P2 - Energy Transfer by Heating
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
How would you test different materials as conductors?
Testing rods of different materials as conductors:
Get rods of different materials, they should be the same width and length for a fair test.
Coat each rod with a thin layer of wax near one end.
Heat the uncoated ends together.
The wax will melt faster on the rod that best conducts energy.
Which materials conduct better?:
Metal and non-metals
Copper and steel
Glass and wood
Metal conducts better than non-metals.
Copper is a better conductor than steel.
Glass conducts better than wood.
How would you test different materials as insulators?
Testing sheets of materials as insulators:
Use different materials to insulate identical cans (or beakers) of hot water.
Ensure the materials have the same thickness.
The volume of the water and its temperature at the start should be the same for each material.
Use a thermometer to measure the water temperature after a fixed time.
Make a table comparing the results between each material.
Safety: Take care if you are using very hot water.
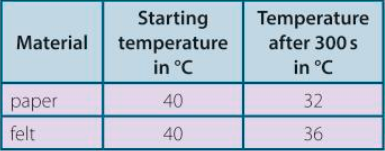
What does the energy transfer by conduction through a material depend on?
The energy transfer by conduction through a material will depend on the material’s thermal conductivity.
The greater the thermal conductivity of a material…?
The greater the thermal conductivity of a material, the more energy per second it transfers by conduction.
Good insulators must have a low…?
Good insulators must have a low thermal conductivity. Therefore energy transfer through them would be as low as possible.
What does the energy transfer per second through a layer of insulating material depend on?
The energy transfer per second through a layer of insulating material will depend on:
the temperature difference across the material.
the thickness of the material.
the thermal conductivity of the material.
How would you reduce the energy transfer through a material as much as possible?
To reduce the energy transfer through a material as much as possible:
the thermal conductivity of the material should be as low as possible.
the thickness of the insulating layer should be as thick as practically possible.
What are electromagnetic waves?
Electromagnetic waves are electric and magnetic waves that travel through space.
Infrared radiation is a type of…?
Infrared radiation is a type of electromagnetic wave, along with visible light, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet rays and X-rays.
What do you need to do in order to see animals and people in the dark?
To see animals and people in the dark, you need to use special cameras that detect infrared radiation. All objects emit infrared radiation.
The higher the temperature of an object…?
The higher the temperature of an object, the more infrared radiation it emits in a given time.
What is a perfect black body?
A perfect black body is an object that absorbs all the radiation that hits it. It doesn’t reflect any radiation, and it doesn’t transmit any radiation.
Why is a perfect black body the best possible emitter?
A good absorber is also a good emitter, so a perfect black body is the best possible emitter as it’s the best possible absorber.
What is black body radiation?
Black body radiation is the radiation emitted by a perfect black body.
An object that has a constant temperature emits radiation across…?
An object that has a constant temperature emits radiation across a continuous range of wavelengths.
What happens to the wavelength if the temperature of the object that emits radiation is increased?
If the temperature of the object is increased, the intensity of the radiation it emits is greater at every wavelength.
If an object has a constant temperature, is the rate at which it emits infrared radiation faster or slower than the rate at which it absorbs it?
An object with a constant temperature emits infrared radiation at the same rate as it absorbs it.
What happens if an objects absorbs radiation faster than it emits?
If an object absorbs radiation faster than it emits radiation, the temperature of the object increases.
Why do rescue teams use light-coloured, shiny blankets on accident survivors?
Rescue teams use light-coloured, shiny blankets to keep accident survivors warm. This is because a light, shiny outer surface emits a lot less radiation that a dark, matte surface.
How does radiation and the Earth’s temperature correlate?
The temperature of the Earth can depend on:
the rate at which light and infrared radiation from the sun is reflected back into space or absorbed by the Earth’s atmosphere or by the Earth’s surface.
the rate at which light and infrared radiation from the sun is emitted from the Earth’s surface and atmosphere into space.
Why would it be really cold on Earth at night if there was no atmosphere?
It would be really cold at night on an Earth without an atmosphere because the surface would not be receiving any radiation from the Sun. It would be emitting radiation into space.
Why do greenhouse gases lead to a warmer Earth (radiation)?
What does the temperature rise of a heated object depend on?
When an object is heated, the temperature rise depends on:
the amount of energy supplied to it
the mass of the substance
what the substance is
What is specific heat capacity?
