Biochemistry Exam 2 - Spring 2023
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/117
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
1
New cards
Why are proteins important?
Proteins mediate every process in the cell
\
Most abundant biomolecule in the body
\
Thousands of different proteins in every cell
\
Proteins from every organism are made from same 20 building blocks
\
Building blocks are called amino acids
\
The order of the amino acids gives diversity to proteins
\
Most abundant biomolecule in the body
\
Thousands of different proteins in every cell
\
Proteins from every organism are made from same 20 building blocks
\
Building blocks are called amino acids
\
The order of the amino acids gives diversity to proteins
2
New cards
Amino Acids Overview
20 Total
\
Asparagine was first discovered in 1806
\
Threonine was last to be identified in 1938
\
All have common names, usually dependent on the source it was identified in
\
Asparagine was first discovered in 1806
\
Threonine was last to be identified in 1938
\
All have common names, usually dependent on the source it was identified in
3
New cards
All amino acids have chiral centers except which one?
Glycine
4
New cards
What does Aliphatic mean?
Contains a hydrocarbon
5
New cards
Where are branched chain AA metabolized?
Muscle
6
New cards
What is Sickle Cell Anemia
Genetic mutation that occurred over time to protect population from Maleria
\
Super painful
\
Valine(nonpolar) replaces Glutamate (polar) in hemoglobin
*This causes the improper folding*
\
Super painful
\
Valine(nonpolar) replaces Glutamate (polar) in hemoglobin
*This causes the improper folding*
7
New cards
What is Maple Syrup Urine Disease
Genetic deficiency of enzymes required to metabolize branched chain amino acids (Valine, Leucine, Isoleucine)
\
Symptoms: Urine with color, odor, and texture of maple syrup
\
If untreated: Can cause brain damage and death
\
Treatment": Avoid high protein food for life
\
Symptoms: Urine with color, odor, and texture of maple syrup
\
If untreated: Can cause brain damage and death
\
Treatment": Avoid high protein food for life
8
New cards
What is Celiac Disease
Prevalence - 1.4% globally
\
Etiology (Cause): Genetic susceptibility → exposure to gluten → environmental trigger and other risk factors → autoimmune response
\
Etiology (Cause): Genetic susceptibility → exposure to gluten → environmental trigger and other risk factors → autoimmune response
9
New cards
What is phenylketonuria (PKU)
Genetic disorder that lacks enzyme (phenylalanine hydroxylase) necessary to metabolize phenylalanine
\
Causes brain damage
\
Treatment:Avoid phenylalanine in diet (low protein)
\
Causes brain damage
\
Treatment:Avoid phenylalanine in diet (low protein)
10
New cards
What is Cystic Fibrosis
Genetic disorder affecting 1/2,000 humans
\
Missing 1 phenylalanine in protein that regulates transport of chloride ions across cell membranes
\
Protein is not folded correctly and this degraded
\
Causes: mucus to build up in lungs and digestive issues
\
Missing 1 phenylalanine in protein that regulates transport of chloride ions across cell membranes
\
Protein is not folded correctly and this degraded
\
Causes: mucus to build up in lungs and digestive issues
11
New cards
Alzheimer’s Disease
Proteins:
Amyloids → normal cellular proteins that unravel and stick together
Lysine is key for holding it together through hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions
\
Tangles → Microtubules become phosphorylated and behave unnaturally
Accumulation can cause cell to rupture
\
Potential Treatments: CLR01 binds lysine and arginine
Lots of research going into treating this.
Amyloids → normal cellular proteins that unravel and stick together
Lysine is key for holding it together through hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions
\
Tangles → Microtubules become phosphorylated and behave unnaturally
Accumulation can cause cell to rupture
\
Potential Treatments: CLR01 binds lysine and arginine
Lots of research going into treating this.
