Qualitative Analysis of Urine and Kidney Function Tests
1/449
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
450 Terms
What are the main functions of the kidneys as described in qualitative urine analysis?
The kidneys excrete waste products from the body and regulate the chemical composition of body fluids.
What is the basic structural unit of the kidney?
Each kidney contains approximately one million working units called nephrons.
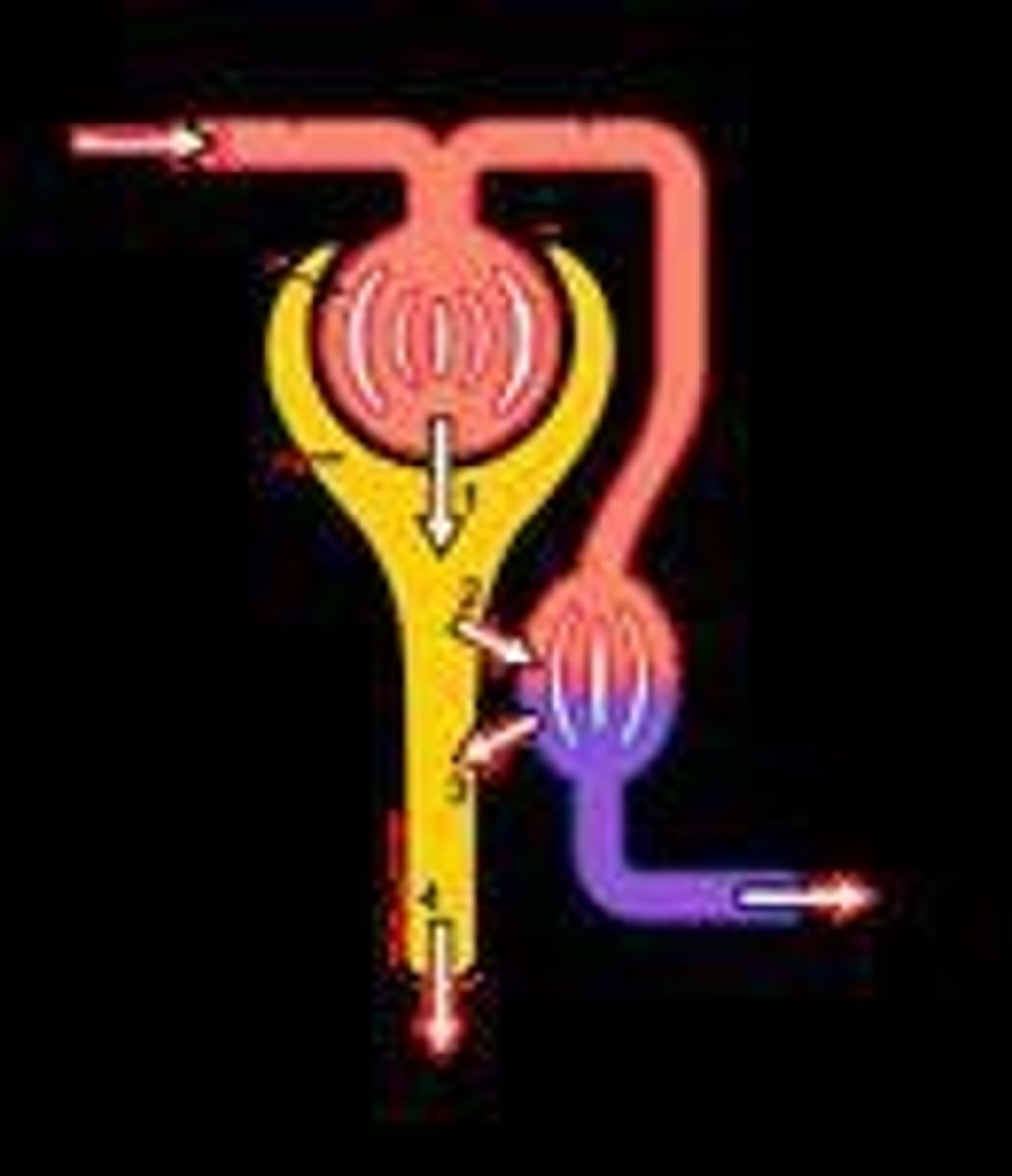
What are the four processes that occur in each nephron?
