Unit 1 Hardware
Controller
Coordinates the other parts of the CPU
ALU
Does Arithmetic Calculation and Logical operation
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Controller
Coordinates the other parts of the CPU
ALU
Does Arithmetic Calculation and Logical operation
Register
Single fast volatile memory. E.g: the program counter
Internal Memory
Holds frequently used instructions and results of calculations (also called cache memory)
RAM
RAM is used to hold running programs and data for them.
ROM
ROM is permanently store data, e.g: it stores BIOS and starts the PC up.
HDD
HDDs have a spinning platter, have moving read/write heads, cheap per GB, slow compared to SSD, affected by fragmentation
SSD
No moving parts, expensive per GB, very fast compared to HDD, not affected by fragmentation, limited number of read/write cycles
Cloud Storage
If the storage is free then it is cheaper than physical storage like HDD and SSD, might be more expensive if you have to pay it monthly, accessible to any device with internet access, accessible to anywhere in the world, automatically backed up, security issue (easier to hack into)
Clock Speed
The speed at which a processor operates, measured in Hertz (Hz), determines how fast the computer can process instructions
Overclocking
Setting the clock speed of a processor to run faster than its original design, but can lead to increased energy consumption and heat production, potentially damaging the CPU
Under-clocking
Setting the clock speed of a processor lower than its original design to reduce power consumption and heat production, increasing battery life in mobile devices
Motherboard
Where all the components of a PC plug into
Hardware Port
Allows peripherals (mice, keyboards, etc.) to be connected to the motherboard
RISC
RISC ( Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
Can process a limited number of simple instruction, to carry out more complex instruction the problem needs to broke down into a long list of simple instruction.
Able to process simple instructiom quicker
Need less power and produce less heat
CISC
CISC (Complex Instruction Set Computer)
Can process a large number of complex instruction, this allows the processor to understand and carry out complex task with only a few instruction
CISC is able to process complex instruction, without breaking them into simpler instruction
Need more power and produce more heat
What is cache memory
Very fast, volatile memory on the CPU, used to store frequently instructions used and result of calculations
What is parallel processing
When a task is split into sub-tasks and two core or more is working on the task same time
Advantages and Disadvantages of parallel processing
Advantages
Executes multiple sub-tasks simultaneously
Faster than single core
Disadvantages
Programs need to be specially written for it
Some tasks can only be done in a linear manner
What is secondary storage
A non-volatile stoarge, it tends to be quite large but slow compare to RAM
What is the GPU
GPU stand for Graphic Processing Unit, and it is a processor just to make display in the screen
What is a sound card
A small seperate component just to produce high quality sound
What is embeded system
A combination of hardware and software to perform a specific task
What is a optical storage
Storage devices that are read by lasers. E.g: DVD, CD and blueray
What is magnetic storage
Storage devices that store data magnetically. E.g: Hard drive and Tape drive
Describe the 3 types of the buses
1. Address bus. It sends the data’s address that are saved or loaded from the memory. The storage address of data always travels along an address bus.
2. Data bus. The path along which data travelled between serval parts of a computer is called data bus.
3. Control bus. The controller uses the control bus to send control signals to different parts of the computer.
Describe the fetch-decode-excute cycle
1. The fetch cycle takes the address required from memory, stores it in the instruction register, and moves the program counter on one so that it points at the next instruction.
2. The control unit checks the instruction in the instruction register. The instruction is decoded to determine the action that needs to be carried out.
3. The actual actions that happen during the execution cycle depend on the instruction itself.
OR
The PC holds the Address of the next instruction,This address is moved to the MAR, The instruction is copied to the MDR, then to the CIR where it is decoded and executed, finally the PC is incremented by 1
What is Von Neumann
It is the idea of storing a program’s instructions in the same memory as the data. The idea resulted in computers tobe more easily re-programmed and is the basis for the fetch-decode-execute cycle, fundamental to modern computer processing.
What is flash memory
A long-life and non-volatile memory widely used in embedded system. The data stored in flash memory can be read and change
What are the disadvantages of ROM compare to flash memory
In flash memory data can be changed
Rank the speed of cache memory, ROM, RAM and flash memory
Cache memory
RAM
ROM
Flash memory
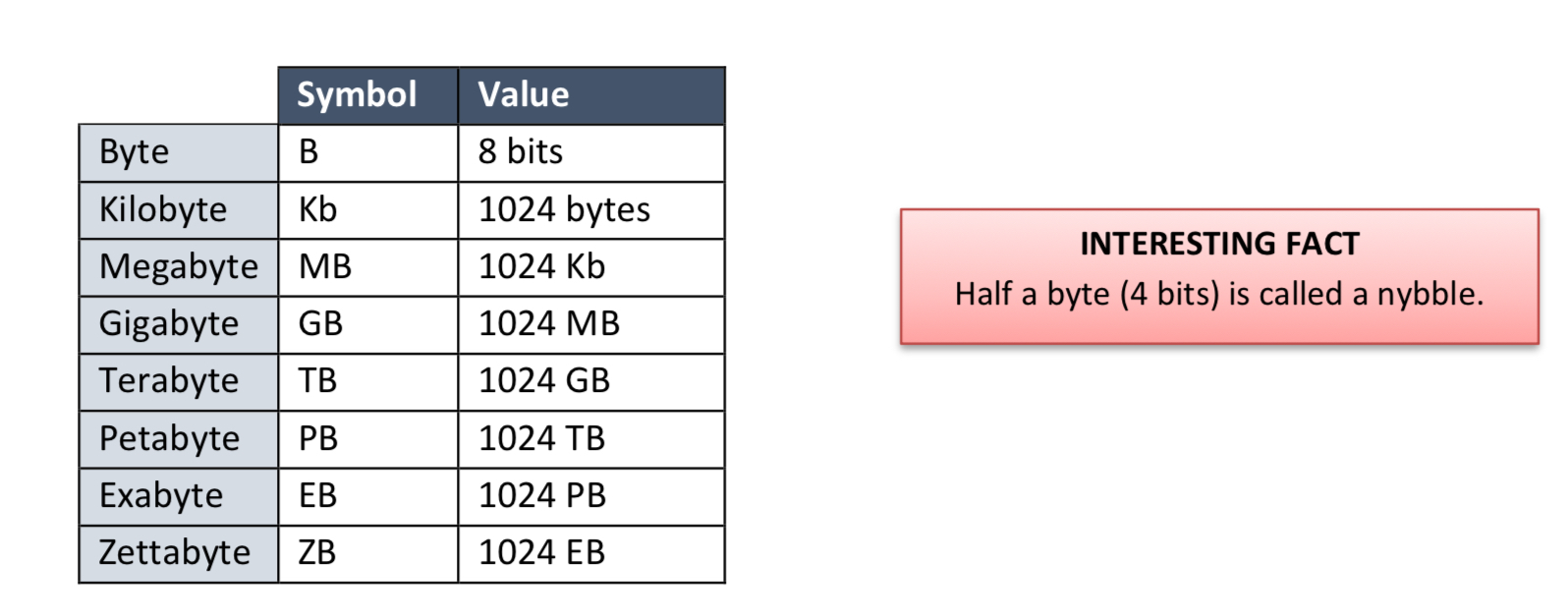
Storage units