The specific heat capacity of a substance is the energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1°C
What is the formula for specific heat capacity? Give units and symbols.
Energy transferred = mass x specific heat capacity x temperature change
ΔE = m x c x Δθ
(Joules, J) = (Kilograms, kg) x (J/kg°C) x (°C)
How would you measure specific heat capacity?
(required practical)
Specific Heat Capacity of any Given Metal Practical:
Equipment needed - joulemeter, metal block of a known mass, insulation, thermometer, heater.
Set up the equipment in this arrangement:
Use the joulemeter to measure the energy supplied to the block.
Use the thermometer to measure the temperature rise of the block.
Insert the measurements into the equation -
c = ΔE / mΔθ
Safety: Wear eye protection and take care with a hot immersion heater.
How would you reduce the rate of energy transfer from your home to the surroundings outside?
Reducing the rate of energy transfer from your home:
Loft insulation
Aluminium foil between a radiator panel and the wall.
Double-glazed windows.
Thicker bricks with lower thermal conductivity.
Cavity wall insulation.
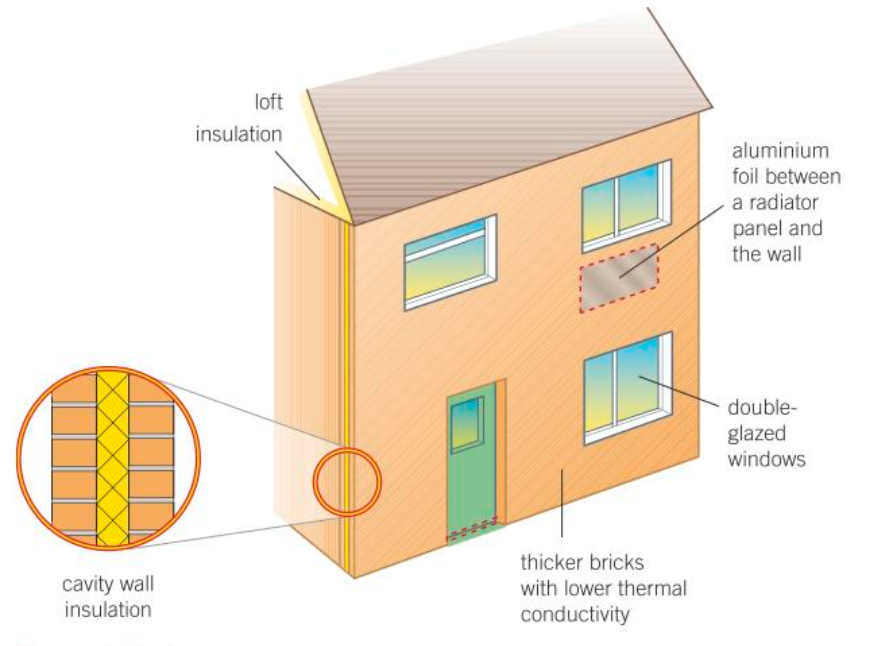
What effect would reducing the rate of energy transfer have on you?
Reducing the rate of energy transfer would reduce your home heating bills.
Why is loft insulation (such as fibreglass) good for reducing the rate of energy transfer through your roof?
Fibreglass is a good insulator, the air between the fibres help reduce the rate of energy transfer by conduction.
Why does cavity wall insulation reduce energy transfer through the outer walls of your house?
Cavity wall insulation is the insulation between the two layers of brick that make up the wall. If cavity wall insulation is placed in the outer walls, it reduces energy transfer by conduction through that wall as the material is a better insulator than the air that would be in the cavity.
How does aluminium foil between a radiator panel and the wall help reduce energy transfer?
Aluminium foil, when placed between a radiator panel and a wall, reflects radiation away from the wall and so reduces the rate of energy transfer by radiation.
Why do double-glazed windows help keep your heating bills low?
Double-glazed windows have two glass panes with dry air or a vacuum between the panes. Dry air is a good insulator and a vacuum prevents energy transfer by convection - therefore, the rate of energy transfer outside your home decreases.
Why would thicker bricks with lower thermal conductivity reduce energy transfer outside your home?
Rate of energy transfer by conduction is at its lowest when the material it must go through is thick and has low thermal conductivity. Therefore a brick with these properties would help make sure energy transfer to the surroundings outside your home is as low as possible.
How do solar panels work?
Solar panels absorb infrared radiation from the sun and are used to generate electricity directly or to heat water directly.