1) Filtration 2) Reabsorption 3) Secretion 4) Excretion.
What is glomerular filtration?
The process where blood flowing through the capillaries of the glomerulus is filtered, containing most constituents of blood except protein.
What substances are typically reabsorbed during tubular reabsorption?
Water, amino acids, glucose, and electrolytes.
What occurs during tubular secretion?
More solutes are added to the glomerular filtrate from adjoining blood vessels as it passes along the tubule.
What is the composition of normal urine?
Urine is a complex aqueous solution of inorganic salts and waste products, consisting of approximately 96% water and 4% solids.
What are the main inorganic substances found in urine?
Urea, uric acid, creatinine, ammonium salts, and ions such as Na+, Cl-, HCO3-, K+, Ca+2, Mg+2, PO4-3, and SO4-2.
What is urobilinogen and where is it found?
Urobilinogen is a pigment from the hemoglobin of blood found in urine.
What is the significance of routine urinalysis?
Routine urinalysis provides indications of general kidney and liver function.
What is the most suitable urine sample for routine analysis?
The early morning sample collected before breakfast, as it is usually concentrated with an acidic pH.
What factors can affect urine volume excretion?
Water intake, diet, environmental temperature, and activity level.
What are the typical physical tests included in routine urinalysis?
Volume, clarity, color, specific gravity, and pH.
What chemical tests are included in routine urinalysis?
Glucose, protein, ketone bodies, creatinine, uric acid, urea, and bile bodies.
What microscopic tests are performed in routine urinalysis?
Examination of urinary sediments.
What bacteriologic tests are included in routine urinalysis?
Tests to identify the presence of bacteria in urine.
What is the average amount of urine excreted by a healthy adult in 24 hours?
Approximately 122-1500 mL.
Why should fresh urine samples be examined immediately?
To prevent bacteria from increasing glucose and urea decomposition, which can make urine alkaline.
What should be done if a urine sample cannot be analyzed immediately?
It can be refrigerated to preserve its composition.
What role does the enzyme amylase play in urine?
Amylase is a constituent of normal urine, indicating certain metabolic processes.
What is the clinical importance of quantitative estimation of urine constituents?
It helps in assessing kidney and liver function and diagnosing various conditions.
What is increased urine output indicative of?
Increased urine output occurs in dehydration, fever, and any types of kidney damage.
What does the term 'anuria' refer to?
Anuria is the complete absence of urine, occurring in kidney failure and urinary tract obstruction.
What is the normal clarity and color of urine?
Normally, urine is clear and yellowish, although turbidity may occur due to mucus or precipitated salts.
What can abnormal turbidity in urine indicate?
Abnormal turbidity may indicate large quantities of cells (red, white, or epithelial) or the presence of bacteria.
What causes the color of urine in healthy individuals?
The color of urine is due to urochrome pigments and varies from almost colorless to dark yellow, depending on concentration.
What does a yellow foam in urine indicate?
Yellow foam in urine indicates the presence of bile pigments.
What is the normal specific gravity range of urine?
The normal specific gravity of urine ranges between 1.008 and 1.025.
What conditions can lead to increased specific gravity of urine?
Increased specific gravity occurs in chronic nephritis and increased fluid intake.
How can specific gravity of urine be measured?
Specific gravity can be measured using a urinometer or a test strip with mounted chemicals.
What is the normal pH range of urine?
The pH of normal urine varies between 4.5 and 8.0, with an average of 5.5.
What does a pink color on litmus paper indicate when testing urine?
A pink color indicates acidic urine.
What does a blue color on litmus paper indicate when testing urine?
A blue color indicates basic urine.
What are abnormal constituents of urine?
Abnormal constituents include reducing sugar, proteins, ketone bodies, bile salts and pigments, blood, indicant, and pus.
What is glycosuria and when does it occur?
