Biology - PLANT MORPHOLOGY AND PHYSIOLOGY
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/66
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
1
New cards
Kingdom Plantae
They are primarily non-motile and live anchored to a substrate.
2
New cards
Dermal, Ground, Vascular
What are the three Plant Tissues?
3
New cards
Dermal Tissues
Forms epidermis, usually one cell layer
4
New cards
Stomata
Pores for gas exchange
5
New cards
Trichomes
Leaf hairs, protect against herbivores and damaging solar radiation
6
New cards
Root hairs
Increase root surface area
7
New cards
Cuticle
A waxy substance that limits water loss, reflects damaging solar radiation, and form a barrier against pathogens
8
New cards
Ground Tissues
The most abundant tissue
9
New cards
Parenchyma
Most abundant, carry out photosynthesis, store protein and starch
10
New cards
Collenchyma
Elongated, thick cell walls, areas of active growth
11
New cards
Sclerenchyma
Thick cell walls reinforced with lignin, programmed cell death, cell walls remain to provide support
12
New cards
Vascular Tissues
Transport System
13
New cards
Xylem
Carries water and minerals from roots to rest of plants, composed of dead cells
14
New cards
Phloem
Composed of living cells, moves carbohydrates from production sites to where they are either used or stored
15
New cards
Leaves, Stems, Roots
What are the PLANT ORGANS?
16
New cards
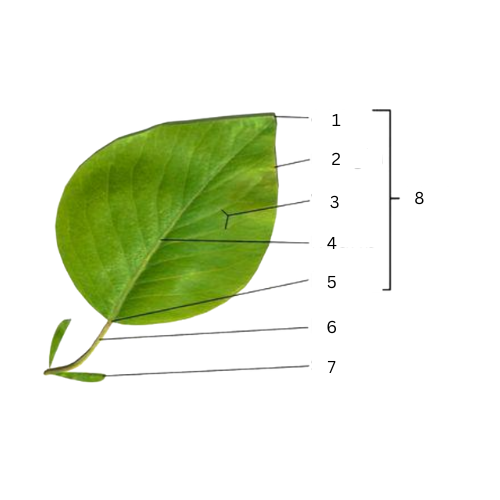
Apex
What is the part of number 1?
17
New cards
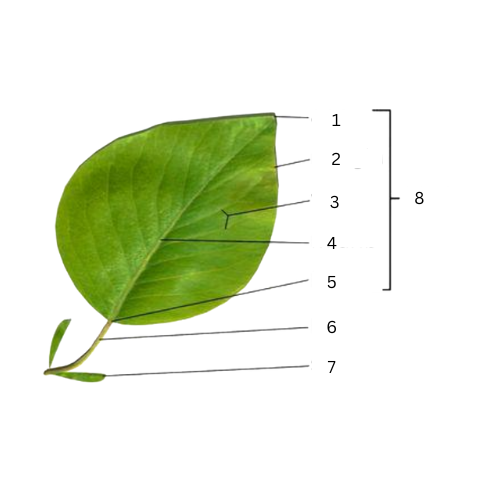
Margins
What is the part of number 2?
18
New cards
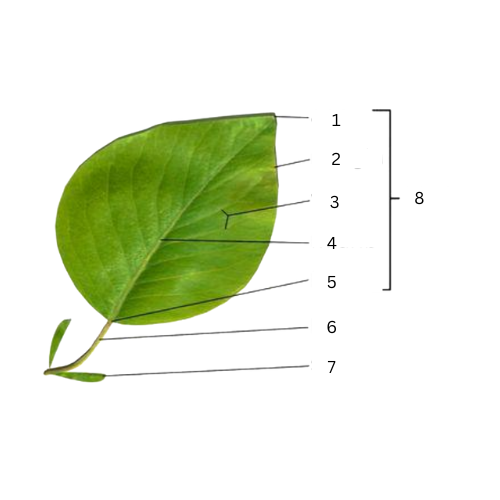
Veins
What is the part of number 3?
19
New cards
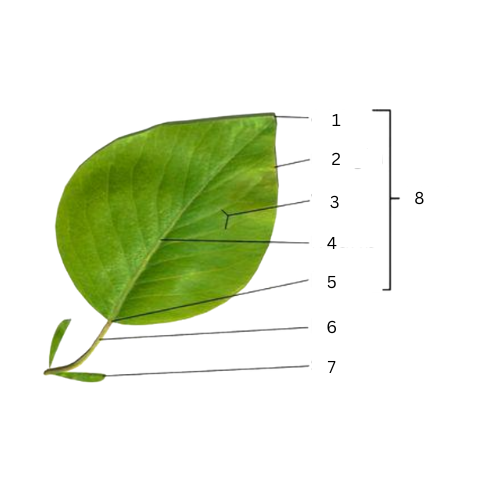
Midrib
What is the part of number 4?
