intro to language development slides
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
language
a complex and dynamic system of conventional symbols that is used in various modes for thought and communication
code
language is a ______
→ word-referent relationships are arbitrary
dynamic
language is ________
→ can change, can add and take-away words
conventional
language is _______
→ there are “rules” that govern language
tool
language is a _____
→ allows for human communication, makes the human species unique
cognition
language = ______
a tool that helps humans develop a picture of the world
a tool that permits people to communicate their thoughts to others
language emerged as a cultural and social evolution
cognitive process
language as a ________ ______
the brain uses language to store information and to carry out cognitive processes
reasoning
hypothesizing
memorizing
planning
problem solving
speech
neuromuscular process by which humans turn language into a sound signal that is transmitted through the air to a receiver
hearing
sensory system allowing speech to enter/be processed by the brain
speech process
respiration
→ air from lungs through trachea
phonation
→ air vibrates vocal folds
resonation
→ air moves through oral and nasal cavities
articulation
→ air is manipulated by articulators (tongue, teeth, lips, & jaw)
how language relates to speech
language is NOT dependent upon speech, but speech IS dependent upon language
language gives speech its meaning
elements of hearing
perception of sound
needed for reception and comprehension of spoken language
acoustics = study of sound
events for speech reception
creation of a sound source
vibration or air particles
reception by the ear
comprehension by the brain
speech perception
how the brain processes speech and language
different from hearing
processing a clap of hands is different than processing the word “coffee”
involves specialized processors in the brain that respond to human speech
communication
sharing information/thoughts from mind of speaker to listener
symbolic/referential communication
the relationship between an object or event and the referent is arbitrary
baby says “bottle'“ because they want a drink
no limit on symbolic communication
preintentional communication
people assume a relationship between a communicative behavior and its referent
baby cries to get a bottle
intentional/iconic communication
clear relationship between the message and its referent
baby points to a bottle because they want a drink
oral communication
the combination of speaking and listening
baby says, “bottle” and mom says, “you can have it at naptime.”
model of communication
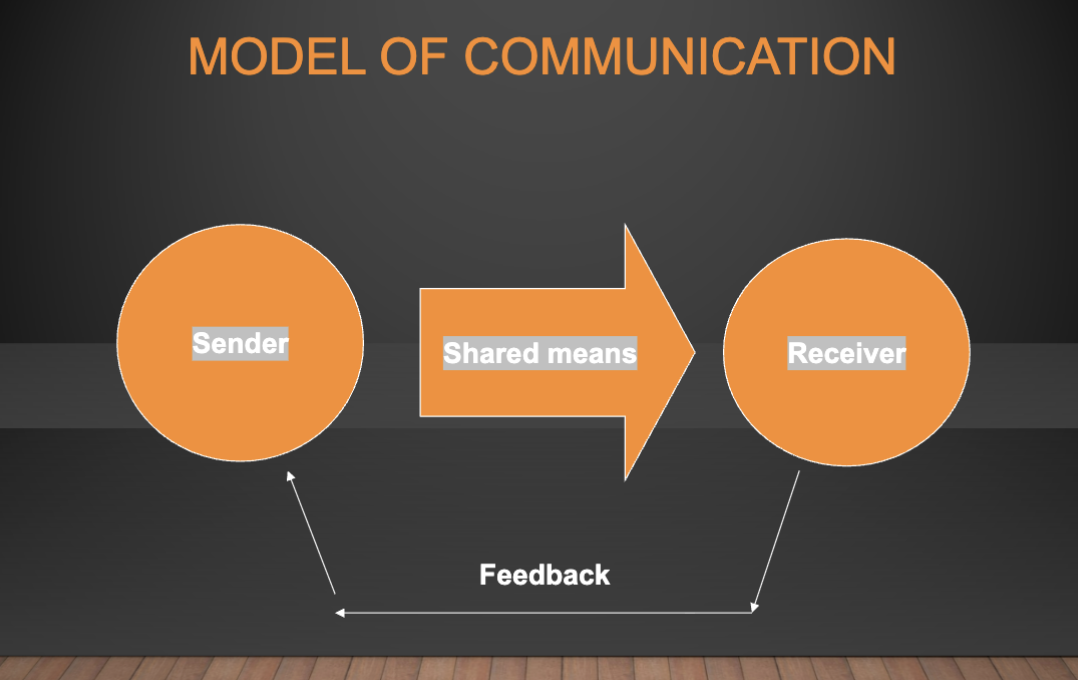
feedback impact on communication
makes communication active and dynamic
needed to make communication effective
linguistic
speaking or vocalizing
“mm-hmm” or “I totally agree”
nonlinguistic/extralinguistic
eye contact
facial expression
posture
proximity
paralinguistic
use of pitch
loudness
communication breakdown
feedback prevents these, which occur when receivers do not provide appropriate feedback
conversational repair
sender/receiver adjusts exchange to mend breakdown
7 purposes of communication
instrumental - ask/request something
regulatory - direct others, give directions
interactional - social conversation
personal - express state of mind/feelings
heuristic - inquire/find out information about something
imaginative - tell stories/role-play
informative - organized description of event or object