Glycosuria is the presence of sugar in urine, occurring when blood sugar levels exceed 180 mg/dl.
What is lactosuria and when does it occur?
Lactosuria is the presence of lactose in urine, which appears during pregnancy.
What is the principle behind the Benedict's test for sugar?
The Benedict's test is based on the reduction of Cu++ to Cu+ due to the presence of free aldehyde in reducing sugars.
What is the procedure for conducting a Benedict's test?
To conduct a Benedict's test, add 0.5 ml of urine to 2 ml of Benedict's reagent, boil for 5 minutes, then allow to cool.
What does the presence of blood in urine indicate?
The presence of blood in urine may indicate various conditions, including trauma or infection.
What can cause alkaline urine?
Alkaline urine can occur in cases of renal damage (anuria) and in individuals on a vegetarian diet.
What is the significance of urine turbidity in a urinalysis?
Urine turbidity can indicate the presence of abnormal cells or bacteria, which may suggest underlying health issues.
What factors can influence the color of urine?
The color of urine can be influenced by hydration levels, diet, medications, and the presence of certain substances.
What color indicates 0% sugar in a product?
Blue fluid (-ve)
What color indicates 0.1% sugar in a product?
Green opalescence with blue fluid (+ve)
What color indicates 0.2% sugar in a product?
Green opalescence and slight yellow ppt. with blue fluid (++ ve)
What color indicates 0.5% sugar in a product?
Definite orange ppt. with blue fluid (+++ ve)
What color indicates 1% sugar in a product?
Heavy-brown ppt. with blue fluid (++++ ve)
What color indicates 2% sugar in a product?
Red brown ppt. with no blue fluid (++++++ ve)
What is the purpose of clinical tablets in urine analysis?
They contain all reagents involved in Benedict's reaction.
What reaction do clinistix strips utilize to detect glucose?
The glucose oxidase reaction.
What is the first step in preparing Benedict's solution?
Dissolve 1 gm of CuSO4.5H2O in 100 ml water and cool.
What is the second step in preparing Benedict's solution?
Dissolve 173 gm sodium citrate and 100 gm anhydrous sodium carbonate in 600 ml water by heating, cool, and dilute to 850 ml.
What is proteinuria?
The excretion of plasma protein in urine.
What types of proteins are typically found in urine due to renal damage?
Albumin and globulin.
What is Bence-Jones protein and where does it originate?
It is a protein not found in plasma, originating in the bone marrow.
What is the principle of the heat coagulation method for protein detection?
Globular proteins coagulate when heated and become permanently insoluble.
What indicates the presence of albumin or phosphate salt in the heat coagulation test?
A cloudy white ppt. appears in the heated part of the urine.
How can Bence-Jones protein be distinguished in urine?
By heating, cooling, and reheating the urine; the ppt. should vanish on cooling and reappear on reheating.
What is Heller's test used for?
To indicate the presence of protein in urine by forming a white ring at the junction of acid and urine.
What does a white ppt. or cloudiness in the sulphosalicylic acid (S.S.A) test indicate?
The presence of protein in urine.
What is the reagent used in the S.S.A test?
A solution of 20% sulphosalicylic acid.
What are the ketone bodies that can be found in urine?
Acetoacetic acid, β-hydroxybutyric acid, and acetone.
What does the presence of ketone bodies in urine indicate?
Excessive metabolism of body fats.
What conditions may lead to the presence of ketone bodies in urine?
Diabetic acidosis, malnutrition, or after anesthesia and toxemia of pregnancy.
What is Rothera's test used for?
Detection of ketone bodies in urine.
Describe the procedure for Rothera's test.
Saturate 5ml of urine with solid ammonium sulfate, add 2 drops of 2% sodium nitroprusside and 1 mL of NH4OH, then mix and observe for a permanganate color indicating acetone bodies.
What does a purple-red ring in Longe's test indicate?
The presence of ketone bodies.
How is Longe's test performed?
Add 5mL of urine to 5 drops of glacial acetic acid and sodium nitroprusside solution, then slowly add 1 mL of NH4OH, observing for a color change.