12
New cards
What is Aspartame
Artificial sweetener made of Aspartate and Phenylalanine
13
New cards
Glucogenic
Used to make glucose, if necessary
Product = Pyruvate
\
Product = Pyruvate
\
14
New cards
Ketogenic
Turned into Kreb’s cycle intermediate, ketone bodies, or fatty acids, if in excess
Product = Acetyl CoA
Product = Acetyl CoA
15
New cards
Know AA Chart
*See Image*
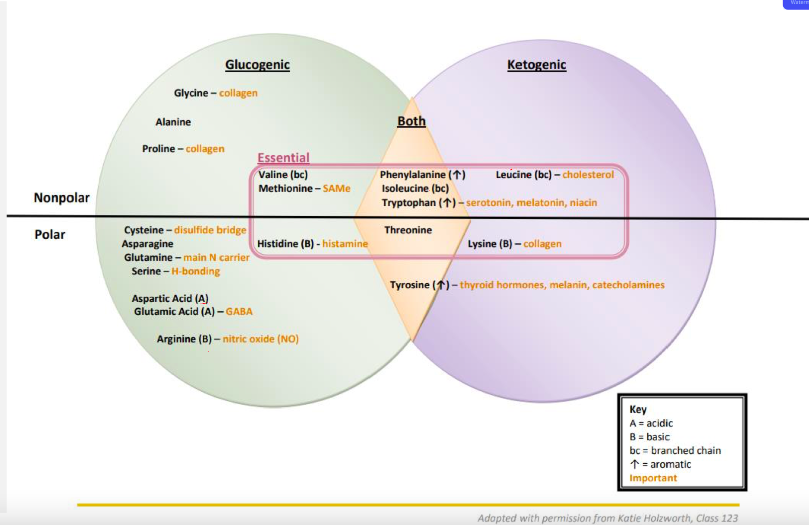
16
New cards
How do AA act as acids and bases?
Amphoteric = dual acid-base nature
\
All have at least 2 charges at physiologic pH, some have 3
\
They are least soluble at their isoelectric point
\
All have at least 2 charges at physiologic pH, some have 3
\
They are least soluble at their isoelectric point
17
New cards
When pH is high, what happens to AA?
AA can donate a H+ and become a proton donor - become an acid
18
New cards
When pH is low, what happens to AA?
AA can accept H+, becoming a proton acceptor - become a base
19
New cards
pKa General Rules
pKa is a lab determined number that is relatively constant
\
pH will change substantially throughout body fluids
\
If pH is below pKa = H+ is still attached
\
If pH is above pKa = H+ is lost
\
\
\
pH will change substantially throughout body fluids
\
If pH is below pKa = H+ is still attached
\
If pH is above pKa = H+ is lost
\
\
20
New cards
What is a Zwitterion?
The point where an AA or protein is neutral
21
New cards
Protein Overview
They are huge
\
In theory could form infinite conformational structures
\
Each protein has a specific 3D structure
\
In theory could form infinite conformational structures
\
Each protein has a specific 3D structure
22
New cards
Structure Themes
3D structure of a protein is determined by its amino acid sequence
\
The function of a protein is dependent on its structure
\
Most proteins exist in 1 or a few stable forms
\
Most important stabilizing force for protein structures are noncovalent interactions
Hydrophobic Interactions → drives folding of nonpolar AA to interior of protein
Carbonyls & Amines → H bond with water
Charged R groups → Participate in electrostatic interactions
\
Common structural motifs are found in most proteins
\
Protein structures are not static, they are dynamic
\
The function of a protein is dependent on its structure
\
Most proteins exist in 1 or a few stable forms
\
Most important stabilizing force for protein structures are noncovalent interactions
Hydrophobic Interactions → drives folding of nonpolar AA to interior of protein
Carbonyls & Amines → H bond with water
Charged R groups → Participate in electrostatic interactions
\
Common structural motifs are found in most proteins
\
Protein structures are not static, they are dynamic
23
New cards
Protein Structure: Conformation
Spatial Arrangement of atoms in a protein
\
Rotation around a bond changes in conformation
\
Rotation around a bond changes in conformation
24
New cards
Protein Structure: Native
Proteins in their functional, folded conformation
\
Most Stable
\
Has the lowest Gibbs free energy
\
Most Stable
\
Has the lowest Gibbs free energy
25
New cards
Protein Structure: Stability
Protein’s ability to maintain the native confirmation
\
Held together by disulfide bonds (covalent bonds between cysteines) and weak (noncovalent) interactions - H bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions
\
Held together by disulfide bonds (covalent bonds between cysteines) and weak (noncovalent) interactions - H bonds, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions
26
New cards
What are the 4 levels of Protein Structure?
Primary → AA sequence
\
Secondary → Initial Folding
\
Tertiary → 3D folding of 1 strand
\
Quaternary → 3D folding of multiple strands
\
Secondary → Initial Folding
\
Tertiary → 3D folding of 1 strand
\
Quaternary → 3D folding of multiple strands
27
New cards
Primary Structure → Peptides & Proteins
Peptide bonds - Formed via condensation/dehydration reactions
\
Trans in nature
\
Not broken by denaturation
\
Peptide bond is rigid → Not allowed to rotate = stuck → Puts constraints on the overall protein structure
\
Trans in nature
\
Not broken by denaturation
\
Peptide bond is rigid → Not allowed to rotate = stuck → Puts constraints on the overall protein structure
28
New cards
Synthesis of ALL macronutrients are what reactions?
