Clin Lab IV Intro to Microbiology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Microbiology
The study of microbes
-bacteria, fungi, and viruses
Normal flora
Microbes found in and on the body that are not pathogenic
-found in GI, skin, parts of respiratory and urinary tracts
normally sterile locations
Spinal column
Blood
Urinary bladder
2 classifications of cells
Prokaryotic-before the nucleus
Eukaryotic- have a true nucleus
Prokaryotic cells
-most organelles are absent
-very small(100x viewing)
-have a cell wall, ribosomes, plasma membrane
-single strand of DNA usually arranged in a loop or circle
bacteria are___ Fungi are___
1. prokaryotic 2. Eukaryotic
Bacteria also contain
Capsules
Flagella
Endospores: allows for dormancy in suboptimal conditions
Clostridium
Naturally occurring GI bacteria with endospores
-can cause diarrhea in excess
Bacteria have special requirements:
Temp
O2 tension
pH: 6.5-7.5
Nutritional requirements
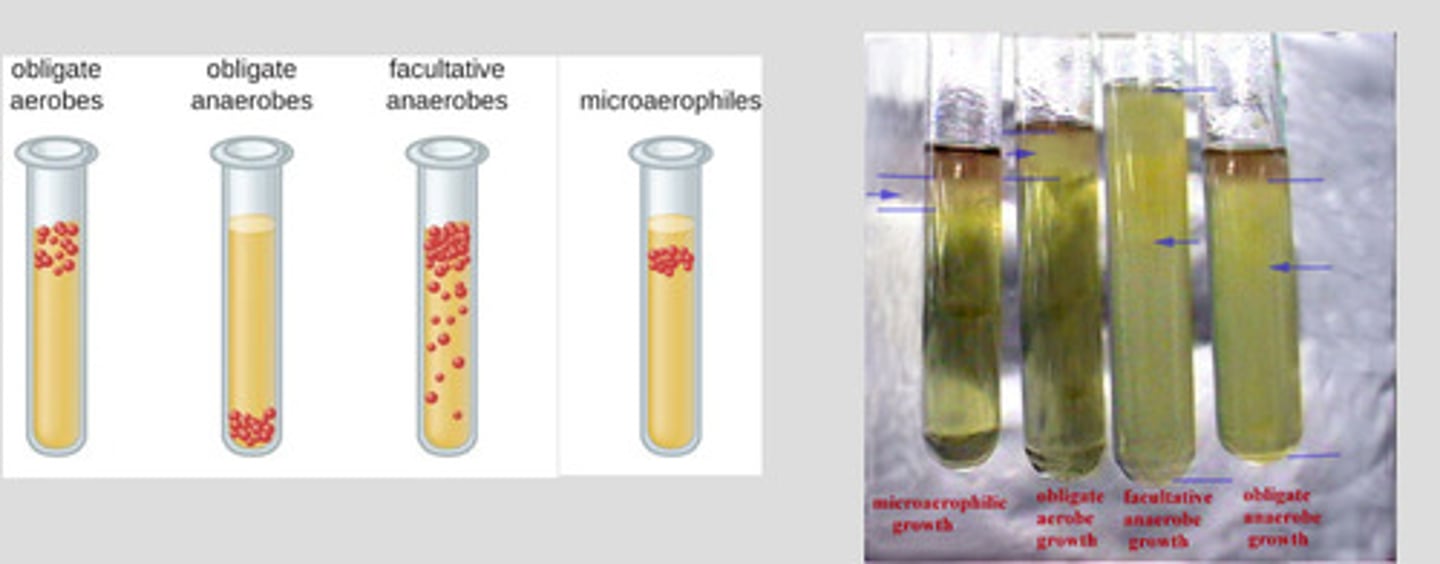
Classifications of bacteria
Obligate aerobes-require O2 to survive
Obligate anaerobes-will die in presence of O2 or growth is stunted
Facultative anaerobes-can survive w/o O2 but growth is limited
Microaerophilic bacteria-function best at reduced O@ tension
Capnophilic bacteria-require high levels of CO2
Fastidious bacteria
require strict nutritional requirements to grow
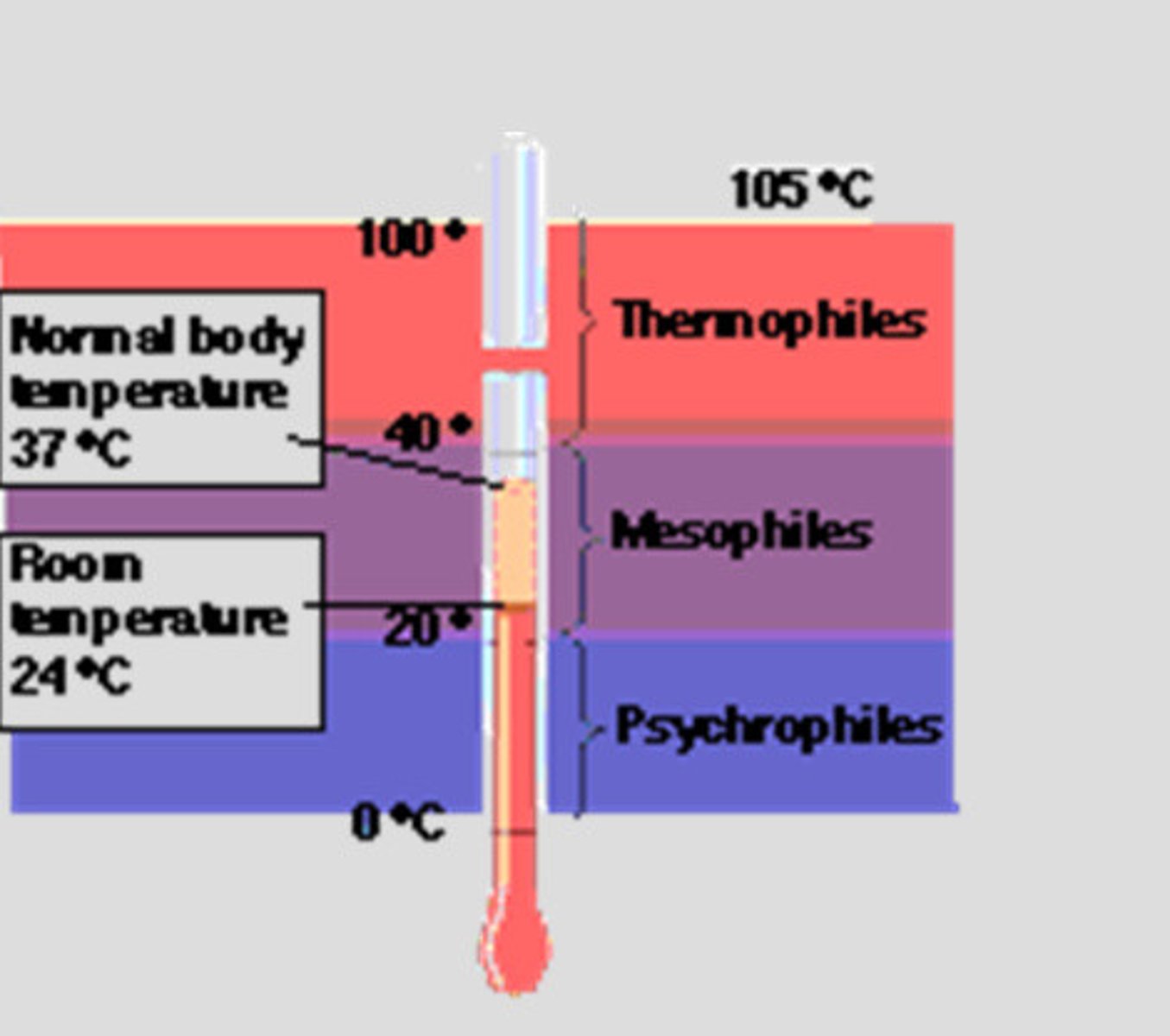
Classification of bacteria based on temperature requirement
Mesophiles: prefer temp between 20 and 40 degrees C and are most common pathogenic bacteria
Psychorphiles: require temp lower than 20 C
Thermophiles: requires temp higher
Bacteria are characterized by
Size
Shape
Arrangement of cells
Chemical reactivity
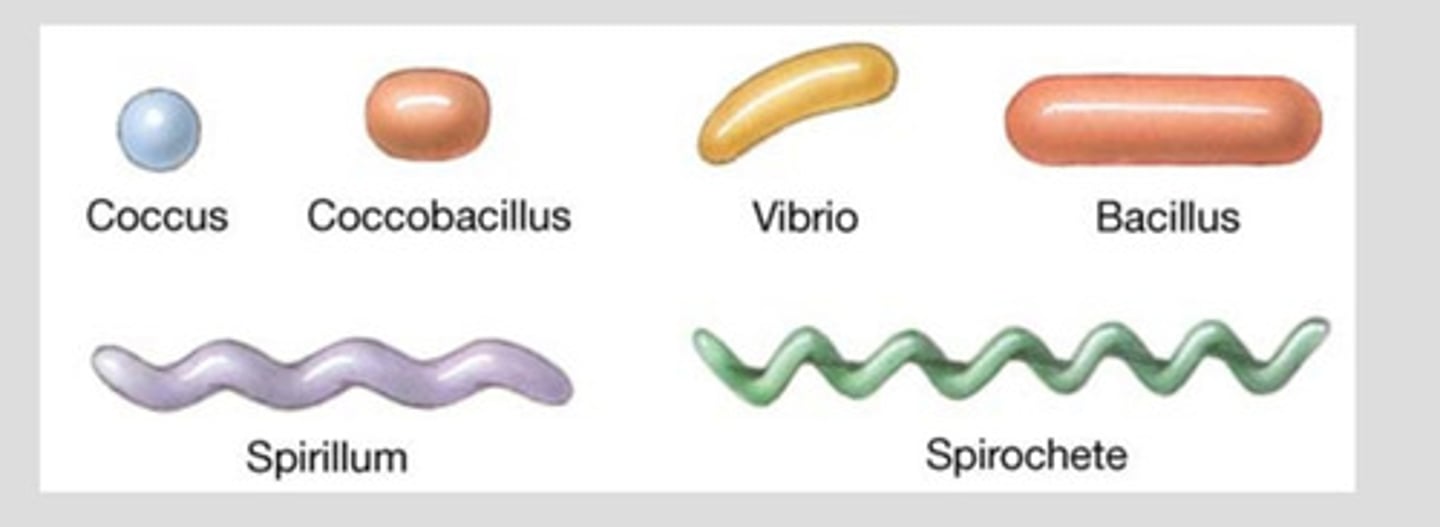
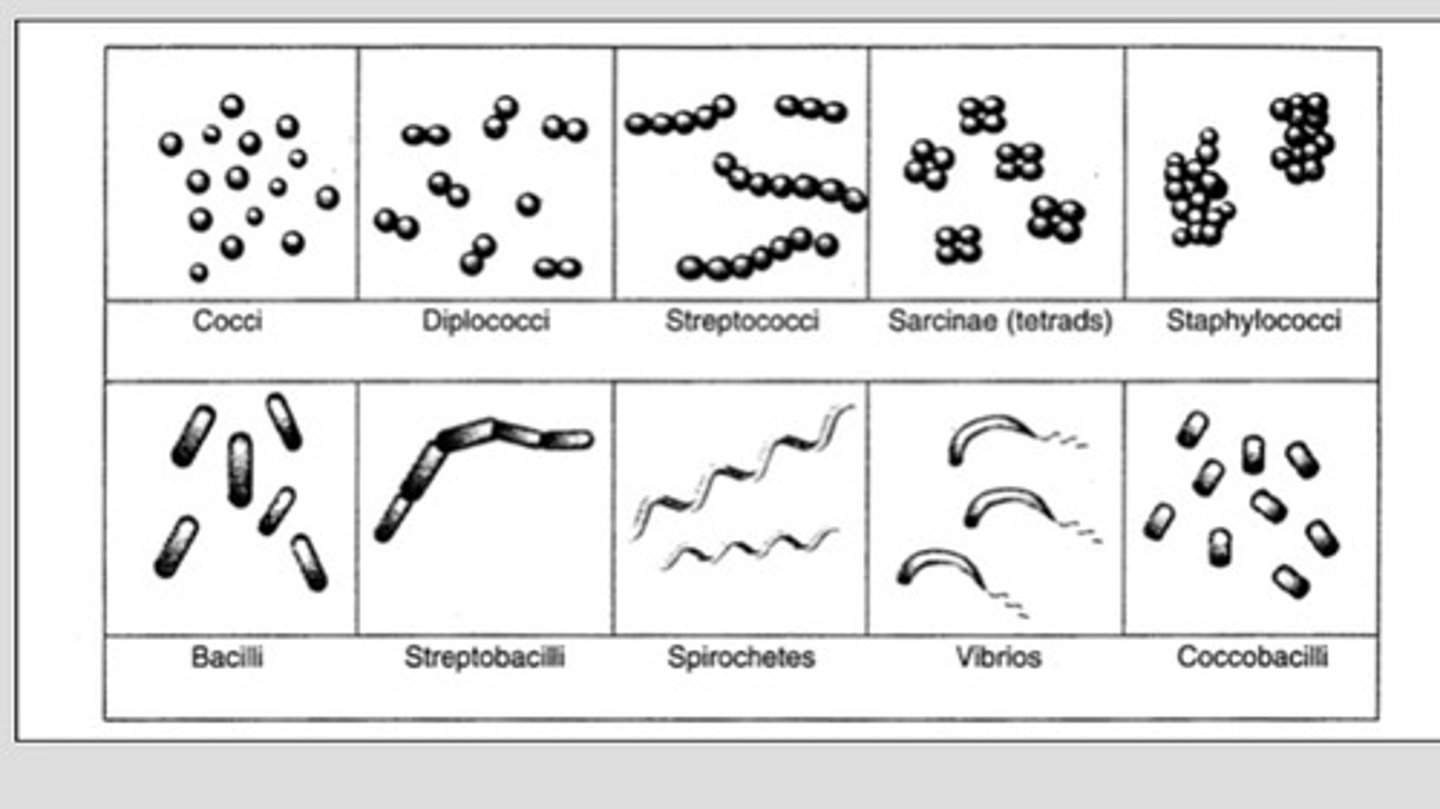
shapes of bacteria
Coccus: spherical cells; staphylococcus aureus (mastitis)
Bacillus: rods or cylinders; anthrax
Coccobacillus: small rod shaped; E.coli
Pleomorphic: range from cocci to rods; staphylococcus aureus
Spiral(spirochetes)
loose spirals: avian borreliosis,
tight spirals: leptospira pomona(red water dz)
comma shaped spirals(Vibrio); Campylobacter fetus abortions in cattle
STAPHYLOCOCCUS AUREUS
a form of staphylococci that commonly infects wounds and causes serious problems such as toxic shock syndrome or produces food poisoning
BACILLUS ANTHRACIS
Anthrax
Campylobacter spp
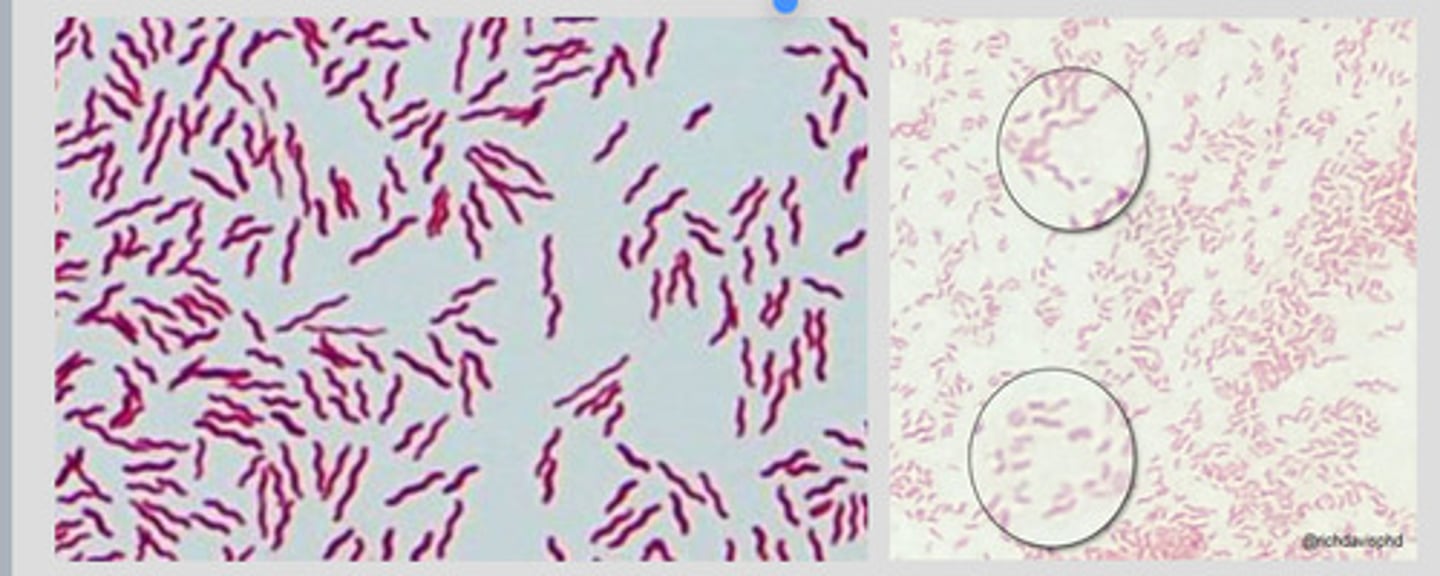
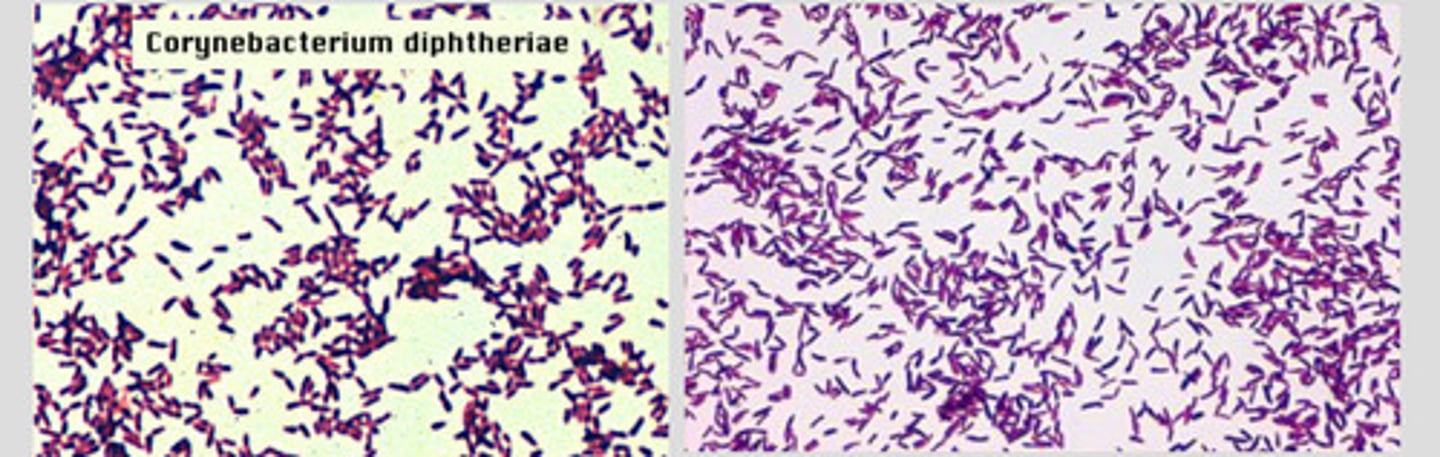
CORYNEBACTERIUM SPP
