AP Psych: Biological Bases of Behavior
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Dendrite
receive messages from other cells
Axon
passes messages away from cell body
Neural Impulse
the electrical signal traveling down the axon; action potential
Cell Body
cells life support center
Myelin Sheath
covers the axon and helps speed up neural impulses
Terminal branches
form junctions with other cells
Glial cells
support, nourish and protect neurons
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that travel across the synapse and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron
Synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the reciving neuron
Reuptake
when the neurotransmitter is reabsorbed by the sending neuron
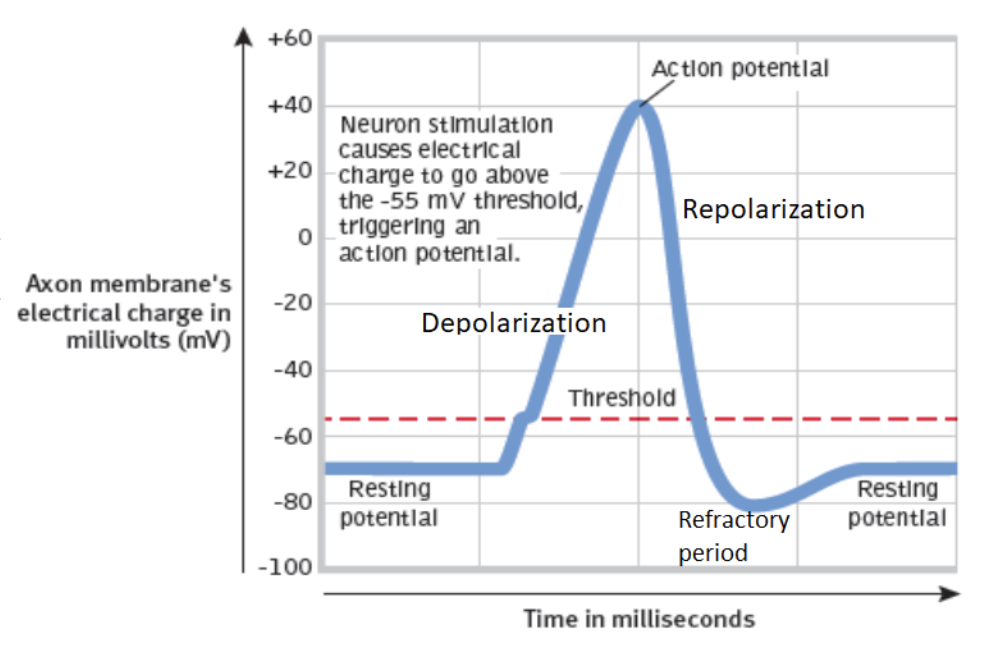
Threshold
the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Resting state of neuron
the outside is positively charged and the inside is negatively charged
Excitatory signal
neurotransmitters that trigger action
Inhibitory signal
neurotransmitters that signal a depress action
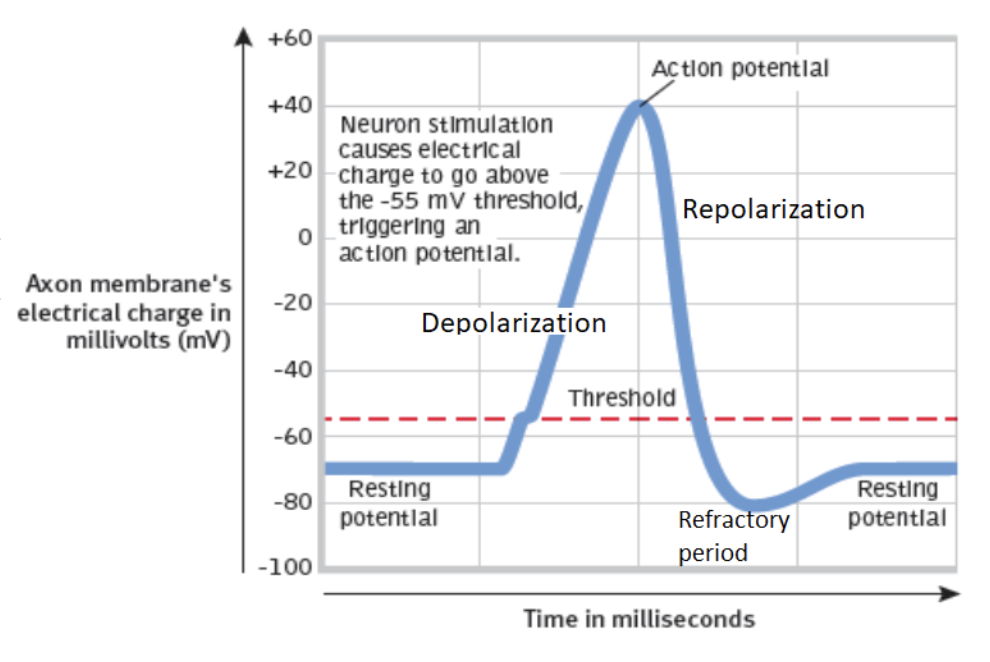
Polarization
resting state of the neuron
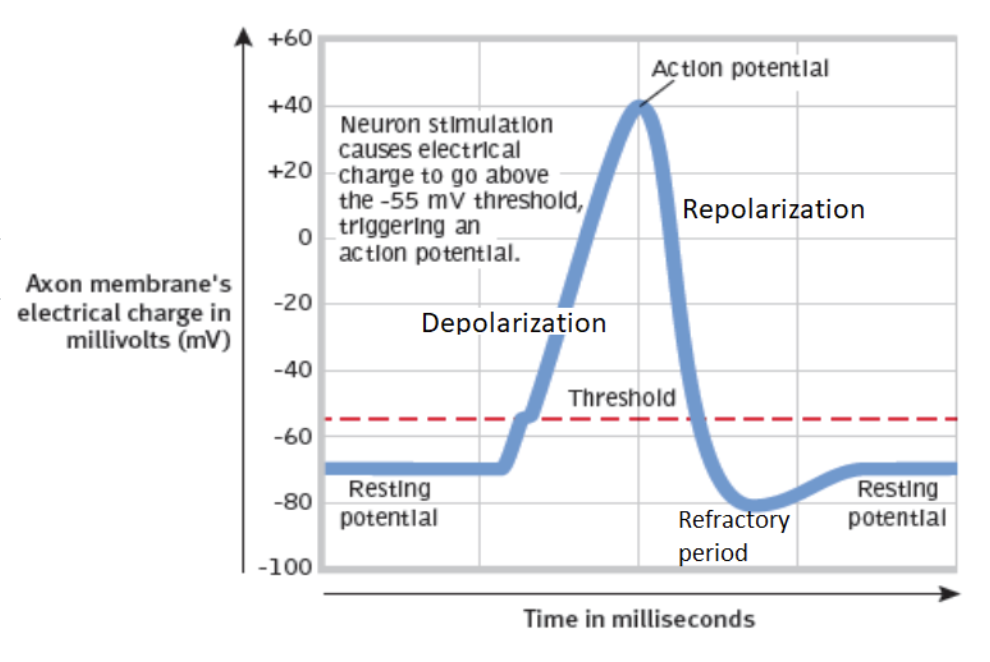
Depolarization
the action potential; positively charged ions rush in and out
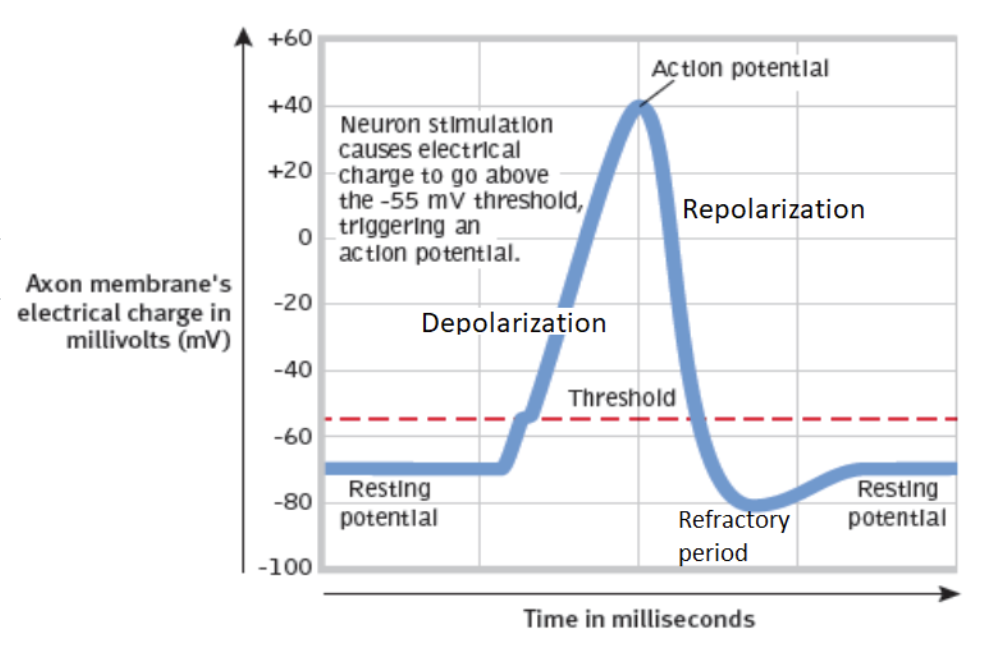
Repolarization
the refractory period; closing the membrane and returning to resting state
Tolerance
That something no longer has a normal effect on you; in the brain, a change in the amount of neurotransmitters normally released to even out the imbalance
Withdrawal
the physical and mental consequences a person feels when the drug is removed
Acetylcholine (ACh)
influences muscle action, learning and memory; correlated to Alzheimer’s and parylization
Dopamine
influences movement, learning, attention and emotion; linked to addiction, schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease
Serotonin
influences mood, hunger, sleep and arousal; linked to depression
Norephinephrine
Influences alertness and arousal; linked to depressed mood
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
A major inhibitory neurotransmitter; linked to seizures, tremors and insomnia
Glutamate
A major excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory; linked to migraines and seizures
Endorphins
influences the perception of pain or pleasure; oversupply of opiate drugs can suppress the body’s natural endorphin supply
