(#10) Pancreas
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
Summary of pancreas hormones
+ adrenal cortex
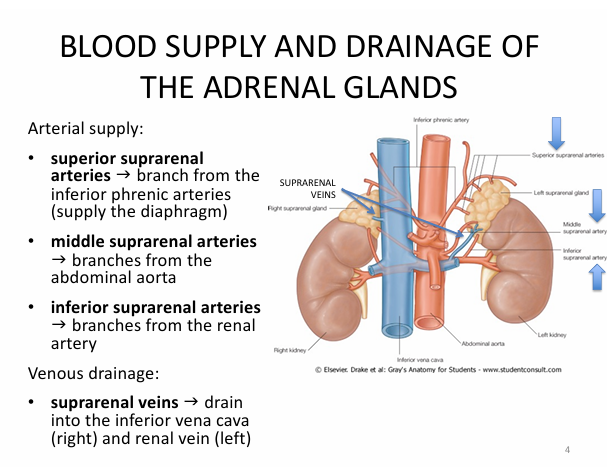
Blood supply + drainage of adrenal glands
Action of aldosterone
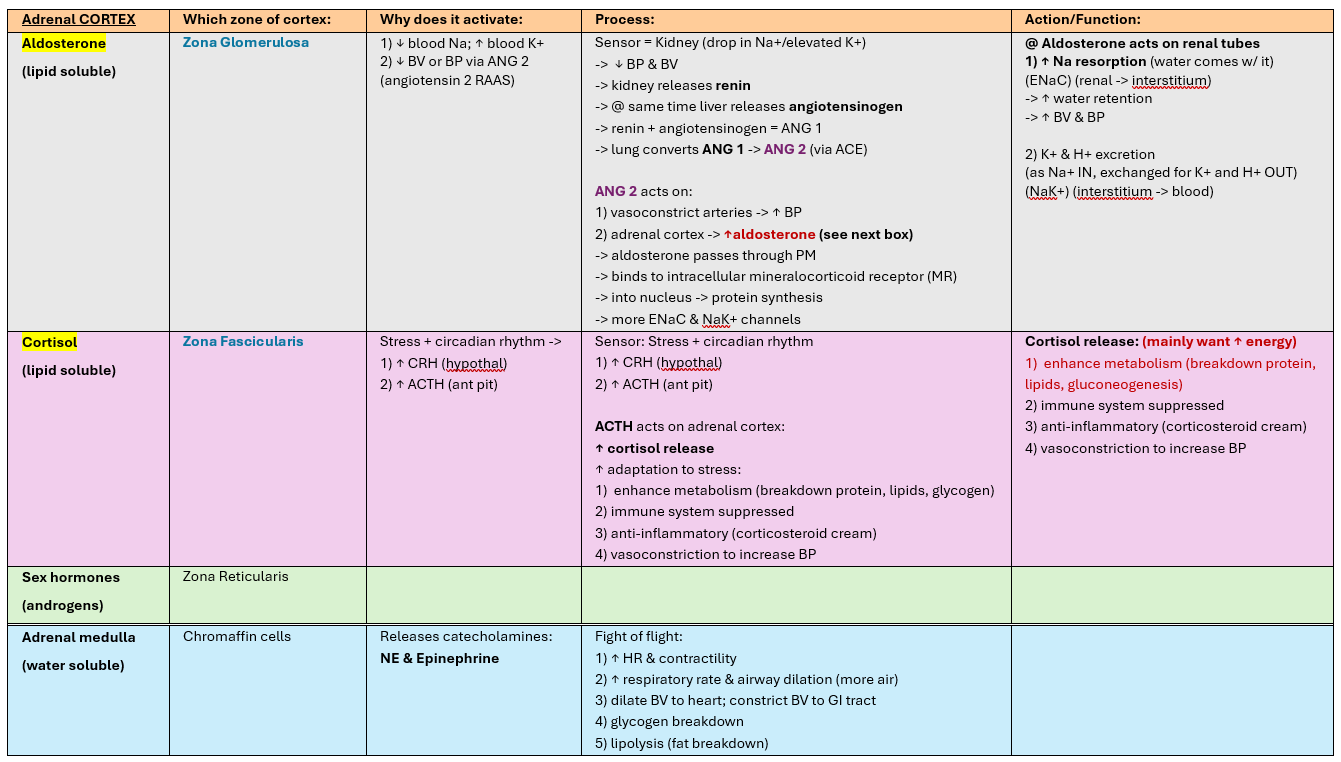
@ Aldosterone acts on renal tubes
1) ↑ Na resorption (water comes w/ it)
(ENaC) (renal -> interstitium)
-> ↑ water retention
-> ↑ BV & BP
2) K+ & H+ excretion
(as Na+ IN, exchanged for K+ and H+ OUT)
(NaK+) (interstitium -> blood)
Action of cortisol
Cortisol release: (mainly want ↑ energy)
1) enhance metabolism (breakdown protein, lipids, gluconeogenesis)
2) immune system suppressed
3) anti-inflammatory (corticosteroid cream)
4) vasoconstriction to increase BP
Adrenal cortex produces what hormones & where
Adrenal medulla produces what hormones and where?