Causes diptheria: a serious infection of the nose/throat in humans
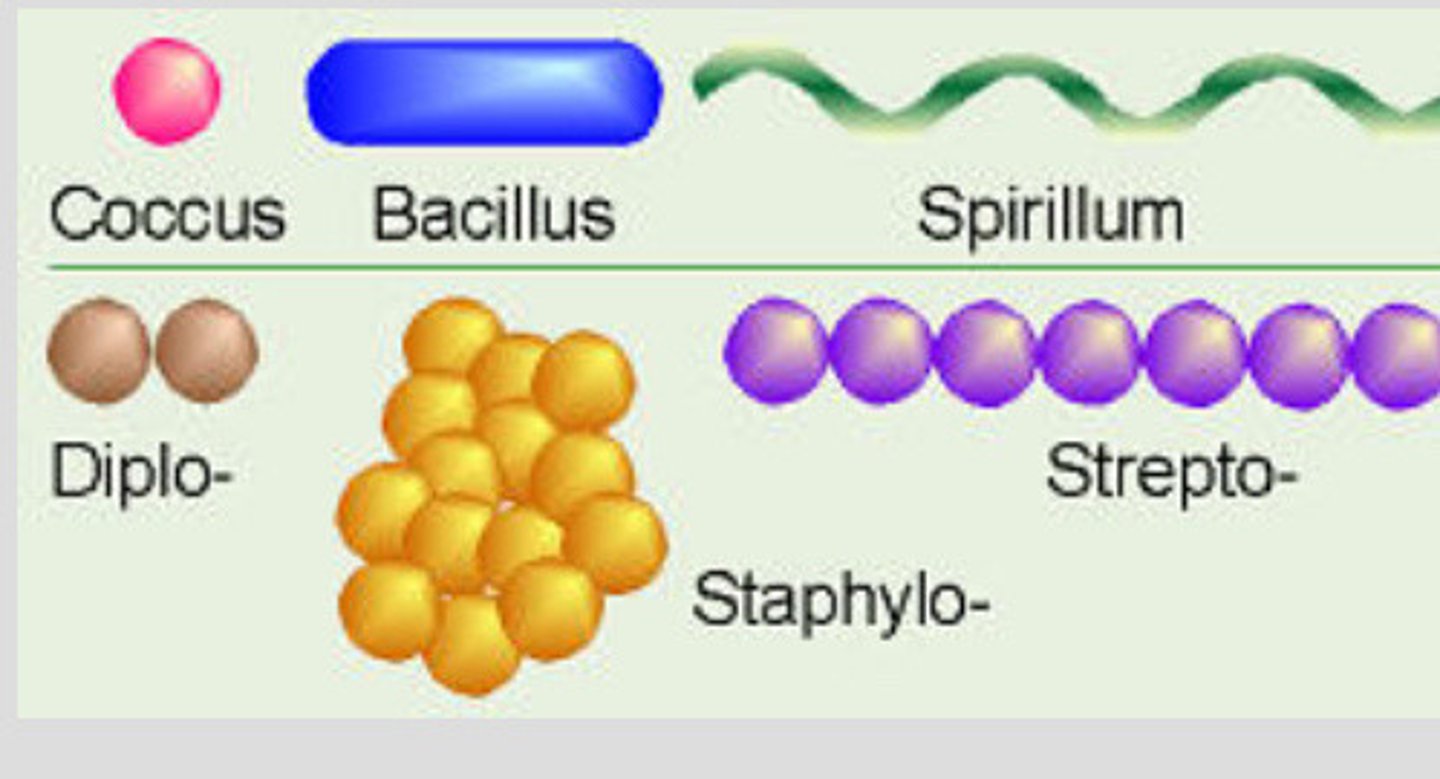
arrangement of bacteria
Single: most bacilli and some spirilla
Pairs: known as diplo-
Chains: strepto
Clusters: staphylococci(cluster of grapes)
Palisades: chinese letters form taken by some bacilli
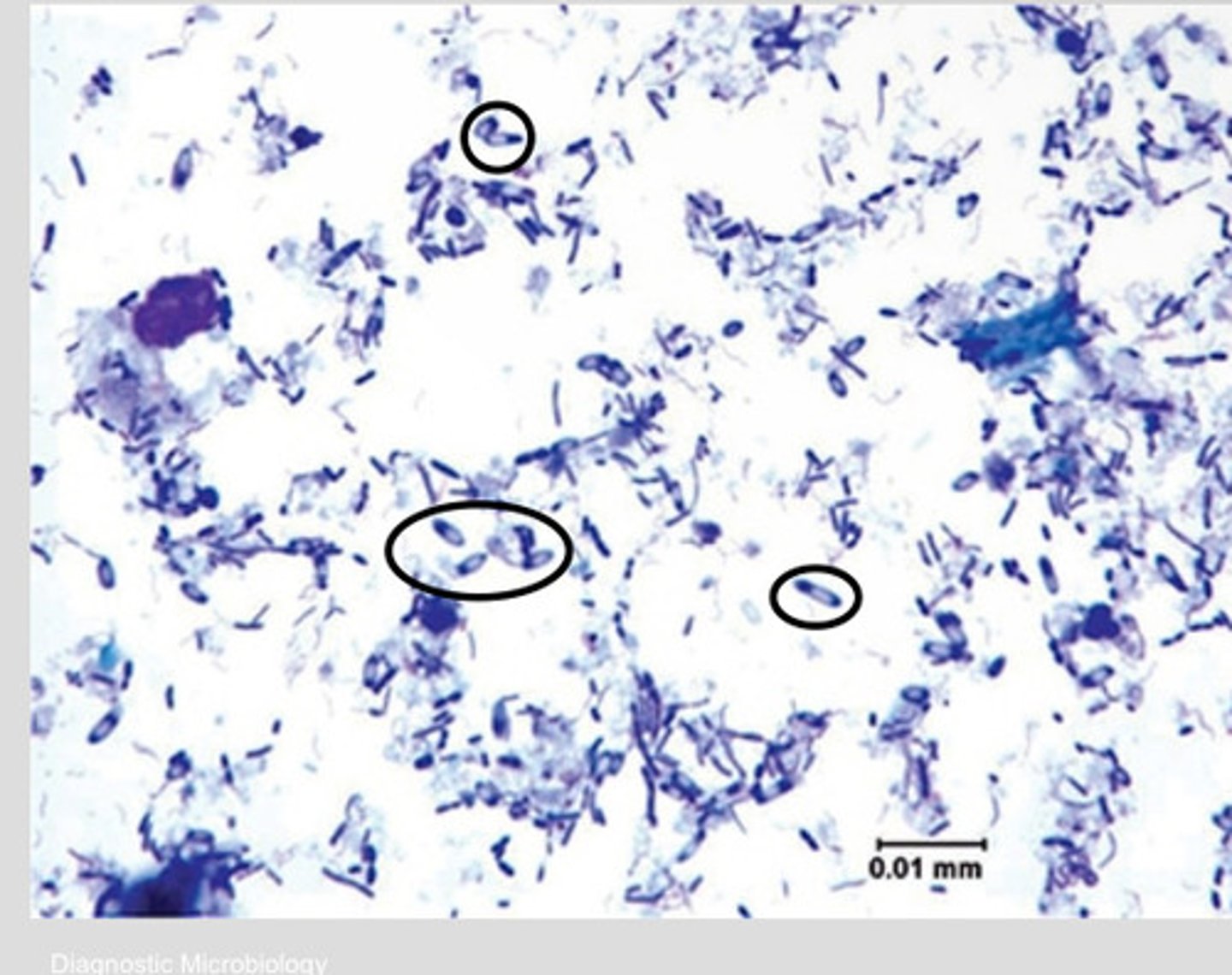
Endospore
-Intracellular refractile body
-resistant to heat, desiccation, chemicals and radiation
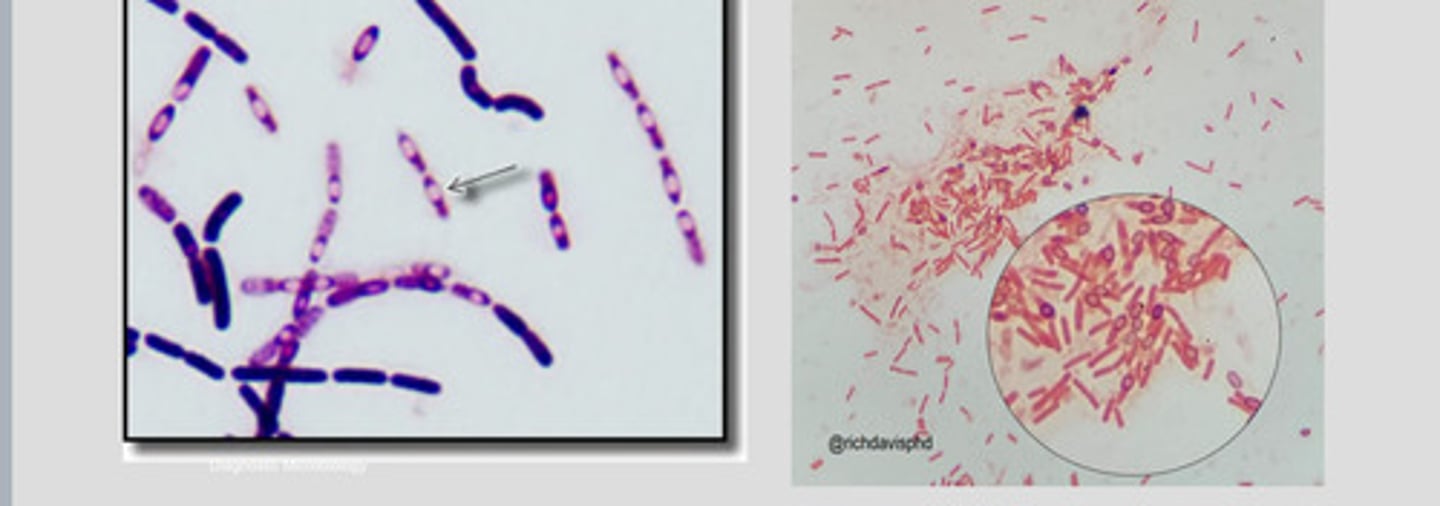
endospore producing bacteria
Ex: bacillus and clostridium sp.
-endospores are visible as nonstaining bodies within bacilli on gram stains
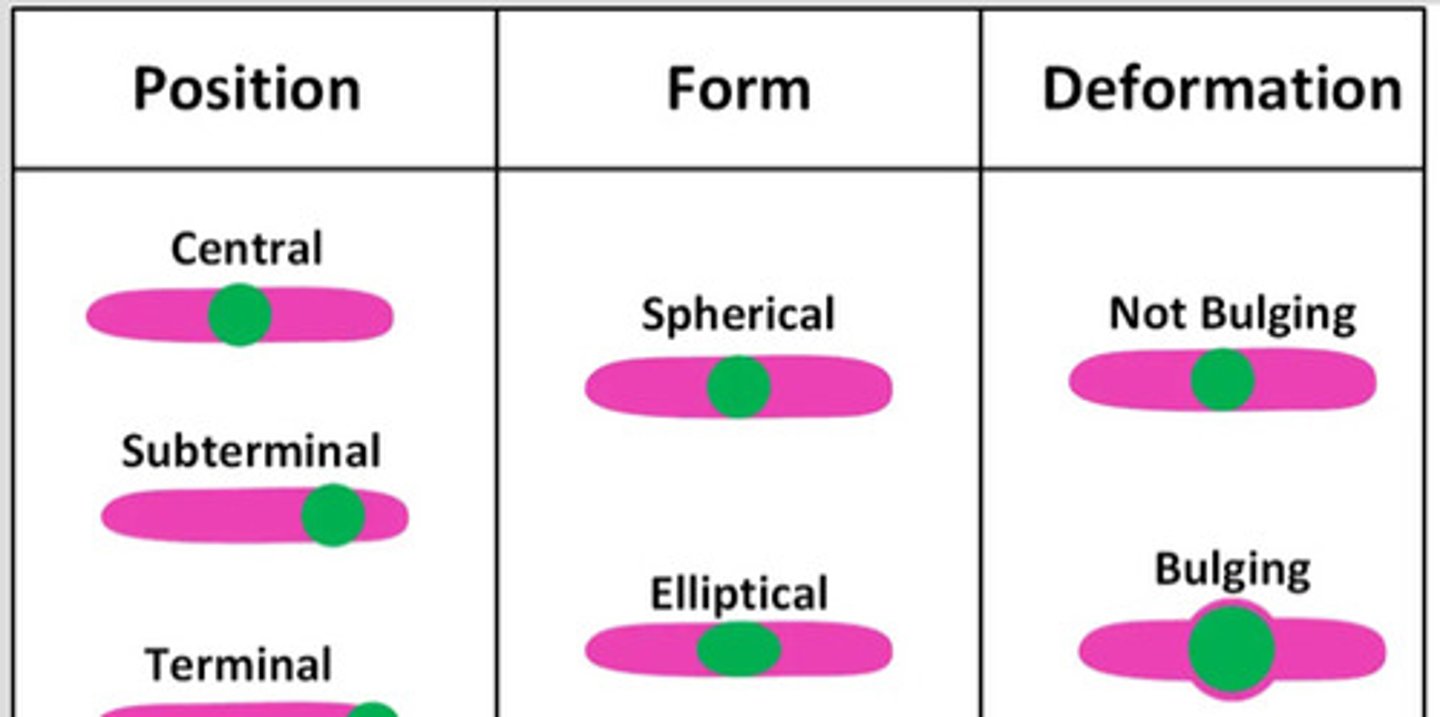
Endospore location
Central
Subterminal
Terminal
Bacteria reproduce by
Binary fission(doubling time)
-most contain a single strand of DNA
-4 stages, lag, exponential growth, stationary, and logarithmic decline
lag phase
bacteria adapt their metabolism to resources in new environment
exponential growth phase
AKA doubling time or generation time
-occurs when growth factors and conditions are right
-continues until nutrients are depleted and waster products accumulate limiting space
stationary phase
total cell numbers show no net increase or decrease
logarithmic decline phase
AKA death phase
-rate of death not necessarily same as rate of initial growth
-endospore formation occurs in this phase
Equipment for microbiology lab
-sterile cotton swabs
-dull scalpel
-3-20mL syringes with 21-25g needles
-collection tubes and preservatives
-Rayon swab(culturette)
-glass slides
-inoculating loops or wires
-culture media(plates or broth)
-antibiotic disks and dispensers
Bacterial culture media
any material solid or liquid that can support growth of microorganisms
-culture media should be refrigerated
solidifying agents used in prep of solid culture media
Gelatin: protein from animal tissue
Agar: dried extract of sea algae
Types of bacterial culture media
Transport
General purpose
Enriched
Selective
Differential
Enrichment
transport media
Designed to keep microbes alive while not encouraging growth and reproduction
-for if bacterial sample is being sent to a lab
general purpose media
AKA nutrient media
-not commonly used in vetmed
-allows any bacteria to grow
Type: Mueller Hinton Media for antimicrobial testing
Enriched media
Formulated to meet requirements of fastidious pathogens
-supports growth of many pathogens
Ex: blood agar, serum, egg, chocolate
Selective media