20
New cards
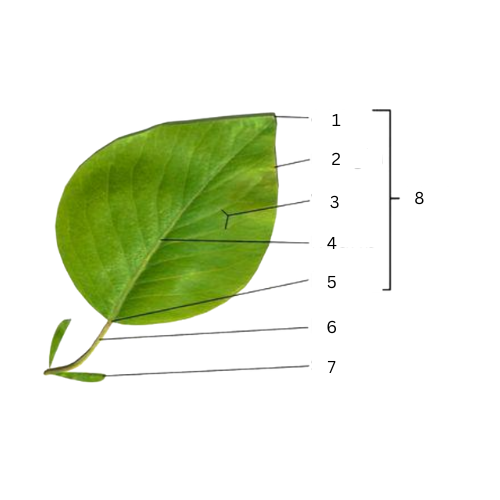
Base
What is the part of number 5?
21
New cards
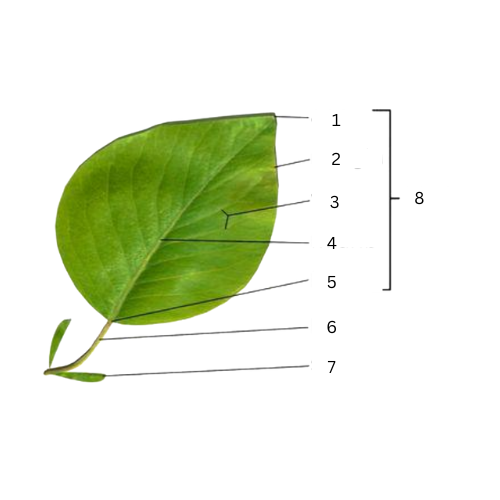
Petiole
What is the part of number 6?
22
New cards
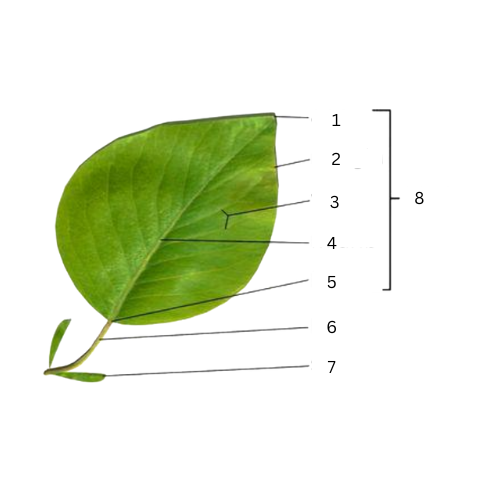
Stipule
What is the part of number 7?
23
New cards
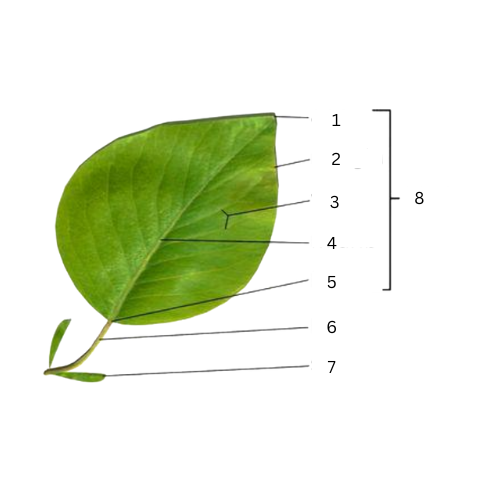
Base
What is the part of number 8?
24
New cards
Spines
In most xerophytes (plants that grow in regions with scarce water), the leaves are reduced to spines but still take the responsibility of doing photosynthesis. The spines help reduce water loss and is also useful in absorbing droplets of water from the fog.
25
New cards
Succulent Leaves
fleshy leaves that that serve as a storage part for water as well as reserve materials. The plants can survive for months without even a single drop of water and may turn brown.
26
New cards
Tendrils
Found in climbers where leaf of plants are modified into elongated structures to help the plants climb efficiently.
27
New cards
Swollen Petioles
Aquatic plants that have bulged petioles filled with air and help the plant float in water.