Dehydration
29
New cards
Secondary Structure
Alpha helix, Beta Sheets, B turns
\
Alpha Helices →
Tightly wound ‘spring’ like structure
Each turn contains 3.6AA
Structure held together by H-bonding
C=O on one AA is H-bonded to N-H 4AA apart
R groups point outward
\
Stability of Helix dependent on:
Likelihood of a-helix formation → Interactions of R groups 3 or 4AA away → Size of R group → Occurrence of proline and glycine → Interactions of AA at ends of helix
\
\
\
Alpha Helices →
Tightly wound ‘spring’ like structure
Each turn contains 3.6AA
Structure held together by H-bonding
C=O on one AA is H-bonded to N-H 4AA apart
R groups point outward
\
Stability of Helix dependent on:
Likelihood of a-helix formation → Interactions of R groups 3 or 4AA away → Size of R group → Occurrence of proline and glycine → Interactions of AA at ends of helix
\
\
30
New cards
Types of Proteins
Fibrous →
Peptides found in long strands or sheets
Contain single secondary structure
Function as providers of support, shape, and external protection
\
Globular →
Peptides folded in a spherical structure
Contain several secondary structures
Function as enzymes, regulatory proteins, and transport molecules
Peptides found in long strands or sheets
Contain single secondary structure
Function as providers of support, shape, and external protection
\
Globular →
Peptides folded in a spherical structure
Contain several secondary structures
Function as enzymes, regulatory proteins, and transport molecules
31
New cards
Keratin Proteins
Found only in mammals
\
2 Alpha-helix coiled together to make a coiled coil
\
Crosslinks between coiled coils held together by disulfide bonds
\
2 Alpha-helix coiled together to make a coiled coil
\
Crosslinks between coiled coils held together by disulfide bonds
32
New cards
Collagen
Provides strength for connective tissue (bone, tendons, cartilage)
\
30 different types of collagen in mammals
\
Contains a unique secondary structure (also a coiled coil, but contains 3 polypeptide chains wound together)
\
AA Sequence is generally a repeating tripeptide unit
Glycine - X-Y
X = often proline
Y = often hydroxyproline
\
30 different types of collagen in mammals
\
Contains a unique secondary structure (also a coiled coil, but contains 3 polypeptide chains wound together)
\
AA Sequence is generally a repeating tripeptide unit
Glycine - X-Y
X = often proline
Y = often hydroxyproline
33
New cards
Scurvy
Due to lack of Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
\
Required for hydroxylation of proline and lysine in collagen synthesis
\
Deficiency leads to degeneration of connective tissue
\
S/S - Corkscrew hairs, bleeding gums
\
Required for hydroxylation of proline and lysine in collagen synthesis
\
Deficiency leads to degeneration of connective tissue
\
S/S - Corkscrew hairs, bleeding gums
34
New cards
Collagen Crosslinking
Lysyl Oxidase
\
Copper (Cu) - dependent enzyme
Deaminates lysine forming reactive aldehyde
Aldehyde condenses with lysine or hydroxylysine on neighboring collagen
\
Copper (Cu) - dependent enzyme
Deaminates lysine forming reactive aldehyde
Aldehyde condenses with lysine or hydroxylysine on neighboring collagen
35
New cards
Collagen Degradation
Half-life of years
\
Constant remodeling occurs due to growth and/or injury
\
Degraded by MMPs
\
Constant remodeling occurs due to growth and/or injury
\
Degraded by MMPs
36
New cards
What are MMPs?
Matrix metalloproteinases
\
Require metals → Ca and Zn
Main class of proteases in the body
Required for tissue remodeling
\
Require metals → Ca and Zn
Main class of proteases in the body
Required for tissue remodeling
37
New cards
Which protein is mostly triple helical and virtually insoluble in water?
Collagen
38
New cards
Which posttranslational modification is extremely important for collagen structure?
Hydroxylation
39
New cards
Which is NOT found in high concentrations in collagen?
Valine
40
New cards
Types of Proteins
Fibrous →
Peptides found in long strands or sheets
Contain single secondary structure
Function as providers of support, shape, and external protection
\
Globular →
Peptides folded in a spherical structure
Contain several secondary structures
Function as enzymes, regulatory proteins, and transport molecules
Peptides found in long strands or sheets
Contain single secondary structure
Function as providers of support, shape, and external protection
\
Globular →
Peptides folded in a spherical structure
Contain several secondary structures
Function as enzymes, regulatory proteins, and transport molecules
41
New cards
What is Motif?