Contain antimicrobial substances in order to select for certain bacteria
-can support growth of some and suppress others
Differential media
Allows bacteria to be differentiated into groups based on biochemical reactions on the medium
Enrichment media
Liquid media and favor growth of a particular organism or group of bacteria
-encourage the growth of the desired organism or that contain inhibitory substances that suppress competition
Blood agar
-Enriched and differential media
-supports growth of most pathogens
-enriched with sheeps blood
-functions to differentiate through 4 distinctive types of hemolysis
4 types of blood agar hemolysis
Alpha: produces narrow greenish band around the colony(partial hemolysis)
Beta: produces a clear zone around bacterial colony(complete hemolysis)
Gamma: no change/no hemolysis
Delta: double zone of hemolysis around colony
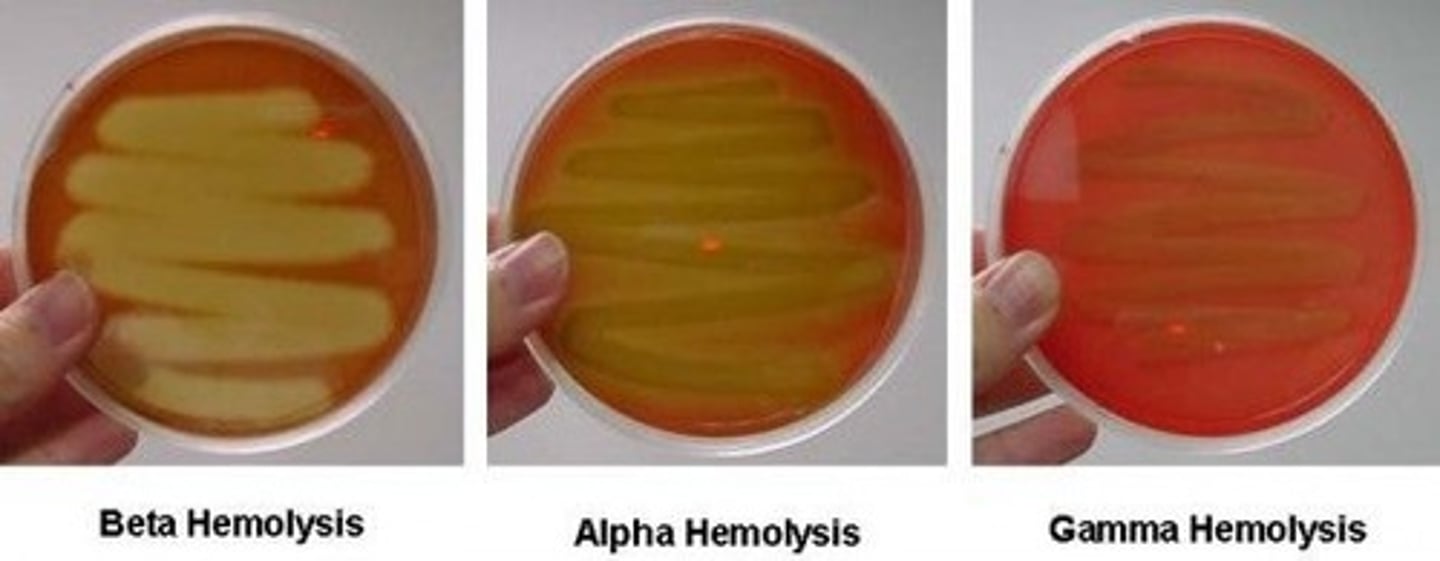
hemolysis
useful tool in preliminary ID of bacteria particularly streptococcus
-bacteria can produce different types of hemolysis that leave different marks in the agar dish
MacConkey Agar and Eosin Methylene blue agar
Both selective and differential media
MacConkey: selective for G(-) bacteria
-if lactose present will produce a pinkish red colony, if no lactose colonies will be clear
EMB agar: will identify lactose fermenting organisms
Chromogenic agar
Supports growth of enteric bacteria
-both selective and differential media
-allows for more rapid ID of bacteria
Ex: used to ID and differentiate E.coli from other enteric bacteria.
-E.coli will appear dark blue-green where other enteric bacteria will be magenta
-non enteric bacteria are inhibited but if they do grow, will be colorless
Thioglycollate broth
Anerobic bacteria to determine the oxygen tolerance of microbes
-stable oxygen gradient, high O2 concentration at the top, anerobic at the bottom
-the broth uses sulfur compounds to inhibit growth of other organisms while permitting salmonella to grow(some selective ability)
-Primarily used as an enrichment media and blood cultures
Urea tubes
-a peach colored medium containing urea
-Urease bacteria will produce ammonia and turn agar a pink color
-slants are streaked with inoculum and incubated at 37C overnight
Triple sugar iron agar(TSI)
Used for initial ID of salmonellae and initial differentiation of enteric bacteria
-classifies organisms based on ability to ferment glucose, lactose, and sucrose
-as well as production of hydrogen sulfide
Mueller hinton media
General purpose media
