memory psychology
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
memory
the process of storing and retrieving information from the brain
Encoding
turning sensory information into a form that can be used and stored by the brain
output
the stored information we retrieve
sensory memory/register
shortest store of memory,
sensory information from the environment input which we pay attention to(before STM) .
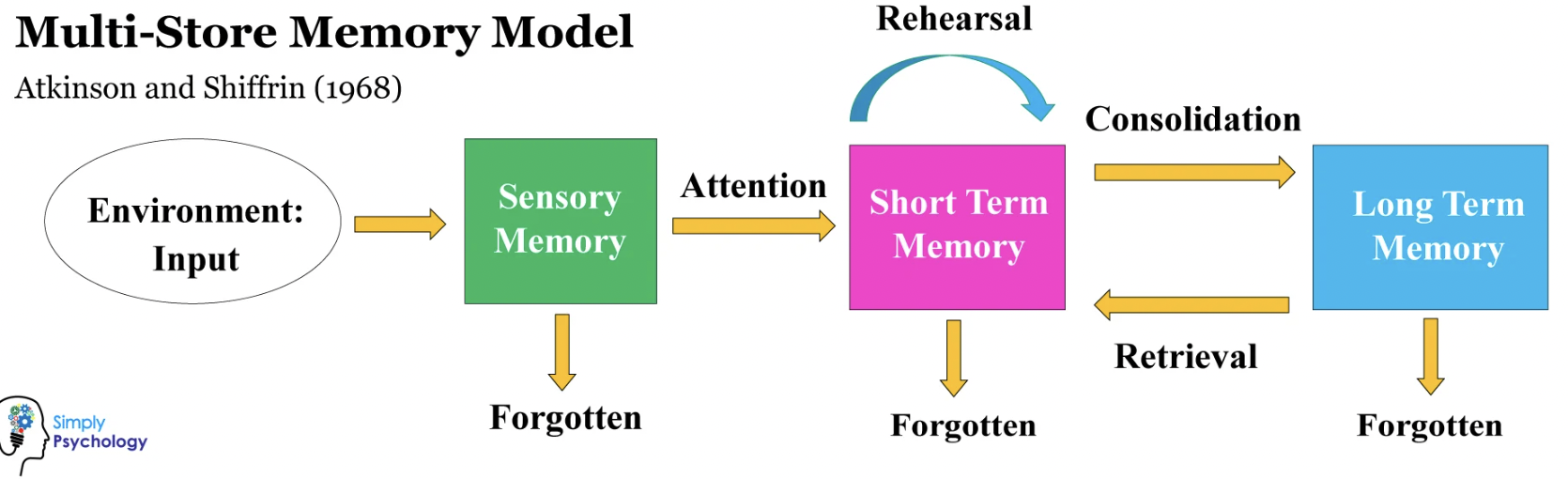
Multistore model of memory
Model proposed by Atkinson and Shiffrin
shows how memory works in terms of 3 stores
describes how information is transferred from one memory to another
how it is remembered and forgotten.
Forgetting
inability to access encoded memories
Decay
memory fades due to the passage of time and lack of rehersal
STM (capacity,duration,encoding forgetting)
capacity - 7 (+/- 2)
duration - 18-30s
encoding - acoustic(sound)
forgetting - Displacement(when STM is full and older info is pushed out) Decay-fading of the memory.
LTM (capacity,duration,encoding forgetting)
Capacitiy - limitless
duration - infinite
encoding - semantic
forgetting - Decay, Retrieval failure, Interference(overwritten by new info(distracting))
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to store long term memories.
Ability to transfer from short to long term memory damaged.
Caused by brain injury.
Patient will remember their long term memories from before the accident.