Nervous System
the body’s electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
Nerves
bundled axons of many neurons that form neural cables connecting the CNS with muscles, glands, and sense organs
Sensory neurons
send signals from sense receptors inward toward the spinal cord
Motor neurons
send signals outward away from the CNS to muscles in the body
Interneurons
in the spinal cord, receives the information from the sensory neurons and send signals back through motor neurons
Central Nervous System
responsible for coordinating incoming sensory messages and outgoing motor messages
Spinal cord
a 2-way connection between PNS and the brain; oversees sensory and motor pathways of reflexes
Peripheral Nervous System
made up of sensory and motor neurons; connects the body to the CNS by gathering information from the senses and transmitting messages from the CNS
Somatic nervous system
controls the body’s skeletal muscles
Autonomic nervous system
controls the glands and muscles of the internal organs and operates automatically
Sympathetic
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy; fight, flight or freeze
Parasympathetic
calms the body, conserving its energy; rest or digest
Endocrine System
the body’s “slow” chemical communtcation system
Pituitary Gland
the master gland; it secretes growth hormones and oxytocin; its secretions direct the other glands to secrete their hormones
Oxytocin
stimulates uterine cintractions of child birth and milk secretions
Hypothalamus
directs eating, drinking, body temperature; linked to emotion and reward; influences the pituitary gland to regulate growth and control other glands
Adrenal glands
When fight or flight is activated, the glands release epinephrine and norepinephrine (adrenaline and noradrenaline) to energize the body
Lesion
brain tissue is destroyed and researchers study the impacts on fuctioning
Stimulation
brain regions are stimulated electrically, chemically, or magnetically and researchers study the impact on functioning
Electroencephalogram (EEG)
electrodes are placed on the scalp to measure electrical activity in neurons
Magnetoencephalography (MEG)
A head coil records magnetic fields from the brain’s natural electrical activity
Computed tomography (CT)
x-rays of the head generate images that may locate brain damage
Position emission tomography (PET)
Tracks where a temporarily radioactive form of glucose goes while the brain of the person preforms a given task