-primary media used when performing antimicrobial sensitivity testing
-allows diffusion of antimicrobials through the agar(to be motile)
Sulfide indole motility tubes(SIM)
tests the ability of an organism to reduce sulfur, produce indole(a chemical compound), and swim through the agar(be motile)
Simmons citrate tubes
differentiates bacteria based on use of citrate
Brain heart infusion broth
General purpose broth that is used to increase the number of organisms before they are plated on solid media
Mannitol salt agar
Highly selective medium for staphylococcus and it could be used to isolate staphylococcus aureus from contaminated specimens
Bismuth sulfite agar
Selective media for Salmonellae
-suppresses the growth of coliforms while permitting growth of salmonella
-strong inhibitory action and suitable for heavily contaminated specimens
Combination and modular culture media
Media that incorporate multiple diagnostic tests into a single platform
-Bullseye and Spectrum CS and multi chambered agar plates that contain both selective and non selective media
-enterotubes microbiology test kit that incorporates multiple types of media
Dermatophyte test media(DTM)
Fungi culture for ringworm
-selective and differential
-contains indicator that turns red in presence of dermatophytes as well as antimicrobial agents to inhibit bacterial growth
-comes in plate and tube form
Specimen collection
Aspiration and swabbing most common way
-imprints also acceptable
-must pay close attention to aseptic technique
-consider risk on contamination from things like normal flora
If sample needs to be evaluated immediately use
-cotton swabs
-Rayon or Dacron swabs
If sample process is going to be delayed
place swab in transport media
-culturette most common and will preserve sample
Sample collection guidelines
-Complete pt history
-specimen taken aseptically
-multiple species kept separate
-label specimen container esp if zoonotic
Most commonly used stains for microbiology samples
Gram stain and acid fast stain
Gram stain
4 step staining process to classify bacteria as either G(+)(purple) or G(-)(pink or red)
-often done before culture is performed
Gram stain is useful for
-helps ID predominant organism in mixed specimen
-helps ID ideal culture medium
-Helps ID antibiotic choice for pt
Acid fast stain(Ziehl-Neelsen Staining kits)
Certain bacteria are not readily decolorized by acid after staining
Ex:Mycobacterium sp(an acid fast organism)
Gram stain prep
