Chapter 6: Government Intervention
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Price Ceiling
The government sets the maximum price that can legally be charged or paid.
Effects of a Price Ceiling
If set above equilibrium price, it results in a shortage.
Illicit Market
A market where a legal good trades at an illegal price.
Search Activity
Efforts to find something from whom to buy or sell.
Shortage
Condition where demand exceeds supply due to price ceiling.
Deadweight Loss
Loss in economic efficiency when equilibrium is not achieved.
Price Floor
The government sets the minimum price that can legally be charged or paid.
Minimum Wage
A price floor that sets the lowest legal wage for workers.
Illegal Hiring
When workers are paid below the minimum wage.
Welfare Effects of Minimum Wage
Marginal social benefit versus marginal social cost, leading to gains and losses.
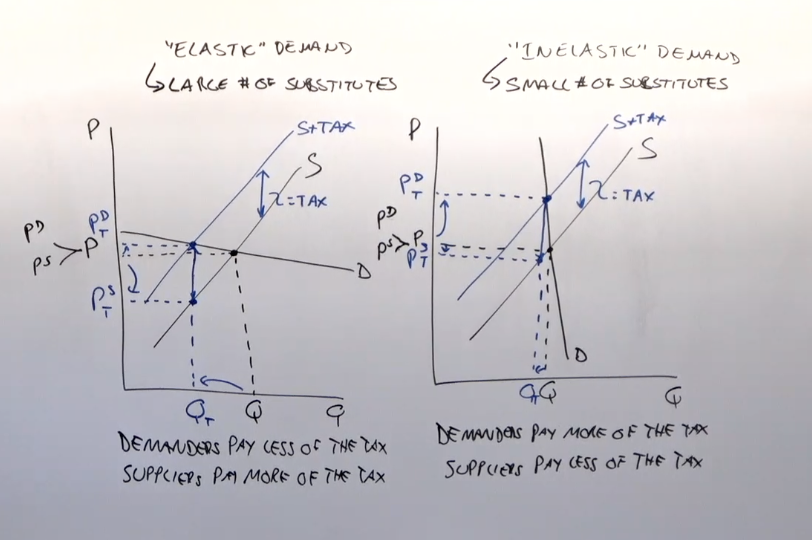
Tax Incidence
Who actually pays the tax; depends on elasticity of demand and supply.
Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Buyers pay the entire tax when demand does not change with price.
Perfectly Elastic Demand
Sellers pay the entire tax when demand changes dramatically with price.
Production Quotas
An upper limit on the quantity of a good that may be produced.
Subsidies
Payments made by the government to a producer to encourage production. Effects are simmilar to tax but the opposite
Market of Illegal Goods
Markets for goods that are regulated and illegal to buy and sell.
Prohibition Impact
Effects of making certain goods illegal on supply and demand.
Cost of Breaking the Law
The illegal status raises the cost of trading due to penalties.
Penalties on Sellers
a decrease in supply as the supply curve shifts left Severe penalties for selling illegal drugs, decreasing supply
Penalties on Buyers
Demand decreases as the demand curve shifts left (D-CBL). Possessing illegal drugs can lead to serious penalties, affecting demand.
Equilibrium Price/Quantity
Price and quantity at which supply equals demand in a legal market.
Debate on Legalization
Discussions about legalizing and taxing drugs as a policy solution.
Supply Curve Shifts
Changes in supply due to penalties can shift the supply curve left.
Demand Curve Shifts
Changes in demand due to penalties can shift the demand curve left.
Effects of Enforcement
Higher penalties can increase the decrease in supply/demand.
Challenges in Enforcement
High costs and limitations in resources affect law enforcement effectiveness.
Ability to Pay Principle
People should pay taxes according to how easily they can bear the burden.
Benefits Principle
People should pay taxes equal to the benefits they receive from government services.
Inefficient Underproduction
When production is below efficient levels due to regulations.
Inefficient Overproduction
When production exceeds efficient levels due to subsidies.
Search for Jobs
Workers searching for employment can lead to unemployment, especially with minimum wage.
Marginal Social Benefit
The additional benefit to society from an additional unit of labor or product.
Marginal Social Cost
The additional cost to society of producing one more unit of labor or product.
Agricultural Products
Commodities that often have price floors set by the government.
Gains from Labor Union
Workers who keep jobs and get higher wages due to union influence.
who pays the taxt
the smaller the elasticity, the more they have to pay and who ever has the lager elasticity pays less and vise versa
production qutota set above the equilibrium quantity quota
no change
production quota set below the equilibrium quantity quota
Results in decreased supply, increased prices, lower marginal costs, inefficient underproduction, and incentives to overproduce.
Effects of subsidies
increased supply, lower prices, higher production quantity, increased marginal costs, government payments to farmers, and inefficient overproduction.
A Free Market for a Drug
Demand Curve (D): Lower drug prices lead to higher quantity demanded.
Supply Curve (S): Lower drug prices result in lower quantity supplied.
Equilibrium Price/Quantity: If drugs were legal, equilibrium would be at price Pc and quantity Qc.