Ocular Embryology
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
gastrulation
process by which a ball of cells rearranges to form 3 germ layers
blastula
ball of cells that goes through gastrulation
endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm
what are the 3 germ layers formed in gastrulation?
ectoderm
outer germ layer; becomes skin, hair, mammary glands, and nervous system
mesoderm
middle germ layer; becomes skeletal muscle, bones, connective tissue, and heart
endoderm
inner germ layer; becomes digestive tract, lungs, thyroid
primitive streak
what initiates gastrulation?
neural plate
thickening of the ectoderm near the cranial pole forms the _________
neurulation
process by which the presence of notochord induces surface ectoderm to form the neural tube
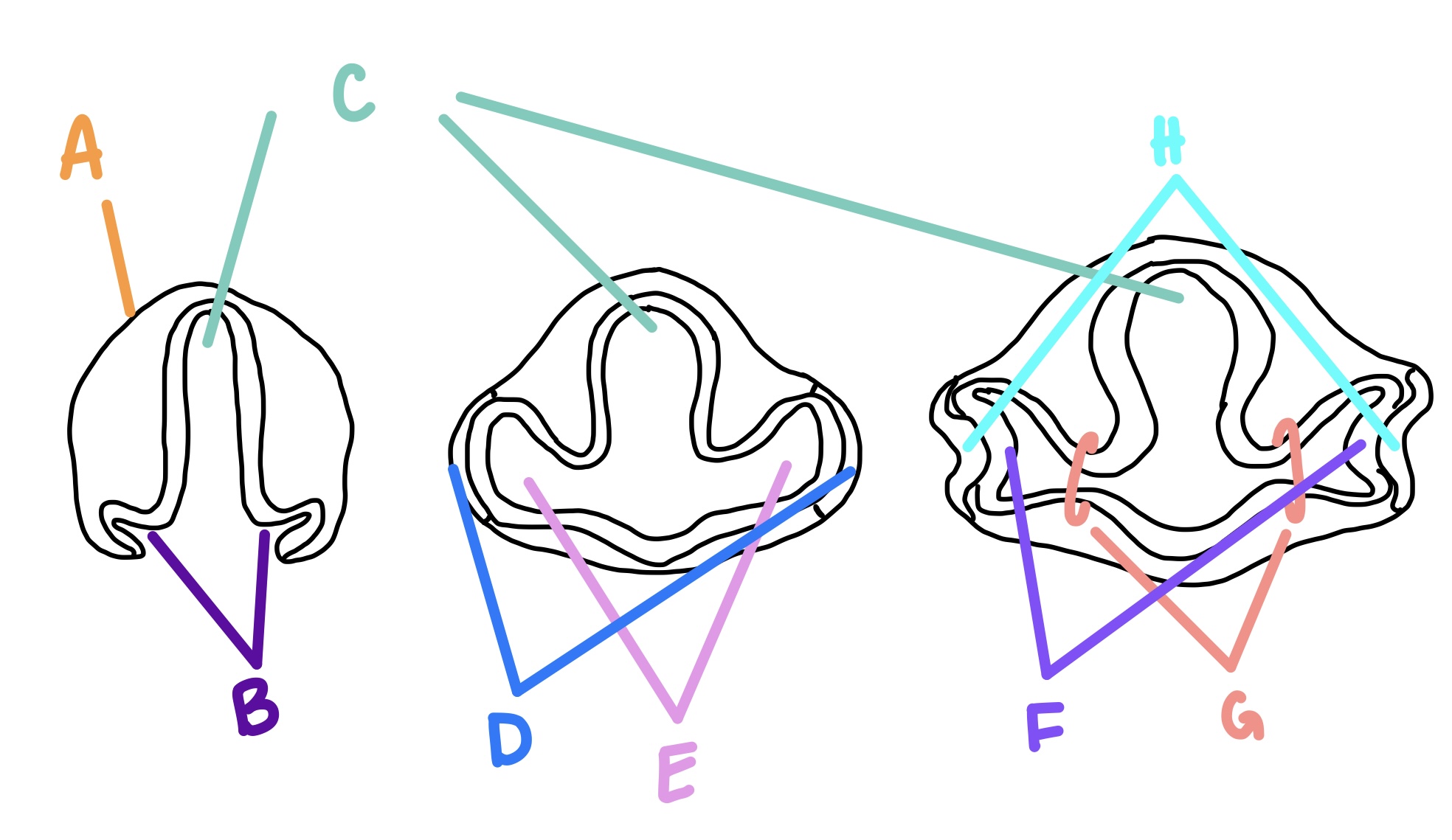
optic vesicles
optic grooves form what?