-apply thin layer of sample to slide
-loop of bacteria from plate can be mixed with a small amount of saline or water
-heat fix slide to kill bacteria and render them permeable to stain
Gram staining steps
Crystal violet: Purple color G(+) fixative
-flood slide 30sec and rinse
Lugol's Iodine: also known as mordant that fixates crystal violet to G(+)
-flood slide 30sec and rinse
Decolorizer: Acetone cleans off G(-)
-wash briefly about 10 sec and rinse
Safranin: counterstain picks up G(-)
-flood slide 30sec and rinse
Gram positive bacteria
Retain crystal violet iodine complex
-bacteria are purple
-most cocci are G(+) but some bacillus rods can be
Gram negative bacteria
Stain red with the safranin counterstain and do not retain crystal violet
-bacteria are pink/red
-some rods will be G(-) like Salmonella sp
possible causes for an organism to stain both G(+) and G(-)
-excessive decolorization
-an overly thick smear
-excessive heat fixation
-old cultures
-poor quality stain
Potassium hydroxide test (KOH)
For gram variable bacteria
-if organism is G(+) the mixture stays homogenous and does not form a strand when lifted
-If G(-) it develops a mucoid appearance and produces a sticky strand when the drop is lifted
Ziehl-neelsen stain(acid fast)
Detect the acid fast organisms of mycopacterium and nocardia species
Stains contain:
-primary stain DMSO(dimethyl sulfoxide) or carbol fuchsin
-Acid- alchohol decolorizer
-counterstain: methylene blue
ziehl neelsen stain procedure
●Slide is air dried and heat fixed.
●Primary stain is flooded on slide.
●Slide heated over flame until stain steams.
●Cool slide for 5 minutes, then rinse with tap water.
●Acid alcohol is used to decolorize—1 to 2 minutes until red color is gone.
●Rinse slide
●Counterstain added then rinsed with water and air dried.
If stain is not removed the organism is acid fast and appears red
-nonacid fast will appear stain blue
Giemsa stain
Used to detect capsules, spirochetes, and rickettsiae
-not generally done in house and samples sent to lab
Flagella stains
uses a substance that makes the dye adhere to thin flagella, making them visible
Capsule stains
A staining method used to observe capsules
Endospore stain
Endospore stain specifically identifies a number of disease-causing bacteria that form endospores. These endospores are resistant to staining by normal methods. In this stain, heat is used to force the dye, malachite green, into the endospore, and thus stain green. Vegetative cells will be red colored.