Recognizable folding pattern containing 2 or more secondary structures
\
Not inherently stable
\
Not inherently stable
42
New cards
Domain
Part of polypeptide chain that is independently stable
\
If removed from polypeptide, the 3D structure remains the same
\
Different domains can have different functions
\
If removed from polypeptide, the 3D structure remains the same
\
Different domains can have different functions
43
New cards
Unstructured Proteins
Intrinsically Unstructured Proteins →
At least part of protein does not have a specific structure
50% of proteins have at least 1 unstructured region
This portion changes into a specific structure when interacting with another protein - gives flexibility with shape
Important in signaling pathways
At least part of protein does not have a specific structure
50% of proteins have at least 1 unstructured region
This portion changes into a specific structure when interacting with another protein - gives flexibility with shape
Important in signaling pathways
44
New cards
Protein Folding
Folded proteins are in their native confirmation
*in it’s functioning state*
\
Determined by the primary structure (sequence of AA)
\
Not Random
\
Some proteins required assisted folding through use of *chaperones*
\
Steps:
Secondary structures fold first guided by electrostatic interactions → Local IMF form → Long-range IMF form between the different secondary structures form
\
*in it’s functioning state*
\
Determined by the primary structure (sequence of AA)
\
Not Random
\
Some proteins required assisted folding through use of *chaperones*
\
Steps:
Secondary structures fold first guided by electrostatic interactions → Local IMF form → Long-range IMF form between the different secondary structures form
\
45
New cards
Defects in Protein Folding
Protein Misfolding → 25% of all proteins fold incorrectly
\
When misfolded, there are 2 options:
\
Degraded →
Which is what’s happening with Cystic Fibrosis
\
Accumulation →
What’s happening with Sickle Cell Anemia and Amyloids in Alzheimer’s
\
When misfolded, there are 2 options:
\
Degraded →
Which is what’s happening with Cystic Fibrosis
\
Accumulation →
What’s happening with Sickle Cell Anemia and Amyloids in Alzheimer’s
46
New cards
Which of the following Amino Acids is normally found in the interior of globular proteins?
*asking about polarity, which one is a non polar*
*asking about polarity, which one is a non polar*
Valine
47
New cards
Protein Unfolding Through →
\
Proteostasis
*Protein Homeostasis*
\
Proteostasis
*Protein Homeostasis*
Coordinated cellular processes that control protein synthesis, folding, refolding, and degradation of proteins
\
Autophagy - Cell eating
\
Autophagy - Cell eating
48
New cards
Protein Unfolding Through →
\
Denaturation
\
Denaturation
Protein no longer functions as it should
\
Increases surface area for digestion
\
*Does NOT change primary structure*
\
Increases digestibility
\
Globular proteins are easier to denature than fibrous proteins
\
Increases surface area for digestion
\
*Does NOT change primary structure*
\
Increases digestibility
\
Globular proteins are easier to denature than fibrous proteins
49
New cards
Other Protein Unfolding Mechanisms
Heat or Excessive Cold →
Alters H-bonds & hydrophobicity
\
Strong Acids/Bases →
Alters net charge, disrupting H-bonds & causing repulsive electrostatic interactions
\
Mechanical →
Unfolding protein, exposing hydrophobic groups
Alters H-bonds & hydrophobicity
\
Strong Acids/Bases →
Alters net charge, disrupting H-bonds & causing repulsive electrostatic interactions
\
Mechanical →
Unfolding protein, exposing hydrophobic groups
50
New cards
Protein Function Overview
Most functions involve reversible binding of a ligand
*ligand can be anything that can bind*
\
Proteins are dynamic and flexible
\
*ligand can be anything that can bind*
\
Proteins are dynamic and flexible
\
51
New cards
Reversible Binding
Molecule reversibly bound by a protein is called a ligand
*ligands can be any type of compound, including another protein*
\
Interactions are transient
*able to respond quickly and reversibly to changing environment*
\
Ligand binds to binding site
*Complementary site on protein that corresponds to size, shape, hydrophobicity of ligand*
\
Able to selectively bind
*Proteins may contain multiple binding sites for different molecules*
*ligands can be any type of compound, including another protein*
\
Interactions are transient
*able to respond quickly and reversibly to changing environment*
\
Ligand binds to binding site
*Complementary site on protein that corresponds to size, shape, hydrophobicity of ligand*
\
Able to selectively bind
*Proteins may contain multiple binding sites for different molecules*
52
New cards
Protein Binding
Binding of a ligand often is coupled with a confirmational change making it easier for the ligand to bind the binding site
*this structural adaptation is called induced fit*
\
Often, binding of a ligand can also cause a confirmational change
*sometimes 1 ligand will bind, the protein changes structure and now a 2nd ligand can bind*
\
*this structural adaptation is called induced fit*
\
Often, binding of a ligand can also cause a confirmational change
*sometimes 1 ligand will bind, the protein changes structure and now a 2nd ligand can bind*
\
53
New cards
Reversible Protein Binding
Ka = Association constant
Measure of the affinity for the ligand to bind a protein
Bigger # = more it likes the ligand
\
Kd = Dissociation constant
Used more in chemistry as a measure of affinity
Kd = 1/Ka
A measure of how much of a ligand must be in solution for 1/2 of the protein to be bound
Smaller he Kd, the tighter the protein will bind the ligand = Greater affinity!
