MCAT Organic Chemistry - Nitrogen- and Phosphorus-Containing Compounds
1/21
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Amino acids
contain an amino group and a carboxyl group attached to a single carbon atom; other two substituents of the α-carbon are a hydrogen atom and a side chain; stereogenic center EXCEPT glycine; L-isomers (S configuration EXCEPT cysteine)
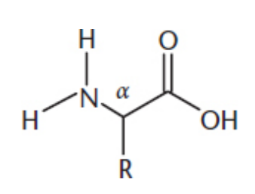
R group
side chain esp. of an amino acid
Glycine
simplest amino acid; achiral; R group is a hydrogen atom
cysteine
R group is thiol (-SH); covalent bonding, only (R) configuration amino acid
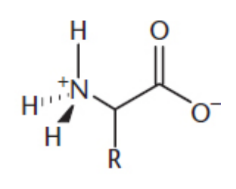
amphoteric
act as both acids and bases
zwitterion
dipolar ion
nonpolar nonaromatic amino acids
tend to have side chains that are saturated hydrocarbons: alanine, valine, leucine, and isoleucine
also include glycine, proline (which is cyclic, with a secondary amine), and methionine (which contains sulfur)
Aromatic amino acids
tryptophan, phenylalanine, and tyrosine
Nonpolar amino acids
hydrophobic and tend to be sequestered in the interior of proteins
Polar amino acidS
tend to have terminal groups containing oxygen, nitrogen, or sulfur: serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, and cysteine
Negatively charged (acidic) amino acids
terminal carboxylate anions
aspartic acid and glutamic acid
positively charged (basic) amino acids
protonated amino group in their R groups
arginine, lysine, and histidine
peptide bonds
condensation reactions of amino acids
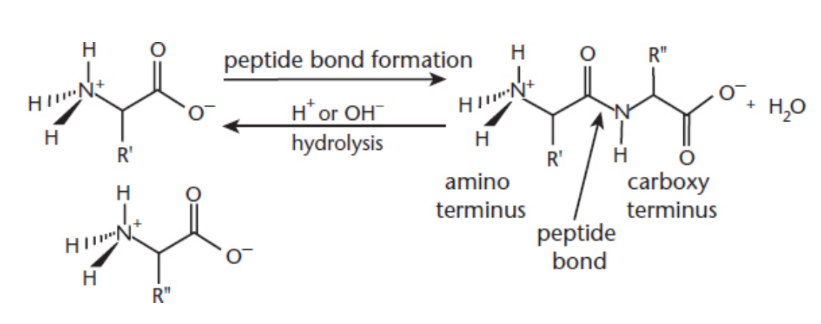
polypeptides
molecules formed from amino acids bonded by peptide bonds
proteins
Biomolecule consisting of folded chains of amino acid residues
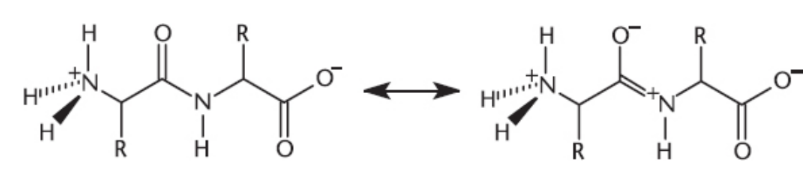
Resonance in the Peptide Bond
partial double-bond character between the nitrogen atom and the carbonyl carbon; limits rotation about the C―N bond, which adds to the rigidity and stability of the backbone
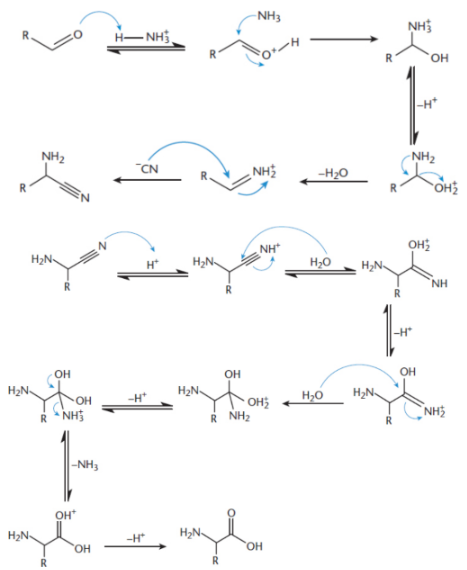
Strecker synthesis
aldehyde, ammonium chloride (NH4Cl), and potassium cyanide (KCN) → aminonitrile → amino acid (racemic)
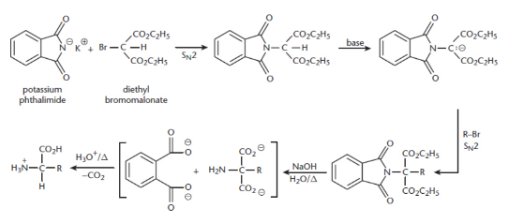
Gabriel (malonic-ester) synthesis
potassium phthalimide + diethyl bromomalonate → phthalimidomalonic ester + bromoalkane → hydrolysed with heat → dicarboxylic acid with an amine on the α-carbon → decarboxylated through the addition of acid and heat → complete amino acid (racemic)
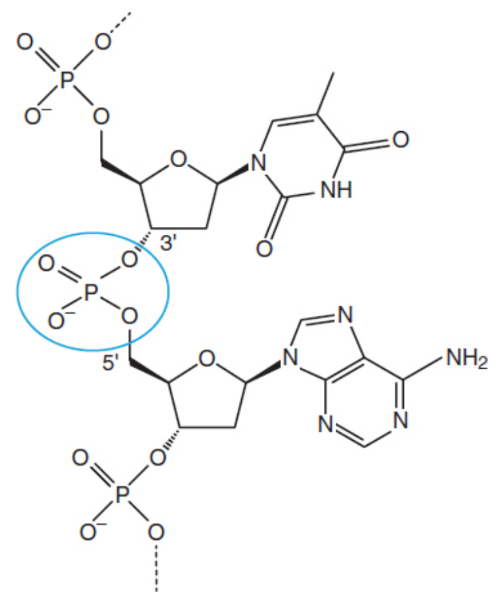
Phosphoric acid / phosphate group / inorganic phosphate (Pi)
forms the high-energy bonds that carry energy in adenosine triphosphate (ATP); three acidic hydrogens when fully protonated; both hydrogen phosphate and dihydrogen phosphate in cell; experience a large amount of repulsion from each other because they are negatively charged
pKas: 2.15, 7.20, 12.32
phosphodiester bonds
linking the phosphate groups and sugar moieties of the nucleotides into nucleic acids
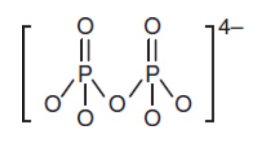
pyrophosphate (P2O74-) (PPi)
ester dimer of phosphate released by nucleotide as it adds to nucleic acidc chain; unstable in aqueous solution and is hydrolyzed to form two molecules of inorganic phosphate that can be recycled
organic phosphates
Nucleotides, due to the presence of the phosphate group bonded to a carbon-containing molecule