Aldosterone = glomerulosa
Cortisol = fasciularis
NE/Epinephrine = chromaffin cells of medulla
Aldosterone activates due to:
Cortisol activates due to:
1) kidney senses DROP in Na/K+
2) stress + circadian rhythm
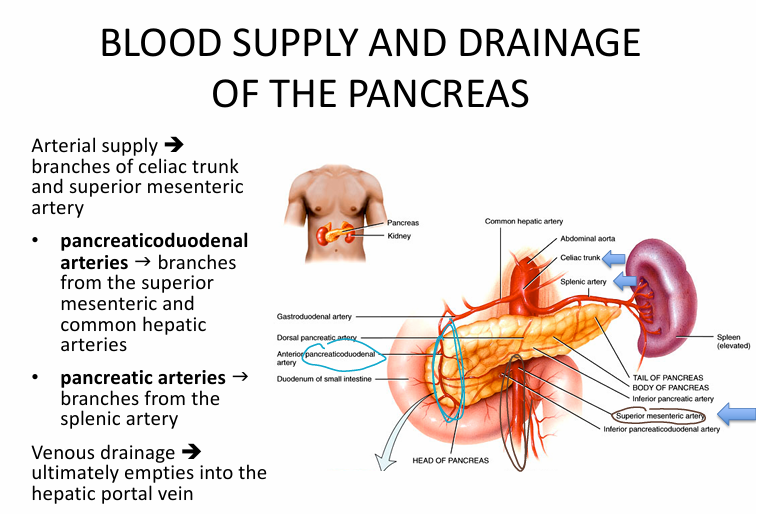
Blood supply + drainage of pancreas
What’s the histology of pancreas?
Pancreatic ACNI = exocrine
Pancreatic ISLET OF LANGERHANS = endocrine (what were interested in)
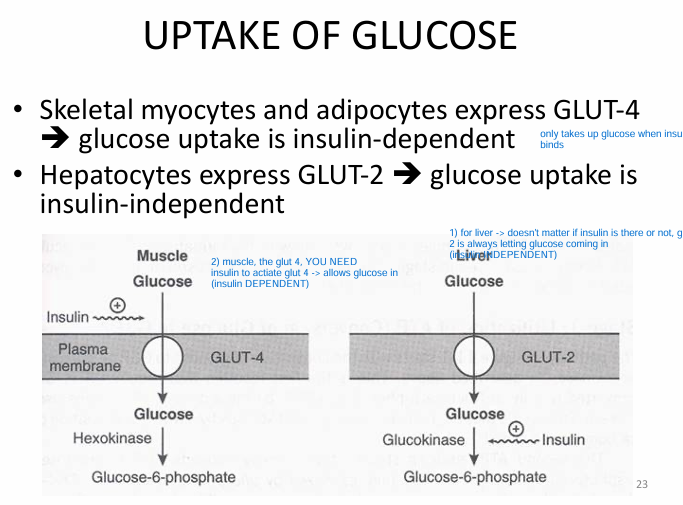
Whats the difference b/w GLUT 2 & GLUT 4?
g2 = liver = insulin INDEPENDENT
- liver will uptake glucose regardless of whether insulin is there or not
g4 = muscle = insulin DEPENDENT
- only uptake glucose if insulin binds to insulin receptor (*not only, but it greatly enhances glucose uptake)
What are the different types of diabetes?