Measure of the affinity for the ligand to bind a protein
Bigger # = more it likes the ligand
\
Kd = Dissociation constant
Used more in chemistry as a measure of affinity
Kd = 1/Ka
A measure of how much of a ligand must be in solution for 1/2 of the protein to be bound
Smaller he Kd, the tighter the protein will bind the ligand = Greater affinity!
54
New cards
Oxygen-Binding Proteins
Specialized proteins with a heme ring are called hemeproteins →
Fe can form 6 bonds:
4 N, 1 Histidine, 1 O2
\
Examples of Hemeproteins:
Myoglobin - Oxygen Carrier in Muscles
Hemoglobin - Oxygen carrier in blood
Neuroglobin - Oxygen and nitric oxide carrier in neurons
Cytoglobin - Oxygen carrier in many tissues *thought to protect tissues from oxidative stress*
\
Fe can form 6 bonds:
4 N, 1 Histidine, 1 O2
\
Examples of Hemeproteins:
Myoglobin - Oxygen Carrier in Muscles
Hemoglobin - Oxygen carrier in blood
Neuroglobin - Oxygen and nitric oxide carrier in neurons
Cytoglobin - Oxygen carrier in many tissues *thought to protect tissues from oxidative stress*
\
55
New cards
Myoglobin
Hemeprotein in heart and skeletal muscle
\
Oxygen carrier for aerobic metabolism (glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, electron transport chain)
\
Number of polypeptides - 1
\
Interior stabilized by hydrophobic interactions
\
1 heme = 1 Fe = 1 O2
\
Oxygen carrier for aerobic metabolism (glycolysis, Kreb’s cycle, electron transport chain)
\
Number of polypeptides - 1
\
Interior stabilized by hydrophobic interactions
\
1 heme = 1 Fe = 1 O2
56
New cards
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Aka Erythrocytes (aka hemoglobin)
\
Produced from stem cells, called hemocytoblasts
\
During maturation, daughter cells produced large amounts of hemoglobin and then cellular organelles lose their function
\
RBCs are incomplete and unable to reproduce
\
Derive energy from glycolysis (since they lack mitochondria, they can’t form ATP through the electron transport chain and can’t burn fat)
\
Lifespan of 120 days
\
Produced from stem cells, called hemocytoblasts
\
During maturation, daughter cells produced large amounts of hemoglobin and then cellular organelles lose their function
\
RBCs are incomplete and unable to reproduce
\
Derive energy from glycolysis (since they lack mitochondria, they can’t form ATP through the electron transport chain and can’t burn fat)
\
Lifespan of 120 days
57
New cards
Hemoglobin
Transports O2 from lungs to tissues
\
Number of polypeptides = 4
\
Can transport CO2 and H+ from tissues to lungs
\
4 heme = 4 Fe = 4 O2
\
2 Types:
\
Oxyhemoglobin →
R state = relaxed
Less electrostatic interactions (ion pairs)
High affinity for binding oxygen
\
Deoxyhemoglobin →
T state = Tense (aka taut state)
More electrostatic interactions (ion pairs)
Low affinity for binding oxygen
\
Number of polypeptides = 4
\
Can transport CO2 and H+ from tissues to lungs
\
4 heme = 4 Fe = 4 O2
\
2 Types:
\
Oxyhemoglobin →
R state = relaxed
Less electrostatic interactions (ion pairs)
High affinity for binding oxygen
\
Deoxyhemoglobin →
T state = Tense (aka taut state)
More electrostatic interactions (ion pairs)
Low affinity for binding oxygen
58
New cards
Oxygen Binding
Degree of saturation of oxygen-binding sites varies from 0% - 100%
Myoglobin can only bind 1, so it is either 0% or 100%
Hemoglobin can cary from 0-100% bound
\
Depends on partial pressure of oxygen (pO2)
Partial pressure is a measure of concentration
Myoglobin can only bind 1, so it is either 0% or 100%
Hemoglobin can cary from 0-100% bound
\
Depends on partial pressure of oxygen (pO2)
Partial pressure is a measure of concentration
59
New cards
Oxygen Dissociation Curve
Myoglobin →
Binds O2 at low concentrations found in muscle
Releases O2 in response to oxygen demand
\
Hemoglobin →
Cooperative binding = binding O2 at one heme increases affinity for binding O2 at other heme sites
Binds O2 at low concentrations found in muscle
Releases O2 in response to oxygen demand
\
Hemoglobin →
Cooperative binding = binding O2 at one heme increases affinity for binding O2 at other heme sites
60
New cards
Cooperative Binding of Hemoglobin
Each hemoglobin can bind a max of 4 oxygens → first oxygen binds T site weakly → causes a conformational change in adjacent subunits → Transitions subunit from T to R state -. Increases affinity to bind next oxygen → Causes a conformational change in adjacent subunits → Transitions from T to R state → Increases affinity to bind 3rd oxygen and so on.
