AP Psych Unit 1.1-1.4 Review
1/119
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
120 Terms
natural selection
the principle that the inherited traits enabling an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations.
evolutionary psychology
the study of evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
behavior genetics
the study of relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on behavior
nurture, nature
__________ works on what __________ provides (fat baby angel)
genome
the complete instructions for making an organism
identical (monozygotic) twins
individuals who developed from a single fertilized egg that split in two, creating two egg that split in two, creating two gametically identical organisms.
fraternal (dizygotic) twins
individuals who developed from separate fertilized eggs.
genetic, experiences
Environments can trigger _______ expression, and genetically influenced traits can influence the _________ we seek and the responses we evoke from others.
nervous system
the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells of the PNS and CNS
central nervous system (CNS)
the brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
sensory and motor neurons
nerves
bundled axons that form neural cables connecting the CNS with the muscles, glands, and sensory organs
sensory (afferect) neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the body's tissues and sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
motor (efferent) neurons
neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles and glands
interneurons
neurons within the brain and spinal cord; they communicate internally and process information between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
duramater
outermost layer of the covering that protects the brain
arachnoid mater
spider web middle layer of the covering that protects the brain
pia mater
the bottom layer of the covering that protects the brain
meninges
protects the spinal cord
somatic nervous system
the division of the PNS that controls skeletal muscles
autonomic nervous system
division of the PNS that controls automatic functions such as breathing and your heart
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight; arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest; calms the body, conserving its energy
neuron
the basic unit in which the entire brain and nervous system are built.
cell body
the cells life support center; contains the nucleus
dendrites
branching extensions that recieve messages from other cells
axon
passes messages away from the cell body to other neuron muscles or glands
myelin sheath
a fatty tissue layer that covers the axon of some neurons and helps speed neural impulses
glial cells
provide nutrition and help protect neurons
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical change travels down an axon
threshold
a level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
all-or-none-response
a neurons’ reaction of either firing or not firing
refractory period
a brief resting pause that occurs after a neuron has fired
negative
the charge inside of a neuron
positive
the charge on the outside of the neuron
dedrites
what is structure A?
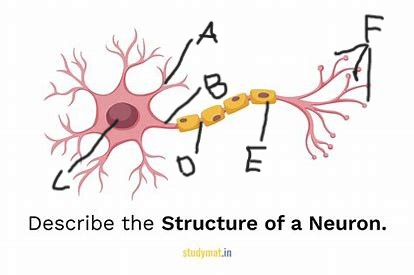
axon
what is structure B?
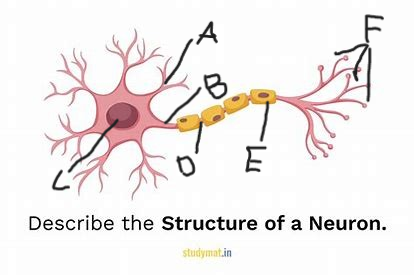
cell body
what is structure C?
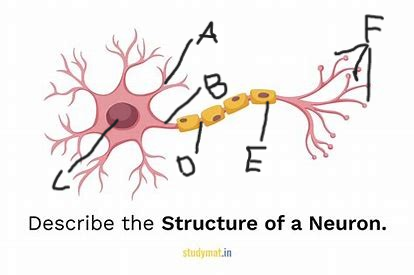
node of ranvier
what is structure D?
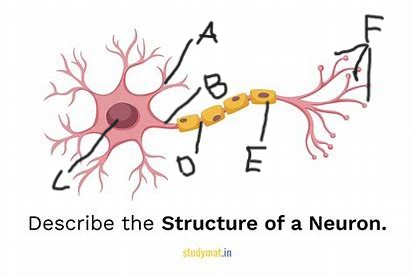
myelin sheath
what is structure E?
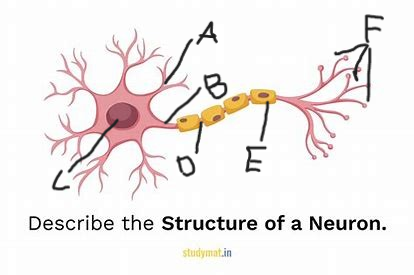
terminal branches
what is structure F?