E
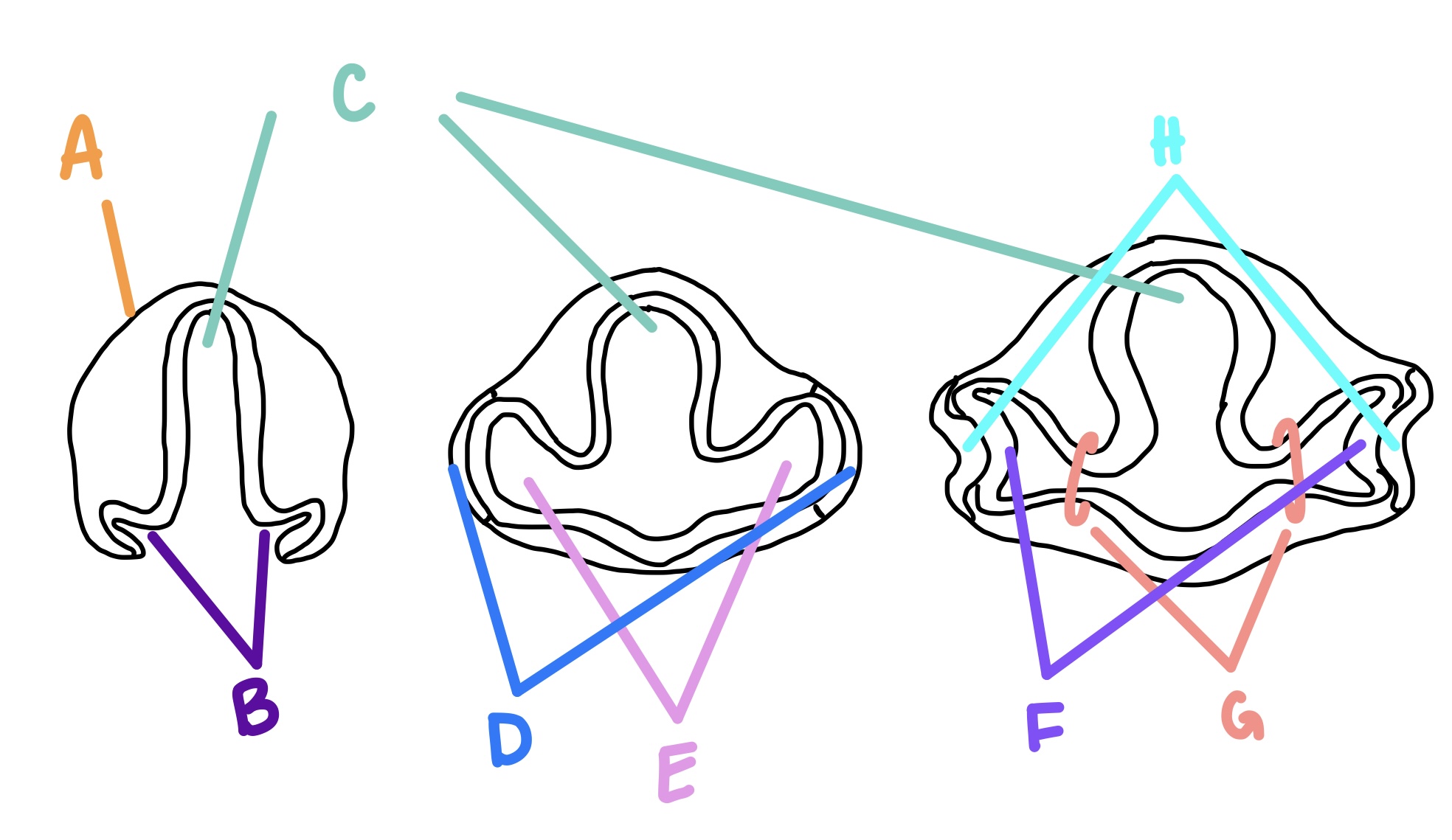
optic cups
optic vesicles form what?