61
New cards
Cooperative Binding
Allows Hb to respond to small changes in oxygen concentrations
\
Lungs = Oxygen saturates Hb (loads)
\
Peripheral Tissues = oxyHb releases oxygen (unloads)
\
Lungs = Oxygen saturates Hb (loads)
\
Peripheral Tissues = oxyHb releases oxygen (unloads)
62
New cards
Allosteric Proteins
Allosteric proteins have several possible structural confirmations induced by binding of a type of ligand called a *modulator*
\
Conformational changes may make the protein more or less active
\
Types of Interactions:
Homotropic → When ligand and modulator are identical
Heterotropic → When ligand and modulator are different compounds
\
\
Conformational changes may make the protein more or less active
\
Types of Interactions:
Homotropic → When ligand and modulator are identical
Heterotropic → When ligand and modulator are different compounds
\
63
New cards
Hemoglobin as an Allosteric Protein
The binding of 1 ligand (oxygen) affects the affinities of unfilled binding sites
*oxygen is both a ligand and an activating homotropic modulator*
\
Hemoglobin has other *inhibiting heterotropic modulators*
CO
CO2
H+
2,3 bisphosphoglycerate
*oxygen is both a ligand and an activating homotropic modulator*
\
Hemoglobin has other *inhibiting heterotropic modulators*
CO
CO2
H+
2,3 bisphosphoglycerate
64
New cards
Hemoglobin Transport
CO2 and H+ are both inversely proportional to O2 binding
\
Decrease in pH shifts toward deoxyhemoglobin (T)
Increase in pH shifts toward oxyhemoglobin (R)
\
Decrease in pH shifts toward deoxyhemoglobin (T)
Increase in pH shifts toward oxyhemoglobin (R)
65
New cards
Bohr Effect
Effect of H+ and CO2 concentration on oxygen binding and releasing → *inversely proportional*
\
Peripheral Tissues →
high H+, low pH, and high CO2 concentrations
Hb affinity for oxygen decreases
R to T state
Facilitates O2 unloading
\
Lungs →
low H+, higher pH, low CO2 concentrations
Hb affinity for oxygen increases
T to R state
Facilitates oxygen loading
\
Peripheral Tissues →
high H+, low pH, and high CO2 concentrations
Hb affinity for oxygen decreases
R to T state
Facilitates O2 unloading
\
Lungs →
low H+, higher pH, low CO2 concentrations
Hb affinity for oxygen increases
T to R state
Facilitates oxygen loading
66
New cards
Heterotropic Allosteric Effector (Inhibitor)
2, 3 - bisphosphoglycerate (BPG) →
Intermediate in glycolysis
Found in high concentrations in RBC
Binds to deoxyHb, decreasing affinity for O2 by stabilizing T structure
Inversely related to O2 binding
Important for physiologic adaptation to less oxygen at high altitudes
Intermediate in glycolysis
Found in high concentrations in RBC
Binds to deoxyHb, decreasing affinity for O2 by stabilizing T structure
Inversely related to O2 binding
Important for physiologic adaptation to less oxygen at high altitudes
67
New cards
Carbon Monoxide
Heterorophic! - Activator
Enhances loading
Binds to heme - preferential to O2
\
Colorless, odorless, heme has a 250 times greater affinity for CO than for O2
\
When CO is bound, it shifts the O2 dissociation curve, not allowing O2 to be released, basically suffocated from the inside out.
\
at 50% bound = coma and death.
Enhances loading
Binds to heme - preferential to O2
\
Colorless, odorless, heme has a 250 times greater affinity for CO than for O2
\
When CO is bound, it shifts the O2 dissociation curve, not allowing O2 to be released, basically suffocated from the inside out.