Retrograde Amnesia
Cannot remember information from before the injury.
case study HM
had both anterograde and retrograde amnesia. Had brain sugery but didnt help he could only remember childhood memories
Iconic vs Echoic memory
Iconic - sensory register for visual info. Lasts 0.5s
Echoic - sensory register for auditory info. Lasts 2s.
others: gustatory,olfactory,tactile
STM → LTM according to multistore model
Atkins and Shiffrin - the more information is rehearsed the better it is remembered. (maintenance rehearsal)
Chunking
Miller noted that people can recall 5 words as well as 5 letters.
Grouping sets or letters into units or chunks
Peterson and Peterson Aim
to test the true duration of memory
Peterson and Peterson (1959) Procedure
24 psychology undergraduates
each student did 8 trials
Each participant was given a trigram
student was then asked to count backwards in 3’s until told to stop (prevents rehersal
told to stop at a different time each trial. (3s,6s,9s,15s,18s)(retention intervals)
When red light came on student had to recall trigram 8 times.
Second experiment : the same but some had time to rehearse before starting to count backwards
Peterson and Peterson (1959) Results + Conclusion
on average
3s : 90% correct
9s : 20% correct
18s : 2% correct
STM has a short duration of 18s if rehearsal is prevented
Peterson and Peterson (1959) Strengths
Used fixed timings for participants to count back from. -reliabilty
Eliminated other factors that might have affected memory. e.g noise - increased validity
good control - standardised procedure to make sure all participants experienced the same thing, scientific, can be repeated.
Peterson and Peterson (1959) Weaknesses
Lacks mundane realism - not something we experience everyday
Demand characteristics - used psychology students who knew about memory and altered their behaviour to help the experimenter. - decrease validity
How do Schemas affect memory (study)
Bartlet found that people recall information differently as they are influenced by their schemas.
Omission definition Bartlet theory
When we leave out unfamiliar, unpleasant or irrelevant details when remembering something.
transformation Bartlet theory
when details are changed to make them more familiar and rational
familiarization Bartlet theory
When unfamiliar details are changed to align with our own schema
Rationalisation bartlet theory
when we add details into our recall to give a reason for something that may not have originally fitted in with our schema
Bartletts theory strengths
Practical real-life applications - help us understand how memories become distorted
Several pictures + real life stories - ecological validity
Police use an interviewing technique - cognitive interview- encourages eye witnesses to avoid omissions and transformations
Bartletts theory weaknesses
Was not scientific in his procedures as he was interested in participants unique experience
Bartlett analysed the results himself and therefore might be biased. ( shows only his interpretation)
Bartlett war of ghosts 1932 aim
to test if personal schemas influence the retelling of a story
Bartlett war of ghosts procedure
20pp
read the story war of ghosts twice
then had to recall the story using serial reproduction where participants retell the story to each other to form a chain(15-30min later)
and repeated reproduction where participants retell a story over and over again(after 15min,days,hours,months,years)
bartlett war of ghosts results + conclusion
using qualitative analysis
for both types of recall: PP were found making changes and connections(rationalisation) and omissions.
Conclusion: participants did not recall accurately and were influenced by schemas however recalled the overal meaning.
strengths of Bartlett war of ghosts
validity- remembering a story is a everyday task: higher ecological validity.
Reliability: study was replicated and the same results were found using various studies
Validity: results were gathered using qualitative analysis. accurate
weaknesses of Bartlett war of ghosts
Validity: story was unfamiliar,illogical and contained strange words, PP changed answers because task was difficult not because they were affected by schemas. Not accurate.
Validity- using qualitative data- unscientific because Bartlett may have been biased towards his theory.
Reliability- participants read story at own pace and recalled after different timed intervals- unscientific-people who took longer to read may have performed better as they had longer to remember it
Modality free
not linked to a specific type of sensory information
Primacy
the tendency to recall words at the beginning of a list when asked to remember it
Recency
the tendency to recall words at the end of a list when asked to remember it.
Processing
the operations we perform on sensory information in the brain
storage
the retention of information in our memory system
Input
for human memory, this refer to the sensory information we recieve from our environment.
