Dental Waxes
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What type of material are dental waxes and what can you do with them?
what state are they on heating and room temperature?
Thermoplastic moulding material that is a solid at room temperature
Heating converts the wax to a liquid phase - easily mouldable
At some point dental waxes are P—ed?
Pyrolysed
What does pyrolysed mean?
At some point, they melt and/or decompose into water vapour and carbon dioxide
Waxes are O—— C——— compounds?
Organic crystalline compounds
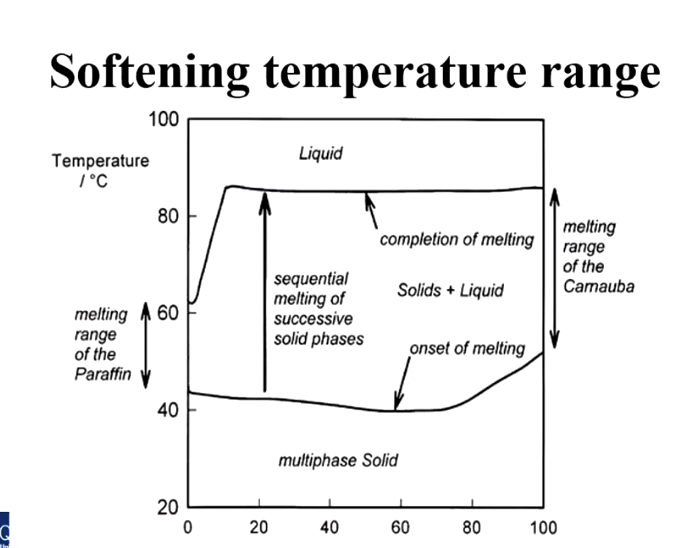
What are the melting properties of individual waxes and how are they changed by manufacturers for dental use?
Individual wax has a sharp well-defined melting point, above which it is a mobile liquid and below which is a solid, as such it would be of little practical use
for dental use, manufacturers blend two or more waxes to give a material with a softening temperature range over which it is a useful mouldable material
What is melting range?
A range of temperatures at which each component of the wax will start to soften and then flow
What is flow in wax?
[occurs at what temp?
what is the viscosity?]
control of flow/melting range is important how?
this happens as the wax approaches what?
The movement of wax molecules which slip over each other
at high temperature the wax has low viscosity and flows
the wax is mobile as it approaches the melting range
important in manipulating wax
What does the melting range for a bite registration wax need to be ?
Needs to be only slightly higher than mouth temperature - if too high a softening temperature then it would be uncomfortable for the patient
What about the melting range for lab wax?
these may have a much higher melting range
Dimensional changes affecting wax?
Compared to other dental materials?
What happens if wax is heated too far above melting range or heated unevenly?
On standing, dimensional changes to waxes occurs from?
therefore what should you do, important in?
Wax expands when heated and contracts when cooled
The thermal expansion and contraction of waxes is greater than any other dental material
expansion above acceptable standards will result in inaccuracies in the final casting
occurs from the release of residual stresses
invest and cast within 30 min after carving the wax
important for pattern waxes-duplicate of the restoration carved in the wax
After wax removal what may remain on the object?
how is his a problem?
important when?
Excess residue - wax film remaining on an object after wax removal
if excess residue remains it may result in inaccuracies in the item being produced
important in the lost wax technique when the wax pattern is melted out of the investment mold
so in summary, 4 main properties of dental waxes?
melting range, flow and dimensional changes, excess residue
waxes in dentistry are composed of? (3 Main)
synthetic and 2 or more natural waxes
small amounts of additives such as - gums, fats, fatty acids, oils, natural and synthetic resins, pigments of various types
What is the aim of this? (3 main)
To give a set of properties over a specific range of temperatures
Contain a range of molecular weights that affects the melting and flow properties of wax
Chemical components of both natural and synthetic waxes impart characteristic physical properties to the wax - determines their usefulness for the intended application
Natural waxes are found where?
C—- combination of O——- compounds?
MWt?
composition can vary depending on what (2)
Distributed in nature
Complex combination of organic compounds
high molecular weight
Composition varies depending on source and time of collection
What are different natural waxes? (7)
obtained from what and reasons for addition?
Paraffin - obtained from petroleum (mainly - everything else are additions)
Microcrystalline - obtained from heavier petroleum fractions
Ceresin - obtained from petroleum or lignite refining - M
Carnauba - leaves of Carnauba palm in Brazil - M, H
Candelilla - small shrub H
Beeswax - Brittle at RT but plastic at body temp
Spermaceti - sperm whale - coating on dental floss
M - increases melting point of paraffin
H - increases hardness of paraffin