\
at 50% bound = coma and death.
68
New cards
Hemoglobin Degradation
Cell membrane of RBC becomes fragile and bursts → Hb is released and phagocytized by macrophages in Kupffer cells of liver, spleen, and bone marrow → Iron released and transported in blood by transferrin → Porphyrin ring converted to bilirubin by macrophages
69
New cards
Jaundice
Caused by large concentrations of bilirubin in extracellular fluid
\
Causes:
Hemolytic → Excessive destruction of RBC
high levels of free unconjugated bilirubin
\
Obstructive → Obstruction of bile duct or liver damage
high levels of conjugated bilirubin
\
Causes:
Hemolytic → Excessive destruction of RBC
high levels of free unconjugated bilirubin
\
Obstructive → Obstruction of bile duct or liver damage
high levels of conjugated bilirubin
70
New cards
Proteins and Ligands in the Immune System
Most ligands bind to a specific amino acid sequence in an area on the protein called a binding site
\
Immune system is important for recognizing foreign compounds
\
Immune response to protein are very specific and extremely sensitive
\
Immune system is important for recognizing foreign compounds
\
Immune response to protein are very specific and extremely sensitive
71
New cards
Enzymes - Biological Catalysts
Globular proteins
\
Speed up reactions without being consumed
\
Do not shift equilibrium, just reach it faster
\
Very specific
\
Speed up reactions without being consumed
\
Do not shift equilibrium, just reach it faster
\
Very specific
72
New cards
Apoenzyme
Protein part of enzyme only
73
New cards
Holoenzyme
Complete (active) enzyme
Protein + cofactor/coenzyme
Protein + cofactor/coenzyme
74
New cards
Cofactor vs Coenzyme
Cofactor →
Minerals
\
Coenzyme →
Vitamins
\
*see chart for more details, some on exam*
Minerals
\
Coenzyme →
Vitamins
\
*see chart for more details, some on exam*
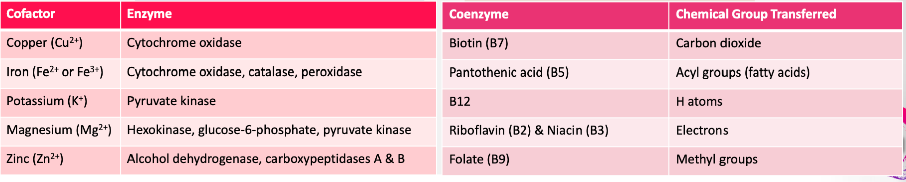
75
New cards
Zymogen
Enzyme precursor (inactive) - must be converted to active form
76
New cards
Name Enzymes
Name is based on:
What it reacts with
How it reacts
Add -ase to ending
Not always, but most of the time
\
Ex. Lactose is milk sugar, digested by lactase
Alcohol dehygrogenase - enzyme that removed hydrogen from alcohol to form an aldehyde
What it reacts with
How it reacts
Add -ase to ending
Not always, but most of the time
\
Ex. Lactose is milk sugar, digested by lactase
Alcohol dehygrogenase - enzyme that removed hydrogen from alcohol to form an aldehyde
77
New cards
What are the 7 classes of enzymes?