holoprosencephaly
spectrum of major developmental defects of the brain in which the embryonic forebrain fails to divide into right and left hemispheres, giving rise to midfacial developmental defects
cyclopia
single eye globe with varying degrees of doubling of intrinsic ocular structures and nasal agenesis with a proboscis above the midline eye
optic cup
formed by optic vesicle invaginating to form this; bilayered, hemispherical, formed at day 27
F
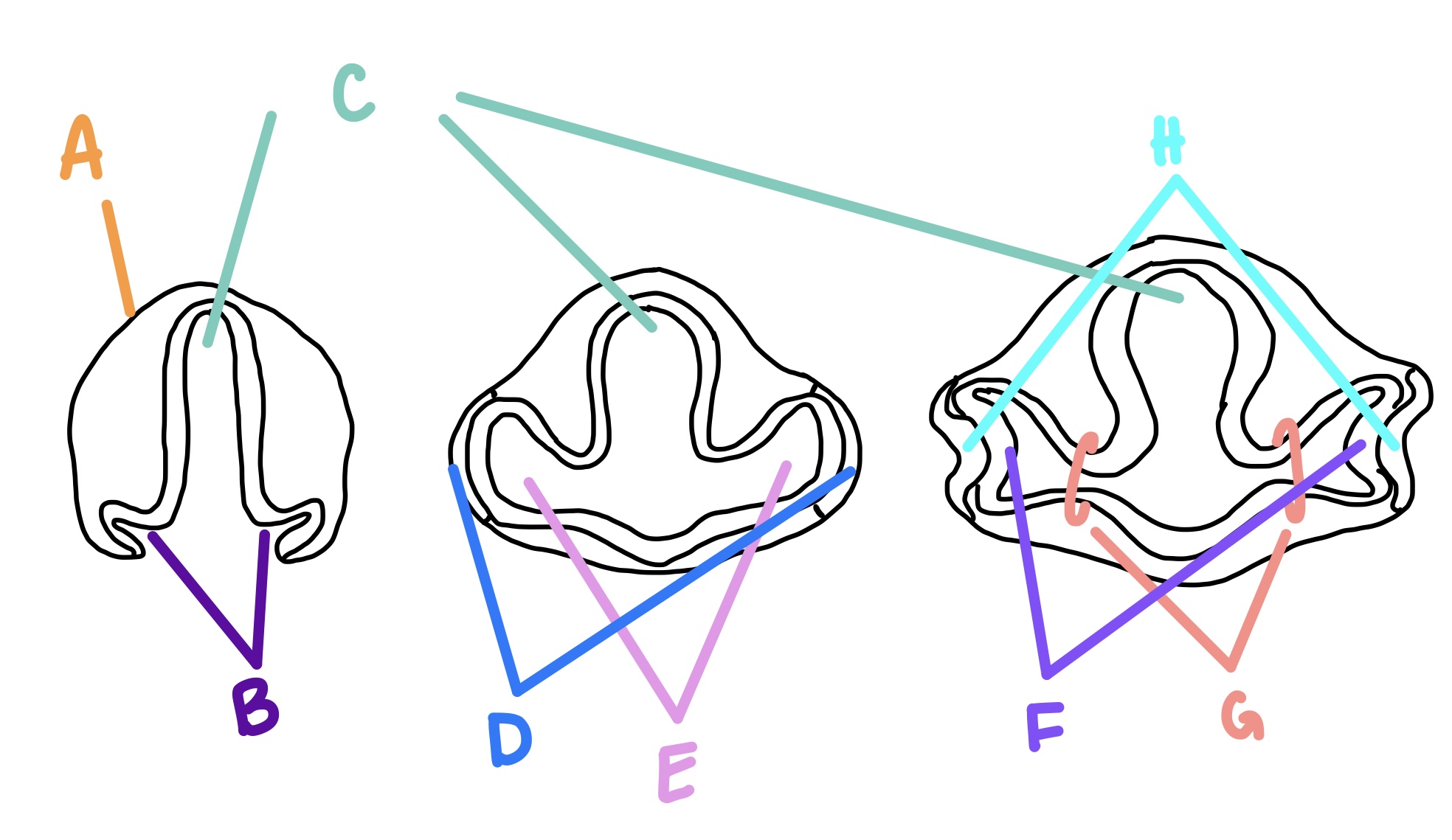
surface ectoderm
what are the lens vesicle and lens pit formed from?
A
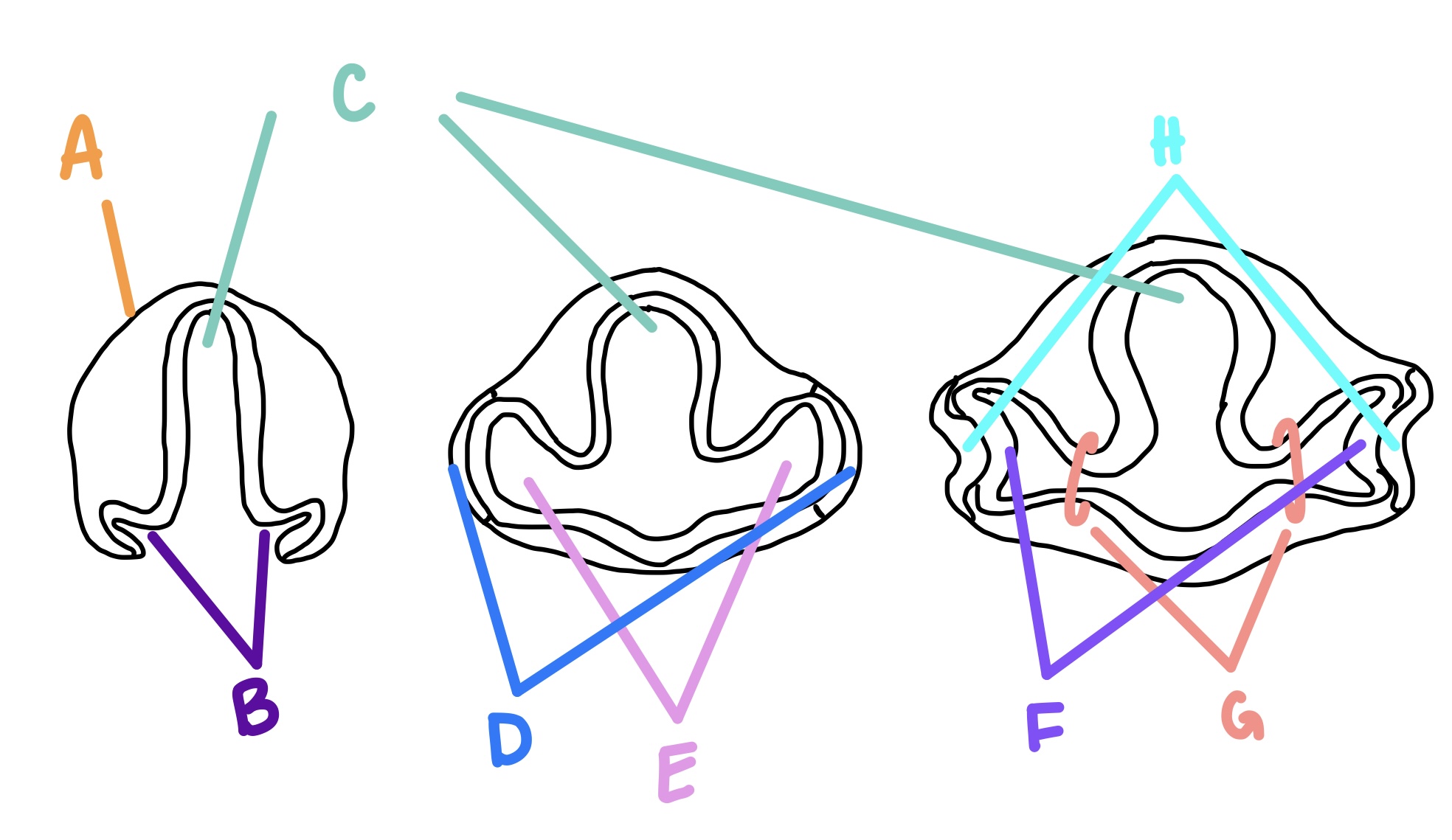
RPE
what does the outer layer of the optic cup become?
retina
what does the inner layer of the optic cup become?
corneal epithelium
what does the resealed surface ectoderm become once the lens is detached?
anterior myoepithelium, pigmented ciliary epithelium, RPE
the outer layer of the optic cub becomes the _______________ in the iris, the ______________ in the ciliary body, and the ___________ in the retina
posterior pigmented epithelium, nonpigmented ciliary epithelium, neurosensory retina
the inner layer of the optic cup becomes _______________ in the iris, the ______________ in the ciliary body, and the ___________ in the retina
hyaloid vascular system
transient set of arterial and venous vessels
week 8
when does the choroid/optic/hyaloid fissure close?
optic stalk
axons of ganglion cells accumulate in the _____ and form the optic nerve
coloboma
incomplete closure of the optic fissure may affect the developing optic cup or stalk or the adult derivatives; pars plana doesn’t fuse in ciliary body due to abnormal choroidal fissure closure
lens, corneal epithelium
what are the 2 key structures formed by the surface ectoderm?
lens pit
what does the lens placode form?