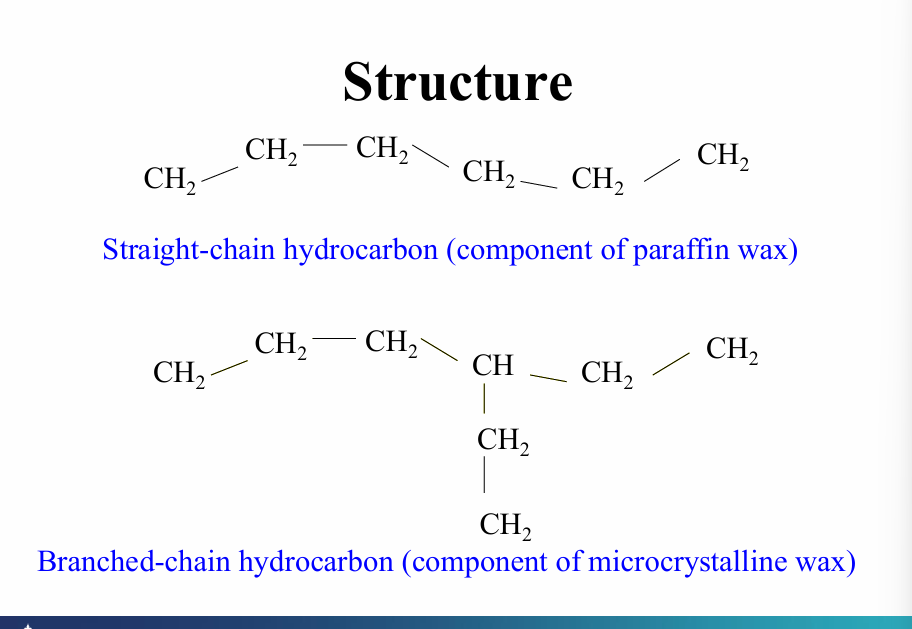
What is the structure of paraffin wax and microcrystalline wax?
How are synthetic waxes produced? (2)
Produced by combination of various chemical in the lab or by chemical action on natural waxes
Give 5 examples of synthetic waxes
Polyethylene
Polyoxyethylene glycol
Halogenated hydrocarbon
Hydrogenated hydrocarbon
Wax esters - (reacting fatty acids and alcohols)

What are 3 other additives ?
Gums - Gum Arabic
Fats - various fatty acids with glycerol
Resins - natural e.g dammar, rosin or shellac from insects
Synthetic resins e.g polyethylene and vinyl resins
What are classifications of natural waxes - initially classified according to their origin? (3)
Mineral: Paraffin, Microcrystalline, Ceresin
Plant: Carnauba, Candelilla
Animal: Beeswax, Spermaceti
Better classified based on their chemical composition: (4)
Hydrocarbons and esters:
Mineral waxes
Plant waxes
Plant and animal waxes

Dental waxes can be classified according to use?
Pattern wax - inlay/casting/modelling
Processing wax: Boxing/utility/sticky
Impression wax: occlusal reg/corrective

Inlay Wax:
Classification according to?
What type of wax is it again - based on use
Type 1 is used for what technique?
Type 2 is used for what technique
What is inlay wax used for?
ADA Sp no 4
Pattern wax
Type 1 (medium) - Direct (wax pattern made inside the Pts mouth)
Type 2 (soft) - Indirect technique (Take impression first)
inlays and crowns - made in wax then converted to metal
making patterns of metallic restorations, patterns for inlays
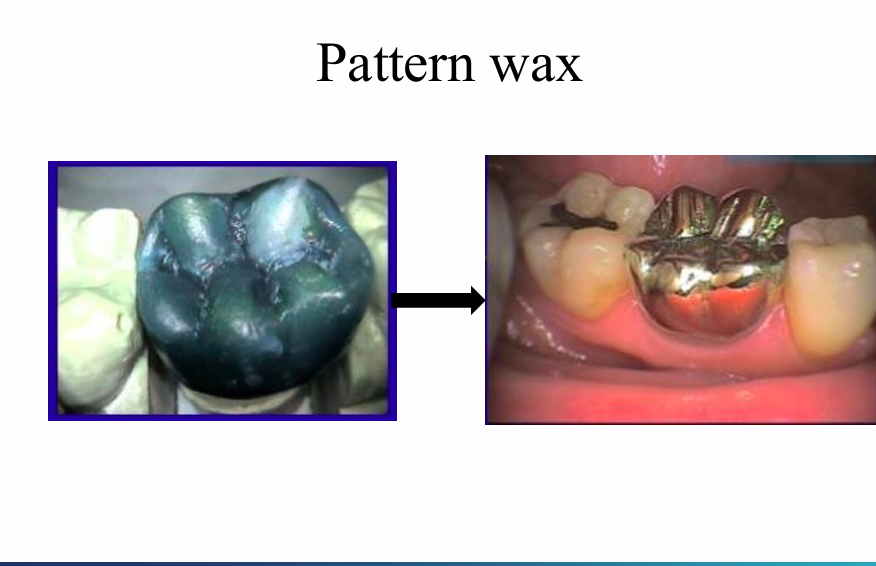
Again uses: (3)
inlays, onlays crown patterns
Ideal properties of inlay pattern wax:
Direct technique
Indirect technique
during use (5)
Soft and plastic above mouth temp (solid at mouth temp)
Solidifies below mouth temp
Can be carved without distortion or flaking
colour contrast from tooth or die
very low residue on vaporisation
low thermal expansion coefficient
no distortion - at moulding temp - no stress set up