28
New cards
Reproductive Leaves
Adventitious buds along their leaf margins. These buds develop roots while on the parent plant as they mature, they fall off the plant and start growing into a new plant when they land on nearby soil.
29
New cards
Sheathy Leaf Bases
Found in plants that lack woody stems. The leaf base is expanded into a sheath that is rolled over one another in layers as new leaves grow. The sheathy leaf bases combine to form the pseudostem that’s supports the plant to stand erect
30
New cards
Traps
Plants that grow in nitrogen deficient places have modified their leaves to get this. The leaves may be modified into a pod which is used to attract insects and other tiny animals to fall inside and digest them. The inner walls secrete digestive enzymes that help digest the insects and extract the nitrogen needed for the plant.
31
New cards
Bulbs
Leaves modified as storage organ.
32
New cards
Bud Scales
Tough, overlapping, waterproof leaves that protect buds from frost, desiccation, and pathogens. Bud scales form before the onset of unfavorable growing seasons i.e. winter.
33
New cards
Bract
A modified leaf or scale, typically small, with a flower or flower cluster in its axil. Bracts are sometimes larger and more brightly coloured than the true flower.
34
New cards
Nodes and Internodes
A plant's stem consists of?
35
New cards
Internodes
The space between nodes on a stem.
36
New cards
Apical Buds or Terminal Buds
Occur at the end, or apex, of stems.
37
New cards
Axillary Buds
Occur at a leaf node, which is where a leaf emerges from the stem of a stem
38
New cards
Lenticels
Helps in the gaseous exchange between the atmosphere and the internal tissue of the stem.
39
New cards
Lenticels
helps in allowing the oxygen into and carbon dioxide out.
40
New cards
Lenticular Transpiration
The lenticels also helps in transpiration called as the __________.
41
New cards
Closes
The lenticular transpiration occurs when the stomata ______.
42
New cards
Rhizome
They are also called creeping rootstalk, horizontal underground plant stems capable of producing the shoot and root systems of a new plant.
43
New cards
Corm
Stem that grows in vertical direction.It is spherical in shape with a flattened base. It has distinct nodes and internodes.
44
New cards
Tubers
Enlarged structures in some plant species used as storage organs for nutrients
45
New cards
Runner/Stolon
Runs horizontally on the surface of the soil. It break off and grow into an independent plant giving rise to vegetative propagation.
46
New cards
Sucker
It moves horizontally under the soil for a distance and then grows obliquely upwards.
47
New cards
Offset
It is found in aquatic plants, it has lateral branch with short internode and each node bearing a rosette of leaves and a tuft of roots.
48
New cards
Thorn
They are straight, pointed, hard or woody structures.
49
New cards
Roots
Anchor a vascular plant to the soil, absorb minerals and water, and often store carbohydrates
50
New cards
Root system
Subterranean or underground part of the plant.
51
New cards
Shoot
Aboveground part of the plant.
52
New cards
Geotropism
The cause why roots are growing downward.
53
New cards
Taproot and Fibrous root
What are the two types of roots?
54
New cards
Buttress
Aerial extensions of lateral surface roots and form only in certain species. It stabilizes the tree, especially in shallow saturated soils.
55
New cards
Prop roots
A modified roots that arise from the stem of certain plants and provide extra support.
56
New cards
Pneumatophores
An aerial root specialized for gaseous exchange.
57
New cards
Aerial/Strangling roots
Extend to the ground, supporting the growing plant, which eventually strangles the host tree.
58
New cards
Storage roots
It becomes enlarged and swollen due to the storage of food.
59
New cards
Fruit
The fleshy or dry ripened ovary of a flowering plant, enclosing the seed or seeds.
60
New cards
Exocarp
The outermost layer of the pericarp
61
New cards
Mesocarp
The middle layer of a fruit, the usually fleshy plump part
62
New cards
Endocarp
The inner region of the pericarp and can consist of layers of different textures or consistency that surround and protect the seed
63
New cards
Drupe
A type of fleshy fruit containing a large seed
64
New cards
Berries
A fleshy fruit formed from the ovary of one flower with a seed or seeds embedded in the flesh.
65
New cards
Pomes
Fruits that have a fleshy area surrounding a core containing seeds.
66
New cards
Hesperidia
Fruits have a thick tangy rind and sectioned pulp inside.
67
New cards
Pepo
Fruits have multiple seeds throughout the flesh or grouped together in the center.