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
People sit or lie in a chamber that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to provide a map of brain structure
Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI)
measures bloodflow to brain regions by comparing continuous MRI scans
Brain stem
automatic survival functions
Medulla
controlls heartbeat and breathing
Pons
controls sleep and coordinates movement
Reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; helps control arousal and filter incoming sensory stimuli
Thalamus
relays the sensory information (not smell) to the brain
Cerebellum
responsible for sensory information, coordinate movement/balance, nonverbal learning and memory
Limbic system
controls emotions, memory and drive
Amyglada
linked to emotion, fear and aggression
Hippocampus
process memories and facts for storage
Cerebral cortex
the body’s ultimate control and information-processing center
Frontal lobe
involved in speaking, motor movements, judjement and decision making
Parietal lobe
receives and processes sensory input for touch and body position
Temporal lobe
each lobe recieves auditory information, primarily from opposite ear
Occipital lobe
recieves visual information, primarily from opposite eye
Motor cortex
controls voluntary movements
Somatosensory cortex
registers information from skin senses and body movement
Auditory cortex
recieves information from ears
Visual cortex
recieves information from eyes
Association areas
areas of the brain cortex that integrates information involed in learning, remembering, thinking and other higher level functions
Broca’s area
is the language center involved in expressive language and speaking
Wernicke’s area
the language center involved in receptive language and understanding
Plasticity
the brain’s ability to change by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
Neurogenesis
the brain’s ability to produce new neurons
Corpus callosum
a wide band of axon fibers connecting the two hemispheres of the brain
Split brain
happens when a scientist separates the brain by cutting the corpus callosum
Left Hemisphere
right side of the body (vision and motor skills); deals with rational/analytical thought, speaking, planning, math/science and logic
Right Hemisphere
Left side of the body (vision and motor skills); deals with intuitive/emotional thought, impulse, imagination, creativity and logic
Visual field