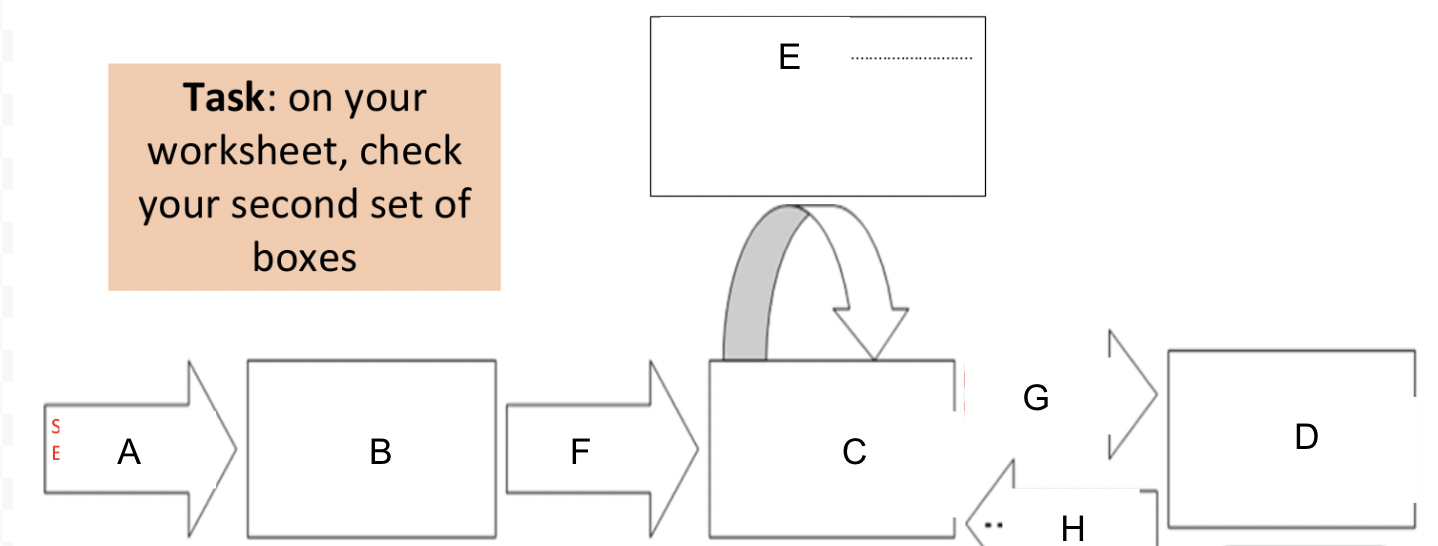
label
A- stimulus from environment
B-Sensory register
C-Short term memory
D-Long term memory
E-Maintanance rehersal
F-Attention
G-maintanance rehersal/consolidation
H-retrival
strengths of multi store model
there is a lot of evidence to support the theory of separate memory stores as some cases of amnesia show that long term memory becomes damadged by a brain injury however short term memory stays intact.
weaknesses of multi store model
overstates the role of rehersal as if we attach meaning to a peice of information we are more likely to remember it.
It is Unlikely that we only have one LTM as some amnesia patients demonstrate that while some long term memories are damadges some stay intact.
Reductionism + Reductionist
Reductionism- A scientific theory of describing something using its simplest/single explanation
Reductionist- the practice of reductionism
Strengths and weaknesses of reduction
strength: scientific- can be appropriate in circumstances where there is a clear single explanation.
weakness: oversimplistic, can misss other social factors that could contribute to behaviour
Holism + Holistic
Holistic- Refers to any approach or study that looks at the whole picture/ individual rather than breaking it down into components.
Holism- the practice of holism
Strength + weakness of Holism
strength - uses qualitative data- gain greater insight into causes of behaviour and try to understand the person as a whole and their beliefs.
weakness - difficult to achieve - investigating a lot of variables at the same time. Unscientific - can only apply to particular individual-cannot be generalised