What are symptoms of diabetes?
1) Type 1 (insulin dependent)
- loss of beta cells → no insulin produced → can’t call for glut 4 transporters
2) Type 2 (insulin independent)
- low levels of insulin production
OR
- insenstivity of insulin receptors (affinity not there)
(decreased senstivity to urine)
3) Poly = excessive
- polyuria = peeing too much
- polydipsia = excessive thirst
- polyphagia = excessive eating (glucose not entering cell → eat more)
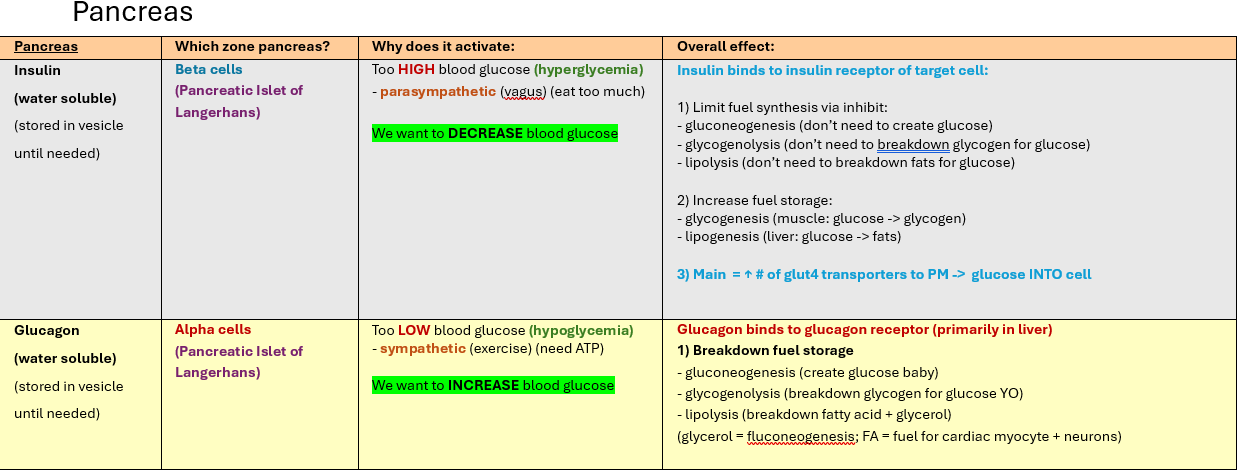
Overall effect of insulin:
Insulin binds to insulin receptor of target cell:
1) Limit fuel synthesis via inhibit:
- gluconeogenesis (don’t need to create glucose)
- glycogenolysis (don’t need to breakdown glycogen for glucose)
- lipolysis (don’t need to breakdown fats for glucose)
2) Increase fuel storage:
- glycogenesis (muscle: glucose -> glycogen)
- lipogenesis (liver: glucose -> fats)
3) Main = ↑ # of glut4 transporters to PM -> glucose INTO cell
Due to:
Too HIGH blood glucose (hyperglycemia)
- parasympathetic (vagus) (eat too much)
Overall effect of glucagon:
Glucagon binds to glucagon receptor (primarily in liver)
1) Breakdown fuel storage
- gluconeogenesis (create glucose baby)
- glycogenolysis (breakdown glycogen for glucose YO)
- lipolysis (breakdown fatty acid + glycerol)
(glycerol = fluconeogenesis; FA = fuel for cardiac myocyte + neurons)
Due to:
Too LOW blood glucose (hypoglycemia)
- sympathetic (exercise) (need ATP)