What are Acetest and keto stix used for?
Detection of ketone bodies in urine.
What is the significance of creatinine in urine analysis?
Creatinine arises from the breakdown of body tissues and its excretion is a function of glomerular filtration.
What is Jaffe's test used to measure?
The concentration of creatinine in urine.
Describe the principle of Jaffe's test.
Creatinine reacts with picric acid in alkaline solution to produce an orange-red color of creatinine picrate.
What is the procedure for Jaffe's test?
Add 0.5 mL of 10% NaOH to 1 mL of saturated picric acid, divide into two tubes, add 3 mL of urine to one and D.W. to the other, then observe for color intensity.
What are bile salts and where are they formed?
Bile salts are dehydrogenated bile acids formed in the liver.
What conditions can lead to the presence of bile salts in urine?
Bile duct obstruction and liver disease.
What is Hay's test used for?
To detect bile salts in urine.
How is Hay's test conducted?
Add 5 mL of clear urine to one tube and 5 mL of D.W. to another, sprinkle sulfur on the surface, and observe if the sulfur sinks in the urine sample.
What does a red-colored solution in Millius test indicate?
The presence of bile salts.
Describe the procedure for Millius test.
Add 5 mL of clear urine to one tube and 5 mL of D.W. to another, then add 3 drops of 0.1% furfural and 3 mL of concentrated H2SO4 to each, mix, cool, and observe for color change.
What are bile pigments and when can they appear in urine?
Bile pigments such as bilirubin and biliverdin may appear when the liver cannot metabolize heme properly.
What is the principle of Foucht's test?
Bile pigments are absorbed on a precipitate of barium sulfate.
What is the daily excretion rate of creatinine in urine?
About 1.2 grams.
Why is creatinine considered a reliable marker in urine analysis?
Because it is not reabsorbed by the tubules and its level is relatively constant, independent of various factors.
What reagents are used in Jaffe's test?
10% NaOH solution and saturated picric acid solution.
What is the role of sodium nitroprusside in the detection of ketone bodies?
It is used in tests like Rothera's and Longe's tests to indicate the presence of ketone bodies.
What reagent is used to oxidize bilirubin to biliverdin and cholecyanin?
Fouchet's reagent (FeCl3 in trichloroacetic acid solution)
What is the color change observed when bilirubin is treated with Fouchet's reagent?
Bilirubin (yellow) is oxidized to biliverdin (green) and cholecyanin (blue).
What is the first step in the urine analysis procedure involving BaCl2 and H2SO4?
Prepare 2 test tubes, adding 10 mL of clear urine to the first and 10 mL of distilled water to the second.
What precipitate is formed when BaCl2 is added to urine and H2SO4?
A white precipitate of barium sulfate (BaSO4) is formed.
What should be done after mixing the urine and BaCl2 with H2SO4?
Allow to stand until most of the precipitate settles down.
What is the significance of using H2SO4 in the urine analysis?
H2SO4 provides sulfate ions.
What is the purpose of BaCl2 in the urine analysis?
BaCl2 provides barium ions which react with sulfate ions to form BaSO4.
What is the expected result when Fouchet's reagent is added to the precipitate?
A greenish-blue color indicates the presence of bile pigments.
What is the procedure for Rosenbach's test?
Pour 10 mL of urine through filter paper, add a drop of concentrated HNO3, and observe for colored rings.
What indicates the presence of bile pigments in Rosenbach's test?
The formation of colored rings on the filter paper.
What is the normal daily value of urobilinogen in urine?
1-4 mg daily.
What does increased urinary excretion of urobilinogen indicate?
It may indicate liver disease or hemolytic anemia.
What does the absence of urobilinogen in urine suggest?
It may indicate biliary tract obstruction.
What is the principle of the Ehrlich test for urobilinogen?
Urobilinogen reacts with Ehrlich aldehyde reagent to produce a red-colored compound.
What is the first step in the Ehrlich test procedure?
Prepare 2 test tubes with 2.5 mL of urine in one and 2.5 mL of water in the other.