lens placode
formed by thickening of surface ectoderm close to the vesicle
D
PAX6
gene that directs development of lens placode
cataracts, coloboma
what are 2 congenital abnormalities in the lens?
lenticonus
lens capsule abnormality, can be anterior or posterior, lens takes on a more cone shape
neural ectoderm
what do the sphincter and dilator muscles originate from?
by birth
when are the sphincter and dilator muscles completely developed?
iris cysts
sometimes formed in region of the former marginal sinus following treatment with miotics such as Pilocarpine, arise in same tissue plane as marginal sinus
cystic elevation
congenital malformation of peripheral iris, arises due to defective migration of neural crest cells
aniridia
optic cup does not migrate over anterior surface of the lens and iris does not form
neuroblasts, marginal zone
inner layer of optic cup is divided into these 2 layers
marginal zone
layer of optic cup that is initially anucleate
inner neuroblast zone
the marginal zone becomes the _________
outer neuroblast zone
the neuroblast layer becomes the _________
transient fiber layer of chievitz
nuclear-free zone that is b/t the inner and outer layers of the inner optic cup; not permanent
ganglion, amacrine, Muller
what cells does the inner neuroblastic layer form?
photoreceptor, horizontal, bipolar
what cells does the outer neuroblastic layer form?
ganglion cells
what are the earliest retinal cells formed?
rods, bipolar, Muller
what are the retinal cells that are formed later on in development?
8
by week __ ganglion cells, amacrine cells, and muller cells develop from the inner neuroblastic layer
12
by week __ photoreceptors align along the outside of the inner layer of the optic cup, ganglion cell layer is evident
cones
which photoreceptor develops first?