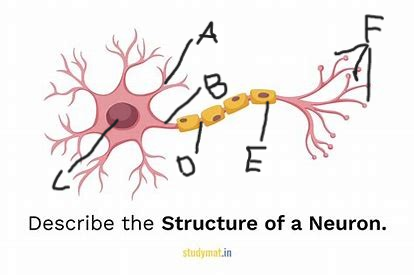
excitatory signal/neurotransmitter
pushes neuron’s “accelorator”, makes a neuron more likely to reach action potential
inhibitory signal/neurotransmitter
pushes neuron’s “brakes”, makes a neuron less likely to reach action potential
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
refractory period
where a neuron cannot fire. prevents one signal from combining with another
endorphins
natural pain relievers and mood enhancers
agonist
binds to receptor sites and mimics the effects of a specific neurotransmitter
antagonist
binds to dendrites of a neuron and prevents or blocks its response
Acetylcholine (Ach)
enables muscle action, learning, and memory
undersupply → Alzheimer’s
dopamine
movement, learning, attention, and emotion
oversupply → schizophrenia
undersupply → parkinsons
serotonin
mood, hunger, sleep, and arousal
90% found in stomach
undersupply → depression
epinephrine
energy and memory formation
fight or flight
in adrenal gland
norepinephrine
alertness and arousal
releases glucose
undersupply → depressed mood
found in adrenal glands
GABA
major inhibitory neurotransmitter
calms the CNS
natural tranquilizer
undersupply→ seizures
Glutamate
major excitatory neurotransmitter
opposite of GABA
oversupply → migraines
Substance P
pain perception
oversupply→ chronic pain
hypothalamus
controls the pituitary gland
hypothalamus
controls the pituitary gland
pituitary gland
controls growth and produces/releases oxytocin
thyroid gland
affects metabolism by secreting thyroxin
parathyroid
regulates the level of calcium in your blood
pancreas
regulates blood sugar
depressants
drugs that reduce neural activity
alcohol, sedatives, benzodiazepines, opiates
barbituates
drugs that suppress the CNS; reduce anxiety and impair memory and judgement
opioids
depress neural activity, temporarily reducing pain and anxiety
stimulants
drugs that excite neural activity and speed up body functions
caffeine, nicotine, cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamines
hallucinogens
drugs that distort perception and evoke sensory images w/o sensory input
LSD & marijuana
neuroplasticity
the brains ability to change by reorganizing after damage or by building new pathways based on experience
hemispherectomy
the removal of one of the halves of your brain
psychosurgery
another name for brain surgery
lesioning
the destruction of selective parts of the brain to reduce a behavior
x-ray
shows bones and solid structures
EEG (electrocardiogram)
measures electrical activity of the brain
MEG (magnetoencephalography)
measure magnetic field from the brains natural electrical activity
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
uses magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images of the body made up of soft tissue
fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
measures blood flow and oxygen metabolism
CT/CAT scan (computerized axial tomography)
2D —> 3D images created of a body part
PET scan (positron emission tomography)
visualize slices of the brain to examine deep brain/body structures
DSI (diffusion spectrum imaging)
images the spectra of water diffusion in tissues
hindbrain
contains the medulla, pons, and cerebellum
essential surviving functions as well as coordination and balance
midbrain
sits atop the brainstem
connects the hind and forebrain
controls some motor movement and transmits auditory and visual information
forebrain
contains the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and hypothalamus
manages complex cognitive activities sensory and associative functions and voluntary motor actions
brainstem
the central core of the brain
control autonomic surviving functions
medulla
hindbrain structure that is the brainstems base
controls heartbeat and breathing
thalamus
the forebrains sensory control center atop the brainstem
directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
reticular formation
a nerve network that travels through the brainstem into the thalamus; it filters information and plays an important role in controlling arousal
cerebellum
the hindbrain's "little brain" at the rear of the brainstem
processes sensory input, coordinating movement output and balance, and enabling nonverbal learning and memory
limbic system
neural system located mostly in the forebrain below the central hemispheres, associated w/ emotions
amygdala
two lima bean sized neural clusters in the limbic system; linked to emotion
hypothalamus
a limbic system neural structure lying below (hypo) the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature) helps govern the endocrine system, and is linked to emotion and reward
hippocampus
neural center in the limbic system that helps process explicit (conscious) memories--of facts and events-- for storage
oxytocin & vasopressin
hormones associated with trust and bonding
released in the hippocampus
cerebral cortex
the intricate fabric of interconnected neural cells covering the forebrain's cerebral hemispheres
the body's ultimate control and information- processing center
frontal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying just behind the forehead.
They enable linguistic processing, muscle movements, higher-order thinking, and executive functioning (such as making plans and judgements)
parietal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the top of the head and toward the rear; it receives sensory input for touch and body position
occipital lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying at the back of the head; it includes areas that receive information from the visual fields.
temporal lobes
the portion of the cerebral cortex lying roughly above the ears; it includes the auditory areas
They also enable language processing.
motor cortex
a cerebral cortex area at the rear of the frontal lobes that controls voluntary movements.
somatosensory
a cerebral cortex area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body touch and movement sensations