Care to prevent contamination when inoculating media
-G(+) and G(-) will grow on blood agar
-keep culture plates closed
-never set lids or caps down on the table
-use only sterile inoculation loops, glass rods, or sterile swabs for inoculation
-aseptic technique must always be maintained
Samples for microbiological evaluation
-are streaked onto a primary medium
-incubated at 37C for 12-48 hrs
-culture plates should be inverted during incubation so that condensation does not collect on the surface of the agar
-should be examined for colonies every 12-24hrs
-bacteria should be gram stained and identified
Streaking an agar plate info
-is done to isolate most populous bacteria and get purest sample
-preferred method is the four quadrant streak method
-do not stab just streak across agar
-the process is continued until a pure culture is obtained(only one bacteria remains)
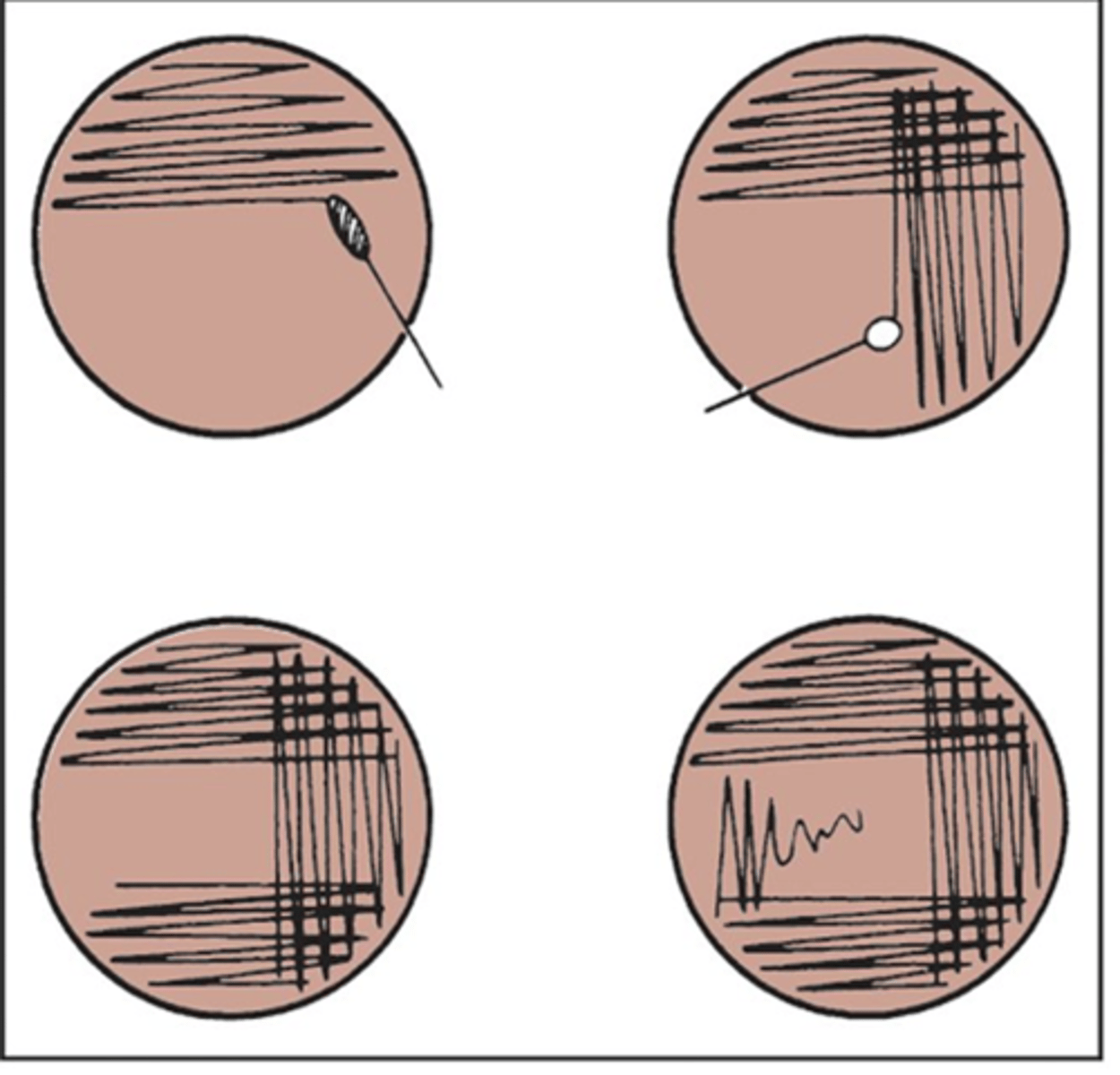
streaking an agar plate process
-streak sample in first quad back and forth w/o overlapping
-keep streaks as close as possible w/o overlapping ever
-with a new sterile swab, streak the next quad passing it through the previous quad only once or twice
-repeat for next 2 quads
-isolated colonies generally grow on the last quad streaked
*may take many plates to obtain pure culture
Inoculation of slants
-only the surface of the slant may be inoculated or the butt
-a straight flamed wire is used to obtain a sample from a primary isolation plate
-the surface of the slant tube is streaked in an S shape
-if the butt of the slant is inoculated stab the tip of the inoculating wire and carefully withdraw up the same insertion path
-the tube cap is to replaced loosely
Colonies can be evaluated by
size, pigment, density, elevation, form, texture, odor, any hemolysis
Antibiotic resistance
Occurs when a microbe changes or mutates that reduces or eliminates the effectiveness of substances meant to prevent infections
-Some bacteria escape the antibiotic and can repopulate
-bacteria can become resistant to specific types of antibiotics
antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Used to determine the susceptibility or resistance of a bacterium to a specific antimicrobial agent
-aids in choice of best antimicrobial
-pure culture will be streaked on a large Mueller Hinton plate for sensitivity testing with the disc diffusion method
Agar diffusion