Oxidoreductase
Transferase
Isomerase
Hydrolase
Lyase
Ligase
Translocase
Transferase
Isomerase
Hydrolase
Lyase
Ligase
Translocase
78
New cards
Oxidoreductase
Addition or removal of a H
\
Requires coenzymes (NAD+ and FAD)
Dehydrogenase - removes H
Reductase - adds H
\
Ex. Enzymes found in electron transport chain in mitochondria, Kreb’s cycle, AA metabolism
\
Requires coenzymes (NAD+ and FAD)
Dehydrogenase - removes H
Reductase - adds H
\
Ex. Enzymes found in electron transport chain in mitochondria, Kreb’s cycle, AA metabolism
79
New cards
Transferase
2R and 2P
\
A-B + C < - > A + B-C
\
Transfer a functional group from one molecule to another
\
Ex. Krebs cycle, AA metabolism
\
A-B + C < - > A + B-C
\
Transfer a functional group from one molecule to another
\
Ex. Krebs cycle, AA metabolism
80
New cards
Isomerase
1R and 1 P
\
A-B-C < - > A-C-B
\
Rearrange functional groups on one molecule
\
A-B-C < - > A-C-B
\
Rearrange functional groups on one molecule
81
New cards
Hydrolase
A-B + H2O < - > A-H + B-OH
\
Causes hydrolysis reactions
\
Water breaks bond
\
Lipase, protease, phosphatase, amylase
\
Ex. Digestive enzymes (enzymes to digest lipids, carbohydrates, porteins, etc.) AA metabolism
\
Causes hydrolysis reactions
\
Water breaks bond
\
Lipase, protease, phosphatase, amylase
\
Ex. Digestive enzymes (enzymes to digest lipids, carbohydrates, porteins, etc.) AA metabolism
82
New cards
Lyase
Cleaves C-C, C-S, or C-N bonds (excluding peptide bonds)
\
\
83
New cards
Ligase
A+B+ATP < - > A-B+ADP+Pi
\
Energy released from removing phosphate drives reaction
\
Generally need energy from ATP to form bond
\
Energy released from removing phosphate drives reaction
\
Generally need energy from ATP to form bond
84
New cards
Translocase
Movement of molecules or ions across membranes or their separation within membranes
\
Ex. cations, anions, amino acids, small peptides, carbs, other compounds
\
Ex. cations, anions, amino acids, small peptides, carbs, other compounds
85
New cards
Oxidoreductase
Removal or addition of H or O (NAD+ or FAD)
86
New cards
Transferase
Transfer of group from one molecule to another
87
New cards
Isomerase
Structural rearrangement
88
New cards
Hydrolase
Water breaks bonds
89
New cards
Lyase
Break bond without water or redox
90
New cards
Ligase
Make bond (uses ATP)
\
Energy is USED for the reaction, phosphate is NOT transfered
\
Energy is USED for the reaction, phosphate is NOT transfered
91
New cards
Translocase
Transport across membranes
92
New cards
How enzymes work
Enzymes contain an active site
\
React with specific substrate
\
Enzymes speed up reaction rates
will not determine how fast the reaction will go
will reach equilibrium faster
\
Negative change in free energy (delta G) will determine if the reaction will occur spontaneously - exergonic
\
Positive change in free energy requires energy to be added to the system for the reaction to happen - endergonic
\
Delta G = 0 at equilibrium
\
Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
\
In a pathway with multiple steps: Overall rate is determined by the step with the highest activation energy - called the *rate limiting step*
\
React with specific substrate
\
Enzymes speed up reaction rates
will not determine how fast the reaction will go
will reach equilibrium faster
\
Negative change in free energy (delta G) will determine if the reaction will occur spontaneously - exergonic
\
Positive change in free energy requires energy to be added to the system for the reaction to happen - endergonic
\
Delta G = 0 at equilibrium
\
Catalysts speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy
\
In a pathway with multiple steps: Overall rate is determined by the step with the highest activation energy - called the *rate limiting step*
93
New cards
Enzyme Active Sites
Much of the catalytic power of enzymes comes from the free energy released through formation of weak bonds in active sites (IMFs) - called Binding Energy
\
Binding Energy also gives the enzyme it’s specificity - the ability to discriminate between substrates
\
Weak interactions are optimized at the transition state
\
\
\
Binding Energy also gives the enzyme it’s specificity - the ability to discriminate between substrates
\
Weak interactions are optimized at the transition state
\
\
94
New cards
How Substrates Bind
Decrease in entropy to binding an enzyme (keeps substrate in the correct orientation)
\
Weak bonds form between E and S, disrupting water layer (desolvation)
\
Binding energy from IMF in transition state drives the reaction
\
Enzyme undergoes conformational change caused by IMF with S (induced fit)
\
Weak bonds form between E and S, disrupting water layer (desolvation)
\
Binding energy from IMF in transition state drives the reaction
\
Enzyme undergoes conformational change caused by IMF with S (induced fit)
95
New cards
Enzyme Kinetics
Vo = reaction velocity
Number of reactions catalyzed by enzyme per second
\
Vmax = maximum velocity
Enzyme is completely saturated with substrate (100% bound)
\
Km = Michaelis constant
affinity for binding
amount of substrate required for 50% of enzyme to be bound (1/2 vmax)
Smaller number = better at binding
Number of reactions catalyzed by enzyme per second
\
Vmax = maximum velocity
Enzyme is completely saturated with substrate (100% bound)
\
Km = Michaelis constant
affinity for binding
amount of substrate required for 50% of enzyme to be bound (1/2 vmax)
Smaller number = better at binding
96
New cards
\[S\]
1-49% of substrate is bound
97
New cards
\[S\] = Km
50% bound
98
New cards
\[S\]>Km
51-99% bound
99
New cards
\[S\]>>Km
100% bound
100
New cards
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Each enzyme has optimum pH, depends on pK or R groups
\
Extreme pH can lead to denaturation
\
Extreme pH can lead to denaturation