20
by week __ ganglion cell layer is well established and reduction in retinal cells by apoptosis begins
24
by week __, no mitosis occurs but retinal growth continues by cell differentiation, growth, and maturation
displacement of inner retinal components to form depression
what is the first stage of fovea development
migration of photoreceptors toward the center which increases cone packing
what is the second stage of fovea development?
maturation of photoreceptors
what is the third stage of fovea development?
post birth
when does fovea development finish?
foveola
what is the retinal region last to reach maturity?
area, volume
the RPE increases in ____ but not _____ over time
RPE
what is the first tissue in the body to form melanosome pigment?
neuroectoderm & surface ectoderm
what does the vitreous develop from?
lens capsule
substrate on which incipient hyaloid arterial system grows to transiently nourish the lens through the active phase of growth
10
at ___ weeks, lens has completed major development and hyaloid vasculature begins to regress
primary vitreous
formation is related to the development of the hyaloid vasculature that enters the developing eye through the fetal fissure
begins to form thin fibrils that originally connected lens vesicles with inner surface of optic cup
syncytium through which mesodermal cells condense to form the endothelial linings of the hyaloid vasculature
cloquet canal
funnel shaped structure that encompasses primary vitreous within the region of atrophying hyaloid canal
tertiary vitreous
zonule fibers that develop b/t lens equator and ciliary body
hyaloid artery
terminal branch of dorsal ophthalmic artery
forms transient embryonic vascular bed to support the rapid growth of the lens and optic cup until adult ocular vasculature is established
peak development around week 12 and atrophy begins around week 12
Bergmeister papilla
glial tissue that persists on the nerve head
Mittendorf dot
pin-point remnant of the hyaloid artery on the posterior surface of the lens
persistent hyaloid artery
remnant of hyaloid artery
epicapsular stars
remnants of primary vitreous; seen as small, brown stellate opacities on the anterior surface of the lens
Coat’s disease
congenital peripheral retinal telangiectasis in which abnormally dilated vessels in the retinal periphery leak serum leading to exudative retinal detachment; almost always unilateral
von-Lindau disease
characterized by formation of hemangioblastomas in the retina, CNS, and other organs
retinopathy of prematurity
vessels are tortuous and do not reach temporal retinal periphery forming an ischemic elevated ridge of vascular shunts that secrete pro-angiogenic factors that can contribute to neovascularization and progression of the disease
neural crest
_______ cells give rise to the corneal endothelium, corneal stroma, trabecular meshwork, choroid, orbital fat and CT and extra orbital muscles
unknown
what is Schlemm’s canal derived from?
Axenfeld-Rieger’s syndrome
causes abnormal formation of angle structures and iris, commonly associated with glaucoma
Peter’s anomaly
very severe dysgenesis of angle, iris, and cornea, usually results from delayed or incomplete separation of lens vesicle from surface, leaving a central corneal opacity due to defect in continuity of Descemet’s membrane and corneal endothelium
neural crest mesenchyme
what does the sclera develop from?
surface ectoderm
what do the eyelids originate from?
fuse
eyelids _____ by week 10
re-open
eyelids _______ around week 26
ablepharon/cryptophthalmos
failure of lids to properly form; absence of palpebral fissure and failure of differentiation of eyelid structures
ankyloblepharon
failure of the eyelids to completely separate and otherwise normal formation of the globe and lids
congenital ptosis
autosomal dominant, surgically correctable, disturbed development of the levator palpebrae superiosis and/or its oculomotor innervation
far apart, closer
orbit bones start _____ and move ______
incomplete canalization of nasolacrimal duct
failure to open the nasolacrimal system prior to postpartum onset of tearing initially results in spilling of tears over the lid margin; often monocular in infants
dacryocystitis
open punctum, but valve of Hasner has not yet perforated, causes in stagnant tears resulting in infection
PAX6
what is the master regulator of eye development?