Bauer Kirby disc diffusion method; most commonly performed
-use of paper discs impregnated with antimicrobial drugs
-allows quantitative measure of inhibitory zones
-concentration of drug in each disc correlates with the therapeutic levels of the drug
-should be kept in refrigerator when not in use
indirect sensitivity testing
-colony sample is taken from a plate and subcultured in a broth media and incubated
-the broth suspension is then applied on the Mueller Hinton media using a swab
direct sensitivity testing
application of an undiluted sample directly onto Mueller Hinton media
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing procedure
-colony taken from culture plate
-subculture in broth media(more than one colony should be included)
-incubate broth to achieve a standard turbidity
-suspension applied to Mueller Hinton plate w the lawn plate inoculation technique
-antimicrobial discs are applied to plate
-use sterile loop to tap discs to agar
-let stand for 2 minutes before inverting
-incubate 24hrs
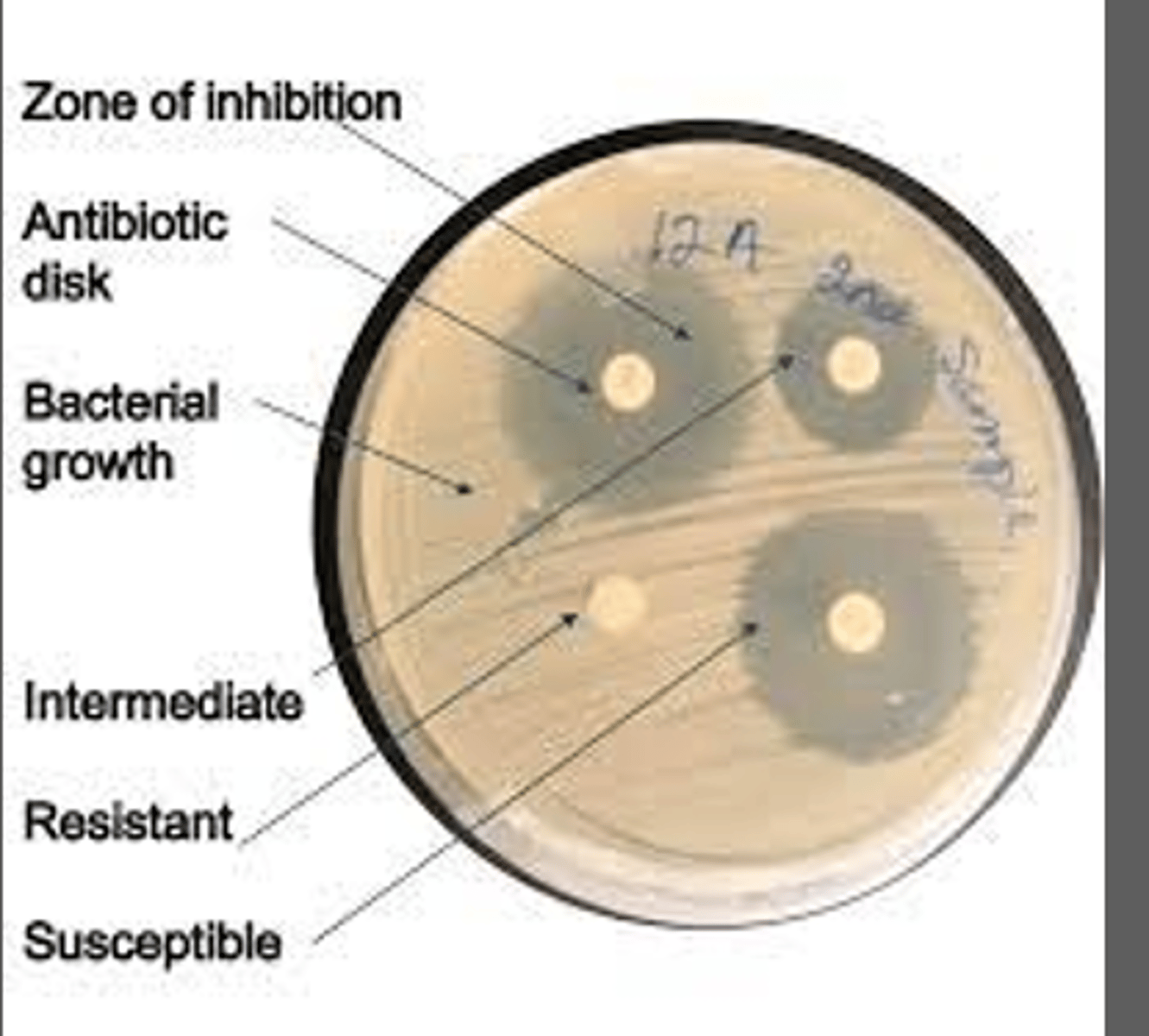
-measure zones of inhibition in milimeters(mm)
Measurement of zones of inhibition
Zone alone is not indicative of the efficacy of an antimicrobial
-the larger the zone of inhibition the the more susceptible the bacteria is to the antibiotic
-direct comparison of zone diameter produced by unrelated antimicrobials are misleading and should not be made
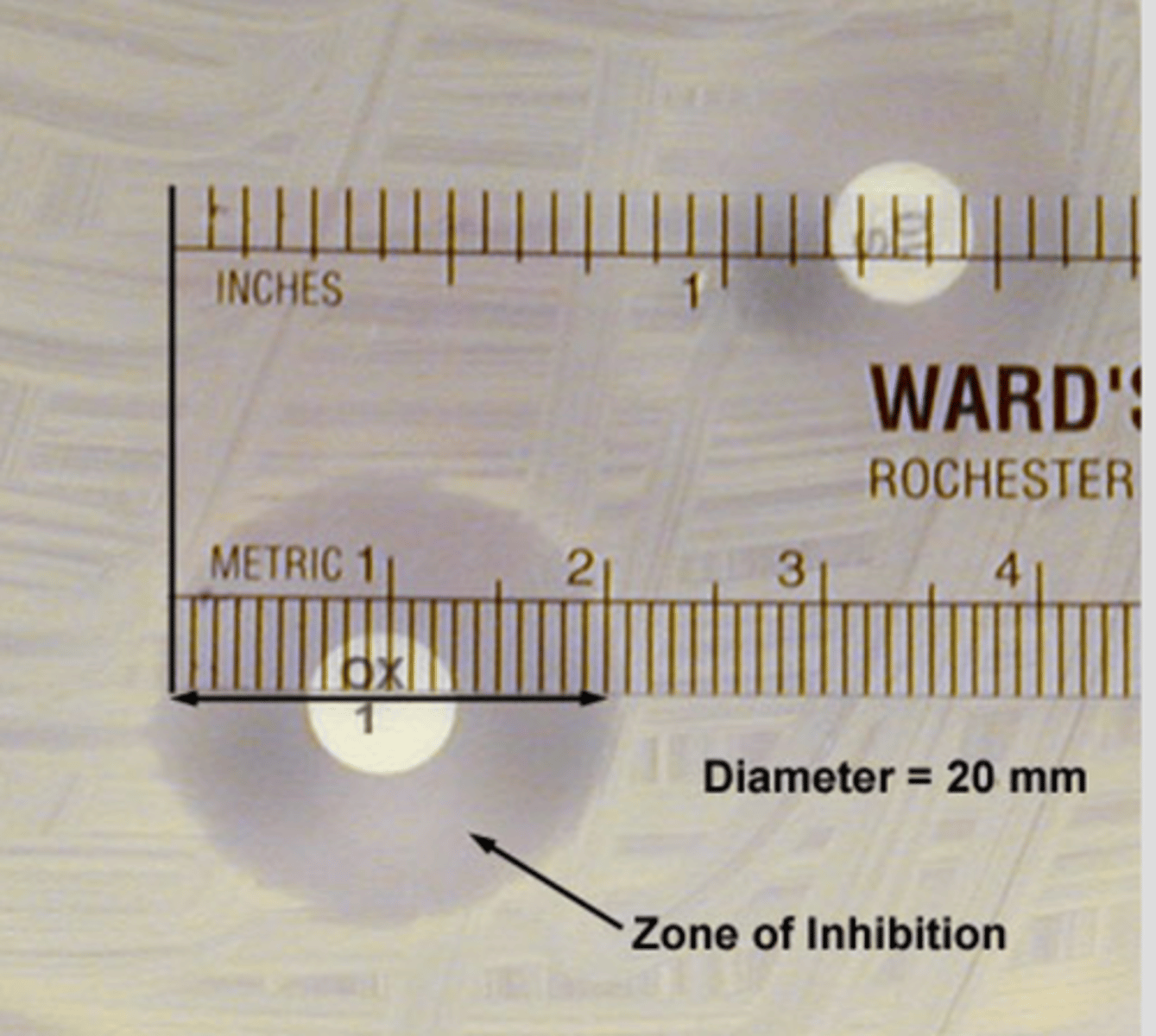
Interpretation of antimicrobial susceptibility testing
Susceptible: Organism is susceptible to ordinary doses of the antibiotic
Intermediate: Organism will likely require higher doses or concentration in tissues to work
Resistant: infected pt is not likely to respond to therapy w this drug
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)
Smallest concentration of antimicrobial that can inhibit the growth of bacteria
-the choice of a specific concentration of an antimicrobial is based of the MIC, site of infection, and the breakpoint
Motility testing
To determine if bacteria is motile or not
Several methods commonly used:
-wet prep
-hanging drop prep
-motility media(with SIM)
Wet prep motility test
-young broth culture is used
-a loopful of this culture is placed on a microscope slide under a cover slip and examined with the high dry objective lens
-you will observe individual cells moving if bacteria is motile
