
M = mol/L
Dilution equation
M1V1 = M2V2
Particulate models
Anions are LARGER than cations.
Opposite forces must be next to each other
Chromatography
Separates things based on IMFs
The more polar a component is, the farther it’ll travel
The less polar, the less it’ll travel
Distillation
Higher vapor pressure → lower boiling point → weaker IMFs
Distillate - the liquid coming out of the condensation tube
Microwave radiation
Molecular rotation (causes molecules to rotate)
Used to determine composition and structure of compounds
Infrared radiation
Molecular vibration (causes bonds to vibrate, bend, stretch)
Higher frequency and shorter wavelengths than microwaves
Ultraviolet and visible radiation
Transitions in electronic energy levels
UV is more energetic = UV has higher energy
Wavelength equation
c = λv
Photon energy equation
E = hv
Beer-Lambert Law
Linear relationship between absorbance and concentration
A = bc