forebrain
C
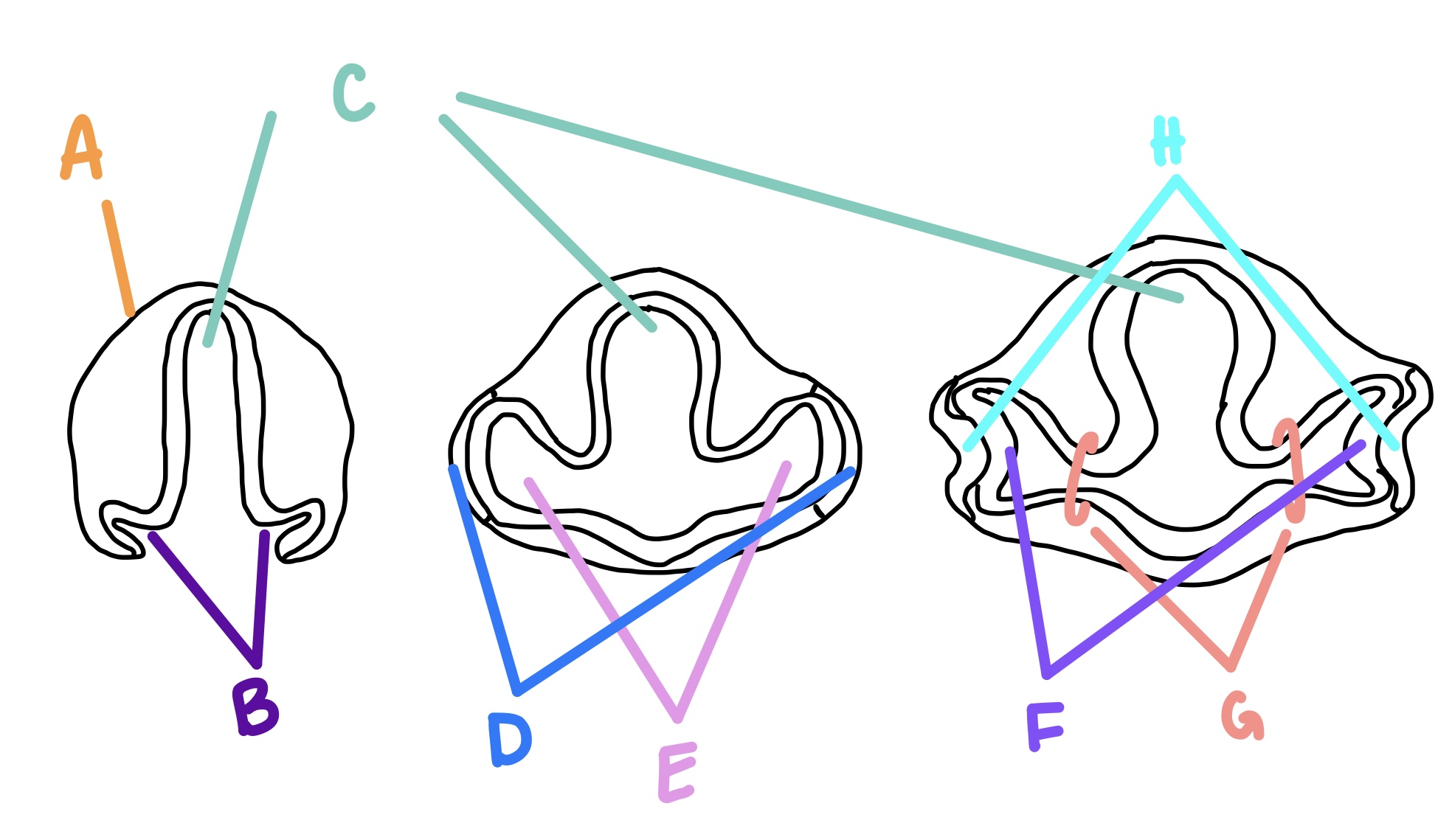
optic grooves
B