along the retina of the eye, sense receptors pick up stimuli that is about two inches apart; the right sides of both retinas gather information from the left side of what you are looking at and vice versa
Consciousness
subjective awareness of ourselves and our environment; helps us cope with novelty and act in our best interests
Cognitive neuroscience
combines the study of brain activity with how we learn, think, remember and perceive
Dual processing
the principle that information is often simultaneously processed on separate conscious and unconscious tracks; the two-tracked mind
Blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it
Parallel processing
the unconscious processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously; generally used to process well-learned information or to solve easy problems; muscle memory; multitask
Sequential processing
the conscious processing or one aspect of a problem at a time; generally used to process new information or to solve difficult problems
Heredity
nature; is the genetic transfer of characteristics from parent to offspring
Environment
nurture; is every non-genetic influence, from prenatal nutrition to the people and things around us
Behavior Geneticists
study the relative power and limits of heredity/environmental influences on behaviorstudy the relative power and limits of heredity/environmental influences on behavior
DNA
a complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
Genes
the biochemical units of heredity that make up the chromosomes; segments of DNA capable of synthesizing proteins
Chromosomes
threadlike structures made of DNA molecules that contain the genes
Human genome
the complete instructions for making a human organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that person’s chromosomes
Identical monozygotic twins
develop when a single fertilized egg splits in two, creating two genetically identical organisms
Fraternal dizygotic twins
develop when separate fertilized eggs share a maternal prenatal environment (uterus); no more alike than siblings
Heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals in a group that we can attribute to genes
Molecular genetics
the study of the molecular structure and function of genes
Molecular behavior genetics
the further study of how the structure and function of genes interact with our environment to influence behavior
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change