Constituents of inlay pattern wax? (5 and why?)
Paraffin - flakes on trimming
Carnauba - increases melting range/glossy surface
Ceresin - toughness and carving
Beeswax - reduces flow and brittleness
dammar resin - improves smoothness, resistance to cracking and flaking, gloss to surface
What is casting wax ?
composition?
property? (1)
Type of pattern wax used in patterns for denture framework (construct metal framework of partial and complete dentures)
exact composition not known but similar to inlay wax
highly ductile - can bend double at 23 degrees Celsius without cracking

Classification of casting wax?
Class: A, B, C

Properties (4 main):
Flow: 35 - max flow 10%
38 degrees - minimum flow of 60%
adaptable at 40-45 degrees
not brittle on cooling
burnt out without leaving residue

What is modelling wax used for?
Used for setting up of artificial teeth for full dentures
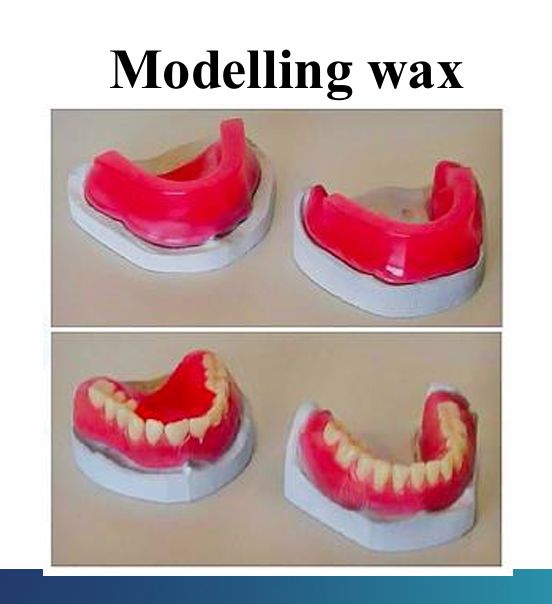
Constituents of modelling wax? (5)
paraffin or ceresin
beeswax
carnauba
natural or synthetic resin
microcrystalline or synthetic waxes

4 ideal properties of moulding wax?
Easily mouldable without tearing, flaking or cracking
easy to carve
capable of melting and solidifying a number of times without changing properties
no residue after removal with boiling water and detergent

Carding or boxing-in wax:
Type of wax?
What is it used for? (2
Processing wax
Build up vertical walls around the impression - box impressions before pouring with gypsum
As beading wax adapted around impression borders
(box as sheets or beading as ribbon)
Ideal properties of carding or beading-in wax? (3)
Pliable at RT
Retain shape at 35 degrees
Slightly tacky
Sticky wax is what type of wax?
uses? (2) for acrylic and partial dentures?
processing wax
an adhesive wax used for temporary joining of items e.g align fractures parts of acrylic denture
align fixed partial denture parts before soldering
e.g preparatory for soldering
constituents to sticky wax? (3)
Resin (rosin), yellow beeswax, gum dammar
Properties of sticky wax?
at RT?
when melted? (2)
does what when movement occurs?
At RT hard and brittle
when melted will adhere closely to applied surface
it is sticky when melted
fracture when movement occurs instead of distorting
Impression wax (corrective or bite wax)
is used for? (2)
replaced by what?
corrective for edentulous impressions
occlusal registry
silicones
Constituents of impression wax?
Hydrocarbon waxes - paraffin, ceresin, beeswax
Metal particles - Al or Cu
Properties of impression wax?
limited to what arches because?
mouth temp it does what (2)/ rt its what?
available as?
Limited to edentulous portions of mouth - distorts when withdrawn from undercut areas
soft at mouth temp, flows a mouth temp - rigid at RT
sheets and cakes
Other waxes: wax rims (bite rim)
are what type of wax?
softening temp is above or below mouth temp?
properties?
uses? (2)
Pattern wax
Above mouth temp
Restoring occlusal relationship
Arrangement of teeth

Other waxes: utility wax
use?, availability in (2) ss
Used to adapt border of impression tray
sticks and sheets

Other waxes: shellac denture base?
properties? (2)
type of wax like resin, which is stable at mouth temp and has a high softening point

Digital dentistry (2 types) vs traditional pattern waxes?
Traditionally, pattern waxes are the foundation materials for pattern fabrication for casting
CAD/CAM blocks pattern materials and 3D printable resins are used
CAD/CAM blocks (wax-resin)
designed for what? (2)
property of the wax? (2 main)
designed for milling frameworks or castable patterns
can be used for fabrication of crown and bridge frameworks and denture framework
blocks are dimensionally stable, can be milled and burn our completely without residue

3D printing resins properties? (3)
no residue on burnout
dimensional accuracy
smooth surface finish
Applications of 3D printing resin? (2)
printing Wax patterns for inlays, onlays and crowns
fabricating frameworks for removable partial dentures

In general dental waxes are composed of 3 major components?
a base wax - usually paraffin
modifier waxes
colorants

Why are there no fillers present?
because it is pyrolyzed - don’t want fillers remaining