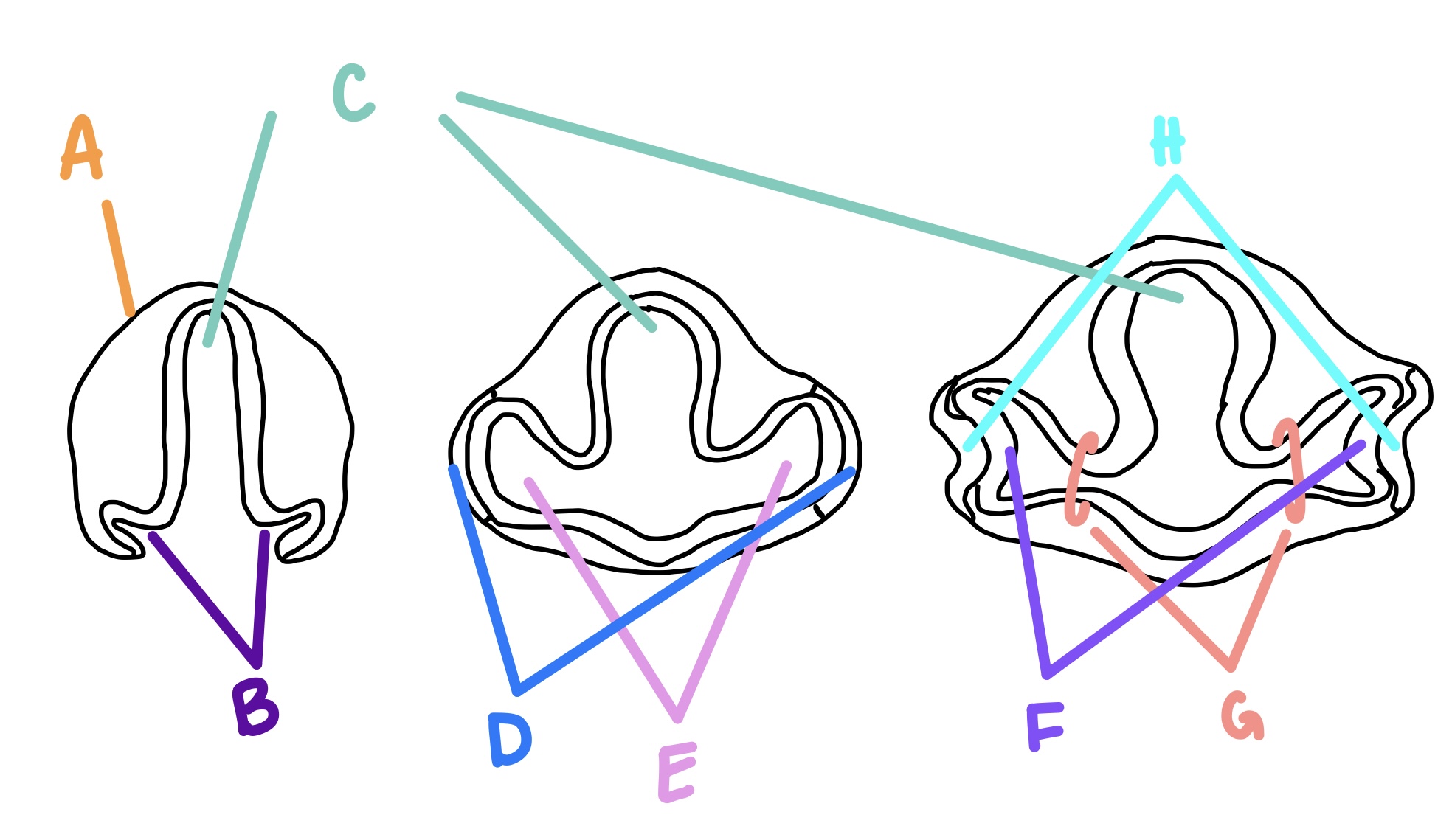
optic vesicle
E
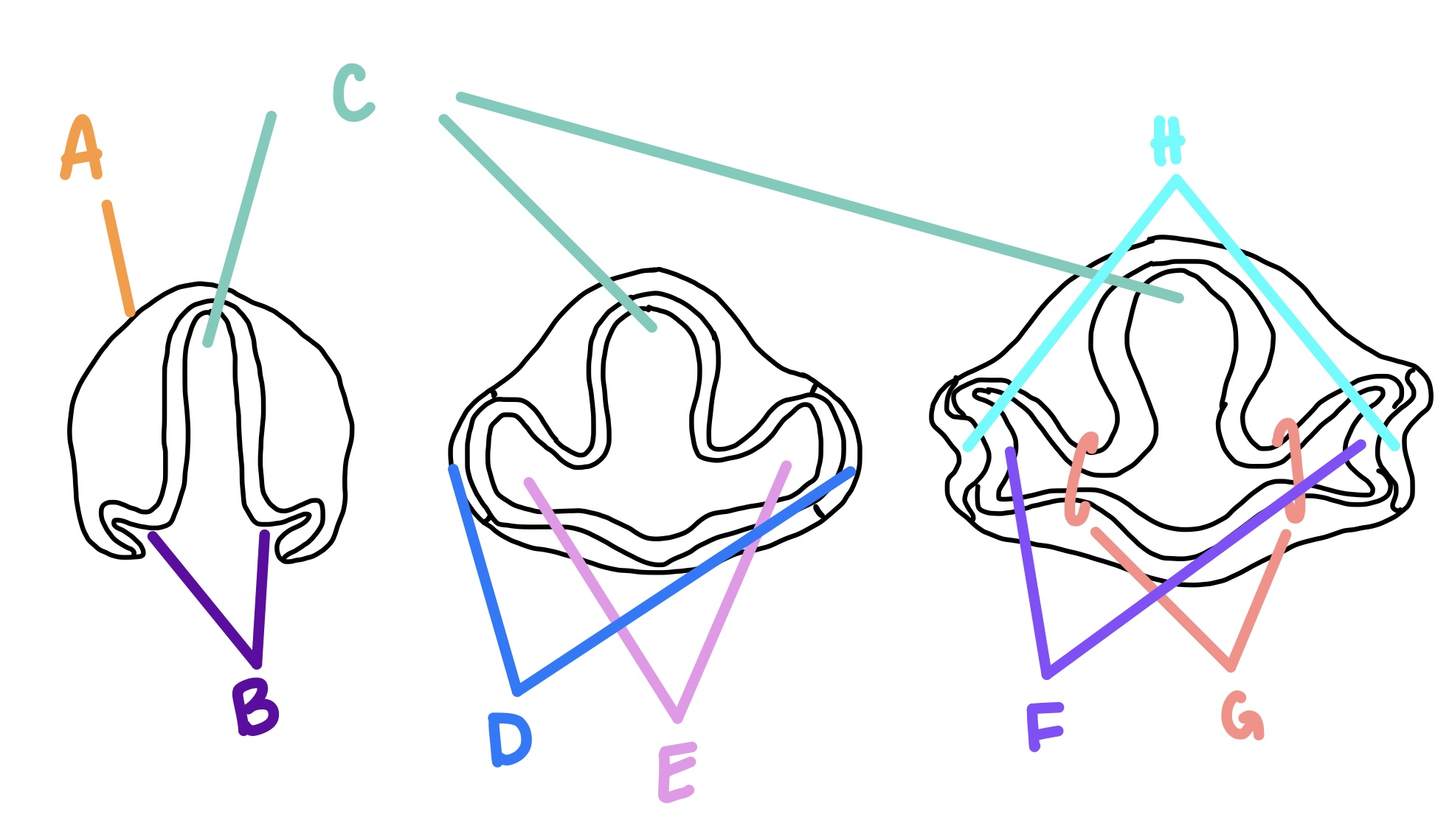
optic stalk