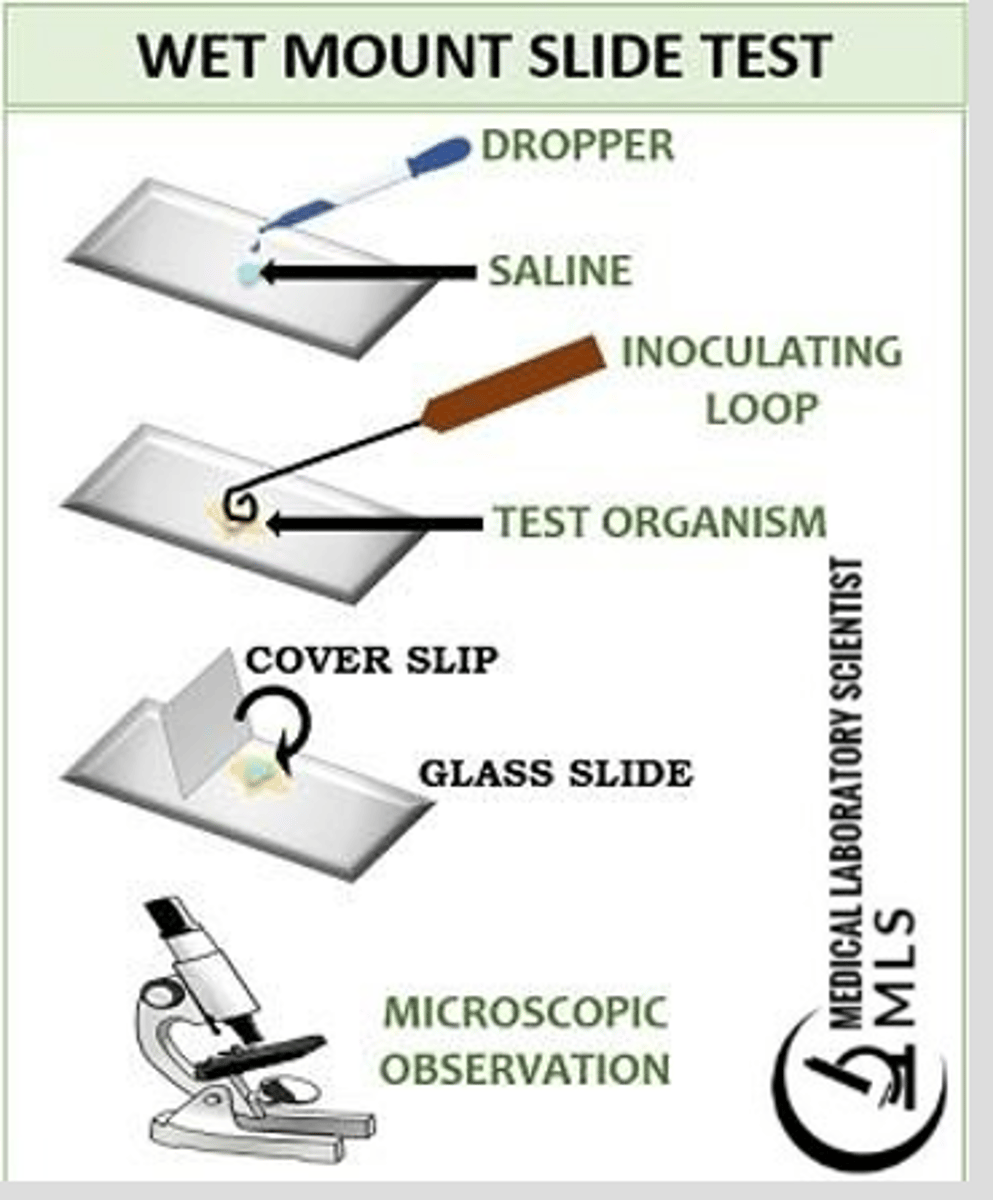
issue with wet preps
They tend to evaporate rapidly under a microscope
-some bacteria may not appear obviously motile w/o extra liquid provided
-the hanging drop can help w this problem
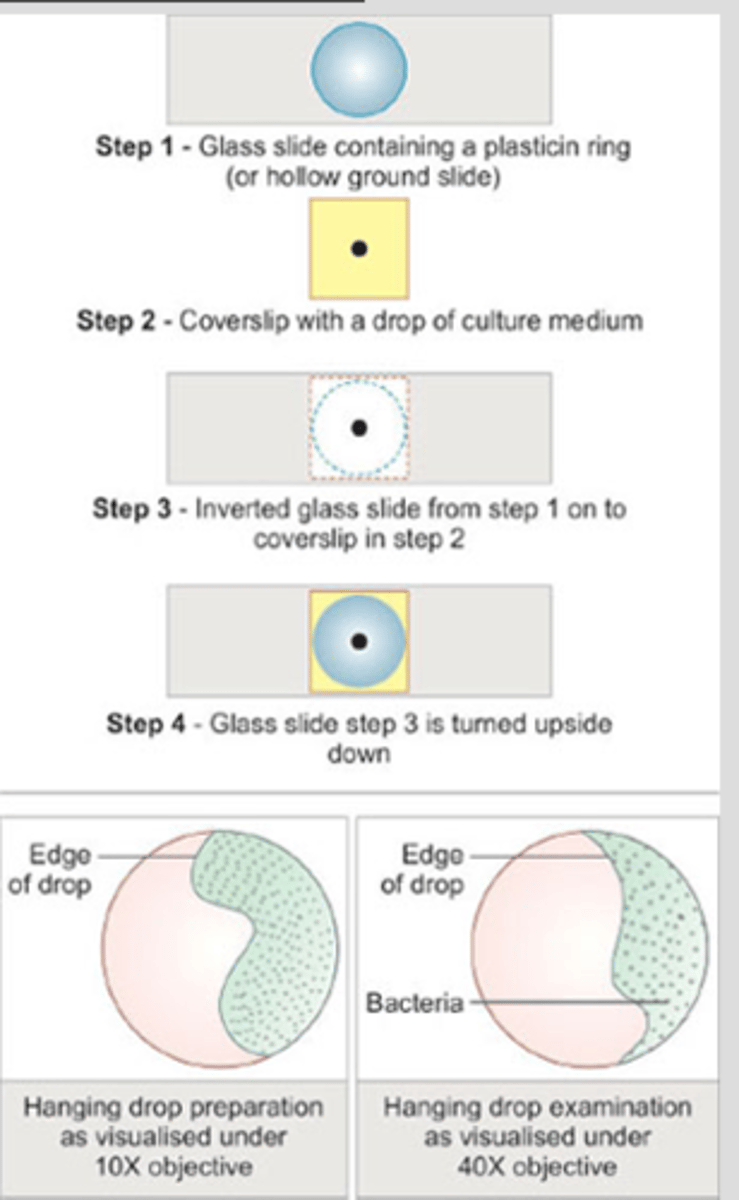
Hanging drop prep
Special slides are available that contain concave depressions in the center
-the slide should be cleaned w alcohol and wiped dry
-a small ring of petroleum jelly is placed around the concave area just before use
-place a drop of bacterial suspension on a coverslip and invert it onto the concave area of the slide
-press the cover slip down slightly so the jelly seals the conclave
-the suspension will be left hanging upside down into the well of the concave slide
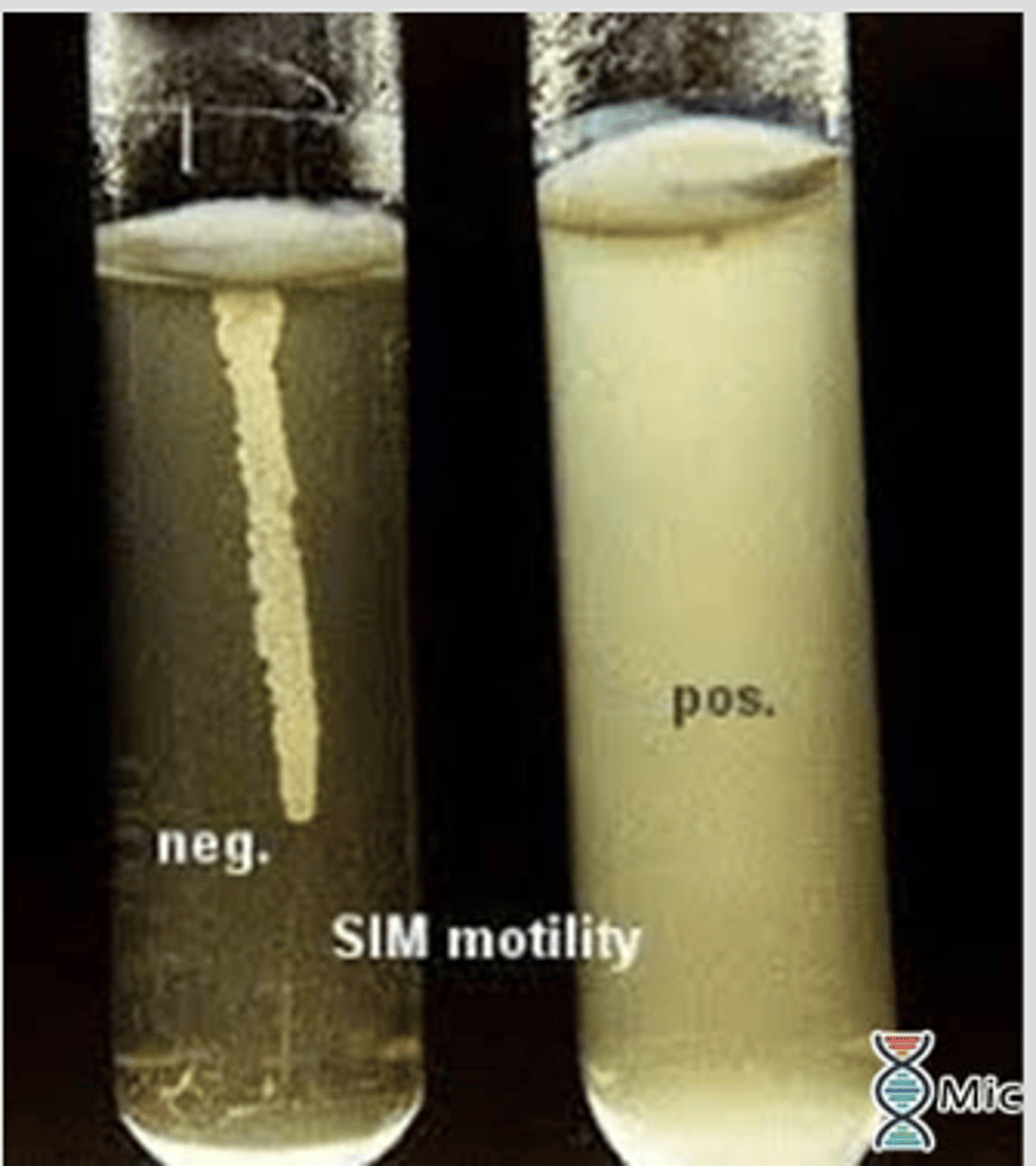
Motility media
If the organisms are non motile on the microscope this media should be used
-2 tubes of a motility medium sulfide indole motility(SIM) are stab inoculated
-one tube is incubated at 27C and the other at room temp for 24-48 hours
-if growth is restricted to the stab inoculation line the organism is not motile
-Diffuse growth throughout medium means it is motile

Indole test
Evaluates the ability of the organism to produce an organic compound called indole
-uses SIM media with Kovac's reagent added to it
-Kovacs reagent is not suitable for testing anaerobic bacteria
-a small amount of colony can be picked up from a pure culture and a drop of Kovacs is added
Indole test results
Kovacs reagent turns red in the presence of indole
Positive=red to pink color change
Negative= no color change
Catalase test
Preformed on G(+) cocci and small G(+) bacilli
-tests for enzyme catalase which acts on hydrogen peroxide to produce water and oxygen
-Catalase positive bacteria will produce bubbles
Catalase test procedure
-small amount of a colony from a blood agar is placed on slide and a drop of catalase reagent(3% hydrogen peroxide) is addded
-be sure not to collect any part of the blood agar because this can produce a slight positive reaction
Coagulase test
Performed on catalase positive G(+) cocci
-staphylococcus aureus produces coagulase which is an enzyme that coagulates plasma
-2 versions available the slide test and the tube test
Coagulase test positive vs negative
Coagulase positive- staphylococcus aureus and intermedius
Coagulase negative- staphylococcus epidermidis or saprophyticus