G
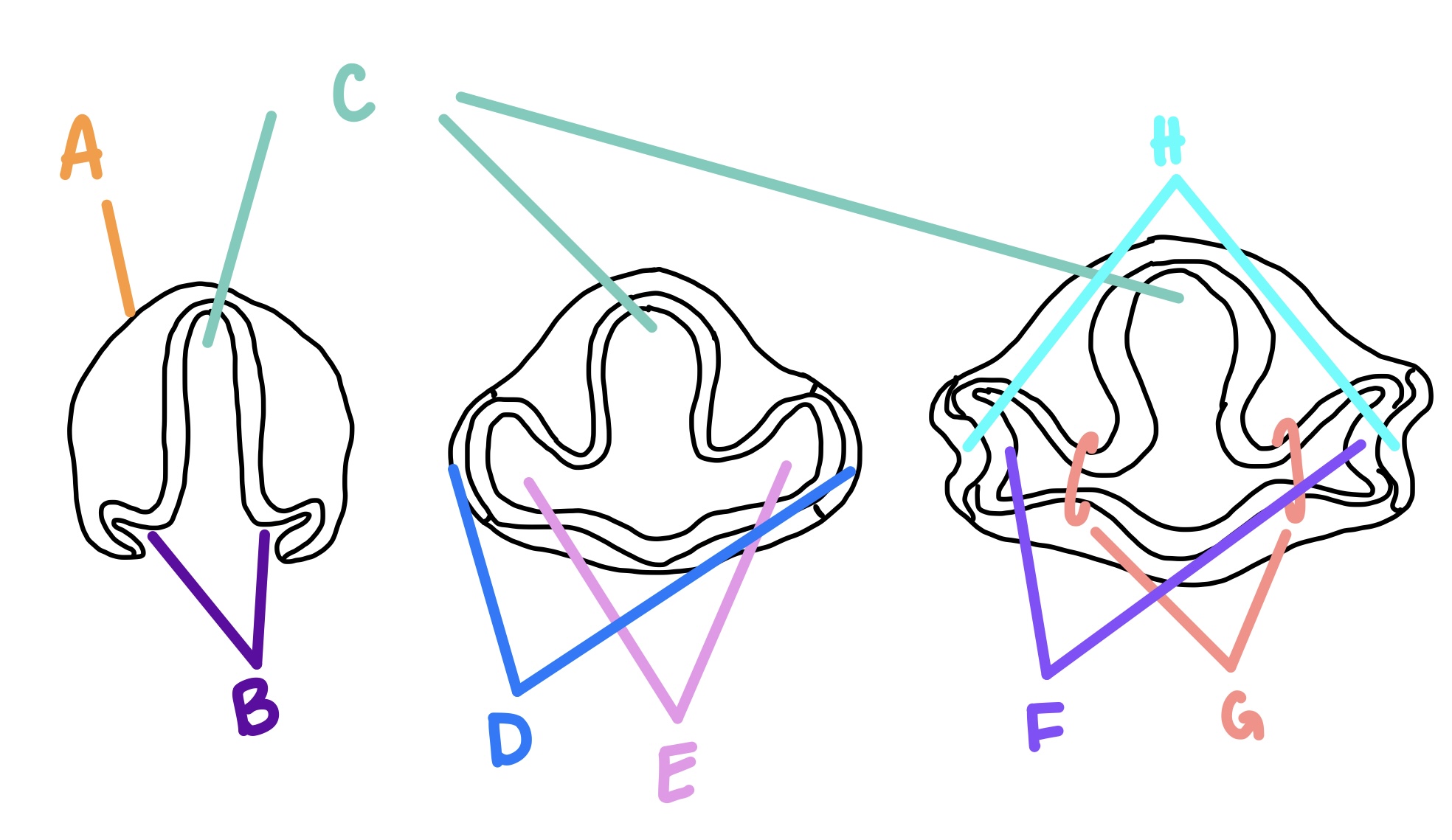
lens vesicle
what does the lens pit become?